Condylomas appear if a person has HPV type six or eleven.
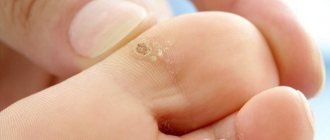
Condylomas are benign neoplasms that appear on the skin or mucous membranes.
The most popular places for their localization are the genitals and the anus.
They are flesh-colored or reddish in color and, when traumatized, often become malignant.
Therefore, any condylomatoses must be treated.
Condylomas can be:
- pointed;
- flat:
- intraepithelial.
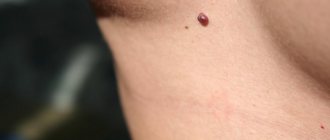
Condylomas acuminata are characterized by the conicity of the neoplasms.
Genital organs, their external and internal parts, favorite places of their localization.
Their presence indicates sexual transmission of HPV.
Flat condylomas are characterized by frequent malignancy.
They grow deep into healthy tissues.
There is a growth of intraepithelial condylomas inside the skin.
Genital condylomas and simple condylomas in children
Condylomas are marked by rapid reproduction and association into large clusters, covered with a crust on top.
When we talk about condylomas, we mean genital warts.
Because flat and intraepithelial ones are much less common.
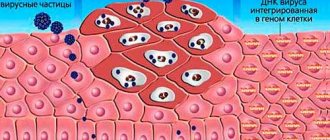
Warts, papillomas and condylomas appear from HPV.
The presence of warts and papillomas is considered practically harmless.
The presence of genital warts in a child requires parental supervision and constant medical supervision, because they tend to malignize.
Children are often infected with HPV vertically – in utero.
The incubation period is long, the first condylomas appear in two to five year old children.
Bathing together with parents or using hygiene items, household items and clothing can also cause infection.
Young children, in general, should be supervised by their parents and regularly examine their skin for the presence of condylomas.
Young children may not complain of skin itching or burning, and condylomas may appear asymptomatically.
This is especially true if one or both parents have HPV.
Causes of neoplasms
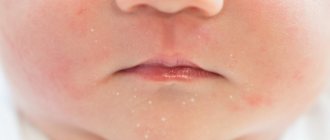
The appearance of papillomas on the chest of newborns is considered a rare phenomenon. And the first thing parents should do when they discover a tumor on a child’s body is to consult a specialist, since often the pathogenic growth is not a papilloma, but a nevus (mole), molluscum contagiosum, melanoma or a congenital skin defect.
Since one of these diseases is more often diagnosed in newborns, the appearance of papillomas is painful for parents, especially if they are faced with this problem for the first time. Ignorance breeds panic, while this virus, although unpleasant, rarely poses a threat to the life of a child.
It is necessary to begin treatment of papillomas in newborns with an understanding of how they formed, because thanks to this, a number of measures can be taken to eliminate existing tumors and prevent the appearance of new ones.
The only reason for the appearance of papilloma on the chest of a newborn is infection of the body with the human papilloma virus. No matter how sad it is, neither children nor adults can completely cope with the virus. Once it enters the body, it remains there forever. For most of its life it is in a dormant state, and is activated only after the onset of provoking factors. This activation leads to the appearance of epidermal neoplasms. Let's consider how a newborn can become infected with this virus.
Ways a child can become infected with papillomavirus:
- From mother to baby . This infection can occur in several ways. First of all, intrauterine infection is possible. Some doctors reject information that a child can pick up the papillomavirus from its mother in the womb, at the fetal stage. But the fact that some children are born with already formed papillomas suggests that intrauterine infection is still possible. It is also supported by the fact that papillomas are diagnosed in newborns born by caesarean section. Another way of transmitting the virus from mother to child is through the passage of the birth canal affected by neoplasms. While children born as a result of cesarean section do not have contact with infected birth canals. And this also indicates the ability of the virus to infect the baby inside the womb.
- Home infection . This implies close epidermal contact of the newborn with the infected person. Transmission of the virus through common household items is also possible, since the pathogen, capable of penetrating and actively multiplying in the body of a newborn, retains its viability outside the human body for more than 3 hours.
- Hospital infection . This can happen both in the maternity hospital where the baby was born, and in a children's medical institution where the child is taken for examination. In this case, the appearance of papillomas can be triggered by skin contact with untreated hands of doctors, reusable medical instruments, and changing supplies.
If a child has already been born with papilloma, then this type of growth is considered congenital, and if the neoplasm appears between the first and fourth weeks of life, such a growth is called acquired.
HPV in children
The formation of neoplasms - warts, papillomas and condylomas - is the most important symptom of papillomavirus.
Moreover, for both adults and children.
For preventive purposes, it is necessary to limit the child’s contact with sick adults and other children.
Because HPV is a very contagious disease.
Removing tumors is a half-hearted treatment.
It is necessary to prevent their recurrence.
It is necessary to use medications that destroy latent papillomaviruses when they are activated.
Children are treated with effective and safe alpha-2b interferon.
Its feasibility in general treatment has been proven.
But complex treatment, using local forms of interferon-containing drugs, is still better.
To increase the effectiveness of treatment and as a preventive measure for recurrent HPV.
The most oncogenic are considered to be genital warts that arise from HPV types six, eleven, sixteen and eighteen.
Incubation time ranges from one month to a year, but the average is about three months.
Children can become infected with HPV not only vertically, but also through household contact.
The contagiousness of HPV is quite high.
New growths need to be closely monitored:
- change in size and color, a reason to immediately contact a specialist;
- before prescribing treatment, it is necessary to conduct a comprehensive study of the nature of the tumor;
- the result of such a study will be the prescription of complex therapy.
Initially, immunomodulatory therapy is used to raise the immune status.
Sometimes, neoplasms self-destruct without surgical or therapeutic intervention.
Advanced cases lead to the use of all kinds of ointments and other medications, as well as to surgical or chemical destruction of tumors.
Methods for treating skin growths
For a newborn child, all treatment methods used in the treatment of warts not only in adults, but even in children are inaccessible. This is due to the ban on the use of both medicinal drugs used internally and externally in newborns. Therefore, specific treatment methods come into force here. Their main task is to boost the newborn’s immunity to activate internal forces to fight the human papillomavirus.
How to deal with warts in newborns:
- Complete nutrition. The World Health Organization recommends exclusive breastfeeding for newborns. Therefore, in order for the child to receive a sufficient amount of nutrients and nutrients not only for proper development, but also to fight the virus, the mother’s nutrition must be complete. If she understands that she cannot provide this, the use of vitamin complexes combined with lactation is mandatory. If, for medical reasons, the baby is bottle-fed, a precise selection of formula for a specific baby is necessary, taking into account all its physiological characteristics and needs. Particular attention is paid to water. A healthy child does not need additional “supplementary feeding”, because... Breast milk is almost 90% water. If there are medical indications, you need to use only water that is specially suitable for this purpose, preferably that which is sold in specialized pharmacies or in children's kitchens.
- Healthy sleep . A baby under 4 weeks of age should sleep 17-18 hours a day. At the same time, continuously - at least 1.5-2 hours. If the child sleeps less or wakes up more often, the problem may be due to improper (often insufficient) nutrition or neurological manifestations. Be sure to show your baby to the pediatrician, since sleep is one of the main components not only of the treatment of warts in newborns, but also of full development.
- Fresh air . Saturation of the body is very important for the formation of strong immunity. If the weather permits, you can walk with your baby from the first days of life. When dressing your child, remember that overheating is no less, and sometimes even more dangerous for children than hypothermia. If it is not possible to go on foot, but there is an equipped loggia or balcony without drafts, this is a completely healthy alternative.
- Hygiene . In babies, the thermoregulation system is at the initial stage of formation. Therefore, children often sweat a lot. This has an extremely negative effect on the epidermis and is a provoking factor for the formation of warts in newborns.
What is the difference between condylomas and papillomas?
When HPV gets on the skin, warts most often appear.
And when genital warts appear on the mucous membranes of the penis, vagina, uterus, and perianal area.
If the presence of condylomas is prolonged, then this is a precancerous condition.
When soft new growths on the skin are pink or flesh-colored, then these are papillomas.
Condylomas are called genital warts because they have a characteristic shape.
The presence of condylomas and papillomas is always uncomfortable.
They are located in places of increased trauma.
Prone to the formation of cracks with subsequent bleeding.
Tests for diagnosing HPV and immunogram
HPV is detected by cytological and histological methods.
Early diagnosis, before the appearance of clinical signs, is carried out by detecting antibodies to the virus.
But this method is not suitable for determining the concentration of the infectious agent.
It has low accuracy for determining the type of papillomavirus.
Together with the cytological method, the Daijin amplification test is also used.
With this new and very accurate test, the concentration of HPV and its specific type are determined.
This means you can find out the degree of oncogenicity of the papillomavirus.
To carry it out, scrapings from the mucous membrane of the vagina or urethra are needed.
The non-amplification PCR method is also used to diagnose HPV.
The material for analysis by this method is smears from the mucous membrane, blood and urine preparations.
If papillomavirus DNA is detected, then we can speak with almost one hundred percent certainty about HPV infection.
But if the analysis technology is not followed and gross errors are made, then false positive or false negative results can be obtained.
The experience and responsibility of a specialist is very important.
To assess the state of immunity, at the moment, it is very advisable to do an immunogram analysis.
This is a comprehensive blood test that does not strictly take into account indicators of the degree of immune response.
Typically, an immunogram consists of immunophenotyping, analysis of humoral parameters and tests for phagocytosis activity.