Everyone is familiar with such an injury as a burn. It is the timely and correct provision of pre-medical care that determines a person’s further condition. In order to quickly navigate and help the victim properly, it is important to know what types of burns there are, how the methods of providing assistance differ depending on the severity of the injury. Pay special attention to actions that are prohibited and priority measures.
Burn: concept, degrees and types
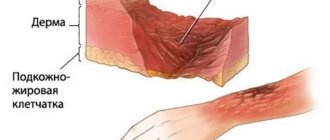
It is a type of physical injury. Occurs due to exposure to high temperature, a special chemical, ultraviolet or ionizing radiation, or electric current. The receiving process is accompanied by severe pain and noticeable damage to the skin, mucous membrane or cornea of the eyes.
The severity of the condition depends on the size of the burned surface and the depth of tissue damage. The larger they are, the more severe the injury.
There are four degrees of damage based on depth:
- The first degree is characterized by redness of the injured area, only the upper layer of the epidermis is affected.
- The second degree is characterized by the appearance of blisters filled with yellowish liquid.
- In the third degree, the skin is deeply affected, and the processes of death and scab formation begin.
- In the fourth degree, necrosis of the skin occurs, accompanied by charring; bones and muscles may be involved in the process.
Depending on the type of injury, burns can be:
- Thermal. The reason is exposure to boiling liquid, steam, a hot object or open fire.
- Electrical. Occurs under the influence of electric current. Characteristic are small wounds at the discharge entry/exit points. They are characterized by great depth and electrical trauma to internal organs.
- Chemical. Occur under the influence of alkaline or dangerous acidic compounds, salts of heavy metals. Not only the skin, but also the oropharynx and esophagus can be affected.
- Radiation. Occur during atomic explosions and as a result of radiation leakage, they are rare. This category includes damage to the skin from exposure to the rays of the sun.
Types and severity
A burn on the hand can be:
- thermal - if the victim was burned by boiling water or steam, touched a hot iron or frying pan;
- chemical - upon contact with an aggressive reagent (alkali or acid).
Depending on the depth of the lesions, the following types of burns are possible:
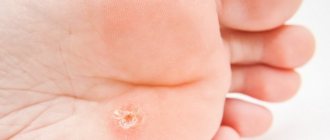
- The first stage - the skin on the hand turns red and swells. The person experiences pain and burning.
- Second degree - blisters appear at the site of the lesion. The epidermis dies and peels off.
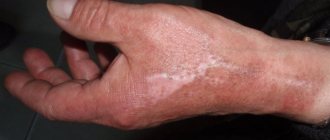
- Third degree - the deep layers of the dermis, muscle and connective tissue are damaged. The skin becomes covered with many transparent blisters and a scab forms. Scars and cicatrices form at the healing site.
- The fourth stage is deep trauma. The skin is charred. The burn affects soft tissue and bones. Possible death.
Rules for first aid for burns
In the vast majority of cases, people receive such injuries at home, in hazardous work, or during outdoor recreation. To save the life of the victim, it is important to know the procedure for providing first aid for each type of burn.
For thermal burns
- Remove exposure to source of damage (eg fire, steam, boiling water).
- Pour cold water over the damaged area for 7-15 minutes (if external signs indicate a 1st or 2nd degree injury). Ice or snow wrapped in a clean cloth is suitable for cooling.
- For a 3rd or 4th degree burn, first apply a moistened bandage to the burn site and cool it in a container of water. Do not direct a stream of running water onto the wound.
- Free the burned area from clothing and accessories. If the tissue is stuck, carefully trim off the excess without touching the wound itself.
- Cover the wound with a clean, damp cloth for grade 3-4 damage.
- Prepare a solution of 0.5 liters of water, ¼ teaspoon of soda and ½ teaspoon of salt, and give it to the victim.
For chemical burns
- Free the damaged area of the body from clothing and accessories.
- Immediately rinse the injured area with cool water for half an hour. If the procedure was not done immediately, then the washing time is increased to 45 minutes.
Attention! If the burn was caused by an organic aluminum compound, you cannot rinse it with water, otherwise it will ignite.
- To avoid worsening the condition, do not dry the burned skin with a towel, even a paper towel.
- If the burn is a result of the action of acid, then wash the wound with a weak solution of baking soda (1 teaspoon per 500 ml of water) or non-contactly treat with soapy water.
- If the cause of the injury is exposure to alkali, then the wound is treated with a non-concentrated solution of acetic or citric acid.
- Cover with a cloth soaked in cool water for 15 minutes.
- Gently cover the wound with a sterile bandage.
If the injuries are extensive and painful, then the victim is given an anesthetic and warm drink, for example, alkaline mineral water. Medicines based on paracetamol, acetylsalicylic acid, ibuprofen and any NSAIDs relieve pain well.
Calling an emergency medical team is mandatory for 3rd-4th degree burns. And also, if an elderly person or a small child received a thermal injury, a large area of skin, organs of the groin area are affected, the respiratory system, eyes, oral cavity are affected, the victim has concomitant heart disease or diabetes.
Electrical burn
- Turn off the power source to stop the current flowing to the affected person. Or move it to the side with a stick/branch to avoid getting hit yourself.
- Lay the victim on his back and place a bolster under his legs and lower back so that his head is lower than his body.
- Cover any injuries found with a clean cloth to prevent infection.
- Check your breathing and pulse. If they are absent, proceed to artificial respiration and chest compressions.
- Call an ambulance. Only a specialist can determine damage from electrical discharge, diagnose internal organs and remove dead tissue.
For sunburn, it is important to cool and moisturize damaged skin and relieve pain. Take a bath with cool water several times a day, drink more fluids, and use local wound-healing agents.
1st-2nd degree burns can be treated independently. The main pharmaceutical products that have regenerating and antimicrobial properties in this case are Panthenol spray, Dexpanthenol cream, Spasatel or Levomekol ointments, Baneocin powder. Miramistin has proven itself well, preventing infection and helping to reduce pain and itching.
Treatment of 3-4 degree burns is the competence of medical workers; hospitalization and complex treatment are required, surgical intervention is possible.
What to do if your hand is burned at home: first aid
The ability to provide first aid to a burned person is the duty of every person.
Some people apply a bandage to the burned area. It is not recommended to do this, as this leads to a greenhouse effect, due to which the skin of your hands will peel off. Better to put on a bandage.
If the victim has scalded the skin with hot steam or boiling water, when providing first aid, adhere to the following steps:
- Remove clothing if it covers the affected area of skin. In this case, you need to be careful so that the bubbles on your hand do not burst. If the item is stuck to the wound and is removed with the skin, you need to stop and wait for the doctor to arrive.
- Place your hand under cold running water and hold it until the pain subsides (at least half an hour).
- Treat the affected hand with furatsilin solution or chlorhexidine to prevent the development of infection. It is forbidden to apply iodine, brilliant green or potassium permanganate!
- Deciding what to anoint your hand with a thermal burn. The problem area can be treated with Dexpanthenol, Panthenol, Rescuer.
- Cover the burned area with a sterile bandage (if there are blisters).
- In case of severe pain, the patient is given an analgesic.
Do not use greasy products for lubrication. They form a film that promotes the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria and prevents heat removal.
Further treatment
Superficial burns of the palm and hands can be treated at home with the help of medications and traditional medicine. The maximum duration of treatment is a month. For deep injuries, therapy can take years.
Medications
There are various medications that solve the question of what to apply to a burn on your hand. Some are designed to relieve inflammation, others to disinfect, and others to accelerate the regeneration of the damaged area. All of them are used externally. Particularly effective:
- Betadine is a widely used antiseptic.
- Karipazim - breaks down blood clots, secretions and dead tissue. Treats severe hand burns (prescribed for 3rd degree).
- Solcoseryl – stimulates regeneration.
- Amprovisol - used for local anesthesia. Soothes and relieves inflammation.
- Levomekol is an ointment with anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial effects.
- Inflarax - has an anti-inflammatory, analgesic and antimicrobial effect.
- Panthenol - restores damaged skin integrity of varying degrees of severity.
All medications have contraindications. Before use, you must read the instructions.
Folk remedies
You can treat mild hand burns at home. If the integrity of the skin is not compromised, the following traditional medicine recipes can be used:
- Sea buckthorn oil will relieve inflammation and speed up skin healing. Apply twice daily.
- Raw potatoes will relieve swelling and relieve pain. Grate the root vegetable and apply to the burn site as a compress. Once the potatoes are dry, replace them with new ones. Repeat the procedure 3-4 times.
- Aloe juice will relieve inflammation, reduce the risk of swelling and speed up healing. Cut the plant leaf lengthwise, apply it to the burned area and secure with a bandage. After an hour, remove the bandage.
- Black tea will reduce pain and relieve inflammation. Soak a sterile bandage in the tea leaves and apply to the injured surface of the hands. Change the compress as it dries. Use for a long time until the affected area heals.
- White cabbage will relieve pain. Grind the cabbage leaves in a meat grinder or blender. Apply the resulting mixture to the problem area of the hand. After anesthesia, wash off any residue with water and bactericidal soap.
When it comes to the question of how to quickly cure a burn, doctors advise using comprehensive measures, that is, using approved folk remedies only in combination with pharmaceutical drugs. This approach promotes rapid healing and recovery of a person after an injury.
What you should and shouldn't do if you have a chemical burn on your palm
Chemical burns to the skin of the hands are possible when in contact with salts of heavy metals, volatile oils, alkali or acid. In this situation, you must first remove the substance. To do this, you need to wash the burned area with water or a neutralizing solution.
Wounds caused by contact with quicklime and organic aluminum compounds should not be washed with water. In the first case, the reagent is removed dryly (with a napkin), in the second - with an alcohol solution.
If the burn is caused by sulfuric acid, the first aid will be to remove the substance from your hands with a dry cloth and only then rinse with water and then apply a sterile bandage. For rinsing, you can use a solution of 1 tsp. baking soda and 500 ml water.
If the injury is caused by an alkali, then a solution with boric acid will help neutralize its effect.
When it comes to the question of how to treat hand burns at home, doctors prohibit self-medication and self-prescription of medications. A person who is far from medicine cannot predict the body’s reaction to one or another component of medicines. Therefore, a doctor must prescribe medications.
Possible consequences
The following complications are possible with burns:
- burn shock (when more than 15% of the body is affected);
- toxemia (nausea, weakness, pale skin, fever, possible vomiting and fever);
- septicotoxemia – typical for 3rd and 4th degree burns. Lasts 1-4 weeks. Manifested by weakness, chills and tachycardia. Septicotoxemia requires hospitalization to avoid death.
If your hand skin is burned, it is important not to panic. The victim needs first aid. If the lesion is extensive or moderate/severe, call a doctor.
Treatment of thermal burns
Of course, the main task and goal of treating a thermal burn is to restore the integrity of the skin. For superficial burns that do not involve the germ layer of the skin, regeneration occurs independently. If the burn damages the germ layer, healing is only possible through scarring, so with extensive deep burns there is a need for skin grafts.
In addition to measures aimed at restoring tissue integrity, treatment of burns has a number of other goals:
- pain relief;
- normalization of hemodynamics;
- restoration of water and electrolyte balance;
- normalization of blood pH;
- restoration of protein metabolism;
- prevention of liver, heart, lung, and kidney failure;
- detoxification of the body.
The first step in treating deep thermal burns is to thoroughly clean the burn wound. Foreign bodies, pieces of tissue, and exfoliated epidermis are removed from its surface under aseptic conditions and under local anesthesia. The wound is washed with hydrogen peroxide, after which the doctor decides on the method of further therapy. With the open method, a bandage is not applied to the area of burned skin. The closed method of therapy involves applying anti-burn ointment and subsequent dressing.