Often common colds result in severe complications. An abscess is considered the most dangerous. It is located in the submucosal tissue. The pathological process progresses rapidly; after a few hours, the formation increases significantly in size. It blocks the airways and prevents the patient from breathing. The risk of death from suffocation increases. If you suspect purulent inflammation in the patient's nose or throat, you should immediately take him to the doctor to decide on surgical treatment.
What is an abscess
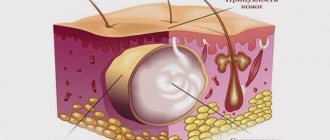
An abscess is a limited purulent inflammation of soft tissues followed by their melting and the formation of a cavity containing pus. Abscesses of ENT organs involve the accumulation of purulent exudate in the tissues of the pharynx, larynx, nose, and ear. The abscess is located in the submucosal tissue. It matures, and the mucous membrane becomes thinner. When it matures, a rupture occurs at this point. Purulent exudate pours out of the abscess cavity.
In the development of the pathological process, the following stages are designated:
- Edema. It is characterized by the presence of severe swelling of the tissues in the affected area. There are practically no clinical manifestations of an abscess. Infiltration. It reveals redness and infiltration of the mucous membrane. There is an increase in body temperature. The disease is detected at this stage in a quarter of patients. Abscessing. With it, a fluctuating formation is found that blocks the lumen of the organ. Anatomical deformation occurs in this area of the pharynx and narrowing of the lumen.
The inflammatory focus containing pathogenic microorganisms is separated from the environment for a long time. The infection is not transmitted to others.
Features of opening abscesses
Opening an abscess can be done in different ways. In particular:
- spontaneous opening;
- forced autopsy performed by a surgeon in a hospital setting.
Spontaneous opening occurs:
- external - this is the outpouring of purulent contents;
- breakthrough inside - emptying the contents of the wound into the abdominal or articular cavity, etc.
- a breakthrough inside the organ - in this case, pus penetrates into the organ cavity.
Forced opening is carried out when conservative treatment of the abscess is no longer possible due to a severe deterioration in the patient’s health and spontaneous opening does not occur.
What symptoms do you see a surgeon for:
- Presence of hernial protrusion
- Daggering pains in the abdomen
- Bloating
- Pain in the right hypochondrium
- Bitterness in the mouth
- Nausea
- Presence of neoplasms on the skin
- Swelling and redness of the skin
- Bone fractures and bruises
- Wounds of any location
- Vomit
- Enlarged and painful lymph nodes
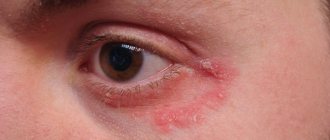
Symptoms of purulent inflammation of the middle ear and nasopharynx
With this pathology, clinical manifestations increase sharply. Severe pain occurs at the site of the abscess. It grows quickly and becomes intense. Over time, a sensation of pulsation appears in the affected area. It radiates to the area of the lower jaw, nose, and ear. Signs of general intoxication appear.
Body temperature rises above 38 ° C. The patient develops severe weakness, severe headache, disrupting sleep. Salivation sharply increases. Putrid odor from the mouth. The nearby regional lymph nodes become enlarged. Over time, the voice becomes nasal and speech changes.
When swallowed, liquid enters the larynx and nasopharynx. The patient experiences a spasm of the masticatory muscles. A sharp pain appears, which intensifies when turning the head. The patient's neck is in a forced position.
The abscess breaks through before the sixth day from the start of formation. The patient's condition is improving. Body temperature decreases and muscle tension decreases.
Technique for surgical opening of an abscess
Surgical opening of an abscess in our center begins with a preparatory stage, which includes preparation of the surgical field - shaving off hair from the site that will undergo surgery, and its subsequent treatment with an antiseptic solution.
Next, depending on the type of abscess, its location and effect on the patient’s well-being, an anesthetic is selected (most often novocaine or ethyl chlorine). In some complicated cases, the operation must be performed under general anesthesia.
After this, the abscess is opened, the resulting cavity is cleaned of the remnants of its contents, after which drainage is introduced into the cavity. After this, the patient must be given dressings and treatment. If the abscess is accompanied by fever and other signs of intoxication, treatment with antibiotics is required.
No matter how the abscess is opened, immediately after this the patient should feel relief, and the wound should heal with full systematic treatment. If after the procedure the patient’s well-being does not improve, the temperature continues to persist, etc., it is necessary to immediately consult a doctor (if he is not undergoing treatment in a hospital).
To avoid complications, it is necessary to consult a doctor in a timely manner - this will avoid serious complications. The center’s specialists are always ready to help, even in the most difficult situations, and answer all questions.
Diagnostic methods in surgery:
- Doppler in surgery
- Colonoscopy
- Angiography
- CT scan
- Gastroscopy
- MRI
- Abdominal ultrasound
- X-ray
- Endoscopy
Prices:
| Code | Name of service | Prices |
| 1 | Initial appointment | 1200 |
| 2 | Repeated appointment | 900 |
| 3 | Calling a surgeon to your home | 3500 |
| 4 | Abdominal ultrasound | 2200 |
| 5 | Ultrasound of veins and vessels | 2400 |
| 6 | Doppler 2-3 trimester | 1200 |
| 7 | Rectoscopy | 1500 |
Preparation for treatment of an abscess in the throat, diagnosis of a retropharyngeal abscess
If you suspect an abscess, you should immediately contact an ENT doctor. Diagnosis of the disease occurs as follows:
- The doctor finds out the complaints and features of the course of the disease. There are often indications of chronic tonsillitis. When examining the throat, nose, and ears, a formation is found. The patient's head is in a forced position of the head and neck. The lymph nodes under the jaw and in the neck are enlarged. When examining the ENT organs using special instruments, a round, fluctuating protrusion of the mucous membrane is revealed. A yellowish spot is visible at its top. Their laboratory tests include a general blood test and culture of the contents of the purulent lesion.
If complications are suspected, MRI, CT scan of the neck, ultrasound, and X-ray of the head and neck are prescribed.
Reasons for formation
Due to their development, there are two types of perimaxillary abscesses:
- Odontogenic. The cause of development is damaged dental elements.
- Non-odontogenic. Not caused by the condition of the dentofacial apparatus.
The most common causes of anomalies are dental diseases:
- Advanced carious lesions of units, pulpitis.
- Deep periodontal pockets.
- Periodontitis.
- Pericoronitis.
- Infected and impacted molars and premolars.
- Root cyst.
The development of a lesion can be triggered by penetration of infection under the periosteum from a diseased unit.
Reasons for the development of non-odontogenic foci of pus:
- Traumatic lesions of the jaws, elements or soft membranes of the oral cavity with infection.
- Nasopharyngeal and ear infections.
- Complications of unqualified dental treatment.
- Spread of infection to the jaw from other organs and systems.
The development of an abscess depends critically on the general health and immunity of the patient.
Progress of the operation to open a purulent abscess
The main task of surgical treatment is the opening and evacuation of pus from the abscess cavity.
The stages of surgery are as follows:
- First they carry out the local one. Infiltration or conduction anesthesia is possible. Antiseptic treatment of the mucous membrane in the surgical area is performed. The abscess is opened at the protruding point where the mucous membrane is most thinned. The edges of the wound are spread apart. Wait until the pus drains completely. Damaged vessels coagulate. A latex strip drainage is installed, which facilitates the evacuation of the wound contents.
With a paratonsillar abscess, the formation is removed along with the tonsil.
Causes of abscess
Many abscesses are bacterial in nature; their causative agents are often bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli, etc. However, in addition to bacteria, the causes of this disease can also be:
- Some drugs that cause what is called a sterile abscess.
- Diseases such as pharyngitis, Crohn's disease, etc.
- A hematoma that at some point began to fester.
- Intramuscular injections that have been infected.
- Infection of cysts of internal organs, etc.
In any case, the occurrence of an abscess, its course and opening should be observed by a doctor.
The easiest for clinical practice are external (superficial) abscesses that can be easily seen. Therefore, people most often present with an external abscess before the onset of health complications.
Deep abscesses are characterized by the fact that a person most often does not notice them, so they often seek help only when a significant deterioration in health has occurred. A gas abscess occurs when its pathogens produce gas.
Abscesses can also be acute or chronic. Acute is a currently ongoing process, accompanied by rapid development, and ultimately its opening and outpouring of contents. A chronic abscess occurs if the emptying of purulent contents from the abscess cavity is not complete, and the process can begin anew and become permanent (chronic).
Useful information about visiting a surgeon at the clinic:
- How to prepare for a surgeon's appointment
- What diseases does the surgeon treat?
- Calling a surgeon to your home
- Surgical care in the clinic
- Surgical care at home
- What symptoms should you contact a surgeon for?
- Treatment of surgical diseases
- Treatment of intestinal pathologies
- Treatment of skin surgical pathologies
- Treatment of bedsores and necrosis
- Treatment of parasitic diseases
- Treatment of inflammatory processes of soft tissues
- Treatment of diseases of the musculoskeletal system
- Diagnosis of surgical diseases
Clinical symptoms
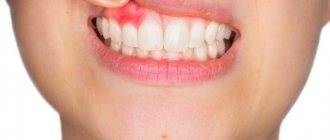
Manifestations of the disease are determined by the location and severity. The pathology clinic is similar to periodontitis. The patient experiences intense pain that increases with palpation or biting on the affected area.
The pathology is characterized by the following symptoms:
- Dense swelling and severe hyperemia.
- Protrusion of a pathological focus from the mucous membrane of the cheeks or periodontium.
- Facial asymmetry, jaw deformation.
- The flow of pus from the fistulous passages.
- Hyperthermia during intoxication.
- Dizziness, lack of appetite, deterioration in general health.
- Allergic reactions.
Some symptoms may be absent or mild. Clinical manifestations depend on the location.
Diagnostic techniques
Initially, the doctor conducts a patient interview and a clinical examination of the oral cavity. The time of onset and nature of the symptoms are clarified. Complaints of deterioration in health, loss of appetite and other manifestations of intoxication are heard.
During the examination, the doctor visually and palpably assesses the condition of the mucous membrane in the affected area. The pain of touch, the presence of carious units, the condition of the skin in projection, the symmetry of facial features, and lymph nodes are recorded. Body temperature and pressure are measured.
If necessary, additional diagnostic measures are carried out: X-ray, ultrasound, EDI, CBC.
Based on the data received, the doctor confirms the diagnosis and draws up a treatment plan.
Schemes for eliminating the disease
An integrated approach to treating the disease is used. Surgery allows you to open and drain the source of infection. Symptomatic therapy, antibiotics, vitamins, anti-inflammatory drugs, and detoxification drugs are prescribed as additional methods. Drug therapy is limited to 1-2 weeks.
When choosing a treatment regimen, the following are taken into account:
- Features of the pathology: stage, localization, prevalence, etc.
- Age and immune status of the patient, concomitant diseases.
The main task of the dentist is to prevent the spread of infection to other organs and systems of the patient’s body.
Surgical autopsy
It is performed under local anesthesia. The operation consists of several stages:
- Opening and removing pus.
- Antiseptic wound treatment.
- Drainage, dressing.
- Daily dressings with antiseptic treatment.
After surgery, the oral cavity must undergo sanitation, treatment or extraction of the affected unit.
Potential Complications
A maxillary abscess is actually a complication of infectious diseases, trauma or caries-affected units. In the absence of timely treatment, the pathology can take dangerous and life-threatening forms: meningitis, phlegmon, mediastinitis, thrombophlebitis of the sinuses of the brain, sepsis.