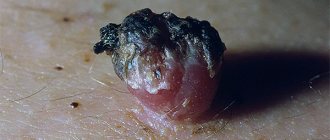
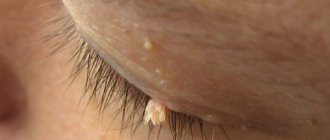
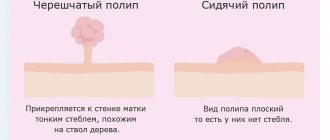
A skin growth on a cylindrical pedicle, sometimes almost invisible, is called papilloma. It often appears out of nowhere and does not appear for a long time. But with any “jump” of immunity or in the heat, it suddenly appears to your eyes, first as a single person: one papilloma “mother” can “pop out” in the armpit or on the eyelid (her favorite places, for example, on the bends of the elbows and in the popliteal fossae), and then “let in” the “babies”, that is, literally “sprinkle” all sorts of places on our body. For some, this phenomenon will only be a temporary disorder - well, they say, it gets in the way, clings to clothes, and if it’s “stuck” on the face, it’s ugly, a cosmetic defect, but you don’t have to notice! But is this small growth so harmless, especially when it forms a whole colony around itself? Should I delete it, or leave it and forget it?
Symptoms of human papillomavirus (HPV)
Genital papillomavirus infection is caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV) and is characterized by damage to the skin and mucous membranes.
Symptoms of human papillomavirus (HPV):
- warts (genital warts, venereal warts, genital warts, exophytic condylomas),
- flat epithelial lesions , most of which are considered precancer.
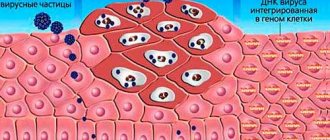
The human papillomavirus infects the skin and mucous membranes, having a high affinity for the epithelial tissues of the genital organs, esophagus, anal canal and respiratory tract. There are more than 130 types of human papillomavirus, about 40 types of which can affect the anogenital area.
There are high- and low-oncogenic types of the virus, which differ in their ability to cause cervical cancer. Most cases of HPV infection are asymptomatic (subclinical forms or intraepithelial squamous lesions). A minority of them are represented by genital condylomas, characterized by exophytic growths of the epithelium. Lesions caused by oncogenic types are strictly associated with cervical neoplasia and, to a lesser extent, with neoplasia of the vagina, vulva, and perianal region (30-50%). 13 highly oncogenic types of HPV have been identified that cause cervical cancer. Other types of human papillomavirus play a role in the development of cancers of the skin, oropharynx, anus, and penis.
Cervical cancer is diagnosed on average 20 years after infection with a highly oncogenic type of HPV, but in recent years, faster malignancy has often been noted.
In 5-30% of women, several types of HPV are detected simultaneously. According to official statistics, approximately 50 thousand new cases of human papillomavirus infection are registered in the Russian Federation annually. According to international studies, the prevalence of HPV among young women reaches 30%.
Getting rid of bleeding
The only correct option is to go to the doctor for an examination as soon as possible (you can make an appointment with a therapist, who, if necessary, will give a referral to a dermatologist or oncologist or surgeon).
To avoid bacterial attachment, it is necessary to use antiseptic agents during bleeding. A sterile bandage or cotton wool is soaked in the solution, and the wound and the skin around it are treated.
Use medical alcohol, a solution of potassium permanganate or Furacilin, Chlorhexidine. A fresh wound is sprinkled with crushed Streptocide tablets. It is possible to use iodine.
The treatment is carried out on an intact area of the skin, avoiding contact of the product with the papilloma - this can cause tissue burns.
If bleeding occurs, there is a considerable risk of infection in the wound, which will increase the likelihood of subsequent transformation of the tumor into a malignant one. In the worst case scenario, melanoma will occur.
In almost 90% of cases, when visiting a doctor with a bleeding papilloma, the patient is referred for removal of the tumor (the operation is performed under local anesthesia). This is the only option to avoid complications and prevent malignancy of papilloma.
When it is removed, a biopsy is required - a small flap of affected tissue is sent for laboratory analysis.
This is done to check for the presence of cancer cells. If they are detected, the patient is referred for examination to an oncologist.
If the papilloma is located in an open area, the wound must be protected from sunlight. Ultraviolet exposure will slow down the healing process.
Clinical picture
It is believed that the incubation period before the clinical manifestation of HPV-associated diseases can be 1-8 months. Condylomas are exophytic formations, sometimes resembling cauliflower, on the skin, perineal and perianal mucosa, as well as on the mucous membranes. They can be multiple, asymmetrical and polymorphic. It is possible to change the size and number of genital warts, often resulting in the disappearance of the rash. In women, HPV most often affects the cervix, vagina, vulva and perianal area.
The classification of HPV-associated diseases is presented as follows:
- changes in the squamous epithelium of low malignancy (anogenital condylomas of the cervix, mild dysplasia);
- changes in the squamous epithelium of a high degree of malignancy (moderate and severe dysplasia and cancer);
- invasive cancer.
Subjective symptoms of HPV infection of the genitals and anal canal are usually absent. Characterized by a rapid increase in the size and number of genital warts, especially during pregnancy. Occasionally, patient problems such as bleeding, discharge and itching in the affected areas are identified.
Cytological examination of material from the cervix
- Regular cytological examination allows for timely detection and treatment of cervical precancer.
- To detect cervical cancer and precancerous diseases, two methods are used: fixing a smear on a glass slide using an aerosol fixative (classic Pap test) and cytological examination of thin-layer smears of liquid preparations (in Russia this method is available in some laboratories).
- Cytologic examination of thin-layer smears of liquid preparations in women who are not at high risk is more sensitive than conventional smear-on-slide examination; such smears are less likely to be unusable. Regular cytological examination of cervical smears is necessary for all sexually active women (3 years after the onset of sexual activity, according to North American recommendations, and from the age of 25 years, according to European recommendations).
- There are recommendations from the Cervical Cancer Prevention Network, according to which, if immunity is normal, cytological examination should be performed annually or every 3-5 years.
- Patients with immunodeficiency, especially HIV-infected patients, require closer attention. Patient management is planned individually. Cervical cancer is more common in women living with HIV and those who have not been regularly screened.
Treatment of anogenital warts
Genital warts are characterized by a persistent recurrent course, but in 90% of patients they completely resolve without treatment within 2 years, especially at a young age due to cellular immunity. HPV lesions of the cervix resolve in 90-95% of cases. However, the disappearance of condylomas does not mean the complete elimination of the human papillomavirus. Regardless of the treatment regimen, in 20-30% of cases, condylomas reappear in the same areas or in other places. All treatment regimens lead to the development of local skin reactions, which usually require a reduction in the intensity of treatment.
Causes of bleeding papillomas
The appearance of blood on papillomas is always preceded by a mechanical violation of the integrity of the neoplasm. The most common situations:
- Papilloma rubs against clothes while walking or running;
- The tumor is located on the neck and is scratched by a chain;
- The papilloma is inflamed and itchy, which is why the patient literally rips it off with his fingers;
- The tumor is located in the perineum and is damaged during sex.
- Bleeds after removal
If the papilloma bleeds, the reason may be a sharp decrease in immunity. The body's defenses decrease due to hypothermia, prolonged use of antibiotics, unhealthy diet and non-compliance with the daily routine.
Papilloma is an epithelial growth that affects the upper and middle layers of the skin and capillaries. In this case, the tumor grows directly into the capillaries (and it is from the blood that the infection receives micronutrients, in particular proteins).
That is why even minor mechanical damage to the papilloma leads to severe bleeding. And to stop the bleeding, doctors recommend applying ice to the wound for just 1 - 2 minutes (necessarily from boiled water).
Another common reason is prolonged exposure to ultraviolet radiation (sunlight, solarium lamps) on the neoplasm.
Under its influence, the process of keratinization of the skin is significantly accelerated, it actively exfoliates, but at the same time, regeneration of the epithelium on the papilloma itself practically does not occur. Accordingly, an open wound appears.
Treatment methods:
- used by patients independently (imiquimod, podophyllotoxin are applied to the rash);
- used by a doctor: cryodestruction (can be used during pregnancy),
- dichloroacetic or trichloroacetic acid (can be used during pregnancy),
- solcoderm (mixture of acids),
- fulguration, destruction by electric current, carbon dioxide laser, surgical treatment.
Treatment of sexual partners in the absence of symptoms is not indicated.
HPV infection in children and pregnant women
During pregnancy, a Pap test is part of routine monitoring. Particular attention in pregnant women with HPV infection is paid to vaginal sanitation and correction of microbiocenosis. If condylomas are an obstacle to the birth of a child, a caesarean section is performed. In 50% of cases, condylomas that appear during pregnancy disappear within 3 months after birth. If genital warts are detected in children over 18 months (especially over 2 years of age), sexual abuse should be excluded.
Outdated and modern methods of removing papillomas on the body
It is impossible to get rid of papillomas at home without consequences. The procedure is performed by a dermatologist, and in the case of precancer, by an oncologist. Before this, the patient must undergo tests, including:
- blood test for tumor markers;
- PCR diagnostics;
- taking papilloma tissue for histological examination.
In St. Petersburg and other Russian cities, several methods are used to remove papillomas on the body. To understand which method to choose, let's look at the table.
| Method | How is it carried out? | Advantages | Flaws |
| Surgery | A radical and very traumatic method of removing papillomas | Large tumors can be cut off | Traumaticity. Risk of infection and bleeding. Clearly visible scars remain forever. |
| Cryodestruction | Removing papillomas using liquid nitrogen | Does not require strong anesthesia, as the cold is freezing | Possibility of injury to healthy tissue. Inability to control the depth of impact. A scar remains. |
| Electrocoagulation | Destruction of a neoplasm by an electrical impulse. It is rarely used in medical centers where there is no new equipment. | Cheap technique | Cauterization is an unpleasant procedure. Possible scarring. Requires strong pain relief |
| Laser removal of papillomas | Destruction of a build-up with a directed laser beam | There is no need for preparation, no rehabilitation required - the wound heals immediately. No scars or scars. The procedure lasts only a few minutes. The laser activates skin regeneration, ensuring rapid healing. | The cost of laser papilloma removal is higher than the price of previous methods. |
| Removal of papillomas with a radio knife | The safest and most painless way to remove papillomas from the body. | No preparation needed. Rehabilitation is also not needed. The radioknife is equipped with a coagulator, which immediately stops bleeding by sealing damaged vessels. After removing papillomas with a radio knife, no scars remain, so the procedure is prescribed to get rid of tumors on the face and intimate parts of the body. Radio radiation activates skin restoration, so the wound heals instantly. | The price of removing papillomas using radio wave techniques is slightly higher than laser removal. |
Observation
- After the disappearance of genital warts, women continue to undergo regular cytological examinations of smears from the cervix (possibly with virus typing) annually.
- If changes are detected in cytological smears from the cervix, patients should be observed once every 6-12 months, depending on the situation, until the process is completely resolved.
- Women with oncogenic types of HPV must undergo cytological and colposcopic examination (if indicated, consultation with appropriate specialists and additional examination).
Can blood be a sign of malignancy?
Bleeding from papilloma causes sad thoughts in a person’s head. People begin to suspect the development of an oncological process. Not all viral growths are prone to malignant transformation.
The patient needs to visit a doctor. After the examination, the patient will be prescribed a laboratory test to identify the type of papilloma virus. In the absence of oncogenic strains, the possibility that papilloma is bleeding due to cancer is excluded.
This process is not associated with cellular mutation: it is only a sign of damage to the growth.
Primary prevention of HPV infection:
- Reducing risk factors by informing the population about methods of preventing STIs.
- Vaccination. HPV infection is characterized by the epitheliophilic nature of the virus, which does not penetrate the blood and does not cause an active reaction of the immune system.
- The vaccine has only a preventive effect and does not have a therapeutic effect.
- Gardasil is directed against four types of HPV (16, 18, 6,11). In the Russian Federation, this vaccine is recommended for use in girls and boys before the onset of sexual activity, starting at the age of 9 years, and in women up to 26 years195.
- The bivalent vaccine Cervarix is directed against HPV types 16 and 18. The use of this vaccine is allowed in girls from the age of 9 years and in women up to 25 years.
Vaccines are effective in preventing severe forms of precancer and cancer of the cervix, vulva and vagina, as well as exophytic condylomas (genital warts).
Using a condom reduces, although does not completely eliminate, the risk of HPV infection.
A significant risk factor for HPV infection is a large number of sexual partners.
What to do if a cut papilloma bleeds
Any disturbances in the healing process deserve attention. When a wound begins to bleed after the virus has been removed, there is a risk of infection spreading to healthy areas. You need to stop the bleeding and seek help from a doctor.
How to stop bleeding
The first method is to apply an ice cube. The cold will constrict the blood vessels, which will stop the bleeding. The water should be boiled to prevent bacteria from entering.
If the growth is located on a limb, it should be raised.
This reduces blood flow and lowers blood pressure. The arms are raised above the head, the legs are in a lying position, above the level of the heart.
You can use hydrogen peroxide. The drug corrodes connective tissue and stops the process.
If the bleeding does not stop, it is better to apply a sterile bandage, secure it with a bandage or plaster and go to the doctor.
Suspected risk factors for cervical cancer:
- smoking (including passive smoking);
- long-term use of oral contraceptives (more than 5 years);
- a large number of pregnancies;
- other STIs (caused by Chlamydia trachomatis, herpes simplex virus type 2, HIV);
- poor nutrition (especially those with low amounts of antioxidants in the diet);
- immunodeficiency (AIDS, organ transplantation, immunosuppressive therapy);
- a large number of sexual partners, early onset of sexual activity, sexual contacts with persons infected with HPV;
- genetic predisposition: polymorphism of some genes that encode proteins that regulate the cell cycle.
Secondary prevention of HPV infection includes screening the population in order to detect the disease at the precancer stage and its timely treatment.
Previous post When do the first signs of pregnancy appear?
Next entry How to calculate the calorie range