Onycholysis is a condition in which the nail separates from the nail bed. In this case, there is no pain.
Usually this is not a one-time event; weakening occurs gradually - under the influence of a repeated or long-term factor.
Once the nail has moved away from the nail bed, it will no longer stick back. The effect of weakening the connection between the nail and the nail bed develops from the distal edge (tip of the nail) to its base (root of the nail). And, conversely, normalization of the situation is associated with the growth of a healthy nail from the nail fold to the distal edge. Most often, onycholysis is observed in women.
What happens during onycholysis?
Onycholysis-detachment of the nail plate
Detachment is a violation of the integrity of the nail plates. form under their surface , which causes the nails to separate from the soft tissues of the fingers.
There is a complete or partial change in the color of the nail plates. They may become pale yellow, whitish-gray, or less commonly bluish or brown. At first, the upper part of the nail or its sides are peeled off as the disease develops , the defect reaches its base - the entire surface moves away from the nail bed. But more often than not, it doesn’t come to this, and the nail plate is not completely separated.
Symptoms
Manifestations of onycholysis and onychodystrophy are associated with changes in the nail plate. Most often, the disease affects the fingernails. As a rule, the disease affects the plates on the 3rd and 4th fingers, less often on the 2nd and 5th. On the big toe, onycholysis and dystrophy of the nail plate develop very rarely.
Dystrophy of the big toe nail is diagnosed less frequently, and the disease mainly affects the nail plate of the big toe.
With onycholysis, the nail plate is separated from the bed from the free edge in the distal or lateral sections to the hole. The detachment line is usually straight. The plate changes color to white-gray. If onycholysis manifests itself as a result of physical impact, the nail may first become bluish and then black due to dried blood. The skin underneath thickens.
As a rule, the disease passes without pain, but if an infection joins the process, pain and discomfort may appear at the site of the lesion.
As the infection develops, the color of the nail changes more dramatically: it can become yellow, brown, or greenish. The consistency of the plate also changes: it deforms and becomes rough. An unpleasant odor may appear. In such a situation, it is important to take timely measures, otherwise the process will progress and may affect the entire nail.
With onychomycosis, the detachment usually has uneven edges. The plate becomes yellow or brown. The structure also changes - the nail becomes loose and crumbly. An unpleasant odor appears.
Possible diseases due to nail detachment
Detachment of the nail plate can occur in some diseases, both chronic and acute. The most common are:
|
These are systemic diseases. Onycholysis is also characteristic of:
|
Is it possible to stop peeling?
The peeling can be stopped.
For this, various treatment methods are used:
- treatment of the nail plate with special medications;
- compresses on damaged areas;
- lubricating problem areas with ointments and creams;
- hand baths.
By applying complex therapy on time, nail detachment can be stopped.
Causes of onycholysis
The causes of detachment of the nail plate can be various factors of both infectious and non-infectious nature.
chemical factor for nail peeling
Non-infectious causes:
- Chemical – the disease manifests itself through frequent contact with household chemicals without the use of gloves or other substances. Such a product may be washing powder, nail polish, or nail polish remover.
- Mechanical – various injuries: strong blow, cutting, squeezing, habit of biting nails. In such cases, a hematoma (collection of blood) forms under the nail, which must be properly removed as soon as possible.
- Allergy. The same household products, latex, and nail polish can cause such a reaction. Often their peeling can be observed after coating with gel polish, which is popular today, but often causes allergies.
- Medications . This includes some groups of antibacterial drugs; the most common cause of nail splitting is treatment with fluoroquinolones.
- Manicures and pedicures performed incorrectly at home are also a common cause of onycholysis. Nails can begin to peel if you cut them carelessly, which leads to deformation, and when filing them, hold the file not perpendicular to the nail plate, but at an angle, and move the tool in different directions.
Onycholysis can be triggered by hormonal fluctuations, lack of vitamins and stressful situations.
Infectious causes include fungi, less commonly bacteria. In 40% of cases of the disease, onycholysis is caused by the first microorganisms. When they get on the nail plates, they destroy it, the nails begin to delaminate and break.
Answers to frequently asked questions
Is it possible to extend nails or do manicures with gel polish during onycholysis?
- No. This will aggravate the condition of your nails and interfere with their healing.
Do I need to cut my nail?
- This is decided by the doctor individually.
Is onycholysis contagious or not?
- If, for example, the cause of development is a fungal infection, then yes.
Which doctor should I contact?
- To a dermatologist.
Is treatment possible at home?
- Usually yes. Not in advanced cases.
What does lateral onycholysis look like on the hands?
- The very first photo in the article.
What complications can there be?
- If the cause of the disease is an infection, it can spread to other nails. Over time, they become brittle and unattractive. With fungus, the disease can spread to the skin of the feet/palms.
Lack of vitamins
Deficiency of vitamins and various macro- and microelements can also provoke detachment of the nail plate. Their deficiency usually occurs when eating poor food.
The diet must contain foods high in iron, calcium, and zinc . large amounts of magnesium, vitamin D, and phosphorus is ideal , without which calcium absorption is impossible.
B, A and E , found in apples, butter and sunflower oil, seeds, dairy products, and nuts, are also important for healthy nails
Also in the diet there should be the presence of protein products, vegetables and fruits containing silicon, amino acids, zinc and folic acid.
What is onychodystrophy
A human nail has a root, a body, i.e. the visible part of the nail, a free edge and a matrix in which the basal cells multiply. They form and move towards the root of the nail, gradually flattening and becoming keratinized. This ensures continuous growth of the nail plate. Between the keratinized cells of the nail and its root is the so-called lunula. It is crescent-shaped and white in color, with a cuticle running along its flat edge. It is a sheath at the base of the nail plate that protects the nail root from damage by pathogenic microorganisms. The nail is limited on 3 sides by folds of skin called ridges. On the side of the free edge there is a thin layer of skin called hyponychium. Over the entire area, except for the free edge, the nail plate is adjacent to the nail bed. It is formed by connective tissue, which is rich in nerve endings and blood vessels.
When disturbances occur in nutrition, metabolism, or changes in the chemical composition of nails under the influence of certain factors, onychodystrophy develops. Moreover, its appearance directly depends not only on the nature of the influencing factors, but also on the characteristics of the chemical composition of the nails, since it can vary quite widely among different people.
As a result of the accumulation of metabolic products in the cells and intercellular space, the structure of the cells of the nail plates may change. This leads to onychodystrophy, which can be manifested by impaired nail growth, its detachment from the bed, brittleness, delamination, the formation of spots, cracks, stripes, etc.
Onychodystrophy is a disease that does not have age, seasonal, racial or other characteristics. It can act as a symptom of the development of other somatic disorders or an independent pathological process. But in any case, onychodystrophy should not be ignored, and its appearance should be considered as the first sign of the occurrence of other disorders in the body until the contrary is proven.
Onychodystrophy can affect both fingernails and toenails. In this case, not all nails may suffer at once, but only one or several.
The importance of timely diagnosis and treatment of the disease is also due to the fact that it can lead to the development of complications. The most dangerous consequences of the lack of treatment for onychodystrophy of any kind are:
- Onychomycosis is a fungal infection of the nail plate, very common in advanced onychodystrophies. As a result of the addition of a fungal infection, the nails become even more deformed and change color, and subsequently the pathogenic microflora through the bloodstream can spread throughout the body and lead to mycoses of internal organs, the development of severe allergies to a number of medications and other complications.
- Subungual melanoma is a serious oncological disease characterized by an aggressive course and capable of claiming lives. It is characterized by the formation of a dark spot of any shape, stripe, etc. under the nail. The disease requires immediate consultation with a doctor.
Diagnosis of onycholysis
examination by a dermatologist
If you notice detachment of the nail plate, you should contact a dermatologist to determine the cause of this problem. If during the diagnostic process the doctor discovers concomitant diseases, he will refer the patient to another specialist . This is necessary in order to eliminate the factors that provoke onycholysis.
At the first appointment, the dermatologist visually examines the nail plates. It happens that the doctor immediately recognizes a fungal infection of the nails and refers the patient for an analysis (scraping), which reveals the type of pathogen. After this, appropriate treatment is prescribed.
If examination of the nails does not reveal the cause of their detachment, diagnostic methods such as:
- taking samples to determine the presence of fungus, staphylococci and streptococci;
- a blood test to assess the general condition of the body.
Other instrumental and laboratory diagnostics are also possible, the choice of which is based on the most likely cause of onycholysis.
Features of therapy in children
It is important to monitor the condition of the skin around the nails in children. A small wound can cause a bacterial or viral infection. Particular concern should be shown if the baby’s nail darkens and peels off from the bed.
The causes of onycholysis in children are similar to those in adults. The differences lie in treatment tactics - for bacterial and fungal infections, if possible, it is necessary to limit yourself to local drugs and abandon systemic ones.
The course of treatment for fungal infection is at least 3 months. Every day, antifungal ointment is rubbed into the nails and affected areas of the skin. The most popular drugs that can be used for children are:
- Clotrimazole.
- Ketoconazole.
- Lamisil.
For bacterial infections, antibiotics are prescribed. The choice of drug depends on the baby’s age, weight and the presence of concomitant diseases. In case of extensive damage, the nail plate is removed, but this procedure is carried out only in a hospital setting. Throughout therapy, it is important to organize proper nutrition and, if necessary, take multivitamin complexes.
Clinical picture
Symptoms of onycholysis depend on the cause that caused it.
In case of a disease that occurs after a nail injury, the following may occur:
- pain syndrome;
- hematoma formation;
- discoloration and weakening of the nail plate;
- bleeding.
If onycholysis is caused by an infection, you may experience:
- thickening of the nail plate;
- change in nail color, it becomes green or yellow;
- redness of the tissue around the nail plate;
- feeling of pain;
- unpleasant odor;
- discharge from under the nail plate.
Symptoms common to all types of onycholysis:
- the nail plate changes color, first stratifies in its upper part;
- unevenness, change in the border line dividing the nail plate into pink and white parts;
- the skin under the nail thickens;
- pain occurs only with secondary infection, due to microorganisms getting under the detached nail plate.
Pathogenesis
With onycholysis, the connection between the nail and the nail bed is disrupted, while the matrix is preserved. The nail plate does not adhere to the nail bed; the nail separates from the distal edge. Gradually, the separation of the nail plate from the bed progresses - this occurs towards the proximal edge, to the area of the nail lunula. Most often, no more than half of the entire nail plate is separated from the bed; all of it is rarely separated. The consistency of the separated plate most often remains normal, the surface is smooth. However, the color becomes white-gray. If the origin of onycholysis is bacterial or fungal, then the plate may become deformed and dramatically change color.
Pathogenesis depends on the causes of the disease. If an injury occurs, the pathological process affects both the plate and the nail bed. hematoma appears between them , the nutrition of the plate is disrupted, as a result of which its elasticity and chemical composition change. Gradually the nail becomes deformed. The trophism of the collagen ligaments that fix the nail is disrupted, the connection between the plate and the bed is weakened, and the nail moves away from the bed. If the area of detachment is large, a secondary infection may occur, leading to the development of an inflammatory process. However, the connection between the nail and the matrix remains unbroken, therefore, after the hematoma disappears and trophism is restored, the growth process of the plate is normalized.
The basis of onycholysis of an infectious nature is an inflammatory process that goes through three stages. At the alteration stage, the dermis is damaged, and the cells of the immune and reticuloendothelial systems of the skin begin to produce cytokines and inflammatory mediators. Blood flow and trophism are disrupted, the structure of the plate changes. At the exudation stage, these processes are aggravated, and water-electrolyte imbalance also occurs. During this period, the nail is especially vulnerable to bacteria and fungi, which can penetrate into the intercellular layers of the nail. As a result, the nail is affected and separated from the bed. The intensity of detachment depends on the severity of the pathological process. The proliferation stage occurs when T lymphocytes and phagocytes destroy foreign organisms. At this stage, hyperkeratosis of the bed and its deformation occur. In this case, hyperkeratotic growth of the nail plate is noted. Normally, the nail begins to grow only after the inflammation has completely stopped.
With the allergic nature of onycholysis, its pathogenesis is similar to an inflammatory disease. But during the period of exudation, an excess amount of antibodies to microbes is produced. This leads to skin hypersensitization and worsening deformation of the skin and nail plate. The regeneration process slows down.
First aid for a nail injury
Hematoma-bruised nail
to place your hand or foot under a stream of cold water as quickly as possible . This is necessary to prevent the appearance of a hematoma under the nail , which provokes detachment of the nail plate. The injured limb should be kept in the cold for at least 15 minutes to constrict the blood vessels and eliminate pain.
To avoid swelling, an iodine mesh is applied to the skin and a tightening bandage is applied. This will minimize the risk of the nail moving away from the nail bed.
puncture to release blood from a hematoma
If a hematoma has formed, you should consult a doctor for a minor surgical intervention: a small hole is made in the nail so that the blood that has accumulated under it can come out.
If it is impossible to visit a specialist, you can try to carry out these manipulations at home under the condition of complete sterility . To do this, you need to thoroughly wash your hands and treat the bruise with an antiseptic solution, take a sterile needle, and heat it over a fire. After making a hole in the nail plate, remove the blood from under it. Then re-treat the nail.
The main reasons for the development of this pathology include:
- Traumatic impact.
- Thermal and chemical burns (most often as a consequence of gel polish)
- Fungal infection
- Non-infectious diseases of nails and skin (for example, psoriasis)
- Taking medications (some antibiotics, cytostatics)
- Symptom of diseases of internal organs (endocrinopathies, respiratory, hematopoietic, digestive systems)
VERY IMPORTANT (!)
in the treatment of onycholysis - establish the cause as quickly as possible and begin proper treatment. This is due to the fact that over time, the onychoblast cells that fix and ensure growth die, and the nail will no longer be able to develop normally; the cosmetic defect remains for life. A big mistake is trying to hide onycholysis under the cover of “until better times”!
Often, onycholysis is complicated by an infectious process - in the cavity formed by the exfoliated nail and bed, a favorable environment is formed for the growth and reproduction of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and mold fungi - “green nail syndrome” occurs.
Treatment includes, firstly, working with the root cause of onycholysis. It is often necessary to involve related specialists - endocrinologists, gastroenterologists, orthopedists, and only teamwork can achieve a good result. Secondly, it is necessary to cope with the complications of onycholysis - to cure infection and inflammation.
Treatment with folk remedies
Alternative medicine methods are used as additional methods for symptomatic treatment and disinfection.
orange juice with salt
A good remedy for strengthening nails is a solution of orange juice, a tablespoon of salt and 60 ml of warm mineral water. 5 drops of iodine are added to these components. Everything gets mixed up. Keep your fingers in this mixture for at least 10 minutes.
Kombucha has analgesic, anti-inflammatory and antibacterial properties. You can make a paste from it. Take a small part, cleared of films. Grind it up. Apply the resulting mass to the affected areas 2-3 times a day.
Several additional ways to treat a bruised nail at home in the video.
Congenital onychodystrophies
Congenital onychodystrophies are the result of gene mutations that have occurred in the patient or when a tendency to nail dystrophy is inherited from relatives. They can appear from birth or arise under the influence of a traumatic factor, an inflammatory process, or the development of disorders in the functioning of internal organs.
Onychomadesis
Onychomadesis is a hereditary nail dystrophy, in which the nail plate is separated from the bed in the places where it adjoins the skin ridges. The disease debuts after a finger injury, and changes increase acutely and at high speed. In addition to the separation of the nail at the ridges from the bed, the development of an inflammatory process and the occurrence of pain can be observed.
With proper treatment, it is possible to restore the function of the matrix, after which a healthy nail grows. This does not guarantee the absence of recurrence in case of repeated injuries. But if they are frequent, complete atrophy of the nail bed and loss of the nail are possible.
Koilonychia
Koilonychia is an onychodystrophy characterized by depression of the nail plate in the form of a cup or saucer. The nails most often affected are the index and middle fingers, although all nails, including the feet, can be affected.
The exact reasons for the development of koilonychia are not yet fully understood. It is believed that the tendency to develop such disorders is genetically determined, and the trigger for their occurrence can be anemia, Cushing's disease, thyrotoxicosis, typhoid fever and some other diseases.
Anonychia
Anonychia is an onychodystrophy, manifested from birth by the absence of one or several nails on the fingers or toes. The disease is rare, but may be accompanied by deviations from the norm in the structure of the hair, the functioning of the sweat and sebaceous glands, as well as other developmental defects.
Platonychia and Micronychia
Platonychia is the thickening and flattening of the nail. As a result, the nail plate is completely flat, devoid of a natural arched shape.
Micronychia is an onychodystrophy manifested by shortening of the nail plates. Most often, such changes are noticed on the fingers, although they are also possible on the toes. It is believed that micronychia can also accompany psoriasis.
Hippocrates nails
Hippocrates' nails are a genetically determined onychodystrophy in which the nails become convex and increase in size. As a result, the fingers take on the shape of drumsticks. Despite all the roughness of nails, they are fragile. This can also be observed in chronic respiratory diseases.
Measures to prevent nail plate detachment
To prevent a disease such as onycholysis, you must adhere to the following rules:
- You should only wear shoes that “breathe.”
- Socks should be chosen from materials that are highly breathable (cotton) . They should be changed every day.
- Do not wear tight shoes.
- After contact with water, wipe your hands or feet dry.
- When working with household chemicals, you should always wear gloves and dry them afterwards.
- It is necessary to properly organize your diet, excluding canned food, fatty and spicy foods . Necessary products are high in vitamins A, B, D, E, calcium and micro- and macroelements that promote its absorption, polyunsaturated acids.
- Treat with antibiotics as little as possible.
- It is imperative to treat chronic diseases in the acute phase.
- Avoid stressful situations, overwork, lack of sleep.
Thus, if preventive measures were not followed and symptoms of onycholysis appear, you should consult a specialist who will diagnose and prescribe adequate complex therapy. Self-medication in this case should not be allowed, since there are many reasons for the detachment of the nail plates, and it is impossible to establish them independently.
What to do if your nail comes off the nail bed on your hand or toe
The method of treating the disease depends on its cause. However, in all cases an integrated approach is used. It is necessary to limit contact with chemicals, detergents and cleaning products, and use protective finger caps or gloves.
Be sure to read:
How to properly shave a man with a razor without irritation
It is not recommended to hide the disease with a layer of varnish. This will only worsen the condition and delay the onset of recovery.
During pregnancy, local medications are preferred.
Vitamins and medications
The following vitamins and minerals are encouraged:
- vitamins A, E, ascorbic acid, β-carotene - restore tissue;
- B vitamins - accelerate metabolic processes and improve the functioning of the nervous system;
- preparations containing calcium, zinc, iron, copper and sulfur.
Vitamin preparation Aevit for onycholysis can be used both for oral administration (1 capsule for 2-3 weeks) and for external use (capsule contents are applied to the surface of the nail and cuticle, course 2-3 weeks).
Important! If a fungal infection is detected, tablets are prescribed: the dosage regimen must be prescribed by a doctor on an individual basis.
The following antifungal agents are generally recommended:
- Intraconazole;
- Griseofulvin;
- Fluconazole;
- Terbinafine.
These drugs are most often well tolerated, and side effects are very rare.
External preparations are used for marginal nail detachment:
- Solcoseryl;
- Heliomycin ointment;
- Sinthomycin emulsion;
- Vishnevsky ointment;
- for fungus - Mycospor, Batrafen, Intraconazole, Exoderil;
- for bacterial infection - Levomekol.
Skin diseases
When working with a client, a manicurist needs to remember that there are various skin diseases, including infectious ones , which must be able to be identified by appearance. Of course, you should not work with people who have infectious (contagious) diseases due to the danger of their spreading over a larger area and becoming infected.
Infectious diseases
Pustular diseases
The most common skin diseases. They are caused by staphylococcal and streptococcal microbes and are characterized by the presence of abrasions, ulcers, and yellow crusts on the skin of the hands and other parts of the body, under which there is purulent discharge.
Boils, folliculitis
Purulent inflammation of the hair follicles (sacs) or sebaceous glands. In these cases, painful red nodes appear on the skin, in the center of which after 3-5 days a purulent “core” appears.
Inflammation of the nail folds
Swelling, redness, and pain in the skin surrounding the nail; purulent contents may be present. This phenomenon is called paronychia (felon)
. It is cured within a short time, but sometimes the participation of a surgeon is required. When treating such a finger, do not touch the inflamed area. You can recommend the client salt baths and heparin-containing ointments and gels to relieve swelling. Vishnevsky's liniment and levomekol can be applied at night under a bandage.
Erysipelas
An acute infectious disease caused by streptococcus. It most often occurs on the legs, but can also affect the skin of the hands. The clinical picture is as follows: bright redness, swelling with unclear borders similar to tongues of fire, pain. The skin is hot to the touch. May have a peripheral ridge.
Mycoses
Diseases caused by different types of pathogenic fungi. Mycoses of the hands are manifested by thickening of the skin, peeling, especially in the skin furrows against the background of slight redness. Often the lesion is limited to raised, scalloped edges. Patients are bothered by itching.
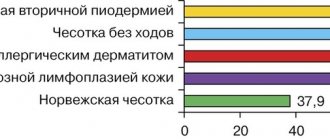
Scabies
A contagious disease caused by the scabies mite. Patients are concerned about itching, especially at night, rashes of small red nodules arranged in pairs, and pinpoint crusts. Typical location: interdigital folds of the hands, wrist area, elbows, as well as the abdomen, genitals, buttocks, and lateral surfaces of the torso.
Human papillomavirus (wart)
Non-inflammatory disease of viral origin. The human papillomavirus most often affects the feet and hands. The disease is transmitted through direct contact or through various objects, so the master should not handle them - there is a risk of accelerated spread. There are different types of warts:
- Vulgar warts
are rough, convex formations with a hard, rounded surface. They are located mainly on the hands.
- Flat warts
are rashes on the back of the hands and in the area of the wrist joints. The shape is different, the color is red-brown, sometimes bluish. - Plantar warts
- located on the soles of the feet, painful, looking like a callus or a small pit. They differ from core calluses in that they are located in soft tissues and are delimited from them by a “side”; they have a structure similar to a bundle of thin tubes.
Herpes
Another viral disease that occurs when working with your hands. It has similar signs as when it appears on the nasolabial triangle (nose, oral and nasal mucosa). Manifestations of herpes can accompany a person throughout his life, disappearing and reappearing when immunity declines. Colds, changing seasons, stress, immune system failures are factors that explain the activation of the virus.
Non-infectious skin diseases
Among non-infectious skin diseases, the most common are hangnails, dermatitis, eczema, neurodermatitis and psoriasis.
hangnail
A hangnail (“hanging nail”) is a common condition of the cuticle in the sinus area. Hangnails appear due to too dry cuticles or as a result of improper cutting or biting off a disturbing piece of skin. The situation can be easily corrected by softening the cuticle with oil. This condition is one of the simplest and most common, but carries the threat of infection with possible consequences in the form of panaritium and subsequent onycholysis.
Dermatitis
Inflammation of the skin, which can be caused by various reasons. They can be of an allergic nature, due to a person’s increased sensitivity to common chemicals (washing powders, cleaning products, varnishes, paints, etc.). Dermatitis can also be caused by ordinary damaging factors (high temperature, cold, concentrated acids and alkalis, etc.). This disease manifests itself as redness, swelling with clear boundaries, burning, pain. There may be small bubbles or blisters in this background. The disease can be treated under the supervision of a dermatologist.
Eczema
A chronic disease, in the mechanism of which the main role is played by allergies to various internal and external irritants. It manifests itself simultaneously with several signs: redness, swelling, itching, the presence of small blisters and abrasions, nodules. Most often, areas affected by eczema become weeping. Subsequently, thickening of the skin and peeling occurs. The disease usually occurs against the background of diseases of internal organs, stress, and damage to the nervous system.
Neurodermatitis
Neurodermatitis (atopic dermatitis) is a genetically determined disease. Occurs in childhood and often recurs. There are areas of redness, thickening, and peeling on the skin of the hands, elbow pits, neck, around the eyes and mouth, and other areas of the skin. The skin pattern is clearly visible. The disease is accompanied by severe itching, so longitudinal abrasions and crusts are visible on the surface of the affected skin. It is necessary to avoid contact of aggressive drugs (alcohols, acetone, alkalis and acids) on the affected area.
Psoriasis
A genetically determined general disease that affects not only the skin, but also joints, kidneys, and liver. It is based on the accelerated reproduction of basal cells of the epidermis, which do not have time to go through all phases of development. The disease can occur at any age. The picture of the disease is as follows: areas of redness, thickening of the skin, covered with silvery scales, appear throughout the skin. They peel off easily, and pinpoint bleeding is found underneath them. The rashes are most often located on the hands, elbows, and scalp.
Pigmentation disorders
Skin conditions associated with pigmentation disorders are not uncommon.
. They can be caused by internal and external reasons, as a result of which an excess or lack of pigment appears in the skin. The function of melanocytes is impaired, the body is more sensitive to ultraviolet radiation. Pigmentation disorders are not a contraindication to nail services.
Well-known examples of such conditions are vitiligo, albinism, chloasma and freckles.
Albinism
Complete absence of pigmentation in the body, including skin, hair, eyes. These people's hair is white. The skin color is pale pink, devoid of any shade. The eyes are pink. When using light-curing materials (gel polish, gel), it is important to apply sunscreen to the skin of the hands up to the middle phalanx of the fingers, avoiding the cuticle area and the nails themselves.
Vitiligo
Characterized by pale pink spots on various areas of the skin.
Chloasma
Large brown spots on the skin of the face, neck, and less often in other places.
Freckles
Small brownish spots on the face and body.
Also, hyper- and hypopigmented spots can remain in place of resolved lesions in some skin diseases, after acne, after incorrectly performed cosmetic procedures, during hormonal changes, etc.
When signing up for a procedure, clients often do not warn the specialist about the presence of a particular disease. To organize your work safely and feel confident even when encountering infectious diseases, we recommend that you read the sanitary standards and rules for processing tools.