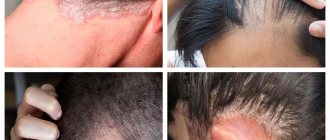
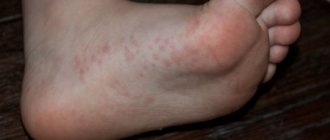
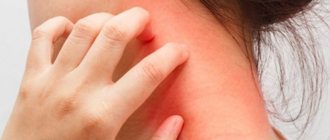
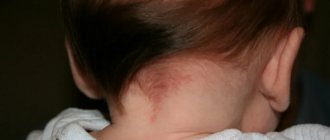
Clinical picture
Symptoms of many dermatological diseases depend on the degree of exposure to the provoking cause and on the individual characteristics of the body.
Red spots are expressed in dotted or unlimited forms, have different colors ─ from pink to burgundy. Extensive rashes can merge, affecting large areas of the skin.
The following clinical manifestations are observed:
- deterioration of general condition;
- headache;
- increased body temperature;
- feeling of heat in the area of redness;
- the rashes are itchy.
What to do?
If you find red spots, rashes or pimples on your child's feet, consult a dermatologist or surgeon if there has been an injury. It is important to find out the correct cause of the changes, since the success of the treatment depends on this.
Pay attention to whether there is a rash and redness in other parts of the body, what other complaints, when and how they started, whether there is pain, problems with supporting the leg or walking. This information will help the doctor refer for additional studies, make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
0 0
Causes of red spots on the legs of children
From constant exposure to internal and external irritants, the child’s fragile immune system becomes vulnerable. As a result, life processes malfunction, and spots appear on the skin as a symptom.
Provoking factors for the rash:
- pathogens of infectious diseases;
- helminthic infestations;
- vascular disorders;
- hormonal imbalance;
- allergic reaction to food, animal and insect bites;
- stress;
- failure to comply with hygiene rules;
- tight clothes;
- increased humidity in the room.
Dermatomycosis
Skin infection by fungi that are able to absorb keratin ─ trichophyton, microsporum, epidermophyton. Infection occurs in everyday life from a sick person or animals. The pathology is dangerous because it becomes chronic.
The severity of symptoms depends on the duration of the disease:
- the rash is round, pink or red;
- bubbles appear;
- wet areas become crusty;
- scales form along the edges of the rash;
- itching, burning;
If infection reoccurs in the same area after healing, scarring and pigmentation may occur.
Allergy
An immunological reaction of the body that occurs after contact with substances that for most are harmless, but due to the child’s individual intolerance, cause allergies. A foreign protein enters the blood, to which leukocytes react, trying to remove it.
Skin allergies come in several forms: urticaria, contact or atopic dermatitis. Red, rough spots in one area indicate the influence of external irritants: plants, clothing, household chemical products. If there is a rash on the arms, torso, or butt, this indicates the presence of a food or drug reaction.
Viruses and bacteria
Many diseases of viral and bacterial origin are characterized by respiratory-catarrhal symptoms and general intoxication. Children's infectious diseases - measles, scarlet fever, rubella - are accompanied by a pink-red rash on the face, torso and limbs.
Chicken pox
A viral infection transmitted by airborne droplets. Symptom ─ a small itchy rash all over the body, which later turns into blisters with liquid, which subsequently burst. Parents should treat rashes with an aseptic agent and avoid scratching.
Pityriasis rosea
An infectious skin disease of a contagious nature, expressed by the appearance of a round scaly spot of red or pink color. A distinctive feature of lichen spots is their inability to merge with each other, as well as clear boundaries. The provoking factor is allergies, hypothermia, overheating of the body. With proper treatment, a recovered child receives immunity for life.
Erythema infectiosum
The disease is caused by a herpes virus, mainly in children with weakened immune systems. The first signs include respiratory symptoms inherent in the early stages of a cold. After a few days, a rash appears on the body in stages. Initially, spots form on the cheeks, then spread throughout the body, and upon recovery they disappear without a trace.
Neurofibromatosis in children
To confirm the diagnosis of neurofibromatosis, the child must have at least 2 of the following signs:
- dark spots
- leiomyomas of the iris
- 2 or more neurofibromas in the form of subcutaneous peas
- heredity
- pathologies in the bones
- freckles under the arms and groin
- optical glioma
To detect tumors and diagnose problems with skeletal bones, two methods are used: MRI and radiography. Children with neurofibromatosis have a larger head circumference than children of the same age without this diagnosis. To diagnose NF2 in children, hearing must be tested. To do this, audiometry is used to check the brain, ear nerves and spinal cord to detect possible tumors.
Studying the child's family history can provide important information. If there is neurofibromatosis of the first or second type, a genetic examination can be performed. But we cannot say that its results are 100% accurate. In some cases, abnormalities can be detected in a newborn baby using chorionic villus sampling or amniocentesis.
To make a diagnosis of neurofibromatosis type 1, consultations with the following specialists are needed:
- ophthalmologist
- neurologist
- surgeon
- dermatologist
- oncologist
- geneticist
- neurosurgeon
The doctor may need to see more relatives if there is at least one member of the family with café-au-lait spots, or if there is a family history that indicates that member of the family.
Differential diagnosis
Cafe-au-lait spots are found not only in the disease in question, but in more than a hundred hereditary diseases and syndromes. It is also necessary to distinguish between neurofibromatosis types I and II. In the second type, the tumors are benign, but more aggressive than in the first type.
The absolute diagnostic criterion for NF1 is the presence of bilateral neuromas of the VIII pair of cranial nerves in the patient. In the second type, gliomas, meningiomas, and schwannomas can be detected.
It is necessary to differentiate neurofibromatosis I from Klippel-Trenaunau-Weber syndrome, Proteus syndrome, disseminated lipomatosis, etc.
Differential diagnosis of NF2 in children is carried out with the following diseases:
- schwannomatosis
- nonpolyposis colon cancer
- McCune-Albright syndrome
- LEOPARD syndrome
- Bannayan-Riley-Ruvalcaba syndrome
- Noonan syndrome
- "piebald trait"
- Proteus syndrome, etc.
Neurofibromatosis has common features with a disease such as spotted nevus , which is a manifestation of genetic mosaicism. Some researchers consider macular nevus as segmental neurofibromatosis. Children with macular nevus may develop NF1. Nevus occurs in a child from birth or is found in a child until he is 3 years old. With a spotted nevus, the child has light brown spots, against their background there are dark-colored inclusions of small sizes.
Nevus in children is large, but can be small. There are cases of 2-sided lesions. Spotted nevi do not leave the child’s body throughout his life. There is a very small risk of malignant degeneration of the disease. When diagnosing, it is very important to distinguish between macular nevus and neurofibromatosis.
In what cases should you immediately consult a doctor?
Red spots on a child’s legs are a serious reason to invite a doctor to your home. You cannot visit hospitals with rashes of unknown origin, because... the existing pathology may be contagious to other children.
Signs when you should call emergency services:
- labored breathing;
- strong pain;
- high body temperature;
- convulsive state;
- loss of consciousness.
Allergy
Allergies occur in response to direct contact with certain irritants. Each child will have their own, depending on the characteristics of the immune system. Allergies manifest as urticaria or contact dermatitis.
With hives, red spots and circles of different sizes and shapes appear on the child’s feet. They rise slightly above the skin and sometimes merge with each other. With contact dermatitis in children, red dots form on the feet, irritation, itching and peeling of the skin are observed.
Allergies can be caused by socks or shoes made of artificial materials, new baby cream, soap, or washing powder. Some children have this reaction to changes in temperature, cold or heat.
Antihistamines help cope with allergy symptoms. For children they are produced in the form of syrups and drops. The specific medicine is prescribed by the doctor. To prevent recurrences of allergies, it is important to identify the irritant and try to avoid contact with it in the future.
Diagnostics
If spots appear on the skin, then to determine their root cause, the doctor prescribes the following examinations:
- OAC ─ detects inflammatory processes and allergic reactions in the body.
- Biochemical blood test ─ assesses the condition of internal organs, reveals metabolic disorders, hormonal imbalance, lack of enzymes, micro- and macroelements.
- Stool analysis is done if helminths are suspected, because their waste products have a toxic effect on the body, causing decreased immunity and allergies.
- Skin tests are done for allergic rashes only in the remission stage. This method allows you to eliminate the irritant. The procedure is performed in a hospital, because... even with the introduction of microdoses, there is a risk of developing anaphylactic shock;
- Biopsy ─ a small tissue sample is taken for histological and cytological examination, the method determines the presence of atypical cells.
- Dermatoscopy ─ tenfold magnification of the dermatoscope makes it possible to study the resulting stain in detail.
Methods and rules of treatment
The treatment tactics for red spots depend on the results of a comprehensive examination, the age of the child, and the course of the disease. Therapy includes the use of medications, diet, and physical therapy.
Medicines
- Antifungals ─ Clotrimazole, Nystatin, Pimafucin, Fluconazole.
- Antihistamines─ Loratidine, Citrine, Erius, Zyrtec.
- Hormonal ointments ─ Advantan, Elokom.
- Reducing itching ─ Fenistil gel, Bepanten and Depanthenol cream.
- Sorbents ─ Enterosgel, Smecta, Atoxil, activated carbon.
- Immunostimulants ─ Imunofan, Viferon.
- Sedatives ─ Glycine, Baby-sed, Persen.
Folk remedies
In addition to basic treatment, you can turn to alternative medicine.
Natural ointments and gels, prepared independently, have virtually no contraindications for children, relieve redness and swelling.
Recommended recipes:
- For ringworm and fungal infections, make garlic compresses with honey, mix in equal parts and apply at night, securing with a bandage.
- Dill juice has a calming effect. For itching, use a fresh remedy, lubricating the rash with it 3 times a day.
- Lotions based on yarrow and celandine. Take dry grass in a 1:1 ratio, pour boiling water over it, leave for about 2 hours, apply the resulting pulp for 20 minutes. This procedure is allowed to be done several times a day.
- Baths with a series can be performed even on infants. Children over 1 year old are allowed combined baths.
- Lemon juice and vinegar relieve swelling, reduce burning and pain after an insect bite.
Infections
Redness and rash on a child’s feet are caused by viral, bacterial and fungal infections.
For example, one of the manifestations of an enterovirus infection caused by the Coxsackie virus will be a rash in the form of ulcers and watery red pimples on the palms and soles of a child. They do not require special treatment and go away on their own within 3 to 5 days as they recover. In the first days, the rash is very itchy. But it is important to ensure that the child does not scratch, as there is a risk of bacterial infection.
Red spots on the feet and palms of a child are caused by chickenpox and measles. In this case, the rash spreads throughout the body. A viral infection can be recognized by a sudden high temperature (up to 39–40 °C), lethargy, moodiness, decreased appetite, and headache. The rash appears 1 to 2 days after the temperature rises.
Red spots on a child’s feet, burning, itching, peeling, cracks are signs of a fungal infection of the skin and nails. If such symptoms appear, consult a podiatrist. Fungal infections often occur in children who use swimming pools. It is necessary to ensure that children do not walk barefoot on the floor in showers and locker rooms. The fungus is treated with antifungal ointments and creams.
Bacterial infections develop when the integrity of the skin is damaged if the damaged areas are not treated with an antiseptic (brilliant, chlorhexidine, iodine) in a timely manner. Pathogenic bacteria easily penetrate the skin through wounds, scratches, and abrasions. Children with diabetes are most vulnerable because high blood sugar levels interfere with rapid healing. More often, bacterial infections occur in the summer, when the baby walks with bare legs and wears open sandals and flip-flops.
What is prohibited to do
A common mistake parents make is self-medication. To avoid complications, adhere to the following rules:
- Before being examined by a doctor, you should not lubricate the spots with coloring ointments: this hides the clinical picture of the rash;
- do not pierce or scratch the rash, this especially applies to formations of an infectious nature;
- Do not give your child medications without a medical prescription (only antiallergic medications that have already been used are allowed).
Prevention measures
Preventive measures are aimed at strengthening the immune system. For this, daily exercises, hardening, good nutrition and healthy sleep, and walks in the fresh air are recommended. Personal hygiene plays an important role. The child's clothes should be made from natural materials.
If you are prone to allergies, you should not eat foods that cause a reaction: honey, chocolate, eggs, citrus fruits, fish. Try not to use perfumes or air fresheners in the house. It is advisable to remove indoor flowers, not have pets, and carry out wet cleaning more often.
Red spots have different etiologies. Effective treatment requires careful diagnosis, which involves the use of hardware and differential methods.