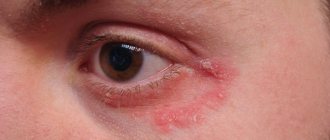
Stye is a disease of the eyelid, which is characterized by inflammation in the hair follicle of the eyelash or in the sebaceous gland near its bulb. The medical name of the pathology is hordeolum. It causes discomfort, since a swollen eye with stye looks unattractive and is accompanied by pain when moving the upper or lower eyelid. Pathology can manifest itself regardless of age - in both adults and children. The disease usually affects one eye.
The appearance of stye on the eye occurs unexpectedly. When the inflammatory process develops rapidly, patients are interested in what to do in such a situation. Immediate treatment is required. This violation should not be treated as a temporary inconvenience. Its occurrence indicates that the body’s immune forces are reduced.
Price
Allergology-immunology
| Name of service | Price |
| Consultation with an allergist-immunologist, primary | 3 500 ₽ |
Advantages
- The latest, constantly updated equipment
- Interest-free installments for all services
- Online consultations with an ENT doctor
- Visit of an ENT doctor to your home
- Friendly and qualified staff
- 24/7 ENT assistance
Furunculosis is a purulent-necrotic inflammation of the hair follicle and surrounding subcutaneous fat. Formed on the hairy parts of the skin. The causative agent of the infection is usually Staphylococcus aureus.
Furunculosis is more common in people with weakened immune systems, adolescents and adults. Furunculosis is rare in children and the elderly. The disease affects men more than women. Unsanitary living conditions increase the risk of infection.
Boils may disappear without any treatment. Sometimes they burst on their own and heal without a trace within 2 days to 3 weeks. However, after healing, they can lead to a complication of furunculosis such as scars. If the abscess is accompanied by fever, pain and other symptoms that affect well-being, the person should seek medical help.
Three or more episodes within 12 months are defined as recurrent furunculosis. In this case, you should also consult a doctor, even if the boils tend to heal on their own.
Treatment of furunculosis
Furunculosis is a rather serious disease that should be treated with great caution and in no case should you self-medicate. You should not make compresses, use ichthyol and Vishnevsky ointment - in most cases this leads to the spread of the inflammatory process.
Treatment of a boil is only surgical, because no other therapy will lead to success if the focus of purulent inflammation is not promptly removed or opened and drained. The basic principle of purulent surgery “Ubi pus, ibi evacua” (where there is pus, excise and open there), known since the time of Hippocrates, has not lost its significance to this day, despite the use of highly effective antibacterial drugs, powerful detoxification, immune therapy, etc. .
Opening a boil is usually performed under local anesthesia and is painless for the patient. The point of treating a boil, like any purulent lesion, is to allow the purulent discharge to drain out, and then ensure constant drainage from the wound.
Simple (uncomplicated) boils can be treated on an outpatient basis and do not require hospitalization. But in the case of a severe course, if the patient develops swelling of the soft tissues of the cheek, lip or eye, emergency hospitalization in the surgical department is necessary to constantly monitor the development of the process and prevent complications.
At high temperatures, strict bed rest, liquid food are prescribed, and the patient is forbidden to talk or chew.
Symptoms of furunculosis
Boils are red, swollen, and painful nodules of varying sizes. The larger they become, the more painful the sensation. The surrounding skin is usually red and inflamed. The nodules quickly fill with pus and may burst at the last stage of furunculosis. If several adjacent follicles are infected, they may grow together and form a larger nodule called a carbuncle. A carbuncle is a collection of boils.
Fever and swollen lymph nodes with furunculosis are rare, but possible.
Boils and carbuncles usually affect the thighs, armpits, buttocks, face and neck. They occur in areas prone to hair formation, sweat and friction.
Vitamin D deficiency: prevention and treatment
Vitamin D deficiency increases the risk of developing diabetes, hypertension, heart failure, Alzheimer's disease, common forms of cancer, autoimmune and inflammatory diseases, and immune dysfunction.
According to numerous studies, vitamin D deficiency occurs in half of the world's population. Almost every cell in the body has a special docking site for vitamin D on its surface - this is the VDR receptor (vitamin D receptor). Such receptors are found in almost all organs and tissues; their highest concentration is observed in the cells of the central nervous system, adipose tissue, cells of the immune system, muscles, pancreas, and tissues of the reproductive system. The uniqueness of vitamin D is that it acts directly on cellular DNA through its receptor. It also affects the concentration of hormones, growth and inflammatory factors, numerous proteins and, of course, the level of calcium in the blood. Vitamin D controls more than 200 genes, but it is believed that this number actually reaches 5,000 genes. It is precisely because of its direct effect on the regulation of gene function that vitamin D is considered not a vitamin, but a hormone.
The term “vitamin D” combines several substances similar in chemical structure: vitamin D2 – ergocalciferol
, formed under the influence of sunlight mainly in plants, vitamin D3 -
cholecalciferol
, formed under the influence of sunlight in the body of humans and animals. Natural forms of vitamin D that play an important role in human life are vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol) and vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol). It is these compounds that are similar in chemical structure that are currently referred to in clinical practice as “vitamin D.” Vitamin D is a fat-soluble substance and is initially a biologically inactive compound. Activation of vitamin D and the implementation of all its biological effects occurs after the formation of active metabolites: calcidiol in the liver and calcitriol in the kidneys.
Sources of vitamin D
The main source of vitamin D (cholecalciferol) is the sun, only 20% of it comes from foods (cod liver, mackerel, milk, eggs, butter, Atlantic herring, salmon, beef liver). For sufficient synthesis of vitamin D in the skin, only UVB rays are needed. The synthesis of vitamin D in the skin is greatly reduced in the presence of clouds, fog, dust, and air pollution. In northern countries in the summer, you can get enough vitamin D by spending 30 minutes a day in the sun (between 10:00 and 14:00), exposing at least 40% of your body surface to the sun. UVB radiation does not penetrate glass or clothing. Sunscreens with a sun protection factor of more than 8 block the synthesis of vitamin D. It should also be remembered that excessive exposure to the sun leads to photoaging and sunburn, active sun increases the risk of developing melanoma, so the option of replenishing vitamin D deficiency by exposure to direct sunlight in for a long time is dangerous.
Why has this problem become so urgent now?
Recently, people's lifestyle and nutrition have changed dramatically. Most of us consume meat from animals, poultry, and fish raised in captivity. Consumption of sweet carbonated drinks and fructose reduces the level of vitamin D in the blood plasma. Many medications (statins, glucocorticosteroids, calcium channel blockers, phenobarbital, etc.), drinking water or using toothpaste with a high fluoride content reduce the level of vitamin D. Often, people’s lifestyle and diet do not leave a chance for the body to produce the proper amount of vitamin D. Vitamin D increases calcium absorption in adults and children by 80%. Maintaining an optimal level of vitamin D (25 (OH) D) in the blood of 30-80 ng/ml reduces the risks of developing cancer, cardiovascular, infectious diseases, and pathologies of the musculoskeletal system. As a result of hypovitaminosis in childhood, the formation of peak bone mass is impaired, which will subsequently affect the strength of bone tissue throughout life. The problem of vitamin D deficiency is relevant for both children and adults (especially in old age). Thus, in Belarus, D-hypovitaminosis is observed in 73.7% of women and 61.7% of men. Severe, long-term vitamin D deficiency results in hypocalcemia and secondary hyperparathyroidism, which leads to increased urinary phosphate loss, bone demineralization, and ultimately osteomalacia (a condition in which bones become thin, deformed, and break easily). Vitamin D deficiency is especially dangerous for women during menopause, since at this time the level of sex hormones decreases, which leads to bone loss. Hypovitaminosis accelerates this process, and as a result, the development of osteoporosis occurs (a disease associated with the loss of calcium in the bones, causing the bones to become more fragile and easily damaged). This condition is accompanied by pain in the joints, large bones and frequent fractures, which in old age can be critical and cannot be fully restored.
The effect of vitamin D on the prevention of cancer
As already mentioned, vitamin D has regulatory activity in relation to a large number of genes, including those affecting the cell cycle, immunity and metabolism. Recently, new data have emerged on the connection between an increased risk of developing cancer and a decrease in vitamin D levels in the blood. Uncontrolled cell division and any other proliferation without differentiation with mutations can lead to oncology. Vitamin D inhibits proliferation and stimulates cell differentiation, prevents the growth of cancer cells, which makes it effective in the prevention and treatment of breast, ovarian, prostate, rectal, stomach, bladder, esophagus, kidney, lung, pancreas, brain cancer, leukemia, myeloma, lymphoma.
Vitamin D and immunity
Vitamin D is a powerful immunomodulator; it strengthens innate immunity and prevents the development of autoimmune diseases. There is a direct connection between decreased vitamin D levels and frequent acute respiratory infections. Vitamin D protects against respiratory infections by increasing levels of antimicrobial peptides in the lungs. The immunomodulatory activity of vitamin D is supported by data from large clinical studies, which show the high effectiveness and safety of topical vitamin D medications in the treatment of psoriasis. Also in this literature, there is a connection between low levels of vitamin D and atopic dermatitis, severe bronchial asthma, rheumatoid arthritis, autoimmune thyroid diseases, and multiple sclerosis.
Vitamin D and the cardiovascular system
Experimental clinical data suggest a connection between vitamin D metabolism and the state of the cardiovascular system, including the development and progression of atherosclerosis. The pathogenesis of some forms of arterial hypertension (AH) involves excessive activation of the renin-angiotensin system. Adequate vitamin D levels reduce the expression of the gene encoding renin. The risk of developing hypertension is reduced.
The effect of vitamin D deficiency on the development of diabetes mellitus
Vitamin D deficiency contributes to the development of insulin resistance. In people with full-blown type 2 diabetes, some studies show a beneficial effect of vitamin D supplementation, especially with calcium, on glycemic control and insulin resistance.
Vitamin D and general psycho-emotional state, as well as the condition of hair and skin
Vitamin D is involved in the regulation of tyrosine hydroxylase, an enzyme that is necessary for the production of dopamine, adrenaline and norepinephrine. The optimal level of these hormones is the most important condition for good mood and well-being, therefore the “sunshine vitamin” protects against depression and memory problems. The condition of hair and skin is also highly dependent on vitamin D. It is involved in the formation of the stratum corneum barrier, proliferation and differentiation of keratinocytes, stimulates and regulates the production of antimicrobial peptides in the skin.
Vitamin D for reproductive health and for pregnant women
The vitamin D profile and the course of pregnancy have been studied for a long time. There was a decrease in the development of atopic dermatitis in children whose mothers did not experience vitamin D deficiency during pregnancy. It has also been noted that vitamin D regulates the gene responsible for converting tryptophan into serotonin. Serotonin plays a critical role in fetal brain development. Vitamin D deficiency reduces the production of serotonin, which can cause neurological defects. The importance of vitamin D for women's health should be discussed in more detail. Vitamin D receptors are found in the tissues of the ovaries, endometrium, fallopian tubes, and placenta.
It is necessary for the synthesis of sex hormones (testosterone, estradiol, progesterone), normalizes the sensitivity of the ovaries and endometrium to sex hormones, and is involved in the regulation of the menstrual cycle. Vitamin D deficiency in women is associated with a high risk of developing endometriosis, fibroids and polycystic ovary syndrome. Vitamin D also affects male fertility. The prostate gland, spermatogonia, and seminal vesicles have receptors for this vitamin and enzymes for its use. In men with low levels of vitamin D, the total number of sperm, and especially their motility, decreases. Taking vitamin D can significantly reduce the risk of developing prostate cancer.
Who is at risk for vitamin D deficiency?
- people over 60 years of age;
- people with dark skin or who overuse sun protection products with a high protection factor;
- people who, for various reasons, are exposed to insufficient sunlight, such as those living north of the 35th parallel;
- patients taking medications that can accelerate catabolism and actively destroy vitamin D (for example, anticonvulsants, glucocorticosteroids, rifampicin, oral anticoagulants);
- obese persons (body mass index 30 or more);
- persons leading an “office” lifestyle;
- vegetarians or people who do not consume foods containing vitamin D;
- persons with kidney, liver and/or gastrointestinal diseases;
- pregnant and breastfeeding women;
- patients with chronic diseases of the intestines, liver and kidneys.
As an independent pathological condition, vitamin D deficiency is diagnosed extremely rarely, only based on the results of a specific blood test.
But at the same time, more than 70% of the population lacks vitamin D. Taking vitamin D is recommended for the purpose of:
- prevention (for healthy people with vitamin D levels (25(OH)D) within the optimal range - 30-80 ng/ml),
- treatment of D deficiency (for people with risk factors and/or existing vitamin D deficiency (25(OH)D less than 30 ng/ml).
The dose and duration of treatment with vitamin D is determined by:
- severity of D-deficiency;
- age, body weight;
- taking medications that affect vitamin D metabolism.
Therapeutic doses of vitamin D for adults start at 2000 IU per day.
All possible vitamin D dosage options are presented in the D3-CAPS line produced by the Minskintercaps Unitary Enterprise. The entire line (D3-CAPS ULTRA 500 IU, D3-CAPS 2000 IU and D3-CAPS 5000 IU, IU, D3-CAPS MAXIMA 50000 IU) is developed for the treatment and prevention of vitamin D hypovitaminosis in adults and children, taking into account international national recommendations, with with the participation of leading healthcare specialists.
To treat vitamin D deficiency, it is advisable to use drugs with a higher content of cholecalciferol, for example D3-CAPS, which is available in two dosages: 2000 IU and 5000 IU. Application of D3-KAPS 2000 ME
Treatment of vitamin D deficiency in adults and adolescents over 12 years of age: 1 capsule per day for moderate D deficiency (25 (OH) D level - 10-20 ng/ml) for up to 6-8 weeks, followed by laboratory monitoring 25 (OH) ) D in the blood to resolve the issue of transferring to prophylactic doses.
For persons over 60 years of age for the prevention and complex treatment of osteoporosis: D3-CAPS 2000 ME
, 1 capsule per day.
D3-CAPS 2000 IU
– daily dose in one capsule for the prevention of low-traumatic fractures in the elderly in combination therapy of osteoporosis. If there is insufficient calcium intake from food, it is necessary to use calcium medications to meet the daily requirement for this element.
Application of D3-KAPS 5000 ME
Treatment of vitamin D deficiency in adults and adolescents from 12-18 years of age: Taking 1 capsule per day
D3-CAPS 5000 IU
with subsequent laboratory monitoring of 25 (OH) D in the blood once every 3 months to decide on transfer to preventive doses or continuation of treatment.
D3-CAPS 5000 IU
– daily dose of vitamin D in one capsule for patients at high risk for D deficiency (poor absorption in the gastrointestinal tract, obesity, chronic liver and kidney diseases). It is important to take into account the fact that for diseases/conditions accompanied by impaired absorption of vitamin D, daily vitamin D intake is more preferable in order to optimize absorption. The recommended dose of cholecalciferol for the treatment of vitamin D deficiency should be 2-3 times the daily requirement of the age group (minimum 6000-10000 IU/day).
D3-CAPS MAXIMA 50,000 IU
Treatment of vitamin D deficiency in adults (from 18 years of age): - Treatment of severe D deficiency (25 (OH) D level < 10 ng/ml) - 1 capsule per week (laboratory monitoring of serum 25 (OH) D once every 3 months ). — Treatment of moderate D deficiency in adults (level 25 (OH) D – 10-20 ng/ml) – 1 capsule per month (laboratory monitoring of serum 25 (OH) D once every 3 months). — When prescribing vitamin D3 at a dose of 5000 IU or more per day, after reaching the target level of 25 (OH) D (30 ng/ml), the patient is transferred to maintenance doses of vitamin D 1000-2000 IU per day.
Contraindications to taking D3-CAPS:
— hypervitaminosis of vitamin D;
- hypersensitivity to vitamin D or drug components; - hypercalcemia and/or hypercalciuria; — nephrolithiasis and/or nephrocalcinosis; - severe renal failure; - pseudohypoparathyroidism (since in the phase of normal sensitivity to vitamin D, the need for it may decrease, which leads to the risk of delayed overdose. In such cases, it is better to use other vitamin D derivatives that allow more precise dosage regulation). 17 Feb 2021
Previous News Feed Next
Causes of furunculosis
The staphylococcus bacteria that cause the infection live on the skin, concentrating in parts of the body where folds are present (furunculosis on the face, in particular furunculosis of the nose and furunculosis of the lips, are the most common places where the disease manifests itself). Usually the immune system keeps them under control, but when the immune system is weakened, they enter the skin through a hair follicle or a cut or scrape in the skin. Furunculosis can be triggered by simple trauma to the skin or scratching it. Boils are often the result of failure to comply with basic personal hygiene standards. When the skin becomes infected, the immune system responds by sending white blood cells to the affected area to destroy the bacteria. Pus is a collection of dead bacteria, dead white blood cells, and dead skin.
The following conditions increase the risk of developing cutaneous furunculosis:
- Diabetes: High levels of sugar or glucose in the blood can reduce the immune system's ability to respond to infection.
- Medications: Some medications weaken the immune system.
- HIV and other diseases that attack the immune system.
- Skin diseases: psoriasis, eczema and acne.
- Excess body weight also increases the risk.
Furunculosis itself is not contagious through contact, but if the immune system is weakened, the infection can sometimes spread when people share the same space or materials, such as clothing and foot spas.
Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12
- is a water-soluble vitamin that belongs to group B. Another name is cobalamins. Cobalamins represent a whole group of vitamins that take part in the metabolism of every cell, influencing the synthesis and regulation of DNA. Vitamin B can only be synthesized by bacteria and archaea (single-celled microorganisms), which have the unique enzymes necessary for its synthesis. The best food sources of vitamin B12 are animal products because they contain bacterial symbiosis.
Forms of Vitamin B12
What is commonly mistaken for vitamin B12 is cyanocobalamin. This form is found in almost most vitamin products. Cyanocobalamin is completely synthetic and does not occur in nature, but is widely used due to its low price and ease of production. When cyanocobalamin enters the body, it must be converted into active forms. The conversion releases toxic cyanide. Although toxic, the amount is negligible to have clear negative effects and therefore should not be considered a clear side effect.
Another problem with cyanocobalamin occurs when it is absorbed. In order for cyanocobalamin to be used by the body, it must go through a process that removes the cyanide molecule, which requires the antioxidant glutathione. The disadvantage of the deacyanation reaction is the unnecessary use of this valuable antioxidant, as well as the dependence of vitamin B12 metabolism on the availability of glutathione.
Unlike cyanocobalamin, two coenzyme forms of vitamin B12 - methylcobalamin and adenosylcobalamin - are biologically active. They take an active part in metabolic and enzymatic reactions.
Methylcobalamin is pre-methylated, which means it is ready to be absorbed by the body. Methylcobalamin is localized in the cell cytoplasm and is a cofactor in methylation reactions. Adenosylcobalamin is important in the oxidation of fatty acids and the main point of its action is the mitochondria of cells.
Metabolism and absorption of vitamin B 12
in the gastrointestinal tract
Vitamin B12 is bound to food protein and becomes available for absorption once released. The process of vitamin elimination occurs under the influence of hydrochloric acid produced by the gastric mucosa. The released cobalamin binds to the R protein and passes into the duodenum, after which the R protein is removed and the free cobalamin binds to intrinsic factor. Intrinsic Castle factor is formed in the glands of the fundus and body of the stomach; it helps convert B12 into an easily digestible form. Vitamin B12-Castle Factor Complex - Absorbed by the distal ileum and the vitamin enters the bloodstream.
Whey vitamin B12 is bound to transport proteins known as transcobalamins. Most of the vitamin, approximately 80%, is bound to an inactive protein called haptocorin. The active transport protein for vitamin B12 is transcobalamin II, which retains 20% of the vitamin in the bloodstream. Holotranscobalamin delivers vitamin B12 to all cells. Low serum vitamin B12 concentrations may be due to transport protein deficiency, while transcobalamin levels and vitamin B12 status remain normal.
Vitamin B deficiency problem12
The main problem with vitamin B12 is that it is difficult to absorb. Nutritional deficiency of vitamin B12 occurs in groups of people who eat only plant foods, minimizing animal products in their diet. Deficiency due to insufficient absorption of vitamin B12 or increased requirements against the background of normal absorption is also common.
A potential risk group includes pregnant women on a vegetarian, vegan or raw food diet.
Elderly people are also a risk group. They are at greater risk of malnutrition due to comorbidities, have difficulty with self-care and food preparation, and tend to suffer from some degree of atrophic gastritis. Inflammatory processes in the gastric mucosa tend to increase in frequency with age, which leads to a decrease in the production of hydrochloric acid, one of the factors in the absorption of vitamin B12.
Castle factor deficiency -
one of the typical causes of vitamin B12 deficiency. The presence of autoantibodies to Castle factor is the leading cause of pernicious anemia against the background of autoimmune gastritis. Resection of the gastric antrum is also accompanied by a deficiency of vitamin B12.
The absorption of vitamin B12 can be impaired in any inflammatory bowel disease. For example, Crohn's disease, parasitic infestations, bacterial overgrowth syndrome - just a small list of the possible list of ailments.
Consequences of deficiency states
Typical manifestations of vitamin B12 deficiency. Disruption of the hematopoietic process with the development of megaloblastic anemia, as well as neurological disorders.
Long-term and chronic deficiency of vitamin B12 is considered as one of the factors in a number of other global medical problems.
The active form of vitamin B12 is directly involved in the metabolism of homocysteine, an independent factor in the development of cardiovascular pathology. By converting homocysteine into methionine, it enhances the synthesis of SAMe (S-adenosylmethionine), the most important donor of methyl groups in the body.
Assessing vitamin B12 status is part of the dementia screening process. Elevated concentrations of methylmalonic acid (MMA) are associated with cognitive decline and Alzheimer's disease. In older adults, low vitamin B12 levels and high serum folate concentrations are associated with increased odds of cognitive impairment. On the contrary, in patients with normal vitamin B12 status, high serum folic acid levels have a protective effect on memory, attention, perception, intelligence, etc.
Vitamin B12 deficiency is associated with the development of age-related macular degeneration (AMD) and the risk of frailty, which are the leading causes of disability in older people. AMD is the leading cause of vision loss in older adults. An increased risk of frailty and disability is associated with poor vitamin B12 status.
Low levels of vitamin B12 are considered a potential risk factor for neural tube defects. Vitamin B12 acts as a cofactor for methionine synthase in the folic acid cycle. When vitamin B12 supply is low, folate remains trapped in the methylation cycle, causing cell replication to fail.
A deficiency of vitamin B 12
can be suspected by such nonspecific symptoms as:
- forgetfulness;
- dizziness;
- pale skin;
- weakness and fatigue;
- tingling in the tips of the fingers and toes.
Laboratory tests can diagnose and confirm deficiency and insufficiency of vitamin B12.
Determination of vitamin B12 deficiency
Traditionally, vitamin B12 status is assessed by serum concentrations, but serum levels alone may not detect subclinical vitamin B12 deficiency or insufficiency.
Methylmalonic acid and homocysteine are recognized indicators of vitamin B12 status. Their measurement is of paramount importance in identifying vitamin B12 deficiency.
MMA is considered a specific indicator of cobalamin metabolism and reflects the availability of adenosylcobalamin in the cell. Homocysteine increases with vitamin B12 deficiency along with a lack of folate and vitamin B. It is the lack of such a coenzyme form as methylcobalamin that provokes an increase in homocysteine levels.
Plasma concentrations of MMA also increase with renal failure, polymorphisms in methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR), or with the use of certain drugs. Plasma MMA concentrations are elevated in renal failure, which is common in the elderly, so this marker is not appropriate for use in this group of patients.
The use of holotranscobalamin as a marker of vitamin B12 status increases the predictive value of identifying subclinical deficiency states. The level of holotranscobalamin reflects the availability of vitamin B12 to all cells of the body, and its determination is desirable when assessing the status of the vitamin in the body.
Conclusion
Vitamin B12 is a particularly important vitamin for women of childbearing age and older adults, but adequate vitamin B12 status throughout life is necessary for optimal health.
Furunculosis: professional treatment
The doctor prescribes tests for furunculosis - smears of cultures from the affected area (from boils obtained by cutting), as well as from carrier areas on the skin.
Sometimes a complete blood test is performed to determine the cause of the skin infection and determine more effective treatment for furunculosis, as well as to rule out other internal disease. Immunological evaluation may be considered if disease recurs or there is evidence of another disease.
A doctor may use a sterilized needle to puncture a furunculosis abscess and drain the pus. Lancing may be enough to clear up the furunculosis, but if the infection spreads to a deeper layer under the skin, your doctor may prescribe antibiotics.
At the Ear, Nose and Throat Clinic, we treat various skin diseases, including furunculosis, at reasonable prices - identifying the root cause and prescribing effective medication and physiotherapy.
A little about vitamins – something you didn’t know about
Murzaeva Irina Yurievna
Endocrinologist, Preventive Medicine Doctor
September 23, 2018
Vitamins are classified as a subtype of micronutrients that are needed by the body in small doses - mcg or mg , but are needed constantly!! Many of the vitamins can influence the formation of the cell genome and, accordingly, influence reproduction and susceptibility to cancer. In our country, hypervitaminosis does not occur physiologically, but multiple vitamin deficiencies do. Deficiency can be of 3 degrees of severity:
- vitamin deficiency (complete absence),
- hypovitaminosis (partial absence),
- subnormal security.
Next they will write about each vitamin separately and in the form of a brief reference. Since vitamins are often closely related to microelements, I will mention them a little.
- The most common deficiency is a lack of B vitamins (B1, B2, B5, B6, B12), especially in schoolchildren. This is due to the predominance of refined foods and stress.
- Allergies to B vitamins (especially injectable ones) are often associated not with “the vitamin itself,” but with sulfites that stabilize the vitamin solution. And if you are allergic to injectable forms, you may not be allergic to tablet forms.
- B vitamins are better absorbed through the gastrointestinal tract, and are used in injections only for acute conditions (radiculopathy, neuritis, etc.).
- MYTH - B vitamins provoke cancer!!! Vitamins B1+B6+B12 do not affect tumor metastasis!!! And they even have an unpronounced antitumor effect.
- Vitamins B12 and D significantly reduce the risk of pancreatic cancer.
- Vitamin E and Selenium in the experiment increased the risk of bronchial cancer - ONLY IN SMOKERS! (more than 1 pack of cigarettes per day).
- Vitamin C + Iron + Manganese (Mn) is the best three for the treatment of IDA (iron deficiency anemia).
- Vitamin B12 + Iodine + Selenium = optimal prevention of autoimmune diseases (note!!! already developed pathologies are not meant ).
- Vitamin PP + chromium (Cr) = excellent option in the treatment of insulin resistance and obesity.
- Vitamin B2 (riboflavin) + magnesium = a great migraine treatment pairing!
- For better absorption of vitamins, movement is necessary! Physical inactivity weakens the absorption of all vitamins!
- To treat osteoporosis, the dose of vitamin D should maintain its concentration in the blood at least 40 ng/ml.
- In case of atopic dermatitis, dry skin syndrome, seizures, dry lips, conjunctivitis and recurrent furunculosis that are difficult to treat, there may be a genetic predisposition to impaired absorption of vitamins (this is a separate article) - today such an analysis is available in Russian practice.
- Boys are more predisposed to polyhypovitaminosis than girls.
- Frequent nausea without signs of infection is a common symptom of vitamin B1 and B6 deficiency.
- Leg cramps are often a deficiency of Iron, Magnesium, vitamins B1 and B6.
- A history of tuberculosis in relatives and a positive tuberculin test in a patient is an almost 100% marker of a genetic disorder in the absorption of vitamin D, which requires treatment with large prophylactic doses of vitamin D.
- Complivit is a vitamin that is suitable for daily use by almost everyone. Supradin - for acute respiratory viral infections and acute respiratory infections, in a short course.
- Folic acid for preparing for pregnancy and treating hyperhomocysteinemia is better absorbed in the form of methylfolate (the active form of folic acid).
- Rosveratrol with a low-calorie diet (low-calorie diet) will help prevent hunger attacks.
- Alphalipoic acid + myoinositol + magnesium + zinc = an excellent 3-month treatment regimen for asthenozoospermia .
- Q10 + Selenium + Omega-3 + Alphatocopherol (active vitamin E) = against the background of dyslipoproteinemia, they can become an alternative to statins in the absence of cardiovascular disease and severe degrees of atherosclerosis.
- Thioctic (lipoic acid) is the best way to treat fatty hepatosis today.
- Zinc + vitamin C in the 1st phase of the cycle/vitamin E + Copper + Magnesium in the 2nd phase of the cycle = a universal scheme for stabilizing menstrual irregularities.
- Large doses of selenium that are tried to be used in thyroidology, more than 200 mcg, are fraught with toxic effects!! A dose of 75-100 mcg is sufficient for the treatment of AIT.
- 25% of the population has a defect in the absorption of vitamin B12. This is expressed by the phenomena of neuropathy - periodic numbness of the toes and hands.
- Magnesium does not have to be combined with vitamin B6; it is perfectly absorbed without B6.
- If you have urolithiasis (urolithiasis) and take vitamin D, so that it does not fall out as a “calcium deposit,” you need to take magnesium citrate. And keep hydrated!
- Vitamin K2 is not as strong a stimulator of vitamin D absorption as it is “painted to be.”
- Vitamin A + Omega-3 = a good treatment regimen for dry skin and acne!
- Anemia and other diseases can impair the absorption of vitamin D by 30% or more. And including reducing its concentration in the blood!!!
- Preventive (safe doses) of vitamin D for adults - 2400-5000 IU/day.
- The adrenal glands accumulate the most vitamin C. A safe daily dose of vitamin C is 500-1000 mg; in the active form, doses can be much higher (but this is only a doctor’s decision!!).
- Zinc is lost quickly during hypothermia, which aggravates the course of acute respiratory infections and acute respiratory viral infections . An excellent solution is 50-70 mg of zinc for 5 days in acute conditions.
- Vitamin A+Selenium+Lutein = treatment regimen for diseases of the organ of vision.
- Algae-based omega-3s are a great alternative for those allergic to omega-3s from fish.
- It is better to take Omega-3 constantly; large doses are indicated only under the control of the Omega-3 blood index and blood platelet level!!!
- Phosphorus (+ calcium) for “strengthening bones” is needed more by children than by adults - in adults, phosphates predominate in food! For adults, vitamin D + calcium is preferred.
- Organic iodine, as well as inorganic iodine (potassium iodide), are absorbed with the same bioavailability. There is no need to isolate organic iodine.
- Vitamin E – proven prevention of bladder and kidney cancer (!)
- Unfortunately, active forms of vitamins are rarely found on the Russian market, which makes it difficult to use them to correct certain conditions.
- Vitamin B5 (pantothenic acid) is very important for the synthesis of steroid hormones, with adrenal dysfunction, for example, and has a healing property for erosive defects of the stomach, etc.
- Recently, science has begun to attract a lot of attention - chronopharmacology , which also studies the absorption of vitamins by time of day. For example, vitamin D and calcium are better absorbed in the evening!
To be continued ….
Prevention of furunculosis
Ways to prevent the disease include:
- keeping skin clean by washing regularly;
- immediate disinfection of all skin wounds, cuts and abrasions, even the smallest ones;
- Cover any cuts with a sterile dressing to prevent infection.
Eating a healthy, balanced diet and regular exercise will improve your overall health and immune system, reducing the risk of developing not only furunculosis, but all diseases in general.
Seeing a doctor in a timely manner will help maintain your health.
Don't delay treatment, call right now. We work around the clock. tel. (24 hours a day)
Multivitamin Review
Domestic and foreign companies are making a lot of efforts to combine several compounds in one drug. They use a special controlled release technology, which allows them to combine incompatible components with different absorption intervals in one tablet. Thanks to such developments, there are quite a lot of multivitamin complexes on the market, the main purpose of which is to provide a person with the daily requirement of all nutritional components.
Multivitamins contain at once all the vitamins that are combined with each other, which are necessary for normal life.
Multivitamin preparations that contain a large number of organic compounds necessary for the full functioning of the human body are popular.
Most multivitamins have the same composition, which contains the most popular compounds:
- Vitamin A – improves vision, condition of skin, hair, improves the rheological properties of blood;
- B vitamins – participate in metabolic processes, improve the functioning of the central nervous system;
- Vitamin C – improves immunity;
- Vitamin D – promotes healthy growth, strengthens the skeletal system;
- Vitamin E – supports normal functioning of the immune and nervous systems;
- Vitamin F and Omega-3 fatty acids are components for the full functioning of brain structures and myocardium.
All these organic compounds are present in any multivitamin medicine, but they are usually supplemented with microelements. The amount of each component depends on the purpose of the medicine itself: for children, adults or pregnant women. Sometimes such drugs have a medical purpose, that is, they are intended as an auxiliary therapy for a specific disease.
Nutritional supplements containing a number of useful components do not contain chemical components. Rich in fat-soluble and water-soluble vitamins, macro- and microelements for the normal functioning of all organs and systems.
Complivit
Complivit contains group B compounds and ascorbic acid. It has a positive effect on the functionality of the body, regulates energy and metabolic processes, accelerates the regeneration of damaged tissues, and increases the body’s resistance to various viral and bacterial infections.
As a preventive measure, Complivit is prescribed 1 tablet per day. In case of vitamin deficiency, the dose can be increased to 2 times a day. The duration of treatment is 30 days.
Supradin
Supradin is one of the three best vitamin and mineral pharmaceutical preparations. Contains 8 vitamins and 12 microelements. It is recommended to use Supradin for the treatment and prevention of vitamin deficiency, unbalanced nutrition, reduced immunity, increased physical and mental stress during the period of active growth of adolescents.
According to many doctors, Supradin is especially effective in the spring, when nutrient reserves are depleted. Like any other pharmaceutical drug, Supradin has some contraindications that you need to familiarize yourself with before taking it.
Vitrum
Its rich composition allows it to be used as a therapeutic or prophylactic agent for a number of diseases. Vitrum not only stimulates the body's protective properties, but also improves the functioning of internal organs and systems.
Regular use of Vitrum completely provides a person with the necessary nutrients, improves the condition of hair, nails and skin, and increases the body's resistance to a large number of diseases. Tablets are taken once a day for 1 month.
The instructions contain a number of contraindications and side effects that you should read before use.
Multitabs
Multitabs is a popular line of multivitamins for adults and children. Recommended as a preventive or therapeutic agent in the fight against various diseases and conditions. Multitabs “classic” contains 10 vitamins and 7 macro- and microelements. A distinctive feature is the presence of iodine, which is absent in other similar medicines.
Multitabs improves the functioning of the cardiovascular and nervous systems, neutralizes free radicals, cleanses the body of toxins, and stimulates the immune system.
The daily dose is 1 tablet, washed down with a small amount of water. Take 1 hour before meals. Contraindications include hypersensitivity to the composition. When taken correctly, side effects are very rare.
Alphabet
The alphabet is designed in different variations for adults and children. The uniqueness lies in the fact that the package contains tablets of 3 different colors. Each tablet contains specific vitamins and minerals and is taken at the prescribed time. Thanks to this combination of nutrients, the risk of developing an allergic reaction or side effects due to incompatibility of the components is significantly reduced. Allows you to provide an antioxidant effect, improve the rheological composition of the blood, and protect against various diseases.
Pikovit
On the pharmacological market, Pikovit is available in 2 forms - tablets and syrup for children. It has a balanced composition, which contains a number of organic compounds. Designed to suit all needs. In addition to the main substances, it contains calcium and phosphorus, vit. D for active and healthy growth, as well as the prevention of rickets.
Taking Pikovit increases learning abilities and supports the functioning of all functions. This multivitamin is most often used in pediatrics. Tablets are recommended for children from 4 years of age, and syrup from 1 year. A small list of contraindications and good tolerability make Pikovit one of the safe and effective multivitamins.
Not all vitamins and minerals are compatible with each other