Pityriasis versicolor or pityriasis versicolor is a superficial skin lesion caused by a yeast-like fungus of the genus Malassezia.
These microorganisms are representatives of typical skin microflora, are found in most people and do not cause the development of the disease. But under the influence of external or internal factors, the pathogen can transform from a non-pathogenic form into a pathogenic one: the fungus penetrates the upper layers of the skin and damages melanocytes - the cellular structures responsible for the pigmentation of the skin.
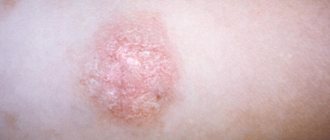
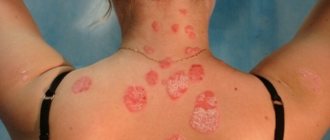
As a result, the patient develops small spots of different colors: from pale pink to red-brown, with noticeable peeling in the center. When touched, the scabs flake off easily and resemble flakes, which is what gives pityriasis versicolor its name.
What is pityriasis versicolor?
Pityriasis versicolor is a dermatological disease, most often diagnosed in people under the age of 30, while it is rare in children and the elderly. A predisposing factor to the occurrence of infection is often excessive activity of the sweat glands, so the disease often develops in the summer, at resorts and in countries with a humid, hot climate.
Lichen versicolor develops against the background of:
- chronic gastrointestinal diseases (gastritis, ulcers);
- endocrine disorders;
- autoimmune diseases;
- hormonal fluctuations, including those caused by taking oral contraceptives, pregnancy, infertility treatment;
- genetic predisposition.
Ringworm can be triggered by taking certain medications, for example, immunosuppressants, glucocorticosteroids. Uncontrolled drug therapy also often causes lichen.
A decrease in the body's natural defenses can also trigger the growth of fungal colonies.
This can lead to:
- recent serious illnesses, injuries or surgeries;
- severe vitamin deficiency;
- hypothermia of the body;
- stress;
- prolonged exposure to adverse factors (for example, work in hazardous industries, contact with chemicals and reagents);
- food poisoning;
- period of increased mental and physical stress;
- sudden climate change;
- alcohol abuse.
Among the external factors that cause tinea versicolor, wearing tight synthetic clothing in the hot season stands out. Artificial materials disrupt natural skin respiration, increase sweating, and irritate the upper layers of the skin. As a result, colonies of the fungus penetrate the epidermis and begin to actively multiply.
Seborrheic eczema
Seborrheic eczema
- chronic dermatosis, manifested by rashes of small nodules, gradually forming plaques covered with dense, greasy scales and crusts, which, when removed, reveal a moist surface. Rashes of seborrheic eczema are localized on the head, behind the ears, on the face, in natural folds of the skin, in the umbilical region, on the skin of the torso and the flexor surfaces of the arms and legs. It is one of the clinical forms of eczema. The disease can occur equally in people of both sexes and of any age. Often seborrheic eczema develops against the background of seborrhea or as a complication of seborrheic dermatitis. In HIV-infected people, it can be one of the first manifestations of AIDS. A feature of seborrheic eczema in such patients is its spread throughout the entire skin.
What does pityriasis versicolor look like?
The first symptom of the disease is the appearance of small spots, most often localized on the torso, arms, scalp or external genitalia. The rash may be accompanied by mild itching or may not cause the patient any noticeable discomfort.
The rashes do not have a sharp outline, are not inflamed and do not swell. Initially they are pink in color, but gradually change shade: from pink-yellow to brown and red-brown. The number of spots increases: the fungus spreads across the skin, occupying more and more surface area of the body. The rash may appear on the hands, legs, face, but never affects the mucous membranes, palms or feet, which is due to the special structure of the epithelium in these areas.
The rashes can increase in diameter (up to several centimeters) and merge with each other. Peeling zones appear in the center - when you touch the spot, the scales easily peel off. An atypical form of pityriasis versicolor includes pityriasis alba, in which the affected areas completely lose their pigment (become white). In this case, there may be no peeling.
A distinctive feature of pityriasis versicolor is a disorder of skin pigmentation. Fungal colonies damage melanocytes, which are responsible for the production of melanin, the substance responsible for the color of the skin. Areas of hypopigmentation are especially noticeable during tanning: the epithelium damaged by yeast remains white. This effect can persist for a long time even after recovery.
Pityriasis versicolor is prone to a chronic course and frequent relapses.
To quickly recover and avoid the unpleasant consequences of the infection, it is recommended to consult a dermatologist at the first symptoms of the disease:
- the appearance of a pink or reddish rash;
- mild itching of the skin;
- a feeling of tightness and flaking in certain areas of the skin of the torso and arms.
Symptoms of seborrheic eczema
Seborrheic eczema begins with the appearance of small pink-yellow nodules on the skin. The nodules enlarge and merge with each other, which leads to the formation of infiltrated disc-shaped plaques. The plaques have a diameter of 1-2 cm and are covered with numerous dense fatty scales. When the scales are removed, a slightly damp surface is revealed underneath; pronounced weeping is not typical.
The lesions of seborrheic eczema have clear boundaries and uneven edges. At the beginning of the disease they may be dry, but then take on a typical “greasy” appearance. Itching, as a rule, is mild and does not bother patients much.
Typically, seborrheic eczema rashes are located on the head: in the hair growth area, on the forehead, in the eyebrows, in the nasolabial folds, around the mouth and behind the ears. When foci of seborrheic eczema are localized on the scalp, they grow along the periphery, eventually moving to the edge of hair growth and to the forehead.
Seborrheic eczema often causes damage to the skin of the eyelids with the development of blepharitis.
How is pityriasis versicolor transmitted?
Pityriasis versicolor is transmitted through household contact, but this is rare: the disease is not very contagious. The causative agent of pityriasis versicolor, a fungus from the genus Malassezia, is present on the skin of most people, but does not penetrate the epithelium and does not lead to the appearance of a rash. However, under the influence of various factors, yeast transforms into a pathogenic form and begins to destroy skin cells. This process can be triggered by various factors: from excessive sweating to endocrine disorders.
Despite the low contagiousness of this type of lichen, patients are advised to adhere to some recommendations:
- do not share bed linen or towels;
- do not wear other people's clothes;
- do not visit baths, saunas, public swimming pools.
You should also take special care to disinfect the patient’s underwear, clothing and hats: wash at high temperatures (possibly boiling), iron with a hot iron, use steam treatment.
Predisposing factors
Pityriasis versicolor is observed more often in adults. The incidence of pityriasis versicolor does not differ by gender (i.e., men and women are affected).
This type of dermatological disease is much less commonly diagnosed in older people and children under 14 years of age .
The occurrence and activity of the fungus are provoked by factors predisposing to the disease:
- hyperhidrosis – increased sweating;
- changing the formula of the secretion produced by the sweat glands;
- oily seborrhea;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- reduction of natural peeling of the dermis;
- dysfunction of the immune system;
- diabetes, tuberculosis, immunodeficiency diseases;
- wet air;
- pregnancy;
- taking hormonal contraceptives, antipyretics, antibiotics, glucocorticoids;
- stress;
- use of low-quality cosmetics;
- genetic (hereditary) predisposition to the disease.
Elimination or correction of the condition that caused the disease speeds up the healing process and prevents relapses in the future. Often, after the elimination of the underlying disease, pityriasis versicolor in a person goes away on its own, without the use of additional therapeutic measures.
Is it possible to cure pityriasis versicolor?
With proper therapy, pityriasis versicolor is easily treated and goes away within 2-3 weeks. To do this, you need to make an appointment with a dermatologist, who will conduct an examination and prescribe additional tests.
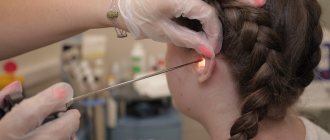
As a rule, the diagnosis is established in the presence of a typical clinical picture, but to confirm it, the following analyzes and tests are performed:
- examination under a Wood's lamp: fungal colonies are illuminated;
- microscopic examination of the scraping: shows the presence of yeast;
- Balzer test using iodine-containing solutions.
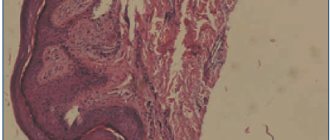
A dermatologist may also prescribe histological studies, general blood and urine tests. Based on the results of the examinations, treatment tactics are developed.
Depending on the severity and severity of the infection and the symptoms of lichen, therapy includes:
- the use of external agents (sprays, lotions, ointments) with antifungal components. If the scalp is affected, special shampoos are prescribed;
- antifungal drugs for internal use. Prescribed to patients prone to relapses of pityriasis versicolor, or to patients with atypical manifestations of infection.
If the patient suffers from severe itching (which is extremely rare), antihistamines may be prescribed.
Diagnosis of seborrheic eczema
The diagnosis of seborrheic eczema is made by a dermatologist. Often, a visual examination of skin lesions is sufficient for this. Dermatoscopy, fluorescent diagnostics, and examination of skin and hair scrapings for pathogenic fungi are also carried out.
To identify underlying diseases and foci of chronic infection, patients with seborrheic eczema may be prescribed consultations with other specialists: gastroenterologist, endocrinologist, gynecologist, otolaryngologist, neurologist. For the same purpose, additional examinations are carried out: gastroscopy, ultrasound of the abdominal organs, hormonal and immunological blood tests, pelvic ultrasound, rhinoscopy, pharyngoscopy, etc. Patients with damage to the eyelids need to consult an ophthalmologist.
Is it possible to cure pityriasis versicolor permanently?
If you follow medical recommendations, pityriasis versicolor responds well to treatment: the rash completely disappears in 2-3 weeks. But the infection tends to become chronic: in this case, relapses occur every time sweating increases, for example, in the warm season, when traveling on vacation, or during intense physical activity.
To avoid this, you must:
- consult a dermatologist at the first signs of the disease. At the initial stage, pityriasis versicolor can be easily confused with other skin infections: tinea versicolor, seborrheic dermatitis, eczema, vitiligo, and so on. Each disease requires specific treatment, which is why it is so important to recognize the disease as early as possible;
- refuse self-medication. Uncontrolled use of medications and the use of “folk remedies” will not only not lead to a cure, but can also aggravate the course of the infection;
- follow your doctor's recommendations. This applies to both the use of prescribed medications and personal hygiene.
In this case, the patient can quickly recover from pityriasis versicolor and avoid its relapse.
Unconventional therapeutic methods
Traditional medicine is sometimes used as an additional treatment method to pharmacological drugs. They are less effective, but are still used in treatment. You can use the following recipes for local application against fungus:
- Sorrel liniment. Using a blender, fresh sorrel is pureed. Non-liquid sour cream (1:1) is added to the resulting substance. Used in the form of compresses.
- St. John's wort powder. Effectively relieves itching during treatment. Before use, the powder is mixed with Vaseline and applied to the skin.
- Apple cider vinegar. It is considered one of the best non-traditional recipes for the treatment of pityriasis versicolor. It is required to use vinegar of natural origin. The skin is lubricated against fungus for 7 days, 5-6 times a day.
Herbal medicines can be used on the skin of the body only after agreeing on the chosen prescription with the doctor. Usually, the combined use of herbal medicines with pharmacological medications for the disease is required.
Is it possible to sunbathe with pityriasis versicolor?
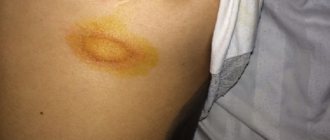
This dermatosis is popularly called “sun fungus”: during the beach season, the yeast is activated and the disease is diagnosed most often. At the same time, the areas of the skin affected by the colonies do not tan and remain white - the patient is covered with light spots, which bring him to the dermatologist’s office.
Since pityriasis versicolor can be diagnosed during rest, patients are often interested in: is it possible to sunbathe with pityriasis versicolor? Opinions differ on this matter. Previously, quartz treatment was prescribed for the treatment of lichen versicolor: under the targeted influence of ultraviolet light, colonies of the fungus died. But now many dermatologists dispute this method of treatment.
UV radiation can be dangerous for an organism weakened by infection. In addition, the occurrence of pityriasis versicolor indicates a decrease in immune strength. Therefore, experts do not recommend exposing the skin to additional stress.
If the patient doubts whether it is possible to sunbathe with pityriasis versicolor, he is recommended to consult a dermatologist. The doctor will give recommendations taking into account the individual characteristics of the body, the severity of the disease, its form and location. If you follow medical prescriptions, the patient will avoid the complications of lichen and will be able to recover in a short time.
It should also be remembered that if the patient decides to sunbathe with pityriasis versicolor, the areas of the skin affected by the colonies will remain light: it will not be possible to get an even and beautiful tan. Therefore, it is better to first get rid of the disease, and only after that return to the beach.
Can pityriasis versicolor be cured with iodine?
Iodine-containing products are used in the diagnosis of lichen versicolor. Yeast colonies are sensitive to iodine, causing them to absorb it to a much greater extent than surrounding healthy skin. Therefore, if you apply an iodine solution to the epidermis, the affected areas will be much darker.
But many patients believe that iodine is suitable not only for diagnosis, but also for self-treatment of pityriasis. An alcohol solution of iodine is a popular antiseptic that is often used to disinfect the skin. Fungi from the genus Malassezia, which cause tinea versicolor, are sensitive to it and are partially killed upon contact with this substance, but it is impossible to completely destroy them with iodine.
In addition, an alcohol solution of iodine greatly dries already damaged skin, which can lead to various complications of dermatosis.
As a result of self-medication:
- the disease drags on - recovery does not occur, and the rash spreads to new areas of the body;
- the likelihood of relapse increases - after the rash disappears, it appears again when the immune system is weakened and is chronic;
- new symptoms are added to the symptoms of the disease: tightness and dryness of the skin treated with iodine, itching may occur.
Pityriasis versicolor can be cured with antifungal medications prescribed by a dermatologist. Special creams and ointments affect only colonies of the pathogen and do not affect healthy epithelium. Also, many products contain care components that additionally moisturize the skin, accelerate its regeneration and promote the resumption of melanin synthesis.
Causes of lichen
Mostly young people suffer from this type. Children do not get infected. The fungus is found on everyone's hair follicles, but it appears in exceptional cases. The causes are often low immunity, disorders of the internal digestive organs, excessive sweating, and prolonged exposure to the sun. Can be transmitted through contact.
With a sufficient level of the immune system, infection does not occur, but examination of the patient’s relatives is required. The peak occurs in the spring-summer season. Relapse may occur during pregnancy.