A sulfuric acid burn is a dangerous chemical injury that is often fatal. The odorless and colorless oily liquid is a strong oxidizing agent. Upon contact with mucous membranes and skin, it instantly destroys epithelial cells. Inhalation of acid fumes leads to laryngitis, bronchitis, and hemorrhagic pneumonia. The degree of tissue damage depends on the percentage of the reagent in the solution. The principles of treating burns with caustic acids differ from the measures used for chemical injuries with other substances.
Why is a burn from sulfuric acid dangerous?
Burns from sulfuric acid are fraught with deep damage to soft and bone tissue. Contact of the reagent with the skin leads to:
- the formation of a white scab;
- ulceration of tissue under the crust;
- toxic poisoning of the body.
Upon contact with acid, skin necrosis occurs, and if large areas of the body are affected, burn shock occurs. Particularly dangerous are liquid vapors that penetrate the respiratory system. The burn causes severe pain and internal bleeding. Contact of the reagent with the eyes in 80% of cases results in partial or complete loss of vision.
Characteristic signs
To reduce the harmful effects of the product on the skin, you need to act immediately.
Pathology has the following signs:
- a white crust forms in the damaged area, which has clear edges;
- Over time, the white crust darkens and becomes gray or brown;
- a dense scab appears;
- surrounding tissues become swollen and inflamed;
- with deep penetration, tissue necrosis develops, muscles and bones are affected;
- sometimes gangrene forms in the damaged area.
When hazardous vapors are ingested, the following symptoms appear:
- severe swelling of the mucous membranes;
- bleeding from the nasal passages;
- severe abdominal pain;
- difficulty breathing;
- Sore throat, wheezing.
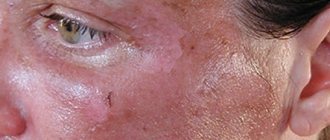
Face after exposure to sulfuric acid
Degree of skin damage
Burns occur due to careless handling of reagents at work and at home. The severity of a chemical injury is determined by the concentration of acid in the solution:
- diluted – the concentration of the oxidizing agent does not exceed 10%;
- electrolyte - a weakly concentrated solution with 22-30% reagent content;
- tower - a solution with nitrogen dioxide in which the acid concentration is 75%;
- concentrated – undiluted 96.5% acid.
When the substance acts on living tissues, intracellular protein is destroyed with the formation of organic and inorganic compounds - albumosis, proteinogenic amino acids, peptones, etc.
Using wet wipes or pieces of cloth soaked in water is strictly prohibited, as this can only worsen the situation.
There are 4 degrees of burns based on the depth of damage:
- First. The outer layers of the epidermis are destroyed, as indicated by moderate redness, pain, and swelling. The burn goes away within 3 days without any traces.
- Second. The epidermis is split down to the basal layer, which is directly adjacent to the dermis. Chemical injury is accompanied by pain, burning, and blistering rashes. By preserving the basal layer, the skin is restored within 2 weeks.
- Third. The reagent partially or completely affects the dermis. With 3A degree burns, the follicles and sebaceous glands are not damaged. A white scab appears on the burned area, with ulcerations underneath. 3B degree burns are characterized by the death of skin cells down to the hypodermis, that is, the subcutaneous fat layer.
- Fourth. Prolonged contact with a caustic liquid leads to charring of the skin, muscles and bone tissue.
Burns with caustic acid lead to the formation of a white, loose crust with clear boundaries, which darkens over time. Outwardly, it seems that the injury is superficial and does not pose a danger. But ulcers form under the scab, and tissue death increases the risk of infectious inflammation.
How much LSD leaves the body
Lysergic acid is an almost elusive type of drug. It does not linger in the body and is eliminated naturally very quickly. This is why tests and laboratory tests often do not show the presence of psychoactive substances. The short-term effects of the drug make it more attractive to young people. They are not afraid to get used to it, they think that they can stop taking Lyzer at any time.
How long does it stay in the blood?
LSD lasts only 1 to 3 hours in the human circulatory system. Therefore, identifying use is a rather difficult task. Usually, it is better to prefer other biomaterials for analysis - urine or hair.
How long does it stay in urine?
Acid can remain in urine for 1 to 3 days. It is much easier to detect drug use by a drug addict’s relatives if you quickly respond to the signs that arise.
First aid for sulfuric acid burns
To provide medical assistance to the victim, it is necessary to have an understanding of the properties of caustic acids. Incorrect actions are fraught with deepening of the burn and life-threatening complications. In certain situations, you cannot even be near the victim without protective equipment - a respirator, rubber gloves, safety glasses. Inhalation of sulfuric acid fumes leads to destruction of the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract.
First aid for burns with sulfuric acid involves:
- Reagent removal;
- cooling the affected areas;
- neutralization of acid with alkali;
- anesthesia;
- applying a sterile dressing.
In case of extensive burns, anti-shock and detoxification measures are carried out, which are aimed at reducing the toxic effect of the chemical on the body.
In case of skin damage
The algorithm for providing first aid if the reagent gets on the skin includes the following steps:
- Reagent removal. It is necessary to thoroughly rinse the affected area with water for 1 hour. Pre-burned tissues are dried to prevent deepening of the burn.
- Neutralization of acid. To do this, use a 10% soda solution - dissolve 1 tsp in 250 ml of water. baking soda. As an alternative, the affected areas of the skin are washed with slightly concentrated potassium permanganate or soap solution.
- Anesthesia. For severe pain, take NSAIDs - Ibuprofen, Ketanov, Naproxen. If the burning does not go away, use Novocaine solution.
Finally, a sterile bandage is applied and a doctor is called to the house or sent to the hospital.
If in eyes
Contact of sulfuric acid on the mucous membrane of the eye or cornea can lead to blindness. To prevent such complications, you should:
- rinse the affected area with plenty of running water;
- instill a 0.5% solution of Dicaine with adrenaline;
- anesthetize the eye with a 2% Novocaine solution.
After emergency assistance is provided, a specialist is called or sent to a burn center. Further therapy is determined by the ophthalmologist depending on the depth of penetration of the reagent into the eye.
In case of damage to the mucous membrane of the mouth and esophagus
The greatest danger to life is caused by burns of the gastrointestinal mucosa, stomach, and esophagus. Accidental ingestion of more than 5 mg of the substance is fatal.
Subsequently, after a chemical burn of internal organs, diseases such as pharyngitis, laryngitis, hemorrhagic pneumonia and others can develop.
In case of damage to internal organs, it is necessary:
- Rinse the stomach. The victim is given a solution of magnesium sulfate, which neutralizes the acids. If the drug is not at hand, use clean water.
- Treatment of the oral mucosa. Rinse with a 5% soda solution. If you inhale caustic fumes, you need to breathe in a soda solution through an inhaler.
- Drink plenty of fluids. Before the doctor arrives, provide plenty of fluids, clean water or milk.
To prevent even greater damage to the ENT organs, windows are opened in the room to allow fresh air to enter. Gastric lavage is effective only in the first 5-6 hours after injury.
It is strictly forbidden to provoke vomiting, as this can lead to rupture of the esophagus.
Thermal burn of the cornea of the eye - treatment before the ambulance arrives
If you or another person has a thermal burn to the cornea of the eye, treatment should begin with eliminating the damaging factor. The injury site should then be thoroughly cooled. Most often, cold tap water is used for this purpose, and rinsing is carried out from the outer to the inner corner of the eye. You can also rinse the visual organs using a rubber bulb, a syringe without a needle, and other devices that can provide sufficient water pressure.
As a last resort, you can use a saucepan or other container with water. Having immersed your face there, you need to blink frequently for 20 minutes.
After cooling, an antiseptic drug (for example, a solution of chloramphenicol or albucide) is dripped into the eyes. If the pain is severe, the patient is given painkillers.
Further recovery
Corrosive acid rarely causes superficial injuries that do not require hospitalization. You should consult a doctor if:
- the burn is caused by highly concentrated acid;
- the affected area is large;
- acid entered the oral cavity, esophagus;
- the patient complains of acute pain.
Local therapy is limited to damage to only the superficial layers of the skin. Typically the treatment regimen includes:
- Baneocin is an antibacterial agent that reduces inflammation and pain. Prevents infectious inflammation of burn wounds.
- Panthenol is a fortified drug that accelerates metabolism. Heals uninfected wounds, increases local immunity.
- Actovegin is a wound-healing gel that cleanses the wound of charred tissue. Relieves pain, affects tissue metabolism, accelerating the healing of burns.
- Solcoseryl is an anti-inflammatory gel that dries weeping wounds. Accelerates the rejection of burned skin, stimulates its scarring.
For antiseptic treatment of affected areas, a solution of colloidal silver is used. For blistering rashes and tissue rejection, bandages with the following drugs are applied:
- Streptocide emulsion;
- Penicillin ointment;
- Vishnevsky ointment;
- Sudocrem, etc.
3rd degree acid burns are dangerous due to purulent complications. In case of wound infection with coccal infection, Miramistin and Chlorhexidine are used. For extensive lesions, systemic antimicrobial therapy is carried out with semisynthetic penicillins, aminoglycosides or cephalosporins - Gentamicin, Cefuroxime, Amoxicillin, Unazine, etc.
Destruction of the basal layer of skin is an indication for surgical intervention. The method of surgical treatment depends on the degree and extent of the damage - amputation, skin grafting. Even after successful treatment, acid leaves noticeable scars in the form of smudges.
In case of a gastrointestinal burn, bougienage is performed on the 7th day after the start of therapy. The essence of the procedure is the introduction of dilators - tubes of different diameters - into the esophagus. They prevent reduction of the lumen of the esophagus and scarring of the mucous membrane.
Types of acid brands, their effect on the body
LSD is a liquid substance that is applied to various surfaces. Diethylamide is applied to sugar cubes, paper or cardboard strips. Various methods of drinking acid are widely used by young people in clubs and bars. The form of LSD in the form of stamps with different designs has gained particular popularity.
Lysergic brand
LSD stamps are pieces of paper with children's drawings. Stamps are quite an expensive pleasure, so avid drug addicts prefer more affordable analogues. Each square of a substance represents one dose.
Heroic acid
Heroin is the most powerful drug in the world. The synthetic substance is obtained by processing morphine. Dependence on a narcotic drug occurs quite quickly, literally after 1 – 2 doses.
Microdots
Microdot is a tablet substance of a psychoactive substance. The shapes of tablets can be very diverse: cubes, spheres, stars.
LSD tablets
LSD tablets are made in various colors: blue, green, red, brown, yellow. Today, pills are the most popular form of LSD use among young people.
Liquid LSD
Liquid LSD substance is used to apply to stamps or inject into gelatin lumps. But, sometimes the solution is taken orally in the form of drops. That’s why the expression “a drop of acid” appeared. Lyser drops are taken through intravenous or intramuscular injections, as a result of which hematomas appear, the vessels become stiff and the passage of blood becomes difficult.
DRUG ADDICTION TREATMENT in MOSCOW
Dangerous complications
The destructive effect of acid is due to dehydration of tissues and the breakdown of protein components in them. The consequences are determined by the concentration of the caustic substance, its volume and duration of contact with the skin or mucous membranes. Highly active acid immediately provokes deep burns with charring of tissue.
Possible complications of chemical injury include:
- vomiting blood;
- toxic pulmonary edema;
- stenosis (narrowing) of the larynx;
- hemorrhagic pneumonia;
- subdural abscess;
- meningitis;
- purulent arthritis;
- phlegmon;
- burn shock;
- sepsis;
- gangrene.
If you do not provide assistance to the victim in time, this will lead to kidney or liver failure. In 93% of cases, such complications end in death. The risk zone includes patients with pyelonephritis, liver cirrhosis, glomerulonephritis, etc. Chemically active liquid provokes delayed complications. In 7% of cases, squamous cell carcinoma occurs at the site of scars.
Precautions when working with chemical agents
Burns from caustic acids occur in 67% of cases in people working in chemical industries. To minimize the risk of injury, you must follow safety precautions when working with concentrated oxidizing agents:
- chemicals must be stored in plastic or glass containers with an airtight lid;
- Before using the reagent, protect your eyes with goggles, your hands with rubber gloves, and your respiratory organs with a respirator;
- After work, the room is ventilated for 1-2 hours.
Chemicals should not be stored on the same shelf as food or medications. The acid should be out of reach of children.
Survival prognosis
The severity of the injury is determined by the concentration of the reagent and the location of the burn. The healing prognosis is determined by the rule of hundreds - the percentage of the burn area in relation to the remaining tissues is summed up with the age of the victim:
- less than 60 – favorable;
- up to 80 – relatively favorable;
- up to 100 – doubtful;
- more than 100 – unfavorable.
The prognosis for recovery depends on the location of the burn wounds and the depth of penetration of the reagent. The outcome of chemical injury worsens with burn shock and intoxication. Burns with concentrated acids are accompanied by prolonged inflammation. During healing, a lot of granulation tissue forms in the lesions. Therefore, burnt people develop noticeable scars that limit joint mobility.