If you find a slight swelling or edema on a child’s body, you can think about the following conditions: inflammation, injury, cyst. When inflamed, the swollen area is pink or red, feels warmer to the touch than the surrounding tissue, and is painful when touched. Swelling after an injury may be a normal color warmer or cooler than the surrounding tissue, and a bruise may appear after some time. Sometimes, with increased sensitivity to any type of food, cold or other factors, edematous areas with clear boundaries quickly develop on the skin - such edema is called angioedema. They are often accompanied by hives (see Allergic reactions), which is another indication of the allergic nature of the condition. Swelling of the skin may be associated with enlarged lymph nodes (see Enlarged Lymph Nodes). General swelling of a limb or torso may indicate an allergic reaction or kidney disease.
THE DOCTOR'S CONSULTATION
Contact your doctor if the swelling:
- does not go away, grows or arose for no apparent reason
- hot to the touch, painful
ATTENTION!
If swelling occurs for no apparent reason, consult a doctor. In any case, it's better to be safe than sorry.
| ASK YOURSELF A QUESTION | POSSIBLE REASON | WHAT TO DO |
| Do you have one or more painful, raised lesions on your skin with a white center? | Boils (inflammation of hair follicles) | Do not try to open a boil by squeezing or piercing it, as this may spread the infection. Wash the area around the boil frequently with soap and water (not the boil itself!). When the boil opens, apply a bactericidal patch. If there is no improvement or new boils form, contact your pediatrician (or dermatologist ): you may need local treatment and antibiotics. |
| Does your child have several painless raised lesions with a rough surface on their skin? | Warts | Warts are caused by viruses and often go away without treatment. Warts that are a cosmetic defect, as well as those that are often injured, can be removed. Talk to your child's doctor (or dermatologist ) |
| Does your child have a soft, painless lump in the groin? Does it disappear with light pressure? | Inguinal hernia | Contact your pediatrician. If necessary, he will refer you to a pediatric surgeon |
| Does the boy have a soft, painless swelling of the scrotum on one side? Does one testicle look significantly larger than the other? Does the swelling decrease when the child lies down? | Hernia; hydrocele | Make an appointment with your pediatrician . He will determine whether there is dropsy, a congenital condition in which fluid accumulates in the scrotum. If your child has a hernia, your pediatrician will refer you to a pediatric surgeon if necessary. |
| Does your child have a protruding formation on the skin of the sole? Is it mildly painful when walking? | Plantar wart | Seek advice from your pediatrician . If necessary, he will recommend treatment |
| Does your child have many red swellings in the shin area? Is he denying the injury? Has he recently had an infection or is he taking medication? | Erythema nodosum | Go see your pediatrician . If necessary, he will prescribe examination and treatment |
| Does your child complain of pain and swelling in the bone area? | Infection; another disease requiring diagnosis and treatment | Contact your pediatrician immediately . Rest the affected limb. |
FOR INFORMATION
Swelling in the wrist area
Sometimes in children, cysts containing fluid appear under the skin of the wrist on top. This happens like this: synovial fluid - the “lubricant” found inside the joint - leaks through the damaged joint capsule and accumulates in the tendon sheath. Most often this happens in the area of the wrist joint. They occur when there is increased load on the joint, for example, when a child holds a pen incorrectly or writes a lot. As a rule, such cysts are painless and not dangerous. They gradually disappear without treatment. However, if your child's cyst is large, painful, or interferes with normal hand function, treatment may be required. In the latter case, a small operation is performed - the cyst is removed and the “leak” is closed. Do not self-medicate.
A hard, smooth, raised lump, usually about the size of a peanut, just under the skin. Most often it forms on the dorsum of the wrist joint, but can also occur on the ankle or finger.
Allergic reaction
A negative reaction to any stimulus often worries infants. The introduction of complementary foods, breast milk, washing powder, cold or heat - all this can cause red spots on the body of a baby. It is divided into several types: reaction to food, dermatitis, urticaria, toxicerma and photodermatosis.
Food allergies
Food allergies occur much more often than others. Most products in the store contain hazardous substances (dyes, flavors). They are harmful even for adults, not to mention the fragile children’s body. Allergic skin rashes can also occur in infants if the mother does not follow a special diet. Experts recommend eating right and switching to artificial feeding as soon as possible.
Highly allergenic foods include eggs, chocolate, honey, tangerines, oranges and lemons, mushrooms, strawberries, and currants. However, in one child such food is well absorbed, while in another it easily provokes diathesis on the face. The presence of chronic and viral diseases, as well as intestinal dysbiosis and weak immunity can contribute to this.
Dermatitis
The disease is classified as a dermatological allergy, in which the child is bothered by flaky spots on the body, pain and itching. If the disease starts, the allergy on the hands in the form of red spots turns into large blisters that spread to the whole body. Over time, they increase in size, burst, leaving behind weeping ulcers and suppuration.
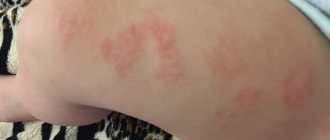
Hives
Another type of dermatological allergy, but has different symptoms. With this disease, small red blisters with a clear outline appear on the body. You may notice that the spots rise several millimeters above healthy skin.
The plaques are very itchy, cover most of the area, and often merge into large lesions. The main causes of allergic spots on a child’s body are: medications, food, parasites in the body, cosmetics, jewelry or materials from which clothing is made. Doctors say that the disease almost never occurs in babies under 6 months of age. However, the older the child, the higher the likelihood of developing the disease.
Sakania Luiza Ruslanovna
Dermatovenerologist, cosmetologist, trichologist
Ask a Question
Urticaria has the ability to become chronic and occur periodically throughout life, so it is important to treat it. In addition, the chronic type often accompanies people with gastrointestinal diseases and leukemia.
Photodermatosis
One of the rarest types of allergic reaction that occurs to sunlight. According to experts, children under three years of age suffer from the disease. Factors that cause red raised spots on the body include:
- viral infections;
- heredity to allergies;
- presence of chronic diseases;
- long-term use of antibiotics.
The allergy appears on the body in the form of pinkish plaques some time after exposure to the sun. In addition, the child suffers from watery eyes, swelling of the face or other exposed areas of the body.
Toxidermy or toxicoderma
The most severe type of allergy throughout the body in a child, causing inflammatory processes on the skin and mucous membranes. Toxidermy includes several types, but most often it is food and drug. Symptoms directly depend on the severity and duration of contact with the irritant.
Usually, severe itching and red spots on the body first appear, then papules form on the itchy areas. There are signs of general intoxication of the body: high fever and rash, nausea or vomiting, weakness, chills. In severe cases, angioedema develops, which can be fatal.
Types of spots on a child's body
There are hundreds of diseases that are accompanied by changes in the skin.
Each disease has its own signs and types of rash. Main types of rashes:
| Primary | Spot | Changed area of skin that differs in color |
| Bubble | Formations on the skin with fluid trapped inside | |
| Blister | Swelling of the dermis with fluid | |
| Pustule | Inflammation of the skin, which implies the presence of a purulent process | |
| Papule | A lump is a nodule that rises above the skin level | |
| Tubercle | Accumulation of infiltrate in the thickness of the skin, rising above the dermis layer | |
| Secondary | Scales | An accumulation of horny skin particles characterized by roughness |
| Crusts | The result of drying out the liquid components of the skin | |
| Cracks | Skin defects of different lengths and depths | |
| Erosion | Superficial disruption of the integrity of the epithelium as a result of an inflammatory or traumatic process | |
| Ulcers | This is a deep epithelial defect characterized by prolonged healing | |
| Scarring | A dense formation resulting from damage to the skin |
Skin defects may differ in size, shape, structure (wet, dry), degree of inflammation and swelling.
Insect bites
Almost always, bites of various insects (wasps, mosquitoes, fleas, ticks) are accompanied by spots. In the first minutes or hours after contact with the pest, the blisters on the child’s body itch and hurt, but gradually all unpleasant symptoms disappear. The difference from allergies is isolated redness on the skin only in those places where the insect has bitten.
If you know for sure that your child was bitten by a mosquito or a bee, then there is no need to see a doctor. As a rule, all unpleasant symptoms will disappear within 24 hours; you can lubricate the red round spot on the body with bite ointment. If you develop signs of an allergic reaction (inflammation, difficulty breathing, swelling of the larynx or face), you should immediately seek medical help.
Stork spot. What is it and why is it formed?
In the medical literature, the stork spot has a completely non-fairy-tale scientific name: nevus of Unna or simple nevus. It can be located not only on the back of the head or on the back of the neck, but also on the baby’s forehead and eyelids. In this case, it is called “the kiss of an angel.”
One may come across the opinion that these spots are a consequence of a traumatic birth, in which the child’s head was compressed for a long time, but scientists refute this. They say that a simple nevus is formed in utero. It is formed due to a failure in the formation of blood vessels: in this area they are slightly dilated and the blood flow in them is increased, so the skin here is more pink. Another version is that the stork spot is formed in the place where the baby’s head is pressed to the mother’s sacrum in the later stages. Due to pressure, the capillaries expand and a spot is formed: have you ever woken up with red marks from a pillow on your face? It's about the same here.
Be that as it may, almost half of babies are born with a simple nevus on the face. There is no need to be afraid of him. This is not a disease. It is not the mother’s fault that the child is born with a mark on the back of the head, and she cannot prevent its appearance in any way.
Infectious pathologies
Many diseases can cause red pimples and blemishes on the body. The most common are chickenpox, measles and rubella. However, the development of more rare diseases is possible, so if you notice a rash on the skin in the form of blisters, you should definitely consult a doctor.
Chicken pox
A childhood disease with skin rashes, most of the population experiences chickenpox in preschool age. The body of the sick person becomes covered with red spots, which then turn into blisters. The baby is worried about fever, weakness, nausea and itching. Often the symptoms are accompanied by redness of the throat and disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract. The disease begins with a rash on the cheeks, between the fingers and armpits, then spreads to the whole body.
Measles
The viral rash is transmitted by contact with an infected person and remains dangerous for up to 5 days. Some time after infection, signs of a cold appear (fever, runny nose, cough, lacrimation), but soon large red spots form on the body. They are characterized by an irregular shape, are localized on almost all parts of the body at once, peel off and acquire a brownish tint.
Scarlet fever
Red, rough spots on a child’s skin and a sore throat indicate the onset of scarlet fever. You can become infected through airborne droplets or through household contact. Epidemics often occur in kindergartens, as the disease is transmitted through toys, dishes, and clothes. If one child becomes ill, it is recommended to strictly observe precautions and isolate other children. Many mothers are interested in: is it possible to bathe a child with scarlet fever? In the first 5-7 days you should refrain from taking a bath; it is better to use wet wipes.
Rubella
With rubella, red pimples on the child’s body do not appear immediately, but only a week after other signs appear. A mild sore throat, lacrimation and conjunctivitis signal the onset of the disease.
Usually body temperature remains within normal limits or rises to 37 degrees. Like all infectious diseases, rubella spreads quickly, so isolation is necessary. Childhood illnesses are very similar, so it doesn't hurt to familiarize yourself with the signs. It is through them that you can notice the disease in time and consult a doctor.
| Signs | Measles | Rubella | Scarlet fever |
| Initial symptoms | Intoxication, which intensifies within 2-3 days, signs of a cold | Rashes on the body, catarrhal phenomena | Chills, fever, intoxication of the body, signs of acute tonsillitis |
| When does the rash appear? | Not earlier than 4 days | On the first day of illness | For 1-2 days |
| What do rashes look like? | Large spots, papules | Small reddish spots | Small red dots |
Roseola
Rashes on the skin in the form of red spots, characterized by an obligatory increase in temperature. It gradually decreases (high levels can remain up to 4 days), but the body continues to be covered with plaques. The disease is caused by type 6 herpes virus, which requires mandatory therapy.
Will the spot on the back of my head go away on its own?
A simple nevus is the most harmless deviation in the formation of skin capillaries. During the first year of the baby's life, the spot begins to lighten until it matches the color of the normal skin tone. It may still appear for some time after intense screaming or severe stress, and by the age of two it usually goes away. But if we talk specifically about the stork spot - a simple nevus located on the back of the head or back of the neck - then it may not completely disappear, but only turn pale. Fortunately, since it is not located in the most visible area, the damage to the exterior is minimal.
When to see a doctor
Having noticed a red rash on a child’s body, there is no need to rush to go to the hospital on your own. If you suspect an infectious disease, you must call a doctor at home so as not to infect others in public places. You should urgently call an ambulance if you experience the following symptoms:
- impaired breathing, wheezing, chest pain;
- fainting, difficulty speaking, or confusion;
- the appearance of watery pimples on the body, which bring severe discomfort to the child;
- a sharp increase in temperature, as well as the ineffectiveness of antipyretic drugs;
- anaphylactic shock, in which blood pressure drops, breathing becomes difficult, and signs of a severe allergic reaction appear.
Before a specialist arrives, you should not treat red spots on your child’s body with anything, be it a soothing cream, brilliant green or iodine. Such measures will blur the clinical picture, which means the doctor will not be able to make the correct diagnosis and tell how to treat the disease.
Dermatological skin diseases
Ringworm
Ringworm in humans is a general concept of which are red spots on the human body (see photo above).
There are several types of lichen:
- Ringworm - eczema
- Shingles (viral infection)
- Pityriasis versicolor (fungal infection)
- Pityriasis rosea - pityriasis (probably a viral infection)
- Ringworm - trichophytosis, microsporia (fungal infection)
- Lichen squamosus - psoriasis
- Lichen planus (Wilson's lichen, lichen planus) - dermatosis of unknown etiology
The disease is of an infectious-allergic nature, except for shingles. It is caused by the chickenpox virus.
When staining, it is necessary to take into account the reasons that stimulated the occurrence of pathology. Vitamin therapy, antibiotics, antihistamines and sedatives have a positive effect.
Psoriasis
Psoriasis (scaly lichen) is a chronic dermatosis. The main symptom is scaly red spots that are covered with silvery-white scales.
At the first stage, the red spots are free from peeling, but even with minor skin trauma, it begins to actively progress. A characteristic feature of the rash is its prevalence and symmetry.
More than twenty different methods and schemes have been developed for treatment, which produce a positive effect, but do not allow complete healing and disappearance of red spots.
In most cases, therapy is relieving. In the fight to progress the fight against the disease, the following have proven themselves well:
- vitamins of group B, E, A;
- detoxification drugs (and Calcium gluconate).
Eczema
Red spots sometimes appear with eczema (tinea versicolor). The reasons for its appearance are not fully understood. But doctors were able to prove that pathological processes in the nervous and endocrine systems have a huge impact on the appearance of red spots.
There is a violation of sweating, thermoregulation, and vascular reactions.
Allergens sensitize the skin and cause an eczematous process. At the first stage the following appear:
- redness;
- severe itching;
- temperature increase.
Treatment of eczema requires a careful approach. It is necessary to get away from the influence of irritating factors, such as:
- chemical substances;
- exposure to sunlight;
- dampness, dust;
- skin parasites.
The diet should be complete and rich in vitamins. Local treatment is prescribed as part of complex therapy. At the same time, desensitization of the body is carried out with autohemotherapy.
Atopic eczema
Atopic dermatitis or atopic eczema - in this case, spots can appear both in early childhood and throughout life.
The pathology is hereditary in nature, not contagious to others, but after treatment in patients it gives frequent relapses.
If both parents suffered from this disease, then 80% of children will develop red spots on the body. The pathology lasts a long time, most often an exacerbation is observed in spring and autumn, and subsides in the summer.
The main symptom is severe itching, which can be periodic or constant, and red spots on the body.
Treatment is aimed at eliminating the allergic factor and relieving itching. Desensitization and detoxification, as well as the removal of inflammatory processes, can reduce the appearance of red spots.
Treatment methods
Therapy depends on the cause of the red rash in the child. You should definitely visit a pediatrician, and if you suspect skin pathologies, a dermatologist. Do not squeeze, open or scratch small red dots on the body. This makes it easy to get infected, and the wounds will leave unsightly marks. Children should not be given medications without a doctor’s prescription; it is only permissible to use antiallergic drugs.
Fenistil, Tavegil, Claritin, as well as Gistan ointment are used against allergies in the form of red, rough spots on the body of infants. In advanced cases, you should choose hormonal drugs: Elokom or Advantan.
A red rash on a child’s face after frost can be eliminated with La-Cri cream, which soothes and heals the affected epidermis. Creams such as Depanthenol, Bepanten and Panthenol have an anti-inflammatory and restorative effect. It is recommended to lubricate the small red rash on the dermis during chickenpox with brilliant green and zinc ointment. In all other cases, consultation with a doctor and his supervision during treatment with medications are necessary.
Do I need to treat?
As we remember, a simple nevus is not a disease, which means it does not require treatment. Be patient and the stork spot will disappear on its own or at least become very pale. There are no creams, ointments or lotions that would speed up this process, so the doctor will not recommend anything to you other than observation. And it is strictly prohibited to use any medicines without a prescription, as well as traditional medicine recipes, when it comes to young children.
Precautionary measures
To protect your child from infectious diseases and other ailments, it is necessary to strengthen the immune system. The body’s protective function can overcome many diseases; to maintain it, it is recommended to regularly give the child vitamin complexes.
It is important to protect your baby from factors that provoke red dots on the skin: junk food, dangerous insects, crowds of people where you can get a serious infection.
Skin rashes in children are not uncommon, but you can’t turn a blind eye to red dots. There are many reasons for the development of small pimples on the body: from a mosquito bite to an infectious pathology. You should definitely make an appointment with a doctor or call him at home if you suspect an airborne disease. You cannot choose a treatment regimen on your own; many diseases have serious consequences, so therapy should be carried out under the supervision of a specialist.
You can ask your question to our author: