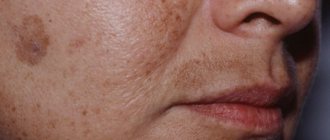
Types of skin pigmentation
PHOTOAGING
The most common type of stain. They gain color after summer, lighten in winter, but do not completely disappear from the skin. You could say they often stay for life.
Ultraviolet radiation activates the synthesis of melanocortin, a pituitary hormone that stimulates melanogenesis in melanocytes and keratinocytes.
During photoaging, melanin is present in the form of granules in melanocytes, keratinocytes, dermal macrophages and in the intercellular space.
POST-INFLAMMATORY PIGMENTATION
Occurs in areas with long-term chronic inflammation: post-acne pigmentation, pigment spots after traumatic procedures, laser therapy and peelings.
Typically, this type of spots disappears once the inflammatory process resolves.
PROTECTING SKIN FROM LIGHT
Trigger factors - ultraviolet, blue light emitted by electronic gadgets (TVs, computers, smartphones...)
Since melanin serves as a shield from solar radiation and other types of rays, it is important to remember - in the fight against age spots of any origin, the first rule is to start using a protective cream with mineral SPF (zinc oxide and titanium dioxide) containing BlueLight filters for blue light and to infrared rays.
How to disguise white spots on the skin?
White spots on the skin are well masked by fresh rhubarb root juice, which is used to lubricate the spots in the morning and evening. As a result, the white spots turn tan color.
An alcohol tincture of green leaves and pericarp of walnuts, taken in equal parts, is also effective. If you apply it to stains twice a day, they will darken for a long time.
St. John's wort for vitiligo
You can use an infusion of St. John's wort (1 tbsp herb to 1 tbsp boiling water, leave for half an hour). Take 1 tbsp. l. 3 times a day after meals. After three weeks - a week break. And so on for 4-6 months.
At the same time, it is advisable to lubricate the white spots with St. John's wort oil. To prepare it you need to take 1 tbsp. l. herbs, pour 1/2 tbsp. vegetable oil and keep in a water bath for three hours. Then filter and squeeze. St. John's wort increases the skin's sensitivity to ultraviolet radiation, so after the procedure it is recommended to stay in the sun: on the first day - only 1-2 minutes, adding 1-2 minutes every day. The course of treatment is at least a month.
Red pepper tincture
Apply tincture of red capsicum (can be bought at a pharmacy) to white spots 3 times a day for 5-10 minutes. Be prepared for a strong burning sensation. After rubbing, you can spend a few minutes in the sun. Repeat the procedure daily for 2 weeks.
Anise oil
Grind 100 g of anise fruit in a mortar, pour in 0.5 liters of olive oil and leave for a month in a dark place. After this, bring to a boil (but do not boil!), cool and strain. White spots should be constantly lubricated with this oil. In a month or two they will darken significantly and will not be so noticeable.
Examples of brightening agents
The SkinBright line of DermaQuest products are unique remedies for age spots on the face of any origin. Effective lightening of diffuse to deep stagnant pigmentation that is not amenable to conventional correction methods. Modern complex formulations guarantee visible results within 2 weeks.
Operating principles of SkinBright line products
Decreased activity of excited melanocytes
Normalization of melanin production
Included
- Snow White lily stem cells,
- Lightening complexes – hexylresorcinol, emblica extract, kojic acid dipalmitate, arbutin, licorice root and white mulberry extract,
- Melanostatin-5,
- Antioxidants: Vitamin C, etc.,
- Vitamin A imitators: Bakuchiol and Chromobrite.
Line drugs
EyeBright cream for skin care around the eyes
Lightening cream "SkinBright"
Serum "SkinBright" from pigment spots for the face
Serum "Brighting" retinol for face
WHITE SPOT DISEASE
This is due to the fact that in limited areas of the skin the production of melanin, the pigment responsible for the color of skin and hair, stops. Patients do not experience pain, itching or other unpleasant sensations. The relevance of the problem of this disease is associated with a pronounced negative impact on the socio-psychological state of such patients.
In the system of dermatological diseases, vitiligo belongs to the group of skin dyschromia, or more precisely, to hypomelanosis. This pathology is common among 0.5% of the world's population.
In most cases, the development of the disease occurs unnoticed. Sometimes the first symptoms of vitiligo are minor skin itching, tingling, and the appearance of whitish or pinkish spots. Subsequently, these spots increase in size, take on different shapes and sizes, and can be surrounded by skin of normal color or with excess pigmentation. Pigment loss can occur quickly, over a few hours, or slowly, over several months.
Such foci can be separate, multiple, single, or merge with each other. Depigmented spots can be located on any part of the body, but most often on open ones: on the neck, in the mouth or around the eyes, in the area of the limbs.
Correct treatment consists of a thorough examination and individual selection of complex therapy, taking into account the possible causes and mechanisms of development of vitiligo, as well as the presence of concomitant diseases. Unfortunately, modern medicine has not established the exact cause of the appearance of white spots on the skin. But the most substantiated theories of the occurrence and development of vitiligo are genetic, biochemical and autoimmune.
In approximately 15–30% of cases, the disease is hereditary . At the same time, vitiligo is often combined with all kinds of autoimmune diseases: rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis, thyroid diseases, autoimmune diabetes mellitus, pernicious anemia, systemic lupus erythematosus, Addison's disease.
The biochemical theory is that in the skin of patients with vitiligo, an excess amount of free radicals (epidermal hydrogen peroxide) accumulates against the background of a decrease in the content and activity of the antioxidant enzyme catalase. These processes lead to damage to melanocytes and depigmentation of the skin.
The autoimmune theory suggests two possible options for the development of the disease. The first is the presence of a primary disorder in the immune system, leading to its errors and the body’s production of antibodies to melanin, melanocytes and tyrosinase (an enzyme that catalyzes the reaction of converting tyrosine into melanin). The second option is damage to melanocytes or their degeneration under the influence of unfavorable factors, which causes the formation of pathological elements to which antibodies are produced. This theory contains many contradictions. But the positive effect of using drugs that suppress immune reactions indicates the participation of the immune system in the mechanisms of the disease.
The diagnosis of vitiligo is made based on the clinical picture and in most cases does not cause difficulties. This is due to the characteristic clinical manifestations of the disease.
If necessary, examination for vitiligo may include consultation with an endocrinologist, testing for antibodies to thyroglobulin; TSH and other studies, if necessary to assess thyroid function or conduct a differentiated diagnosis; additional immunological examination if there is a high risk of other autoimmune diseases. Skin biopsy is rarely performed. Microscopy of a sample from patients with vitiligo reveals a complete or partial absence of melanocytes, altered collagen fibers, and a large number of melanosomes in the rim surrounding the lesion.
Treatment of vitiligo is aimed at curbing the progression of the disease, reducing its cosmetic manifestations and restoring melanin production. Today, vitiligo is increasingly spoken of as a multifactorial disease, which necessitates an integrated approach to its treatment.
Treatment must begin with a series of therapeutic measures. This is, first of all, consultation with a dermatologist. It is also advisable to consult a psychologist, since the patient essentially needs to learn to live with this disease.
The psychosomatic status of the patient and concomitant autoimmune diseases are determined. The prognostic criteria for the effectiveness of therapy are assessed: the duration of the disease, its clinical form, stability over the last 6 months, and the effectiveness of previous treatment.
Vitiligo is a difficult problem for dermatologists due to the lack of a clear treatment plan. A peculiarity of patient treatment is that many methods have off-label status[1]. Therefore, it is important to explain to patients all existing treatment methods, cut out unnecessary ones and protect them from unnecessary costs.
There are two fundamentally opposing methods of treating vitiligo, aimed at creating the same type of skin pigmentation. The essence of the first method is to bleach small, normally pigmented areas of skin located against the background of continuous depigmentation. The second method is more common and is aimed at enhancing the formation of pigment or using various cosmetics to mask skin color defects. This treatment method can be carried out either surgically or non-surgically.
Conservative treatment of vitiligo includes several areas. First of all, this is treatment with topical corticosteroids of moderate strength ( mometasone furoate and methylprednisolone aceponate ). They are off-label drugs and are prescribed for an average of 6–8 weeks.
Calcineurin inhibitors (local immunomodulators) also have off-label status and are prescribed for 10–18 weeks. Both topical corticosteroids and calcineurin inhibitors are most effective when combined with phototherapy.
You can also prescribe therapy with calcipotriol (the effectiveness of its use increases in combination with phototherapy and excimer laser), 5-fluorouracil, 10% L-phenylalanine . But these drugs are best used in the preclinical or initial clinical stages, i.e. their effectiveness in the treatment of vitiligo is not very high.
Phototherapy methods for vitiligo are a priority because they are most effective. It is best to use narrowband mid-wave UVB therapy (311 nm), spectrum phototherapy (SPT) and PUVA therapy. Irradiation is carried out using a general (over the whole body) or local method, when the effect is directed to the affected areas. The PUVA therapy method involves taking internally or externally photosensitizing agents that improve the perception of ultraviolet radiation - psoralen, psoberan , etc. After this, after a few hours, local or general UV irradiation is carried out. However, it must be remembered that PUVA therapy carries a fairly high potential risk of developing skin cancer. Therefore, all over the world the qualification for the number of such procedures has been significantly reduced. And PUVA therapy must be prescribed with great caution.
When using an excimer laser, the effectiveness of treatment also increases significantly. Laser therapy improves metabolic processes in the skin and promotes the production of enzymes responsible for the formation of melanin.
Systemic therapy for vitiligo is prescribed when the disease progresses rapidly and local treatment is ineffective for 6 months. It consists of pulse therapy[2] with systemic corticosteroids, for example, dexamethasone (5–7.5–10 mg 2 days a week in a row for 1.5–3 to 6 months). This is a fairly safe regimen that can be used for a long time and is indicated only for the progressive stage of vitiligo, when it is necessary to stop the depigmentation process.
If conservative treatment of vitiligo does not give the desired result, surgical intervention . There are several indications for surgical treatment of vitiligo: if the lesions are located in open areas of the body, are a significant cosmetic defect and violate the psychological status of the patient; for 12 months there is no result from local and systemic therapy; the disease is in remission; for one to two years, new spots do not appear, and existing ones do not grow.
Surgical treatment of vitiligo consists of epidermal transplantation using finely perforated grafts. Also in recent years, with the development of microsurgery, the transfer of pure melanocyte cultures or mixed epidermal cultures to the prepared area has become increasingly used.
Another, fundamentally different, method of treating vitiligo is to whiten normally pigmented skin . It is used when the patient's depigmented lesions occupy large areas of the body and it is not possible to cause their repigmentation. In such cases, to color the patient’s skin in one tone, small areas of normal skin are bleached (depigmented) using 20% hydroquinone ointment .
The main class of drugs for vitiligo are various concealers, dermatocosmetics, and sunscreens. Cosmetics help make the manifestations of the disease less noticeable. Today, dermatocosmetological products have been developed that allow you to even swim and sunbathe without fear.
It is very important to consider the clinical stages of vitiligo when choosing treatment methods. The preclinical stage is characterized by a deficiency of melanocyte growth factor in the system. It is unknown where the next outbreaks will appear. In this case, as the disease progresses, it makes sense to prescribe systemic therapy that can stop the pathological process. At this stage the disease is reversible.
At the initial stage, possibly reversible, there is a decrease in the amount of melanin in melanocytes. Here the success rate of therapeutic interventions is approximately 50%.
At a late stage, which is considered almost irreversible, melanocytes are destroyed. In this case, so-called cellular technologies can help, or, if the process is widespread, it is preferable to get rid of single areas of pigmentation.
Modern drugs and treatment methods make it possible to slow down or stop the developing process to a certain extent. But it is possible to achieve restoration of pigmentation only in some patients and mainly in the early stages of the disease[3]. Currently, the search for effective methods of treating this disease continues.
Almost all experts agree that vitiligo does not affect the general condition of the body in any way and is a concern only for aesthetic reasons. And some doctors are even inclined to believe that vitiligo is not a disease, but a cosmetic defect.
But while vitiligo is not medically dangerous, the appearance of white patches on the skin can have a negative impact on a person's emotional and psychological health and sense of self-worth. That is why the psychological aspect of vitiligo treatment is so important.
White spot disease also affects famous people. And some even manage to turn the disease into a plus.
Michael Jackson has repeatedly stated that his skin became light not because of plastic surgery, but as a result of vitiligo. The King of Pop took the path of bleaching the areas of remaining pigmentation.
Here is another example - Winnie Harlow - the first and so far the only model in the world with vitiligo, winning not only the world catwalk, but also the hearts of millions of fans around the world. She is proud that she managed to overcome two barriers : social and psychological - the one that prevents people who are different from others from expressing themselves and achieving success.
Various treatments can minimize, disguise, or in some cases eliminate white spots on the skin. But a lot also depends on your attitude towards your disease. Sometimes your disadvantages can still be turned into a big and fat plus.
Prepared based on materials from the IX International Forum of Dermatovenereologists and Cosmetologists
————- [1] Off-label (English off-label, from off - outside, label - label, instructions) - the use of medicines for indications not approved by government regulators bodies not mentioned in the instructions for use. [2] Pulse therapy is the intravenous administration of ultra-high doses of glucocorticoids for a short period of time. [3] Proper treatment of vitiligo can slow the progression of the disease and cause the lesions to grow back. However, according to some data, 60% of successfully treated patients relapse after some time (months or years).
Rules for choosing an effective lightening product for the face
- Buy only products from professional cosmetic brands . Cheap drugs and widely available products will not contain the necessary substances/concentrations for effective depigmentation.
(the advice is banal, but it will allow you to avoid unnecessary waste of money and time)
- Use preparations with a complex composition of lightening ingredients .
There are many mechanisms that bring pigment cells into a state of hyperproduction of the melanin pigment, and it is also necessary to block these processes in a comprehensive manner. Look for products with a composition of brightening ingredients that work at different points of application and enhance each other's effects.
- Remember that your daily care should at least include the use of a lightening cream + sunscreen !
Free consultations are available from leading cosmetologists of the Russian representative office of DermaQuest and Circadia.