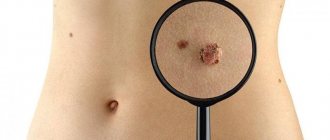
A mole becomes lighter - this is an alarming symptom that forces you to pay attention to the nevus. The condition may be accompanied by changes in the size and shape of the growth. A consultation with a doctor and laboratory tests will determine the cause of the pathological process. The specialist will prescribe the necessary treatment to prevent negative consequences.
Causes of nevus recurrence
In most cases, the nevus appears again, because... the mole that existed before it was not completely removed. Some of the nevus cells remained in the skin and after some time began to actively produce brown pigment (melanin). This is what we see at the site of the mole some time after removal. At the same time, in my practice there are already 5 cases where a relapse of the nevus developed after complete removal of the mole. Why this happens and where nevus cells appear where there were none are questions that, so far, have no answer.
Possible reasons for a mole changing color to light
The number of nevi depends on the production of melanin in the cells of the body. The gradual lightening of a pigmented area does not always pose a threat to human health, foreshadowing a possible disease. The process often begins in adulthood. The spot turns pale and disappears completely, leaving no traces.
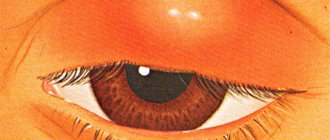
If a white border begins to appear around the growth, this is evidence of a malfunction of the pigment cells. A clear symptom of the onset of the disease is vitiligo, which is not a direct threat to the human condition.
In some cases, lightening indicates degeneration into a malignant tumor.
A change in the color of the nevus, its malignancy can develop as a result of hormonal imbalance, causing long-term weakening of the body. Constant aggressive exposure to the sun cannot be ruled out.
You cannot make a diagnosis on your own or look for the cause of the situation. A timely visit to a doctor will help determine the nature of the formation. A dermatologist or oncologist will prescribe an examination and the necessary tests.
Is nevus recurrence dangerous?
In answering this question, the key point is the histological examination of the removed mole. If it was carried out and the benign quality of the formation was confirmed, a relapse is not dangerous to health.
If the removal was without histology, there is a possibility that the mole was malignant, i.e. melanoma. In this situation, the health risk increases in proportion to the lost time. The tumor remaining in the skin can begin to grow rapidly and metastasize.
In order not to create panic, I will emphasize: the likelihood of a situation with melanoma not being completely removed is not very high. However, it exists.
Main reasons
Has the nevus turned into a bubble with liquid contents? This may be caused by:
- chemical or thermal burn due to contact with acids, alkalis, open fire or boiling water, prolonged exposure to direct sunlight in hot weather;
- damage to the surface of the skin - people sometimes accidentally cut off moles with a razor, rip them off with a comb or chain, or wash them off on clothes;
- an allergic reaction to cosmetics, household chemicals, synthetic fabrics and even food - in this case, several watery blisters usually appear at once.
If a mole suddenly becomes watery and grows rapidly, this may also indicate malignancy of its cells. Any nevus initially consists of benign cells, but over time and under the influence of a number of unfavorable factors it can transform into a malignant tumor. Associated symptoms of such degeneration are:
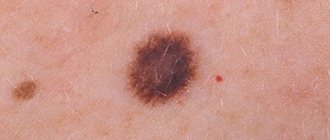
- change in color - benign nevi have a uniform color over the entire area, malignant nevi have inclusions of a different shade, darker or lighter areas;
- the appearance of discharge - pus, blood, exudate;
- loss of hairs growing in the mole;
- the appearance of wounds, inflamed areas, cracks on the surface of the neoplasm or near it.
If there was no histology...
Calmly remember whether the doctor performed any additional research methods. Dermatoscopy? Scraping or puncture?
If yes, with a probability of about 95%, everything is fine and this is really a relapse of the nevus, and not melanoma. It requires nothing more than observation and, most likely, will not grow or change.
If there were no other examinations or histology, it seems to me advisable to excise the relapse with mandatory histological examination.
Yes, this is not easy or pleasant, but only such a step can confirm the absence or presence of melanoma.
If a mole, which was removed without histology, not only appears again, but has grown to its previous size, you need to go to an oncologist URGENTLY.
Can it fall off on its own?
Nevi under the influence of external and internal factors can fall off on their own. There are many invisible moles on the human body, face, and mucous membranes. They darken and change in size throughout life. Sometimes birthmarks cause inconvenience and are located in areas of high friction. Growths on the neck cling to jewelry, on the back to clothing, during bathing they are rubbed with a washcloth, on the face they interfere with shaving, on the head they interfere with combing.
Cells with a large amount of pigment, under the influence of external and internal factors, die and flake off. The processes take place in the summer. After tanning in the sun or treatments in a solarium, during puberty, menopause, pregnancy.
Constant mechanical impacts on the formation damage its integrity. Often such growths get rid of. Sometimes they dry out and fall off on their own. A good reason to see a dermatologist. There is a possibility of conversion to melanoma. If the process is started, malignant cells grow, moving through the lymphatic and circulatory system. Without diagnosis and lack of proper treatment, death is possible.
Briefly about the main thing:
Recurrence of nevus, i.e.
a brown spot at the site of removal may be hazardous to health in rare cases. The likelihood of developing melanoma after removal increases if neither dermatoscopy, nor scraping/puncture, nor histological examination were performed . If this is exactly what happened to you, please consult an oncologist about re-excision with histology.
If you still have questions about the removed mole, you can ask me in the online consultation section or come to an appointment at the address in St. Petersburg - Asafieva 7/1.
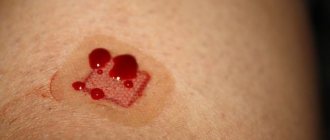
Are weeping moles dangerous?
If a mole on the surface of the skin begins to become weeping, this is a sign of abnormal behavior of a benign tumor; it may begin to transform into melanoma. Dangerous symptoms:
- fluid, ichor or blood oozes from under the formation;
- the formation of wet blisters on the surface of the formation and the area around it;
- changes in the size, shape and color of the nevus;
- inflammatory process with redness and swelling of the formation. The neglected condition leads to the release of pus with an unpleasant odor;
- long-healing wound;
- itching, burning, pain when touched;
- loss of hair from the birthmark, increase in the area of pigmentation.
If treatment is not started, characteristic symptoms may develop:
- increased fluid secretion;
- increased pain;
- rapid growth of nevus, change in skin color around;
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- the formation of ulcers on the surface, which can produce an unpleasant odor and pus;
- painful formations appear;
- bleeding;
- compacted structure of formations.
Melanoma grows by metastases, their signs:
- chronic obsessive cough;
- a sharp decrease in body weight;
- headache;
- muscle spasms.
The nevus begins to become wet due to the development of malignant melanoma, which manifests itself in different shades and asymmetrical shapes of nevi measuring more than 6 mm. Timely treatment will help avoid serious complications that can lead to death. The tumor can spread quickly, growing through several layers of the skin, traveling through the blood and lymphatic vessels. The liver, brain, and lungs are often affected.
Early diagnosis methods
Each person should regularly examine their skin for the presence of suspicious nevi. Paying attention to your body is a simple and effective diagnostic method. However, a person who does not understand medicine cannot always distinguish a healthy mole from a dangerous neoplasm - a sign of oncology.
At the hospital, doctors use the following diagnostic methods.
- History The collection of information by a doctor allows you to determine the root cause of the malignancy. The doctor will ask about sun exposure, injuries to the mole, and any actions taken with the neoplasm.
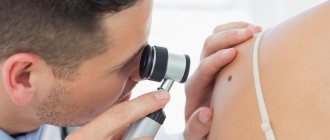
- Dermatoscopy Examination of the skin with dermatoscopes is an effective diagnostic method. The doctor will examine the color of the nevus, examine the relief and structure of the integument.
- Histological examination Examination of a skin sample under a microscope.
What symptoms should you see a doctor for?
The symptoms of the pathology have pronounced characteristics. White spots localized near moles cause a number of unpleasant moments for a person:
- stable itching, provoking scratching of the affected area of the epidermis at a certain point;
- peeling of the epithelial layer in the area of the nevus. Cracks may appear near the hair, on the back, face;
- pigmentation disappears gradually, starting from the middle;
- Sometimes a person experiences sharp pain.
A flat spot is not a cause for concern. The form of the disease informs doctors that the nevus has not transformed into a malignant structure. Examination of the affected area becomes inevitable if the spot changes in shape and color.
Doctors visually examine patients and collect materials to study histological parameters. Tissue analysis will reveal the exact reasons for the transformation of a nevus into melanoma. An effective technique is dermatoscopy. It is better not to risk it and visit a qualified dermatologist in the clinic.
In babies, a white or pinkish halo often appears around a mole. As a rule, this is associated with hormonal dysfunctions of a fragile body. Infants should be protected from ultraviolet radiation. Systematic consumption of vitamin D and microelements will not hurt.
Treatment and prevention
If, in addition to lightening, no other changes occur in the nevus, then no special treatment is required. Therapy is limited to procedures that improve skin condition. This includes physical therapy and taking vitamins.
But when pathological processes develop in a mole that contribute to its darkening or lightening, complex treatment is prescribed. To identify the nature of the neoplasm, the doctor performs a puncture of the skin. If, under the influence of processes that have changed the mole, it has become malignant, external treatment is not carried out. After excision of a nevus, the risk of relapse and dangerous complications increases.
Medical statistics say that malignant degeneration of a mole occurs in 13% of cases, mainly in women.
A favorable prognosis for treatment of a cancerous tumor is possible only under the supervision of an experienced doctor. The doctor performs a histological analysis. It makes it possible to determine the degree of malignancy of the mole and prescribe the optimal course of therapy.
What to do after radical removal of melanoma?
After therapy is completed, doctors will continue to monitor the patient closely. Along with the risk of recurrence of melanoma, other complications may occur. Postoperative monitoring of the patient's condition will include:
- regular examination of the skin and the condition of the lymph nodes - independently and by a doctor;
- depending on the stage of the disease, control instrumental studies (X-ray, PET, CT, etc.) may be needed;
- in some cases, to prevent recurrence of skin melanoma, techniques using radiation therapy (local irradiation of the tumor defect area), as well as protocols using immune drugs, can be used.
In some cases, after surgical treatment of melanoma, protocols using irradiation of the tumor defect area are used to prevent local tumor recurrence. Although this approach does not guarantee a reduction in the incidence of distant metastasis, according to statistics, it reduces the likelihood of local relapse.
Recently, techniques using intensity-modulated radiotherapy have been actively introduced into practice, which allows for maximum focusing of radiation with minimal damage to healthy tissue.
The use of stereotactic radiosurgery for metastatic melanoma makes it possible to directly irradiate the tissue of the secondary tumor, which limits the rate of its malignant growth.
The use of immunodrugs and the use of targeted therapy in the treatment of common tumors in 70% of cases makes it possible to transfer tumor cells to a “switched off” state. At the same time, intoxication is reduced, quality and life expectancy are increased.
Dangerous accompanying symptoms
Oncologists and dermatologists determine the malignancy of the growth by symptoms:
- the size and shape of the birthmark changes;
- darkening, increase in pigmented tissue, appearance of a black dot in the center of the formation;
- peeling;
- severe itching of the growth and the skin around it;
- the appearance of erosion, bleeding ulcers;
- pain of increasing nature.
If any of the symptoms appear, contact the clinic immediately for help.
Medical signs of degeneration
The acquisition of a lighter color by a mole may be a consequence of its degeneration. But there are other warning signs as well. Dermatologists have developed a special scheme that allows you to record all detected symptoms, which helps to timely track the degeneration of a mole into a malignant formation. It is called ACORD - after the first letters of the signs that should alert you:
A – asymmetry. Any two halves of a healthy nevus must be absolutely identical in shape, color, and structure.
K – edges. A sign of pathological changes are disturbances in the outline of the mole, the appearance of unevenness and blurriness.
O – coloring. Not only darkening, but also lightening of the nevus serves as an alarming signal. In a benign formation, the color is distributed evenly.
R – size. A mole that is too large in diameter or clusters of small skin growths merging together is cause for concern.
D – dynamics. This is a change in various parameters of the nevus (shape, size, color, etc.). Any pronounced dynamics forces us to pay closer attention to the mole.
Is the white halo dangerous?
In most cases, a white border around the mole (ring shape) is a harmless phenomenon. At the same time, light pigmentation is a sign of degeneration. Dermatologists and oncologists advise not to delay visiting specialized clinics. Timely treatment is the key to health and longevity.
The system of preventive measures consists of following a number of measures:
- when going outside, rub yourself with creams and ointments for protection;
- Do not overuse the solarium. People with pale and dark skin should not visit such places;
- do not go out into the sun in the hot summer from 11 a.m. to 3 p.m. Otherwise, the mole may turn white/light;
- buy natural cosmetics from famous brands;
- minimize the number of salon procedures;
- follow the recommendations of experienced cosmetologists after performing certain manipulations with the body;
- promptly and efficiently treat acne;
- treat endocrine dysfunction systemically;
- periodically get tested for the development of skin diseases;
- adhere to a healthy lifestyle and quality nutrition;
- Take medications and dietary supplements in recommended doses under the supervision of a doctor.
Discolored skin develops a small rim over time. Constant stress and depression can provoke the formation of a structure. Syringomyelia is the source of the disease; the cavity in the spinal cord becomes inflamed. Metabolism affects the condition of the area around the mole. If this process is disrupted, difficulties will arise. Benign tumors are also possible.
High-quality drug therapy can inhibit the pathogenesis of the light spot. To do this, dermatologists create effective regimens using modern drugs. Medicines eliminate pigment and normalize endocrine functions. As a result, the liver is activated. The therapeutic method PUVA (photosensitizers) is effective. Doctors often prescribe hormonal substances based on the copper element and ascorbic acid. The above measures stop the progression of the pathology.