Every person has moles, and if they don’t get in the way or are not in visible places, we simply don’t notice them. But it happens that a mole makes itself felt - it hurts, itches, or even falls off. In this case, a trip to a dermatologist is inevitable, because such formations are classified as oncogenic, i.e. capable of developing into cancer.
Dermatological diseases and peeling moles
A very large group of reasons for peeling skin over moles.
The most common:
- allergic processes;
- genetic – ichthyosis;
- psoriasis;
- pityriasis versicolor;
- seborrhea;
- contact dermatitis.
The list can be continued for a very long time.
It is important to remember one thing: if dermatological pathology manifests itself as peeling and affects areas of the skin with moles, then this is a reason to consult a dermatologist and undergo a course of treatment.
Problems usually arise among those who do not want to be examined by a specialist and try to cure themselves.
Allergies
are a very common cause in modern civilization.
Character traits:
- the skin turns red;
- small urticaria-type rashes or large, dense papules appear;
- the involved areas itch, itch unbearably;
- As the allergy resolves, fairly large areas of peeling may remain at the site of the rash, including moles.
The beginning of the process after contact with an allergen (which one is an individual matter) indicates in favor of an allergic component.
Ichthyosis
This genetic pathology is not that uncommon.
There are cases in dermatological practice when large areas of the dermis of children peel off along with the moles located on them.
External signs depend on the severity of the disease: from dry skin to deep cracks.
Psoriasis
Another common reason for peeling.
Moreover, such a process is a characteristic sign of this disease.
The scales peel off almost like flakes.
But since only the epithelium of the stratum corneum (which is continuously renewed) disappears, the moles located deeper (nevi) do not disappear anywhere.
True, they can hide under plaques and become invisible.
Pityriasis versicolor
This is a fungal disease, the sign of which is a limited area of peeling, as if consisting of several spots.
The shape is round, the edges are uneven, scalloped.
The formation is painless, but in some people it itches.
Naturally, the focus of pityriasis versicolor can occur above the mole.
If it is also small in size, then sometimes it seems as if a mole is peeling off.
Although this is not true.
Seborrhea
A common phenomenon is when sebum synthesis is too active.
Quite often such problems arise on the head.
Foci of different sizes are formed, covered with loose yellowish scales, which literally peel off in layers.
Seborrhea occurs in children and adults.
The affected surface shines and peels, which is why it becomes a frequent reason for contacting dermatologists.
Contact dermatitis
Most often, these will be local allergic reactions in response to contact with allergenic fabric, detergent residue, grass, and so on.
They differ in that itching, redness and peeling occur to a limited extent.
Only on the surface of the body that came into contact with the allergen.
Problems with a mole
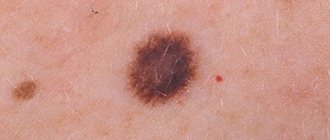
The greatest danger that nevi pose is the risk of degeneration of benign pigmented neoplasms into an aggressive tumor of melanocytes - melanoma.
This cancer accounts for only 4% of all skin tumors.
However, the particular aggressiveness and tendency to metastasize make melanoma a very dangerous process.
The high incidence of skin cancer is not associated with melanocytes, but descavamation is very characteristic of them.
When to see a doctor
If a mole, for no apparent reason, has dried out or changes in size or color have occurred, this is an alarming signal to immediately contact a doctor who will examine the formation and determine whether there is an indication for removal. Signs include:
- excessive peeling, dryness, roughness of the growth;
- if a benign formation does not meet the standards - an irregular shape, compaction has appeared, a change in the surface of the growth;
- if blood oozes from the mole, pus or ichor is secreted, there is an unpleasant odor;
- growth, the area around becomes denser;
- there is pain when touched;
- changes color to red, black or white;
- severe itching.
If a dangerous sign is present, removal is prescribed to help avoid the development of complications and prevent skin cancer.
Non-melanocytic processes during desquamation
Their source is the cells of any of the layers of the dermis or epidermis.
Let's look at the most common causes of cancer processes that are not directly related to moles.
Seborrheic keratosis, seborrheic wart or keratoma.
It starts with a small spot covered with yellowish scales.
It grows gradually and after a few decades reaches 6 cm in diameter.
Because of its coloring and loose scales, seborrheic keratoma is sometimes mistaken for a mole that has begun to grow and peel off.
Classification
There are 2 main groups of moles:
- 1. Vascular, or angiomas. They are formed during the rapid growth of subcutaneous capillaries with a change in the structure of their walls.
- 2. Pigmented, or nevi. Occurs when an excess amount of melanin appears in cells.
They are also divided according to their depth into:
● epidermal (on the top layer of skin);
● intradermal (located slightly deeper than the previous ones);
● borderline (develop between the epidermis and dermis).
Papillomatosis as a cause of peeling
A very common process, often provoked by human papillomaviruses.
Outwardly it looks like a small outgrowth of skin, single or multiple.
People sometimes call this formation a pedunculated mole, although papillomas are not classified as pigmented formations.
Unfortunately, they can become malignant and transform into squamous cell skin cancer.
The most common malignant cause of peeling is basal cell carcinoma.
This is a relatively rare metastatic tumor.
It grows slowly and often appears on the scalp, face and other exposed parts of the body.
One form, nodular basal cell carcinoma, may contain patches of melanin, which makes it resemble a large, growing mole.
Areas of peeling are observed around the pigment spot, crusts are formed, and the color of the node becomes uneven.
For squamous cell carcinoma, desquamation is not as common.
This process often occurs with lesions at the site of previously benign tumors.
For example, where there was recently a hanging mole.
Separately, it is worth dwelling on hemangiomas.
These are vascular, benign tumors that in the early stages look like a reddish spot and can easily be confused with a mole.
Often found in children.
Typical location:
- on the lip;
- on the skin of the back;
- on the genitals (labia, vulva, foreskin of the penis).
Hemangiomas of the abdomen and extremities are less common.
Peeling is not typical for them.
It may indicate either a near resolution of the process (spontaneous recovery from hemangiomas is not uncommon) or a progression of the pathology.
Treatment methods
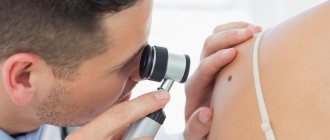
photo dermatoscopy of moles
The most popular methods for removing birthmarks and convex moles are the laser method, cryodestruction, electrocoagulation and radio wave method. These methods are used to get rid of elements up to 2 cm in size. Excision with a surgical scalpel is carried out with ambiguous biopsy results and at the discretion of the doctor.
- The laser method is considered the most effective way to get rid of skin tumors. Painful sensations during removal are minimal; local anesthesia can be used by subcutaneous injection of lidocaine. The wound heals quickly - within 2 weeks. Healing takes place under the scab, so it does not have the opportunity to fester. The operation is bloodless.
- The cryodestruction method is inferior in cost to the laser method and does not require such qualified personnel. Liquid nitrogen or dry ice freezes the tissue, which leads to the destruction of the nevus. This method is painful and therefore requires anesthesia. Healing is slower and the likelihood of infection is high.
- Electrocoagulation is a method of using electric current. The operation is bloodless, but quite painful. After removal, a scar remains.
- The radio wave method allows you to get rid of small elements. Removal is almost painless and highly effective. There is no bleeding. This method involves contactless removal of the tumor. The healing process takes 1.5-2 weeks.
Ignoring changes that occur with moles and age spots can have serious consequences. Melanoma is considered the most insidious and malignant tumor, as it metastasizes to internal organs with a tumor thickness of 2 mm. In order to prevent the degeneration of a benign neoplasm, it is necessary to exclude or minimize direct sunlight on moles, maintain proper immune activity and visit a dermatologist 1-2 times a year if there are a large number of moles.
Melanocytic processes during desquamation of a mole
Let us remember that melanoma accounts for only 4% of malignant skin tumors.
However, even this possibility must be taken into account.
Almost all melanomas develop from nevi (moles).
When this happens, five visually detectable parameters of pigment formation change:
- Asymmetry appears.
- The edge is “blurred”.
- The color changes - it lightens or darkens, the nevus can become spotted.
- The diameter increases.
- Changes increase (the focus evolves) over a relatively short period of time, several weeks or days.
At the same time, the degenerating mole itches, hurts, is easily injured, and at times peels off.
However, desquamation is not typical for most melanomas.
Should I delete
Removal of a scaly spot is indicated when a transformative process into a malignant tumor is identified or a nevus is located in a place that spoils a person’s appearance. There are several effective methods that can be used to get rid of dangerous or unwanted stains:
- Laser removal. The impact of the laser helps the mole fall off. Among the advantages of the method are the absence of scars and pain during the procedure.
- Radio wave removal. Using a radio knife, the doctor excises the formation and cauterizes the vessels to prevent bleeding.
- Cryodestruction method. Liquid nitrogen freezes cells and blood vessels, causing the nevus to disappear. Used for small formations.
- Electrocoagulation. Excision occurs using alternating or high-frequency current, which cauterizes vessels and tissues, as a result the growth dies and falls off.
- Removal using a scalpel. The method is used for large formations. The disadvantage of surgical intervention is the presence of scars and scars after the operation. It is not recommended to remove nevi located in a visible place with a scalpel. Among the advantages is the low cost of the procedure.
The need for removal and the choice of method are determined by the doctor based on the examination.
Diagnosis of peeling moles
You should always contact a dermatologist when:
- the mole grows rapidly, increasing in size daily or weekly;
- the structure of the nevus changes - it thickens, becomes hard, or vice versa, disintegrates, falls apart;
- peeling above it covers new areas or, on the contrary, becomes concentrated, limited and transformed into crusts;
- a mole was injured with bleeding (even if the bleeding stopped quickly);
- the spot hurts and itches a lot;
- the nevus falls off on its own, as if peeling off;
- and in any other cases when a mole behaves suspiciously or a patch of peeling appears on the body.
Every year or every 6 months, all people who have many moles (more than 50) need to see a dermatologist.
And if they also begin to peel off, then you need to make an appointment immediately.
Diagnosis is quite simple: dermatoscopy.
An experienced dermatologist examines the suspicious area of skin under multiple magnification and good lighting.
And, if he finds signs of infiltrating growth, he suggests removing such a focus.
However, there are indications for removal for ordinary, benign nevi.
When they are potentially dangerous by degenerating into a cancerous tumor.