How does the disease manifest? Signs of liver problems
- External manifestations
- Internal manifestations
The liver is the largest gland in the human body, so its diseases have a serious impact on overall health. At the same time, it is very sensitive and extremely susceptible to various disorders. Doctors often hear the complaint “I have pain in the liver area.” But can the liver itself hurt and what sensations does a person experience when various diseases appear?
Content:
- How does alcoholic cirrhosis of the liver develop?
- Classification
- Symptoms of the disease
- Diagnostic features
- How to treat alcoholic cirrhosis of the liver
- How long do people live with cirrhosis of the liver?
The human liver is the main organ that protects the body from the effects of poisons. It takes the brunt of alcohol and neutralizes toxins. In this difficult and sometimes unequal struggle, it itself is gradually being destroyed. As a result, inflammation develops - hepatitis, which, with continued alcoholization and the destructive influence of alcohol, turns into alcoholic cirrhosis of the liver. This complication is life-threatening and, in the absence of sobriety and adequate treatment, leads to disastrous consequences. Therefore, the sooner the patient begins to get rid of this disease, the greater his chances of regaining health. Healing pathology is included in the tasks of the main course of anti-alcohol treatment. Hepatologists deal with advanced stages.
Causes of cirrhosis
According to statistics, about 50% of liver cirrhosis is associated with alcohol abuse and the development of alcoholic liver disease (ALD). 1Moreover, 25% of them had a history of viral hepatitis.1
Other causes of cirrhosis include2:
- metabolic diseases associated with excessive accumulation of iron, copper and other elements;
- Autoimmune lesions;
- Primary and secondary biliary cirrhosis;
- Diseases of the vascular system (Budd-Chiari disease);
- Long-term use of medications that have a toxic effect on the liver;
- non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), which is associated with the accumulation of large amounts of free fatty acids in hepatocytes (liver cells), is characterized by a chronic course and potential progression from stage to stage: steatosis - steatohepatitis - fibrosis - cirrhosis (same as alcoholic disease liver, but the likelihood of developing cirrhosis in AFLLD is 10 times higher).5
Regardless of the cause, cirrhosis develops in the same way: the lobular structure of the liver is disrupted with the formation of nodes in place of destroyed hepatocytes—the so-called false lobules.
- Small nodular - the size of fibrous nodes is no more than 3 mm;
- Large nodular - nodes 3-5 mm;
- Mixed.
How does alcoholic cirrhosis of the liver develop?
This painful process leads to the death of cells - hepatocytes. In their place, fibrous connective tissue appears, which forms the essence of cirrhotic changes. In the classification of all existing cirrhosis, alcoholic diseases occupy from 30 to 50%. Ethanol entering the blood is neutralized by hepatocytes. Free radicals released during detoxification destroy the cell membranes of the organ. Vessels also suffer from destruction. Their subsequent spasm and hypoxia lead to worsening destruction. The dead zones are replaced by fibrous formations. The main functions of the liver are gradually and progressively lost. In advanced stages they are irreversible. Only transplantation can help the patient. As a result of observing people who drink, it was revealed that the cirrhotic process develops in 35% of alcoholics. The disease occurs more often in men, and is more severe in women.
3.Risk factors
Risk factors that affect the likelihood of developing liver disease:
- Work in chemical laboratories conducting analyzes of body fluids;
- Increased levels of cholesterol and triglycerides in the blood;
- Work involving chemicals and toxins;
- Some medicines;
- Alcohol abuse;
- Piercing and tattoos;
- Blood transfusion;
- Unsafe sex;
- Obesity;
- Diabetes.
About our clinic Chistye Prudy metro station Medintercom page!
Classification
The disease is divided according to changes in the organ and severity. The following types of cirrhosis are distinguished:
- Small-knot.
- Large-knot.
- Mixed.
Stages of alcoholic cirrhosis of the liver:
- Compensated – without pronounced symptoms.
- Subcompensated – with initial manifestations, but with preservation of functions.
- Decompensated – accompanied by partial and then complete failure of functioning.
Appearance of the abdomen with cirrhosis at the last stage
Big belly and prominent veins
During the first stage, notes Prokishechnik.Ru, it is problematic to detect obvious symptoms and respond in a timely manner. With the development of liver cirrhosis to the last stages, external signs become clearly visible. You can see them in photos of people with this diagnosis.
Patients with liver cirrhosis begin to experience stomach problems, discomfort, possible nausea, and loss of appetite. Ulcers may bleed and intestinal spasms may appear. In this case, a change in the structure and color of the stool is observed, and an unpleasant odor comes from the mouth.
Fluid accumulates in the stomach, the volume of which can reach 26 liters. The skin acquires a yellowish tint and becomes rough. In the final stages, the stomach looks like a swollen ball. These symptoms are called ascites, which appear in the last stages of the disease.
Symptoms of the disease
As such, there are no symptoms at the early stage of compensation. On this basis, identifying the cirrhotic process is quite difficult. Therefore, the disease is not detected for the first few years. Initial suspicions arise against the background of hepatitis with increased organ size. When receiving compensation, the patient complains about:
- Decreased appetite and nausea.
- Emaciation.
- Weakness.
- Belching, heartburn, flatulence.
- Unpleasant sensations in the right hypochondrium.
When examining the patient, an increase in the size of the liver borders is determined. At the stage of subcompensation, the following is revealed:
- Severe asthenic syndrome: constant weakness and increased fatigue, apathy, depression.
- Great emaciation with aversion to food.
- Low blood pressure.
- Tachycardia.
- Redness of the skin of the face, hands and feet.
- Visible enlargement and palpation of the parotid glands.
- Specific obesity: thin limbs and fat deposits in the abdomen and thighs.
- Gynecomastia in men.
- Testicular atrophy, infertility, impotence.
- Changing fingers in the form of drumsticks.
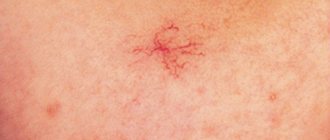
- Yellowish skin with spider veins.
- Contractures of the muscles of the palms with gradual loss of their functions.
Decompensation is characterized by:
- Signs of portal hypertension with ascites - accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity.
- Rectal hemorrhoidal and esophageal (esophageal) bleeding.
- Jaundice with liver failure, enlarged spleen.
- Vomiting, complete lack of appetite, constant diarrhea.
- Coma.
- Hepatic encephalopathy with personality changes and disturbances of consciousness.
Palpation of the abdomen reveals a sharply compacted liver. High numbers of transferases indicate an advanced process. Cirrhosis is often complicated by dysfunction of the lungs, heart, and pancreas. Polyneuropathy appears on the part of the nervous system.
Sweat and body odor
The role of the skin as an organ of the human excretory system is very important. are the leading ones in performing this function .
Sweat contains:
- 98% water,
- 1% table salt dissolved in it,
- 1% - metabolic products (urea, uric acid, ammonia), toxins and waste from the blood.
The sebaceous glands secrete from 100 to 300 g of sebum during the week. It contains cholesterol, proteins, fatty acids, salts, as well as toxins and wastes that enter the sebaceous gland from the blood. That is why, in advanced stages of liver slagging, an unpleasant odor constantly emanates from the surface of the human body. In an effort to get rid of it, a person visits the shower several times a day and tries new and new deodorants. However, a few hours after the next shower, the smell is felt again.
Diagnostic features
When identifying cirrhotic changes, the existing symptoms are taken into account. Additionally, clinical and biochemical blood tests are taken from patients.
They define:
- Anemia.
- Less commonly, leukocytosis.
- Decreased platelets.
- Increase in gamma globulins.
- Increase in AST (more) and ALT.
Ultrasound data plays an important role. They reveal a decrease in the size of the organ and foci of fibrosis. Computed tomography provides an even more accurate picture. With its help, not only the structure is assessed, but also pathological changes in nearby anatomical formations. Informative methods include elastography, and the most accurate is liver biopsy. All obtained data are examined using a special Child-Pugh scale, which allows you to accurately determine the phase of the disease: compensated, subcompensated, decompensated.
Clean blood means healthy skin, hair and nails
Do you have dry or too oily skin? Are more and more wrinkles appearing? Is your hair thinning and falling out?
You probably spent a lot of time and money on visits to beauty salons, but the problem is still with you.
Unfortunately, it cannot be any other way.
After all, poorly filtered blood with poisons and toxins nourishes every cell of our body, including the skin and hair follicles. The consequences of this are peeling, irritation, acne, intense formation of wrinkles, dry, brittle or too oily hair, hair loss.
Subscribe to our INSTAGRAM account!
To better understand why this happens, let's remember the structure and functions of our skin. Skin is the outer covering of a person. This is a barrier between the external environment and the human body.
Skin performs many important functions. It has its own closed immune system.
The skin regulates body temperature with the help of 2.5 million sweat glands. It protects internal organs from mechanical influences (shocks, pressure, friction).
The presence of an antiseptic environment on the surface of the skin protects the body from the penetration of pathogenic microbes. The skin protects a person from the harmful effects of sunlight and maintains the necessary level of moisture inside the body.
The skin, like the kidneys, belongs to the organs of the human excretory system. It consists of three layers:
- epidermis,
- dermis,
- subcutaneous fat tissue.
The outer layer, which is directly affected by the environment, is called the epidermis (lat. epidermis). Its thickness is approximately 0.03-1 mm. The thinnest epidermis is on the eyelids.
Peeling of the epidermis is a normal physiological process. Approximately two billion keratinized scales are shed from the surface of the skin every day. Every three to four weeks, epidermal cells should normally be renewed.
Skin restoration occurs due to the division of cells in the basal layer. This is the deepest layer of the epidermis, bordering the dermis. This happens mainly at night when we sleep.
Within 3-4 weeks, young cells from the basal layer rise to the surface of the epidermis. During this process, they become flatter, drier, lose their cell nucleus and settle on the surface of the skin as flat and dead keratin scales, forming the stratum corneum. There they are layered on top of each other, like the bricks of a fortress wall.
The upper part of the stratum corneum gradually separates. Normally, we should not notice this skin renewal.
The exfoliation process becomes noticeable only when the keratinized cells are separated in large groups (500 - 1000 pieces each) in the form of scales.
Below the epidermis is the dermis . This is a much thicker layer of skin (up to 2.4 mm).
The dermis consists of connective tissue cells and the so-called “ground substance”, which contains collagen and elastic fibers.
Dermal cells produce all components of the ground substance, including fibers.
The condition of these fibers determines whether the skin will look taut and elastic or flabby and flaccid.
Collagen fibers are capable of absorbing and storing a lot of moisture. The more moisture they retain, the smoother and more elastic our skin looks.
How to treat alcoholic cirrhosis of the liver
Therapy implies that the drinker must completely stop drinking alcohol. Only in this case is it possible to achieve a positive result. The second important condition for healing is the selection of a special diet. The food should be dominated by products containing a complete complex of proteins and vitamins. Fried, smoked, salted and preserved foods are excluded. These goals are best met by the fifth liver table. Drug therapy includes:
- Long-term use of hepatoprotectors.
- Ursodeoxycholic acid.
- Multivitamins. After the injection course, they continue to be given in tablets.
- Hormone therapy.
- Ademetionine is the best way to restore and stimulate hepatocytes, protecting them from destruction. It can improve the flow of bile, has detoxifying properties and protects the brain from the effects of poisons. It has an antidepressant effect.
- Protease inhibitors. With their help, inflammatory phenomena are reduced and fibrosis processes are prevented.
Treatment of complications includes eliminating the cause of portal hypertension (increased pressure in the hepatic vein system) by restricting blood flow in the veins of the esophagus. For this purpose they prescribe:
- Pituitary hormones.
- Nitrates.
- Beta blockers.
- Diuretics.
Lactulose is prescribed for intestinal detoxification and improvement of digestive processes. When ascites appears, large doses of diuretics and albumin are administered. Excess fluid from the abdominal cavity under the influence of drugs is actively excreted by the kidneys. When hepatic encephalopathy develops, the following is carried out:
- Active detoxification.
- Antibacterial therapy.
- Prescribing a special diet to minimize protein.
In case of complete liver failure, it is recommended to treat the patient in a surgical hospital for the purpose of organ transplantation.
Treatment of cirrhosis
Treatment of cirrhosis involves:
- Treatment of the underlying disease that led to the development of cirrhosis;
- Specific therapy for complications, including medications: for example, the prescription of diuretics for ascites, the prescription of antibiotics for spontaneous bacterial peritonitis, etc.
- Surgical treatment of ascites and bleeding from dilated veins of the esophagus and stomach1
Important components are diet, exclusion of harmful effects on the liver, such as alcohol, hepatotoxic drugs, treatment of concomitant chronic diseases.4 If the measures taken are ineffective, organ transplantation is indicated1.
How long do people live with alcoholic cirrhosis of the liver?
Prognostic expectations depend on the stage of the disease, complete abstinence from alcohol, the age of the patients, compliance with dietary recommendations and existing complications. The more advanced the form of the disease, the worse the survival rate. The answer to the question of clients of drug clinics: does alcohol cause cirrhosis of the liver is always an unequivocal yes.
The text was checked by medical experts: Head of the socio-psychological service of the Alkoklinik MC, psychiatrist-narcologist L.A. Serova.
CAN'T FIND THE ANSWER?
Consult a specialist
Or call: +7 (495) 798-30-80
Call! We work around the clock!
Treatment prognosis at the last stage
The disease affects the entire body, so it becomes impossible to cure it at the last stage. The patient has only the ability to: completely change his lifestyle, give up bad habits, change the menu, thanks to which he can extend his life. Organ replacement surgery may be required, followed by constant monitoring by doctors.
With cirrhosis of the liver, a person's appearance changes, as can be understood from the photographs. It’s not so easy to see internal changes, but it’s worth knowing that to maintain the whole body you will have to take medications, regularly give injections and IVs. The task of doctors is to prevent the development of other diseases caused by liver failure.
Medicines, notes prokishechnikRu, can only be prescribed by a doctor, having selected a suitable menu and set of remedies. Self-medication can lead to a sharp deterioration of the condition or death. Medicines prescribed by a doctor can be divided into several groups:
- diuretics;
- vitamin complexes;
- diuretics;
- hepatoprotectors;
- adsorbents;
- glucocorticoids.
For the rest of his life, it is important for the patient to maintain a certain diet, avoid alcohol, smoking, eat light, healthy foods, and lead a healthy lifestyle.
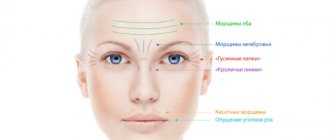
Acne and more: external signs of liver problems
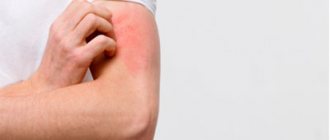
Acne due to liver disease is a common and understandable problem, but there are other types of skin problems. Redness on the face due to the liver may be of allergic origin. This happens when the body cannot cope with the full processing of, for example, medications. Yellowness and sallowness of the skin are usually caused by excess bilirubin, which is normally excreted by the liver. But these signs usually appear when there are significant health problems. And acne, as the very first marker of problems, breaks out at the slightest problem.
Acne due to the liver is not always a sign of serious pathologies or chronic damage. Rather, on the contrary, a certain number of acne that are resistant to lotions and cleansing simply indicate that the liver needs support, for example, a diet, or giving up some bad habits. Also, acne on the face due to the liver can signal that the medications taken are not suitable for the body.
How it works?
Does the liver affect the skin directly? No, the connection and the mechanism for its implementation are much more complex. The liver, as a natural filter of the body, must transform, bind and remove all toxins, poisons - that is, everything that cannot be removed without additional processing. Since the temperature inside the organ is always higher, the components of almost any poisons disintegrate much faster there into suitable for excretion. But there is a nuance: during the filtration process, the liver itself can become damaged. A simple example is that regular processing of large doses of alcohol disrupts self-healing processes and triggers organ destruction.
A diseased liver “creates” acne in two ways - either the body tries to remove toxins through the skin, and this reduces the immune defense by changing the pH to a more alkaline one. Either more sebum is released through the skin - a little fat is normally excreted through the pores, which in small quantities protects the skin from drying out and helps maintain its elasticity. Increased sebum secretion often indicates problems with the liver: when the skin begins to “shine” 2-3 hours after washing, it’s time to contact a hepatologist. Acne due to liver disease with severe excess secretion of the sebaceous glands is a secondary problem. A large amount of fat is a breeding ground for bacteria and fungi. And if both problems are combined, acne lesions appear with a large number of pimples.