Causes and symptoms of dermatitis on the hands
The cause of contact dermatitis on the hands is mechanical, physical, chemical or biological effects on the skin: wearing metal jewelry, latex or wool gloves, exposure to household products, plant sap, pollen, ultraviolet radiation, cold, cosmetics such as nail polish or skin cream. hands
Allergic dermatitis on the hands develops under the influence of allergenic substances that enter the body - medications, food products, dust, chemical fumes. In this case, acute inflammation of the skin is called toxicerma. Allergic hand dermatitis often develops in people who have a predisposition to other allergic diseases, for example, bronchial asthma, seasonal allergies, etc. The appearance of skin lesions on the hands can take from a few minutes to several months after the allergen enters the bloodstream.
Genetically determined hypersensitivity of the immune system to a certain factor is the cause of atopic dermatitis.
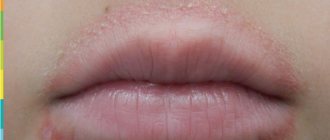
Dermatitis on the hands is accompanied by vivid symptoms. The first of these is itching, which leads to scratching of the skin. Redness, burning, small watery blisters or blisters appear on it. The joints on the hands - fingers and wrists - become difficult to bend due to their swelling, the skin loses its elasticity, and deep, weeping cracks appear. It becomes difficult to move your hands, even washing them or putting on gloves causes pain. In addition, due to discomfort and itching, sleep is disturbed; the patient may wake up several times during the night.
Treatment is real!
How to treat allergic dermatitis is an individual question. Sometimes it is enough to eliminate the irritating substance, sometimes drug therapy is necessary.
Treatment of any type of dermatitis, even such a complex form as chronic itching, begins with determining the source of such a reaction. Often you just need to stop contact with the irritating substance, and the reaction on the skin will gradually go away on its own. In more complex cases, therapy with antihistamines is necessary.
Treatment at home is only possible for mild skin lesions and a known cause. If you have any suspicions or doubts, you should contact a professional.
The answer to the question “How to cure dermatitis?” should be added a little: treatment of dermatitis should be accompanied by maintaining a healthy lifestyle. After all, irritation on the skin can occur with general weakening of the body. Therefore, it is necessary to switch to a diet of natural hypoallergenic products, maintain hygiene of the affected areas, and limit the use of decorative cosmetics that do not allow the skin to breathe.
An important aspect is the impact on the symptoms of the disease in order to relieve itching, eliminate the feeling of dryness and tightness of the skin - this is usually what worries patients the most, preventing them from leading a full lifestyle.
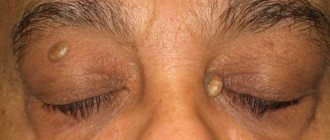
Dermatitis on hands photo
Photo 1. Dermatitis of the palms.
Photo 2. Dermatitis on the back of the hand.
Photo 3. Dermatitis on the hands.
Photo 4. Dermatitis on the hands.
Causes of dermatitis: contact with an aggressive chemical environment.
Prolonged exposure to low temperatures.
Dermatitis on the hands is not only a physical problem, but also a cosmetic one. Most of the time, hands are seen by strangers, who may react to rashes, papules and scratching in completely different ways. The patient’s experiences and psychological discomfort aggravate the course of the disease. According to statistics, the risk group consists of women living in big cities, but dermatitis on the hands can appear in anyone, regardless of gender, age, and lifestyle.
In addition to mental factors, the treatment of dermatitis on the hands is complicated even by hygiene and contact with the environment: with air (which can be dusty, dry, etc.), cleaning products, water, and various surfaces, sometimes contaminated. That is why dermatitis is called a disease of civilization: the development of industry and the emergence of new household chemicals have led to the fact that people are constantly faced with new types of cleaning, washing, dyeing, and adhesive products. Even the rules of hygiene, so necessary in a modern city, can do a disservice to a patient with dermatitis on the hands. Public and home toilets, money, door handles and handrails - contact with these objects, firstly, increases the risk of infection of diseased skin, and secondly, makes frequent hand washing necessary, which leads to drying, peeling, and cracking of the skin.
Through wounds formed at the site of scratching or bursting dry skin, infection can enter the bloodstream. In turn, this can lead to serious consequences for the body, including a general decline in immunity and the spread of dermatitis to other parts of the body.
Complications of dermatitis
Any form of dermatitis accompanied by skin damage can be complicated by infection.
In the chronic course of the disease, thinning of the skin and the appearance of small dilated vessels - telangiectasia - are possible. With prolonged atopic dermatitis, a child may develop asthma and allergic rhinitis. Among the adverse consequences of the seborrheic form of the disease are acne with the formation of visible skin defects, abscess, and baldness. The most serious are considered generalized complications such as Quincke's edema, Lyell's syndrome or Stevens-Johnson syndrome.
Treatment of dermatitis on the hands - selection of therapy
The selection of therapy for inflammation of the skin of the hands depends on the form and severity of the disease. The first step to recovery is identifying the allergen and stopping contact with it. If the reaction is caused by food products, a hypoallergenic diet is prescribed; if household chemicals or inks or paints are used, then rubber gloves must be used when working with them. If dermatitis on the hands appears upon contact with a certain metal, it is worth replacing it with another or completely abandoning jewelry. Often, for mild contact dermatitis, this treatment is enough to relieve symptoms. More serious cases of the disease require drug treatment and observation by a dermatologist.
The second stage of therapy is to relieve the acute stage of inflammation, during which severe itching, swelling and redness of the skin, and even pain are observed. Drugs are prescribed for internal and external use.
Diagnosis of dermatitis
The diagnosis is made based on the existing symptoms, the results of an external examination of the patient’s skin and mucous membranes, visual assessment and localization of pathological changes.
An anamnesis of the disease must be studied in order to establish the possible cause of dermatitis and its genetic cause. Laboratory diagnosis of dermatitis includes the following studies:
- General clinical blood test. During an allergic reaction, an increase in the number of eosinophils is observed, and an accelerated ESR indicates inflammation.
- Blood chemistry. Includes determination of the concentration of AST, ALT, total bilirubin, triglycerides, cholesterol, total protein.
- Determination of the level of immunoglobulins in blood serum, antibodies to food, household antigens, antigens of plant, animal and chemical origin.
If necessary, it is possible to conduct a histological examination of the biomaterial obtained through skin biopsy. Genetic blood testing helps determine hereditary predisposition to the development of atopic disease. In the presence of a purulent process or severe inflammation, a microscopic and bacteriological examination of the smear is prescribed in order to clarify the causative agent. Additionally, for dermatitis, tests are carried out for giardiasis and other forms of intestinal parasites, and the organs of the digestive tract are examined.
Preparations for internal use
Thus, tableted antihistamines are prescribed to inhibit inflammatory processes and reduce the harmful effects of allergens. Depending on the degree of damage, drugs are prescribed for a period of 2 weeks to several months. To treat dermatitis on the hands, products of various generations are used.
First generation antihistamines (diphenhydramine, mebhydrolin, chloropyramine, clemastine, cyprohepadine, promethazine, quifenadine) have a powerful antipruritic and decongestant effect, and also reduce muscle tone and cause drowsiness. They are recommended for therapy in the acute period.
Second-generation drugs have virtually no effect on the nervous system and do not reduce physical activity, but can negatively affect the functioning of the heart, so they should not be taken by people with cardiac diseases and elderly patients. Second generation antiallergic drugs include terfenadine, astemizole, acrivastine, dimethendene, loratadine.
If it is impossible to provide the patient with bed (home) treatment, third generation . They do not affect the functioning of the brain and heart muscle, which means they can be taken by people whose work involves mental activity. Third generation antihistamines on the pharmaceutical market include cetirizine, fexofenadine, desoloratadine, and hifenadine.
To quickly remove allergens from the body, medications are prescribed that stabilize the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. Sorbents absorb and remove toxins accumulated in the liver and intestines from the body. These include activated carbon, enterosgel.
Chatterbox
Prepare a semi-alcohol solution: to do this, dilute 40 ml of alcohol with the same volume of water. Add 2 ml of 2% lidocaine or novocaine to the resulting solution - this will help relieve the painful symptom.
Add 30 g of dry white clay and the same amount of powdered zinc. Mix thoroughly until smooth.
The finished mash is applied to the affected skin, previously cleaned with an antiseptic, in a thin layer, the mixture is left on the skin for 20 minutes. There is no need to apply a bandage on top; excess talker can be carefully removed, and the remaining part on the skin forms a protective film.
Remember! Do not self-medicate, consult a doctor!
Cutaneous dermatitis is a general name for skin disorders caused by various irritants. All irritants can be divided into 2 large groups: those that cause irritation upon direct contact and those that affect the body when they get inside.
Sources:
- Molochkova Yulia Vladimirovna, Dermatology. Brief reference book, publishing house: GEOTAR-Media, 2017
- Baumann Leslie, Cosmetic Dermatology. Principles and practice, publishing house: MEDpress-inform, 2016
- Ratner Desiri, Avram M.R., Avram M.M., Procedures in Dermatology. Clinical cosmetology, Publishing house: GEOTAR-Media, 2019
- Sukolin Gennady Ivanovich, Clinical dermatology. A short guide to the diagnosis and treatment of dermatoses, publishing house: Notabene, 2017
Photos of dermatitis
Photo album on the diseasePreparations for external use
Dermatitis on the hands is often accompanied by itching, which gets worse at night. Many patients complain of waking up in the middle of the night and being unable to fall back to sleep. In such cases, it is recommended to wear cotton gloves before going to bed and take a light herbal sleeping pill.
Acute inflammatory process is relieved with glucocorticoid ointments or creams. Depending on the severity of the lesion, the use of drugs of weak or moderate effect is prescribed. If skin lesions spread and affect not only the skin of the hands, but also other parts of the body, the use of strong hormonal drugs is necessary. Since dermatitis on the hands is accompanied by swelling and burning, patients are often prescribed creams. Due to their structure, they have a cooling effect, which helps reduce swelling, and a rapid antipruritic effect. Weak hormones include hydrocortisone, and moderate hormones include prednisolone, fluocortolone, and prednicarbate. Glucocorticoid creams are used for a limited amount of time, usually no longer than a week.
Relieving acute inflammation is only the first step of therapy. The chronic stage is also characterized by itching (albeit not as intense) and, most importantly, dry skin. Dryness provokes peeling and cracks that interfere with the healing of the skin. To normalize metabolic processes in the skin, including water balance, it is necessary to resort to additional hydration. The greatest effect comes from applying creams after hygiene procedures. Under the influence of warm (but not hot) water, the epidermis softens, and the crusts dissolve and come off.
However, it is worth noting that washing your hands with soap will most likely lead to a negative result, since alkali dries out the skin and, once it gets into the wounds, causes tingling and exudate. Delicate care is provided by special medicinal and cosmetic care products for inflamed skin. Thus, “Losterin” body gel, which can also be used as hand soap, does not contain surfactants, fragrances or dyes. And 4 types of vegetable oils in its composition, deresined naphthalan and Japanese sophora extract provide both cleansing, bactericidal effect, and moisturizing of the skin. In the acute period, it is recommended to cleanse the skin of the hands with micellar water and clean soft wipes.
After water procedures, the skin is carefully blotted (do not wipe!) with a towel and moisturizer is applied. For hand skin dermatitis, creams containing vegetable oils and panthenol are useful, which create a thin fatty film on the surface of the skin and do not allow the liquid to evaporate. Vegetable oils can be applied to the skin in the form of lotions, or they can be included in creams. Traditionally, olive, flaxseed, sea buckthorn, sunflower oil, avocado and jojoba oils are used in dermatology. In addition, products with the addition of plant extracts and vitamins are needed. These components provide nutrition to skin cells and accelerate regeneration. Preparations containing tar, naphthalan, salicylic acid, and zinc help relieve skin itching.
The restoration of epithelial cells is facilitated by preparations with propolis. This natural remedy has desensitizing, anti-inflammatory and regenerative properties due to its composition. Propolis contains flavonoids, aromatic and fatty acids, free amino acids, proteins, alcohols, minerals, sugars, vitamins, steroids, and many microelements. However, ointments, sprays and creams with propolis can be prescribed only to those people who are not allergic to honey and pollen. In other cases, the product may cause a severe allergic reaction.
In most cases, chronic dermatitis on the hands can be treated with external herbal medicine. It can be combined with hygienic procedures. For example, after an evening shower, it is useful to take hand baths with extracts or infusions of pine needles, chamomile flowers, oak bark, calendula, birch buds, string, burdock root, plantain leaves, poplar buds, and lungwort. After a 10-minute bath, the skin of the hands is also dried with a towel and moisturizer is applied.
How to distinguish psoriasis from seborrheic dermatitis?
Diseases are often confused. Although both diseases share common features, they also have many differences. Common characteristics include a chronic type of disease and an undulating course, the presence of rashes, itching, and peeling of the skin. What is the difference between psoriasis and dermatitis?
- Prerequisites for development. If psoriasis appears under the influence of autoimmune, endocrine, and genetic disorders, then seborrheic dermatitis is caused by increased activity of the sebaceous glands and yeast-like fungi.
- Symptoms. Despite the fact that in both cases the skin is covered with scales, their structure and appearance are different. When oily yellow crusts appear, we are talking about seborrheic dermatitis, and when dry gray, white or silvery scales form, psoriasis can be diagnosed.
- Localization. Psoriasis can affect almost all areas of the skin, and seborrheic dermatitis is localized mainly on the scalp, neck and face.
If you experience skin rashes that could be a sign of both dermatitis and psoriasis, be sure to consult a dermatologist. Usually, a qualified doctor can determine what it is by the external manifestations of the disease. If mixed symptoms occur, the dermatologist will write a referral for additional examinations.
Losterin cream for the treatment of dermatitis on the hands
Natural remedies must be used every day for several weeks or even months, depending on the severity of the disease. It is important that they do not have synthetic fragrances, and that their active components quickly penetrate deep into the epidermis. These requirements are fully met by the “Losterin ” cream, intended for daily care, moisturizing and protecting the skin of the hands. Almond oil regulates water balance. Sophora japonica extract reduces the intensity of inflammation and peeling, and deresined naphthalan is a natural product that has been used in the complex treatment of dermatitis for more than 100 years. Naftalan has bactericidal, vasodilating and regenerative properties, and in combination with urea and salicylic acid it has a powerful antipruritic effect. For hygiene procedures, people with dermatitis are offered the “Losterin” shower gel, which does not contain alkali, does not irritate the skin and has a desensitizing effect.
How to care for skin with dermatitis?
Helping herbs
Many plants have an amazing property - when absorbed into the skin, they reduce inflammation and normalize its structure. Therefore, a common remedy for the treatment of dermatitis is herbal compresses, wraps, and herbal ointments for dermatitis.
You can use a single plant or herbal mixtures that contain several herbs.
- Grind the celandine and squeeze the juice out of the resulting mass. Dilute the juice with boiled water in a ratio of 1 to 2. Use the solution for compresses: soak gauze in it and apply to the affected skin for 10-15 minutes.
- 1 tbsp. Pour 100 ml of boiling water over a spoonful of dry crushed string and leave until a dark brown solution is obtained. Moisten gauze or bandage in the prepared concentrate and apply it to the irritated skin until completely dry (not with weeping dermatitis, otherwise the bandage may dry to the skin). The procedure can be carried out 3 times a day.
Recipe with tar soap
The healing properties of tar have been known for a very long time. This thick oily liquid has a positive effect on the condition of the skin. Birch tar has an anti-inflammatory and antiseptic effect, improves blood circulation and stimulates skin regeneration.
You can find tar soap on sale and use it to wash skin affected by dermatitis, or prepare soap according to a folk recipe.
- Mix 100 g of crushed and melted baby soap with 2 tbsp. spoons of any oil, add 2 tbsp. fly in the ointment and 100 ml of water. Mix the resulting mixture until smooth.
Possible consequences
As mentioned earlier, treatment of dermatitis should not be delayed for a long time. Otherwise it may cause complications. This especially applies to allergic dermatitis. Lack of treatment for this type of disease can lead to a chronic form of dermatitis.
In its chronic form, the disease can last for several years and cause a lot of moral and physical problems. Also, if treatment is not timely, this can lead to bacterial infection and the appearance of a fungal infection that can affect damaged areas of the epidermis.
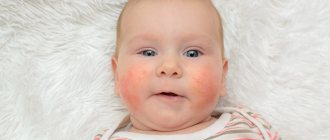
Allergic dermatitis in children
The main feature of allergic dermatitis is that it is not a contagious disease. Allergic dermatitis is hereditary. The disease is characterized by the formation of a rash on the child’s skin, which can either disappear or appear again, which causes severe suffering to the baby.
Allergic dermatitis in children appears after reaching one year of age. If treatment is not started in a timely manner, the disease can become chronic.
Symptoms
Symptoms of the disease in children most often appear at the same time. And this greatly simplifies the process of treating a child.
The main symptoms of allergic dermatitis in children:
- Manifestation of allergies on the child’s legs, arms and face
- Inflammation of formations on the body
- The formations may dry out and become covered with a yellow crust
- Presence of itching
Types and forms of the disease
Treatment for finger eczema depends on what stage of development the disease is at. It is characterized by a wave-like course: exacerbations are replaced by periods of remission. Hands are most often affected by dry eczema, in which papules with exudative fluid do not form on the skin. The disease can occur in one of the following ways:
- Ostrom. Symptoms appear suddenly, swelling quickly develops, and redness forms. The disease develops within a couple of days, and sometimes even in a matter of hours.
- Subacute. Eczema does not develop as rapidly and is less pronounced than in the acute form. The disease itself lasts for several months and only then subsides for an indefinite period of time.
- Chronic. The most common form of eczema, in which relapses and periods of improvement regularly follow each other.
What can you do yourself?
To restore damaged hand skin, you need to follow a number of simple rules:
- wear gloves in cold weather;
- Use warm water and a little mild detergent to wash your hands;
- rinse off the soap well and dry your hands;
- often (at least every time after washing your hands) use moisturizing and skin softening products, as well as those that prevent skin dehydration. These are usually creams with petroleum jelly, lanolin, glycerin, ceramides, dimethicone, propylene glycol, urea, etc.
It is recommended to relieve inflammation with the help of corticosteroids (in the form of cream, lotion, foam or, better yet, ointment). If the dermatitis is severe or chronic, with noticeable thickening of the skin and is not on the face or in the area of skin folds, then clobetasol, diflucortolone, etc. are used for 2-4 weeks. In less severe cases, betamethasone, diflucortolone, mometasone, triamcinolone, etc. are used (also for 2–4 weeks). When dermatitis is on the face or in the area of skin folds, weaker corticosteroids or corticosteroids in lower dosages are used: triamcinolone, betamethasone, hydrocortisone, etc. for 1–2 weeks.
It is highly advisable not to scratch the sore spot, otherwise additional damage to the skin may create a suitable environment for bacterial infection.
After a case of acute dermatitis, recovery takes about a month if there is no further exposure to the irritating agent. With chronic contact dermatitis, symptoms may not go away for months or years.
For allergic contact dermatitis, the most important thing is to avoid the substance that caused the disease and relieve inflammation. The methods are approximately the same: wear gloves, overalls, a mask and goggles, use corticosteroids for 1-2 weeks (in severe cases it is better to take systemic drugs, that is, in tablets) or calcineurin inhibitors (for example, pimecrolimus cream).