Cutaneous staphylococcus (Staphylococcus epidermidis) is a potentially fatal bacterium that is commonly found on the skin, oral mucosa, and genitourinary tract. Who is at risk of contracting cutaneous staphylococcus? What diseases does cutaneous staphylococcus cause? How to treat Staphylococcus epidermidis infection?
E. coli and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA bacteria) are dangerous and very fast-spreading bacteria. Staphylococcus aureus infection can cause diseases such as pneumonia, myocarditis, phlebitis and meningitis. In turn, the bacterium Escherichia coli (Escherichia coli), the cause of urinary tract infections, urethritis, and cystitis. The consequences of E.coli infection largely depend on the strain of bacteria.
Escherichia coli bacterium
Meanwhile, it turns out that Staphylococcus epidermidis, that is, cutaneous staphylococcus, is a much more dangerous bacterium. This bacterium becomes increasingly resistant to antibiotics and causes life-threatening infections after surgery.
What is cutaneous staphylococcus?
The content of the article
Staphylococcus epidermidis, a close relative of MRSA bacteria. It is so common that it is found on almost every person's skin. Cutaneous staphylococcus is part of the natural bacterial flora and is not dangerous when you are healthy - it is a deadly microorganism that is found throughout the world and remains dormant in most cases.
This type of staph is often ignored in clinical trials, and due to its ubiquity, it can evolve and genetically mutate between bacteria very quickly.
The problem with cutaneous staphylococcus occurs when immunity is reduced - then Staphylococcus epidermidis infection can cause a number of complications and become a risk factor for many diseases. Cutaneous staphylococcus is especially dangerous for people who have undergone invasive procedures.
General information
Staphylococcus aureus
Staphylococcus aureus belongs to a type of spherical bacteria of the genus Staphylococcus. Microorganisms are gram-positive - they retain pigmentation when washed using the Gram method.
The bacterium has the ability to survive on mucous membranes and outer skin. It doesn't always cause illness. A person may simply be a carrier. There are up to 40% of such people around the globe.
Carriage can be of a different nature - permanent or transient. This circumstance is influenced by the state of the competing microflora, the type of strain and the health of the carrier. The existence of Staphylococcus aureus was discovered by Scottish surgeon Alexander Ogston in 1880.
In 1884, the bacterium was described. The research was conducted by the German physician Ottomar Rosenbach, professor of therapy and pathology. The species is named because of its appearance under a microscope. Most bacteria are colorless when viewed closely, but these microorganisms have a golden hue.
Their color is ensured by the presence of a coloring pigment from the group of carotenoids found in the tissues of organisms. The length of the staphylococcus chromosome is up to 1 micron, and it contains a huge number of genes - more than 2.5 thousand.
Cocci are immobile during their life cycle and attach to the epithelium in pairs or singly. In appearance, their colonies resemble bunches of grapes, which is also reflected in the name of the genus (“staphula” translated from Greek means “bunch of grapes”).
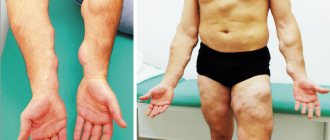
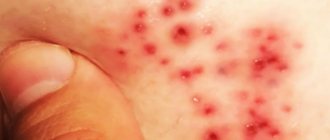
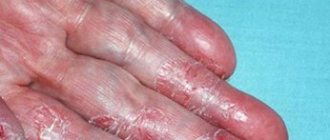
Cutaneous staphylococcus - symptoms
Symptoms of activation of staphylococcal infection:
- skin changes;
- boils and skin rashes;
- pain at the site of a staph infection;
- ulcer formation.
Staph Infection
Symptoms of cutaneous staph are nonspecific—each case of cutaneous staph may have slightly different symptoms depending on what part of the body is affected. People undergoing surgery should pay attention to the symptoms of cutaneous staphylococcus.
What diseases do staphylococci cause?
The content of the article
The main causative agents of purulent-septic diseases are staphylococci (from the Greek "staphyli" - clusters, "kokkos" - kernels, balls, which corresponds to the appearance of these microbes under a microscope) and streptococci (from the Greek "streptos" - chain).
We owe to these microorganisms such diseases as boils, carbuncles, pyoderma, abscesses, phlegmons, panaritiums and other suppurations of the skin. When the mucous membranes are damaged, conjunctivitis, stomatitis, otitis, and enteritis develop.
Severe forms of the disease are pneumonia, osteomyelitis (bone tissue lesions) and septic - generalized inflammatory processes in internal organs when staphylococci and other microorganisms circulate in the blood (blood poisoning) are especially dangerous.
After purulent infections, various complications arise, including those that can lead to a chronic course of the disease and disability (myocarditis, heart defects, thrombophlebitis, peritonitis - inflammation of the peritoneum).
Losses associated with loss of ability to work only from staphylococcal diseases exceed those caused by all infectious diseases, with the exception of influenza. The number of newborns and adults who die from staph infections is more than twice the number who die from other contagious diseases.
Cutaneous staphylococcus in a child
A child's immune system is more sensitive than an adult's, so cutaneous staphylococcus can be dangerous even for the youngest. If a child has skin lesions, he should be carefully treated, dressed and protected from external factors to avoid infection. If your child has skin changes for no reason, consult a doctor.
Staphylococci in a child can cause folliculitis, staphylococcal sycosis, and multiple abscesses. Conditions such as bullous impetigo, bullous inflammation and peeling skin can occur as a result of staph infection in newborns.
Causes and types of diseases, mechanism of infection
Very often, infection occurs in a hospital setting.
Staphylococcus aureus ranks high on the list of pathogens that enter the body of patients while in a hospital setting.
The range of diseases caused by bacteria is striking in its diversity:
- Skin infections - carbuncles, boils, cellulitis, folliculitis, bullous impetigo.
- Respiratory tract infections - pneumonia, sore throat.
- Infections of the central nervous system - meningitis, brain abscess, thrombophlebitis of the superficial veins of the brain.
- Urinary tract infections – cystitis, urethritis.
- Infections of bones, joints, muscles - osteomyelitis, purulent arthritis, purulent myositis.
The causes of staphylococcal infections include the following factors:
- presence of chronic diseases;
- weakened immune system;
- taking a large number of medications;
- avitaminosis;
- frequent stress;
- infection from a carrier;
- living conditions that do not meet sanitary and epidemiological standards.
Infection with Staphylococcus aureus is particularly dangerous for both children and adults. Microorganisms are highly resistant to most drugs and adverse external factors.
A peculiarity of this species is its ability to produce endotoxins, which cause general intoxication of the body, and with late medical intervention - sepsis and infectious-toxic shock.
Prevention of staphylococcus
To prevent infections associated with staphylococcus, it is recommended:
- washing hands before eating and after going outside;
- treating any cuts, abrasions and wounds with antiseptics;
- strengthening the immune system through hardening, proper nutrition and exercise.
“SM-Doctor” is a clinic where real professionals work. If you detect the slightest signs of infectious processes in a child, you should immediately seek help. Timely initiation of proper treatment is the key to the health and well-being of every child. Contact us!
Antibiotic resistance of staphylococci
The more we attack, for example, pathogens of purulent-septic infections with antibiotics, the more often antibiotic-resistant microorganisms appear.
Under the influence of antibiotics, the inhibitory effect on staphylococci of other microbes - common inhabitants of our body - is disrupted. Moreover, sometimes antibiotics simply stimulate the development of staphylococci and streptococci. Therefore, without medical prescription, the independent use of antibiotics (and other antibacterial agents) in the event of purulent skin lesions should be excluded.
Any treatment for staphylococcal skin pathologies should be prescribed by a dermatologist! Diseases of other organs are treated by appropriate specialists - gynecologists, urologists, therapists.
Why is staphylococcal infection dangerous?
Staphylococcus is especially dangerous in association with viruses and fungi, as well as with concomitant childhood droplet infections that reduce the overall reactivity of the body. It is not without reason that in many diseases local or general complications caused by staphylococci are observed.
Thus, during influenza epidemics, staphylococcal pneumonia is not uncommon, which most often turns out to be the cause of a child’s long-term illness and is the most common prerequisite for death.
Staphylococcal and streptococcal toxins have pronounced sensitizing properties, causing allergies and toxic damage to the heart muscle, kidneys and other important organs. Unlike a number of pathogens of childhood infections, the site of action of which is limited to certain areas of body tissue, staphylococcus and streptococcus are “omnivorous”.
They can cause inflammation of the gallbladder (cholecystitis), toxic dyspepsia and gastroenteritis, inflammation of the joints (arthritis), and genitourinary tract (urethritis and endometritis). In newborns, staphylococcal and other purulent inflammatory phenomena begin with the umbilical wound or other skin lesions that are invisible at first glance (scratches, abrasions).
It must be emphasized that up to 90% of cases of sepsis in young children are associated with staphylococcus.
Symptoms and forms of development of staphylococcal infection
Of course, the symptoms of Staphylococcus aureus depend on how and where the patient became infected. Much also depends on how well the patient's immune system works. But the most common symptoms are the following:
- Hyperthermia.
- Swelling, purulent rash, itching, red eyes.
- Impaired sense of smell and breathing, in general.
- Vomiting and nausea.
- Sore throat, cough.
- Rotovirus infection.
- Severe headache, epilepsy, shortness of breath.
- Myalgia, arthralgia.
Most often, patients do not show signs of Staphylococcus aureus The person feels the same as before, there are no signs of illness. But as soon as something provokes a weakening of the immune system, the development of pathology begins.
causes of staphylococcus
There is some difference in the effects of staphylococcus on a woman and a man. A woman has an anatomically short urethra located next to the vagina. This feature allows saprophytic flora to enter the bladder and cause cystitis.
Young children do not yet have a strong immune system. Therefore, they are at risk of contracting staphylococcus. This predisposition decreases with age. And at an older age, this infection is not so terrible for a child. At an early age it can cause many problems. And in the most difficult cases, even lead to the death of the patient.
Symptoms of staphylococcus
The clinical picture of the disease in children can vary significantly. With sufficiently active immunity, the phenomenon of asymptomatic bacteremia can even be observed, when the pathogen is detected in the patient’s blood, but does not affect his well-being and the functioning of his internal organs. Factors that influence the severity of the pathological process are the individual characteristics of the child’s immune defense, his age, the type of bacteria, and the amount of pathogen that has entered the body. Possible symptoms of the disease are:
- pustular skin lesions with the formation of boils or even carbuncles;
- itching of the skin, the appearance of red rashes or areas of increased pigmentation;
- local inflammation of the oral mucosa (stomatitis), eye conjunctiva (conjunctivitis) and the like;
- increased body temperature;
- emotional lability;
- general weakness, loss of appetite, disruption of normal sleep rhythm;
- nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, flatulence, diarrhea;
- enlarged tonsils and redness of the throat.
If at least a few of these symptoms are detected in a child, you should immediately seek help. Specialists will be able to quickly determine the type of pathogen and the cause of the deterioration of the baby’s condition, and will also prescribe adequate drug treatment.
About pathology
Colonies grow on a medium - blood agar. The bacterium got its name because of its golden color. In fact, approximately one-quarter of the world's population is carriers of this bacterium.
Staphylococcus aureus
Its favorite locations are the armpits, nasal cavity and groin area. But, despite its normal presence on the skin, it does not cause any diseases in humans. It is classified as normal skin flora.
It is worth noting that it does not cause any pathologies as long as it is in moderate quantities. As soon as its quantity exceeds the permissible norm, the development of the pathological process begins. As a rule, staphylococcus begins to penetrate into the deeper layers of the skin through the presence of scars, cracks and other damage. As a result, a skin infection or even an abscess develops.
Basically, all body systems are damaged. First of all, the liver and spleen are affected. Then the musculoskeletal system. But that’s not all, because often the consequences are much more serious. Therefore, you should not neglect the first symptoms of the disease and immediately go to a specialist.
Diagnosis of staphylococcus
“SM-Doctor” is a multidisciplinary clinic, which is equipped following the example of leading clinics in Europe. Thanks to our own laboratory and modern equipment, our doctors can quickly and accurately identify the cause of deterioration in the condition of a child of any age and determine the strain of bacteria in order to select an effective treatment. Diagnosis of staphylococcal infections begins at the stage of the first consultation. Our specialists collect anamnesis, carefully analyze the complaints of the parents or the patient himself and conduct a comprehensive examination. This allows you to almost immediately decide on treatment tactics. To clarify the diagnosis, the following procedures are used:
- a set of standard laboratory tests (general and biochemical blood and urine tests);
- bacteriological examination of blood, skin scrapings, feces, urine;
- enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) - the technique allows you to identify specific antibodies to a specific pathogen;
- Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is one of the most effective diagnostic methods, which makes it possible to detect DNA or RNA particles of any bacterium in a minimal amount of test material.
In addition, all young patients are examined by related specialists.
In case of staphylococcal infection, consultation with a cardio-rheumatologist, sometimes a nephrologist, neurologist and other doctors is required. Our specialists pay special attention to the fact that in the absence of timely treatment of staphylococcal infection of any origin, it shows a tendency to generalize, which is fraught with septic conditions and death for the patient.
Diagnostic search
For a proper diagnosis, you need to see a doctor. But it is worth conducting research only if there are symptoms. The fact that biological material contains staphylococcus is an absolute norm. Initially, you need to collect the material. Be sure to conduct dynamic tests. If the number of bacteria constantly increases, this is a staphylococcal infection. It is necessary to understand what type of infection caused it in order to choose the right treatment tactics for Staphylococcus aureus .
diagnosis of staphylococcus
Causes of staphylococcus
All types of staphylococcal infections occur against the background of the activity of the bacteria of the same name.
It is capable of producing exo- and endotoxins, which negatively affect the functioning of the child’s internal organs and systems. In practice, doctors at the SM-Doctor clinic encounter the following variants of staphylococcus:
- Saprophytic. It is rarely found in children; it most often affects the organs of the genitourinary system.
- Epidermal. It affects the baby’s skin, but with the development of primary or secondary immunodeficiency. The bacterium can be present on the surface of the child’s skin without provoking purulent lesions.
- Hemolytic. The pathogen can affect almost any part of the patient's body, even the endocardium (the inner wall of the heart). In the absence of adequate treatment, a septic condition develops.
- Golden. The most aggressive strain of bacteria, which causes a pronounced clinical picture with an increase in body temperature and a serious deterioration in the child’s well-being.
Staphylococci are transmitted from sick people by airborne droplets, nutrition or contact. Schoolchildren often get sick from eating unwashed foods, infants get sick through the air, etc.