Fibroadenoma is a benign breast tumor that most often occurs in teenagers and women under 30 years of age. It is often confused with breast cancer, but it is better limited and mobile to the touch.
Fibroadenoma consists of two types of tissue: connective and glandular.
A fibroadenoma can be described as a hard, smooth, and rubbery collection of tissue with a specific shape. This is a painless knot that looks like a small, smooth ball.
This tumor increases during the menstrual cycle and during pregnancy as a result of hormonal stimulation.
Some women may develop multiple fibroadenomas in their breast tissue.
After menopause, the tumor usually decreases in size.
Fibroadenoma can vary from 1 to 10 cm, usually has an oval or round shape.
The breast consists of lobules - glands that produce milk, and milk ducts through which milk flows to the nipple. These structures are the main components of the breast at a young age.
Fibroadenomas develop from the lobules of the mammary glands as a result of increased sensitivity of the glandular tissue to the female sex hormone estrogen.
If the patient chooses surgery, this tumor is very easy to remove because it is well isolated at the edges.
There are two types of fibroadenoma:
- Pericanalicular fibroadenoma is a predominant glandular component in combination with wide tubules or cystically dilated tubules.
- Intracanalicular fibroadenoma is the predominant connective component, manifesting as a nodule that occurs primarily in the upper outer quadrant of the breast. It can be felt as a tangible moving node. Additionally, this type of tumor is sensitive to hormonal stimulation, meaning that it grows when it enters the menstrual cycle.
Both types of breast fibroadenoma do not show a tendency to malignant changes, so the prognosis is good.
In addition to these two main types of fibroadenoma, there are two more subtypes:
- Tubular adenoma of the mammary gland is clinically equivalent to a regular adenoma of the mammary gland, with a predominance of the glandular component. This occurs during lactation (the production and secretion of milk from the glandular tissue of the breast).
- Juvenile giant fibroadenoma of the mammary gland - can grow up to 20 cm in a short time. It develops during puberty, so at this age it can show signs of very rapid growth and become very large.
Simple fibroadenomas do not increase your risk of breast cancer, but complex fibroadenomas may increase your risk slightly.
Breast tumor
If a biopsy of a benign breast tumor reveals proliferation or atypia , this is just an alarming factor: with this process, the risk of cancer is higher than without it (maximum 4 times). Without proliferation and atypical hyperplasia, all benign breast tumors - papilloma, fibroadenoma, cyst, FAM or FCM - have no higher risk of cancer than all other women .
- Operations for fibroadenoma
- Treatment of breast cysts
- Breast papilloma
- Surgeries for gynecomastia
- Plastic surgery for benign breast diseases
- Mastitis or inflammation of the breast
Breast tumor
Facts of the degeneration of a benign tumor into cancer are described only for atypical ductal hyperplasia and for benign processes with proliferation and dysplasia. All of these conditions cannot be determined by examination, ultrasound, mammography or other non-invasive tests. They can only be detected by a biopsy and examination under a microscope of the formation that was found using the above non-invasive diagnostic methods.
Even the detection of atypical hyperplasia, dysplasia or proliferation does not guarantee the development of breast cancer: these conditions only increase the risks by a maximum of 4 times. In most women, these conditions never develop into cancer.
Not every tumor found in the breast is necessarily malignant or will become so!
Why is fibrocystic mastopathy dangerous?
Mastopathy is always characterized by the formation of both cysts and fibrosis. When this process is balanced - equal parts of both, and it is distributed throughout the entire gland - then they speak of fibrocystic, diffuse or mixed mastopathy.
Fibrous mastopathy
Fibrous mastopathy is characterized by a predominance of the fibrous component over the cystic component in the development of fibrocystic mastopathy.
Increased formation of connective tissue at the site of former proliferation makes the breast gradually denser and more painful. It becomes difficult to evaluate her with mammography and even place her in a mammograph (due to pain). CESM and MRI are more suitable for diagnosis and screening .
Nodular mastopathy
Sometimes, with fibrocystic mastopathy, denser nodes appear in the breast tissue, often in the upper outer quadrants (where there is initially more glandular tissue). They often look suspicious for cancer upon examination and on mammograms and require MRI (or CESM ) and biopsy for definitive diagnosis.
Mastopathy compaction
Often such patients are even offered surgery—sectoral resection for localized fibroadenomotosis—as cancer is suspected. The operation can be combined with a breast lift, reduction or breast augmentation with implants.
Cystic mastopathy
Cystic mastopathy is characterized by the predominance of the process of cyst formation over fibrosis in the development of fibrocystic mastopathy.
These cysts are always multiple. At first they are small, but over time they can merge, reaching large sizes. puncture brings relief .
If the cysts recur, it is proposed to remove them, which can be combined with lifting, reducing or enlarging the mammary glands with implants.
Regarding mastopathy, monitoring for cysts and for preventive examinations of the mammary glands, we recommend that you consult a doctor:
Subbotina Olga Yurievna , AF-clinic, Spassky lane 11, M. Sadovaya, Sennaya, Spasskaya, tel. 310-00-33 and
Sokolova Valentina Ivanovna , Nova Vita Clinic, intersection of Engels and Thorez Ave., tel. 8(911)007-20-02
Dushina Irina Ilyinichna , SMT Clinic, Moskovsky Ave. 22, tel. 777-9-777
Raevskaya Natalya Aleksandrovna , Polyclinic No. 83, M. Sportivnaya, tel. 498-09-22 and 8(921)944-10-45.
Symptoms of mastopathy
Pain is the main symptom of mastopathy.
Connective tissue can swell and hold liquid (like white films on meat dipped in water). Completely similar - overformed connective tissue in the mammary glands during mastopathy - swells with excess fluid in the body. The swollen tissue mechanically affects the nerve endings in the mammary gland tissue, causing pain.
This happens physiologically in phase II of the cycle - when progestins (ovarian hormones) promote fluid retention in the body (normally). Therefore, pain in the mammary glands with mastopathy also occurs before menstruation.
In addition to pain with mastopathy, women find vague lumps in the mammary glands, usually painful and during the period of premenstrual tension. Ultrasound, mammography and MRI usually show nothing, or multiple cysts are found.
Variant of the norm
Some women - after a close examination of the mammary glands - begin to fear for their health. Examining the bumps, they suggest that this may be an inflammatory process or even a neoplasm.
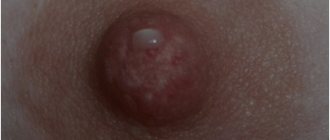
However, every woman has glands in this area of her body that form the so-called Montgomery tubercles.
Signs of anatomical formations:
- location strictly inside the areola;
- dry spots on the chest;
- lack of redness of the glands;
- itchy chest;
- matching the shade of the tubercles to the color of the nipple;
- nipples itch;
- nipples swell;
- absence of painful syndrome.
The average woman has nipple bumps ranging from 10 to 12, but sometimes this number increases to 30 or decreases to 5. The peak for bumps is during pregnancy.
The number of tubercles depends on the area of the areola (in some women it reaches 10 cm in diameter). The larger it is, the more glands on its surface.
Mechanical irritation and other influences
Spontaneous scratching of the nipples during sleep leads to the appearance of wounds that cause the appearance of points similar to tubercles. Excessive friction, as well as exposure to synthetic substances, also increases the risk of developing Montgomery tubercles.
READ ALSO: For those who have acne due to hormones, how do you cope?
Powders, body creams, clothing, and tight bras are possible causes of allergic dermatitis. If dots appear near the nipples, then it is worth considering the option of insect bites, including bedbugs. Neglect of hygiene rules also leads to blockage of the ducts and swelling of the tubercles.
During puberty
In teenage girls, lumps appear suddenly, so they are also interested in the nuance associated with why pimples appear on the nipples at a young age. The phenomenon develops before the first menstruation, which indicates the girl’s emerging ability to bear children.
After the cycle normalizes, Montgomery's tubercles decrease, while the first menstruation sometimes causes them to become very swollen and red. Occasionally, nipple problems are observed throughout the entire period of hormonal changes.
Inflamed bumps that release white contents are often acne. It usually disappears after puberty ends. Acne also disappears on other parts of the body.
Changes during pregnancy
Fertilization is the initial stage of preparing the body to feed the unborn baby. An additional purpose of the glands is to increase the child’s appetite, which is caused by the secretion of a special secretion.
By acting on the tubercles, hormones lead to an increase in their number. After the end of the feeding period, the tubercles become noticeably smaller. In the presented photos you can see how the size of the tubercles changes during gestation.
The reason for the thickening of the pimples is a protective mechanism invented by nature. It prevents infection from entering the nipple and reduces damage during breastfeeding.
Herpes
The appearance of a skin area in which there is an area of small white rashes is a sign of herpetic infection. A common location of the lesion is the area near the nipple (usually under it).
READ ALSO: How to treat acne due to hormonal imbalance - All about acne
The pimples have moist content inside, so they burst within a week after they appear. Damage to the capsule leads to micro-wounds, which increase the risk of infection.
A nipple affected by herpes comes into contact with the baby's mouth, which will certainly become infected during breastfeeding. It is recommended to express milk to reduce the risk of infection, or even switch to artificial feeding.
Treatment of mastopathy
In the treatment of mastopathy, it is necessary to influence the causes of its occurrence: stabilize the menstrual cycle, treat pathologies of the thyroid gland and metabolism, and exclude “unhealthy” foods from the diet. This is often due to changes in lifestyle and established habits, sleep and eating patterns, pregnancy and breastfeeding.
How to treat mastopathy
Without normalizing the above options, treatment of mastopathy will be aimed at: reducing pain (pain relief and reducing swelling due to diuretics while limiting Na +), reducing the patient’s perception of his illness (sedatives), placebo (distracting prescriptions with unproven effectiveness).
About the treatment of breast oncology (cancer) see here.
Breast oncologists at our University Breast Center perform all types of operations for benign breast tumors: fibroadenoma, cyst, cystadenopapilloma (ductal papilloma), gynecomastia, etc.
Our Center is one of the few institutions in the city where it is possible to remove a tumor from the breast (fibroadenoma, cyst, papilloma, gynecomastia) under a compulsory medical insurance policy, voluntary medical insurance, or for a fee.
Removal of a benign breast tumor can be performed from various incisions: above the tumor, along the border of the dark part of the nipple (areola), along the border of the mammary gland (closer to the armpit), along the fold under the mammary gland. The choice is up to the patient.
Some women before surgery worry that after surgery they will have a shortage of breast tissue at the site of tumor removal. We always use breast tissue transfer techniques to evenly fill tissue gaps. If this is not enough, we have a lipofilling method in our arsenal that allows us to fill the volume deficit.
When discovering any tumor, lump or lump, every woman has an absolutely adequate question: “Isn’t this cancer?” First, do a simple test in front of a mirror: raise your arms up.
If, when you raise your arms, a retraction or area of skin appears at the site of the tumor (as in the first and third pictures), if the nipple, when you raise your arms, is pulled into the gland (as in the second picture) or is bent towards the tumor (as in the third photo) - hurry to get examined USE THIS ALGORITHM and contact an oncologist-mammologist.
The next step is to try to squeeze the breast tissue away from the tumor as in the photo:
If skin retraction appears above the tumor, also hurry up and undergo examinations using THIS ALGORITHM and contact a breast oncologist.
If you don’t find anything similar (as in the pictures above) , exhale and relax: most likely you do not have breast cancer.
Even if you squeeze your nipple and squeeze blood out of its ducts, as in the photo below , most likely it will be a benign process - ductal papilloma , and not breast cancer.
| We recommend that you be examined by specialists: |
Pediatric mammology
Hello, dear parents!
Allow me to introduce myself: Sergey Vladimirovich Kaplunov – I am a pediatric surgeon and pediatric oncologist. And today I would like to talk with the parents of my potential patients aged 0 to 18 years on such a very rare topic as pediatric and adolescent mammology. The relevance of this topic is due to the fact that parents do not know who to contact with this or that problem that has arisen in such a sensitive and intimate area, and doctors - pediatricians, gynecologists and ordinary pediatric surgeons are not fully aware of all the variants of pathology that can occur in the area of the mammary glands in children of different ages, and therefore cannot prescribe qualified treatment.
Let me look at breast problems in children according to the age at which these situations may arise.
But first, just a little bit of anatomy: both girls and boys have rudiments of glandular tissue located immediately under the nipple area - so from these tissue rudiments in adolescence, girls will develop glandular tissue of the mammary gland, and in boys these rudiments of glandular tissue will develop. the tissues will normally remain in their rudimentary form.
I. Newborn period. During this period, the so-called “sexual crisis” often occurs, one of the manifestations of which is engorgement (swelling, thickening, increase in volume) of those same rudiments of mammary gland tissue due to the passage of female sex hormones (estrogens) from the mother to the newborn child (sometimes it can even be released scanty secretion from the nipples) – usually this condition can be observed on the 3rd – 10th days of the child’s life, followed by a slow decrease in the severity of tissue engorgement in the nipple area.
But when infections penetrate through the thin and therefore easily vulnerable skin of a baby, against the background of this transient and physiological state, purulent-inflammatory diseases such as mastitis of newborns and necrotizing phlegmon of newborns (which is often localized in the area of the anterior chest wall) can occur.
Already in the neonatal period, parents may notice various developmental anomalies associated with the mammary glands in the child, such as:
atelia - absence of a nipple (absence of a nipple can be a symptom of syndromic pathology - an anomaly in the development of all tissues of the chest wall on the side of the missing nipple);
polythelia - an increase in the number of nipples: most often there is one additional nipple (on one side), which is located along the so-called “milky line” (from the armpit to the groin area), as a rule, the additional nipple is smaller in size (the nipple itself is also reduced and the surrounding areolar area of the skin) – a vestigial appearance
II. Girls in the period from 9 months to 1.5 years. During this period of life, female children sometimes experience a “second wave” of tissue engorgement in the area of the future mammary glands and, as a rule, this condition occurs precisely in those girls whose mothers continue to feed them breast milk. This condition is explained by the fact that hormonal changes occur in the mother’s body associated with the resumption of the cyclic production of sex hormones (as before pregnancy).
III. Pre-adolescence in girls. Often, mothers are concerned about the fact that the first signs of the beginning of the formation of mammary glands in girls begin at 8–9 years of age. This very often looks like a one-sided thickening (engorgement) of tissue in the retro-nipple area, measuring no more than 1 cm (“pea-sized”) on one side. On the opposite side, such engorgement is either absent or less pronounced. So this unilateral engorgement of the tissue under the nipple (girls complain of some tactile pain in this area) can be perceived by parents as a tumor (neoplasm) or as premature development of the mammary gland. However, we must remember that tumor diseases at this age in the area of the future mammary glands in girls are extremely rare, and the asymmetry of the beginning of the growth of the mammary glands in the first few months is not a sign of pathology starting from 8-9 years of age. Moreover, it has been noticed that more often it is the tissue of the future mammary gland on the left that begins to swell. The development of glandular tissue of the mammary glands often occurs not smoothly, slowly and gradually, but spasmodically. And, as a rule, a noticeable increase in mammary gland tissue begins only from 10 to 12 years of age - at this age, tissue development occurs more or less symmetrically.
But an increase in the size of the mammary glands in girls under 8 years of age - “thelarche” - requires the attention of both parents and a doctor! Thelarche can be isolated (i.e., only an increase in the size of the mammary glands without the appearance of secondary sexual characteristics) or as one of the symptoms of premature sexual development. Premature sexual development of a girl requires, first of all, the exclusion of hormone-producing tumor processes (most often in the ovaries) and a careful detailed examination by an endocrinologist! False thelarche can be mistakenly mistaken for true thelarche (proliferation of glandular tissue of the mammary gland) - this is an increase in subcutaneous tissue in the area of future mammary glands due to adipose (and not glandular) tissue. This condition usually occurs in overweight girls, and in diagnosing this condition, the key diagnostic role is assigned to an ultrasound specialist.
IV. Teenage years. This period accounts for the maximum amount of various pathologies, because during this period the greatest activation of the development of glandular tissue of the mammary glands occurs. Let's look at just a few of the problems.
The growing mammary gland requires the most gentle approach to itself in order to avoid problems with breastfeeding in the future associated with the presence of scars on the skin and inside the breast tissue, which will interfere with the formation and release of milk and the very process of feeding the baby. In such cases, there is an equally effective alternative to surgical treatment - a puncture type of treatment, which does not leave any scars behind!, is less painful, there is no need for general anesthesia and long-term painful dressings. The choice of treatment method for a purulent process in the mammary gland (surgical or puncture or even conservative) is, of course, a matter for an experienced specialist and depends on each specific clinical situation. The main rule for parents is to contact a specialist early with inflammatory changes in the mammary gland area in a teenage girl.
The most common tumor in the mammary glands in teenage girls is fibroadenoma - a benign tumor! Cancerous tumors of the mammary glands in children under 18 years of age (carcinoma, lymphoma, sarcoma) are a rare situation.
It is believed that fibroadenoma is a hormonally dependent tumor, the development of which depends on the reaction of breast tissue to the increasing concentration of estrogen in the growing female body. Often, fibroadenomas can be multiple, ranging in size from 5 mm to 5 cm (sometimes they occupy most of the breast tissue - leaf-shaped or phylloid fibroadenoma).
The only method of treating breast fibroadenoma is a surgical approach - operations in this case (especially in adolescents) should be organ-preserving and aesthetic in nature. Incisions and sutures are made using cosmetic techniques, and only the tumor is removed without involving surrounding healthy tissue.
In this informational article, I focused only on some of the most common problems that can arise in the mammary glands, mainly in girls. A separate topic is the occurrence of tissue proliferation (increase) in the area of the mammary (mammary) glands in boys - this is especially relevant (emotional, cosmetic, social aspects) in adolescence: the so-called gynecomastia. There are also a number of nuances and differences here. This topic will be discussed in the next information article.
Kaplunov S.V.
pediatric surgeon, pediatric oncologist of the highest category
Make an appointment
Make an appointment
Mastopathy
In the International Classification of Diseases (ICD), mastopathy is coded as N60.1 and refers to benign mammary dysplasia. This means that mastopathy is not an ancestor and does not increase the risks of its occurrence .
The World Health Organization (WHO, 1984) in the Histological Classification of Tumors (evaluates the process under a microscope) defines mastopathy as a dishormonal hyperplastic process in the mammary gland or fibrocystic disease (FCD), characterized by proliferative and regressive changes in the mammary gland tissue with an abnormal ratio of epithelial and connective tissue components.
Diffuse FAM
NB! This abbreviation is very often used after any examination of the breast (ultrasound, mammography, examination). This is due to the fact that in budget clinics, if the doctor does not find any pathology during the examination and does not make at least some diagnosis, the insurance company does not pay for this consultation and examination to the institution. Therefore, there is an unspoken instruction to doctors to “put at least something.” This is how it is implemented. It is impossible to write “Normal variant” or “No pathology detected”!
In private centers, in most cases, there is an unobtrusive recommendation to encourage repeat visits of patients and their additional examinations. Therefore, they also “find” FAM, FCM or mastopathy during a simple preventive examination without the patient’s complaints - in order to be able to prescribe a “control” examination, examination or even treatment with dietary supplements (which are often sold right there) with a second “appearance in 3-4 months” .
Fibroadenoma - treatment
In most cases, fibroadenomas do not require treatment. However, some women, for safety reasons, prefer to remove the seal. If the doctor determines the presence of fibroadenoma during clinical trials, then surgery will probably not be needed.
You can avoid surgery because:
- surgery can distort the shape and texture of the breast;
- fibroadenoma can sometimes shrink or disappear.
Typically, they only need to be monitored regularly for size and appearance using ultrasonic inspection.
Causes of mastopathy
WHO considers the cause of mastopathy or fibroadenomotosis dishormonal changes that can occur with:
- disruption of hormone synthesis during an unstable menstrual cycle
- for problems with the thyroid gland
- in case of metabolic disorders with excess body weight (adipose tissue itself synthesizes estrogens - ovarian hormones of the first phase of the cycle).
- late birth and short duration of breastfeeding.
WHO does not consider options for dishormonal changes due to consumption of cheap foods with hormones - broiler meat, animals and fish that received hormonal growth stimulants; animal tissues with a high content of endogenous hormones - udder, adipose tissue, uterus, ovaries, milk - which are not thrown away, but processed and used for the manufacture of cheap semi-finished products. A number of plant products contain substances that are not actually hormones, but which our body perceives as hormones - hops in beer, soy, palm oil components. When consumed regularly, they can also cause dishormonal changes and provoke not only mastopathy.
Normally, a passage of secretion occurs in the mammary gland: hormones of the corpus luteum - phase II of the cycle initiate the proliferation of cells of the mammary gland lobules (which secrete milk during feeding) - as preparation for a possible pregnancy - without pregnancy, their regression occurs. The cells of the lobules die and the products of their death move along the ducts towards the nipple, where what is left of them is absorbed in the sinuses. In mastopathy, due to dishormonal changes, the process of proliferation in the lobules is more pronounced. As a result, more regression products of these cells appear, which form clusters (cysts). Severe regression promotes aseptic inflammation and the formation of connective tissue. With a deficiency of vitamins A, E and D, rough scar tissue forms at the site of regression, disrupting the movement of secretions and aggravating the problem in subsequent cycles.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding help normalize the condition of the mammary glands, while abortion provokes a non-physiological hormonal shock to the mammary gland tissue.
The synthesis of all hormones occurs mainly at night from 23:00 to 3:00, provided that the person is already sleeping at this time. For this process to occur normally, you need to go to bed after 10:00 p.m. It is believed that this process is also negatively affected by excessive lighting. At night, during sleep, all the damage that happened to the body during the day is restored. Lack of sleep and light pollution from artificial lighting disrupt the natural process of hormone synthesis and body restoration, causing illness.
Also, excess Na+ content also contributes to fluid retention in the body. Each sodium ion can hold up to 4 water molecules. Sodium ions are part of sodium glutamate (a flavor enhancer - a food additive for cheap food) and salt (NaCl), which is found in abundance in processed foods, sauces and seasonings.
Pathological conditions
Some pimples around and inside the nipple of the breast are a consequence of the development of pathology.
- Eczema. A complicated form of allergy, the result of excessive friction or hormonal imbalance.
- Neurodermatitis. An allergic reaction develops after nervous stress and mental disorders.
- Atheroma. A subcutaneous clot of adipose tissue forms not only on the dermis, but also on the nipples. Blockage of the duct leads to the accumulation of secretions, which leads to the formation of a wen. The symptom is the presence of a rolling ball inside.
- Telit. Redness of the entire surface of the nipple is called by this medical term.
- Mastitis. The inflammation is located inside the mammary gland and spreads to the nipple and areola (blood is often released from them).
White pimples that appear around the nipples in women are a sign of furunculosis. Entering the epidermis through wounds, pathogenic microflora causes inflammation, often transforming into a purulent process.
READ ALSO: Adult acne - causes and how to deal with it
If they appear, then urgent treatment is needed: some nodules lead to necrotic processes and abscesses. Doctors recommend opening pustules, but only under the supervision of a specialist.
There are three answers to the question of which doctor you should contact. When there is a suspicion that the activity of the mammary gland is impaired, then go to a mammologist, or a skin specialist - a dermatologist. If you suspect the development of a neoplasm, it is better to visit an oncologist.
Paget's disease is a malignant disease that is accompanied by the appearance of ulcers and pain. In most patients, the pathology is localized on the nipple, less often - near the areola.
Conclusion
Suddenly appearing pimples on the nipples in women are mainly related to anatomical formations, but there are also manifestations that are caused by diseases.
Doctors warn! Shocking statistics - it has been established that more than 74% of skin diseases are a sign of parasite infection (Accarida, Giardia, Toxocara). Worms cause enormous harm to the body, and the first to suffer is our immune system, which should protect the body from various diseases. The head of the Institute of Parasitology shared the secret of how to quickly get rid of them and cleanse your skin, it turns out that’s enough. Read more .
White bumps are the consequences of the effects of herpes on the body, and doctors can only eliminate them with medication. Purulent processes are also dangerous, so they should be neutralized as soon as possible.
News MirTesen
Signs of mastopathy
WHO considers all the problems mentioned in the paragraph above to be the cause of mastopathy - when, under the influence of these hormonal changes in the mammary gland, glandular tissue is stimulated (proliferation), and after the stimulation stops, excessively proliferating tissues die with the formation of cysts, after which - the formation of scar tissue. As a result, multiple cysts appear in the breast, and the connective tissue causes fibrosis.
All this leads to an increase in the density of the mammary glands and the occurrence of pain - first before menstruation, and with an unstable cycle - it may not depend on it.
Pain in mastopathy is never one-sided and precisely localized: the entire chest hurts, right and left, maybe somewhere a little stronger (for example, in the upper outer quadrants - where there is more glandular tissue), but ALL! It bothers me while lying and standing, without changing from body position.
If signs of mastopathy appear or intensify while taking hormonal drugs (contraceptives), it means they were chosen incorrectly - coordinate their use with a gynecologist. At the same time, being treated at the same time by a mammologist is absurd.
If the pain is local in nature - on the one hand, and you can accurately show its location, but no compaction is detected in this place - most likely it is associated with intercostal neuralgia due to physical inactivity and problems with the thoracic spine. This pain will go away depending on the position of the body (tilting left and right, bending over, lying down and standing up) and inexperienced specialists and patients often confuse it with mastopathy. According to the results of breast examinations (mammography, ultrasound), nothing is found with her either.
When to see a doctor?
If there is a lump in your breast, you should definitely consult a doctor. Although fibroadenoma is not dangerous, its condition should be monitored regularly.
If a new lump appears that looks different or is accompanied by other signs, such as nipple discharge, you should see your doctor. These symptoms may indicate breast cancer.
If a woman is planning a pregnancy, it is recommended to remove the fibroadenoma. The tumor can grow during this period under the influence of hormones.
Fibroadenoma also increases during breastfeeding. If the tumor is large, it can block the milk ducts, which leads to additional complications.
FAM (fibroadenomotosis) or FCM (fibrocystic mastopathy)
FAM stands for fibroadenomotosis. This is the same as FCM - fibrocystic mastopathy. This term refers to a pathological process in the mammary gland (breast), characterized by the appearance of cysts and fibrous tissue. More cysts - cystic FAM or FCM, more fibrous tissue - fibrous FAM or FCM.
If the process evenly affects the entire tissue of the gland, it is a diffuse form. If the process is local - focal FAM or local. Local fibrous FAM is often mistaken for cancer. Suspicion is excluded by MRI and biopsy, or by surgery to remove a suspicious tumor.
Very often, the diagnosis of FAM is made not because of the presence of pathology, but in order to properly fill out documents for the visiting patient at an appointment at a budget clinic: if you write on the card that “no pathology was detected,” the insurance company will not pay for the appearance at the clinic.
The most common cause of FAM is hormonal changes (read more HERE).