Molluscum contagiosum or contagious molluscum is a viral infection of the skin or mucous membranes. It is often called "water warts". It belongs to the group of sexually transmitted diseases. And although this is not a classic STD disease, sexual transmission is one of the most common.
The causative agent is a DNA poxvirus called molluscum contagiosum virus (MCV). It can only infect people. There are four types of MCV:
- MCV-1;
- MCV-2;
- MCV-3;
- MCV-4.
MCV-1 is the most common, while MCV-2 is more common in adults.
What is molluscum contagiosum
This is a viral skin pathology that mainly occurs in children under 10 years of age.
The disease also occurs in young people aged 20-30 years, during the period of their most active sexual life. This disease is characterized by the appearance of hemispherical nodules with a diameter of 2-5 millimeters on the skin or mucous membranes. Regarding the prevalence of this infection, rates in different countries vary from 1 to 22%. It is difficult to determine the exact incidence rate because the virus is easy to spread. To do this, you just need to come into contact with a patient or a virus carrier. The virus remains active for some time on the surface of objects, so infection is also possible when using things and objects shared with the patient.
Molluscum contagiosum is not considered a dangerous disease. It does not threaten the life and health of a child or adult. The presence of the disease, as a rule, indicates a reduced immune status. This is why the infection most often affects children whose immunity is just developing. The risk group also includes people with congenital or acquired immunodeficiency.
Important! You can become infected with molluscum contagiosum again. After illness, patients do not develop stable immunity, which makes reinfection possible. Minimizing the risk of infection is mainly associated with strengthening the immune system and compliance with preventive measures.
Similarities with other diseases
Molluscum contagiosum consists of a huge number of elements. This is why it is very easy to confuse it with other skin diseases.
These include:
- Genital warts;
- Flat warts;
- Vulvar micropapillomatosis;
- Hyperplasia of the sebaceous glands;
- Pearly penile papules;
- Syringiomas.
If a single large element is detected, differential diagnosis is made with keratoacanthoma, basal cell and squamous cell skin cancer.
Causes of molluscum contagiosum
The causative agent of the disease is viruses of the orthopoxvirus family, which belong to the smallpox virus family. Molluscum contagiosum virus is abbreviated as MCV (Molluscum contagiosum virus). Today, 4 varieties of such viruses have been identified, but the most common viruses in the human population are MCV-1 and MCV-2. Moreover, if the first occurs in adults and children, the second occurs mainly in adults, since it is transmitted through sexual contact. Characteristic skin manifestations of infection appear in those areas where the virus has penetrated. Most often these are the limbs, face or genitals.
Molluscum contagiosum virus. Photo: PHIL CDC
All smallpox viruses, including orthopoxviruses, are large DNA viruses. This means that the mutation rate of such viruses is much lower than that of RNA viruses (for example, influenza viruses). This is due to the fact that when copying genetic material, DNA viruses use DNA polymerase, which also performs editing functions, clearing the genome of mutations.
The incubation period for this pathology ranges from one week to several months. Most often it is 2-8 months. In most adults and children, characteristic symptoms develop within a specified period of time after infection.
Important! A patient with molluscum contagiosum remains contagious until all skin manifestations disappear.
How does infection appear? Main symptoms
Infection with the virus occurs in various ways.
Both the result of sexual intercourse and domestic infection are possible.
The incubation period of molluscum contagiosum lasts from two weeks to several months.
After this stage ends, the main symptoms begin to appear.
The clinical picture of the disease is quite pronounced. Localization of molluscum contagiosum:
- external genitalia,
- hip area,
- buttocks or lower abdomen.
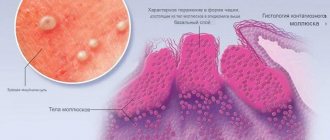
Raised nodules appear on healthy skin. They have a hemispherical shape. The color matches the natural color of the skin or is slightly pinker, single or multiple.
In the middle of the hemisphere there is a depression, slightly reminiscent of a human navel.
The nodules are smooth to the touch and only slightly differ from the natural color of the skin. The skin around these formations usually does not change. But sometimes the rim around them becomes inflamed. The person does not experience any particular discomfort.
A significant increase in manifestations is observed after approximately 3 weeks. And with slight pressure a cheesy plug is released.
It is worth considering that in most cases, symptoms can go away on their own after six months. Clinical manifestations are dense nodules, sometimes with a light pearlescent hue.
Painful sensations may not be observed at all. Often these are small skin rashes that are localized in certain small areas.
Such nodules can have different sizes. This significantly complicates diagnosis. But a specialist will immediately understand what the problem is. Because the symptoms are quite specific. If you press on the manifestation, a slightly whitish liquid will appear.
In some situations, patients complain of itchy skin. However, the risk of bacterial infection should not be excluded. Few people know, but symptoms can appear for several years. The appearance of these bubbles is possible anywhere. But such formations are rare on the palms and soles. Most often, the “abode zone” of the mollusk is the face and neck.
The first sign that should alert you is a small lump on the skin. Then other nodules appear.
In the case of small sizes, they merge into a single seal. It can be 1 cm in size.
Therefore, it is quite difficult not to notice it. Already at this stage, it is important to immediately consult a doctor.
As for general malaise and fever, this is rare.
Interesting fact: apart from its appearance and slight itching, mollusk on the skin does not cause discomfort. Therefore, the child may not be aware of his illness. After the course of therapy there are no scars left on the skin. Only slight depigmentation occurs. In some situations, inflammation of the skin around the nodules occurs. In this regard, the use of antibiotics is relevant.
Methods of infection and provoking factors
Infection with the virus occurs through contact with a patient or carrier of the virus. Using things and objects shared with the patient also poses a danger, since orthopoxviruses remain active for some time on various surfaces. For this reason, children often become infected when visiting sports sections, where the likelihood of infection spreading is especially high due to the large crowd of people who use the same sports equipment. Contact sports (such as combat sports) also pose a risk because close contact increases the likelihood of transmitting the virus.
Children's judo section. Photo: nomadsoul1 / freepik.com
In young people who are sexually active, infection most often occurs through sexual contact. As in young children, in older people the provoking factor for infection is weakened immunity. HIV-infected people, as well as people suffering from atopic dermatitis, are at risk. One of the factors in the development of the disease is long-term use of glucocorticoid drugs and cytostatic agents that reduce the activity of the human immune system.
Important! If molluscum contagiosum is sexually transmitted, many people mistakenly believe that they can protect themselves from the virus by using a condom. This is a big misconception, since a condom is only effective in protecting against infections concentrated directly in the urethra, penis, semen or vagina. It is impossible to completely protect yourself from sexually transmitted infections such as molluscum contagiosum, syphilis or genital herpes using a condom.
Transmission routes
To protect yourself as much as possible, you need to know which routes of transmission of molluscum contagiosum are common. In this case it is:
- Household contact with a sick person or with contaminated things. Usually these are the patient’s personal belongings - for example, a towel.
- Sexual contact with an infected person. Often the rashes are localized on the genitals, lower abdomen and inner thighs.
- Transmission from mother to child. This is not a common option, but it is still possible.
- Infection during the tattooing process occurs in situations where the instruments are unsterile and the artist does not follow safety rules.
If there is a person with such an infection in your immediate environment, you need to be very careful, since the routes of transmission of molluscum contagiosum are quite simple.
Symptoms
The main symptom of a skin infection is painless nodules 2-5 mm in diameter with a small dimple in the center. Let's take a closer look at the main characteristics of rashes and other symptoms.
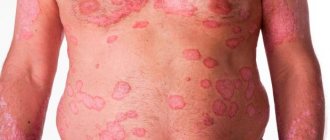
- The rashes have the appearance of dome-shaped papules. The surface of the papules may be smooth or waxy. The consistency of the papules is dense, and as the tumor grows it softens. In patients with HIV infection, as well as in people with weakened immune systems, the diameter of the rash reaches 10-15 mm.
- Papules are flesh-colored, pink, or darker in color. When pressed, curdled contents come out of the papule. Sometimes pearlescent stains, like a pearl, are clearly visible on the papules.
- Papules form at the sites of viral infection penetration - in various parts of the body. They are often grouped into one or two areas, but diffuse distribution of papules over a specific area of the skin is also possible. Often in people with weakened immune systems, the rash affects large areas of the skin.
- The rash is painless, but the area of the rash may become inflamed, which is accompanied by itching.
- In approximately 10% of cases, patients develop eczema in the affected area - an inflammatory skin lesion (dermatitis).
- Papules never appear on the palms or soles. Very rarely, rashes form on the mucous tissues of the oral cavity.
- Skin tumors with molluscum contagiosum grow slowly. The papule increases in size and is filled with a light, cheesy mass consisting of skin cells, sebaceous gland secretions, as well as dead leukocytes and the viral particles themselves.
- Around the 12th week, papules reach their peak size, after which their growth stops. Then the tumors gradually die off.
Figure 1. Molluscum contagiosum rash on the face. Source: Ben Naafs/Community Eye Health/Flickr
Symptoms in women
In adults, rashes most often affect the genital area. This is due to the predominance of transmission of infection through sexual contact. For infection, genital contact itself is not at all necessary; just contact with the infected area of the partner’s skin is sufficient.
Most often in women, papules form in the lower abdomen, on the thighs, pubic area or external genitalia.
It is noteworthy that pregnant women are especially susceptible to infection due to a natural decrease in immunity. The manifestations are indistinguishable from the classic clinical picture of the disease. The virus does not pose a threat to the life and health of the fetus. However, if the baby comes into contact with the mother's infected skin, the child runs the risk of becoming infected.
Symptoms in men
In men, as in women, the rashes are predominantly located in the genital area. This is the groin area, penis, inner thighs. Men are more likely than women to rub papules on clothes, which leads to the release of viral particles and re-infection. Therefore, the rash affects not only the area of contact with the infected partner, but also nearby areas.
How does the infection manifest in children?
Skin manifestations in children mainly affect the face, limbs and chest area. The rashes do not cause any inconvenience to children other than aesthetic ones, especially if they are located on the face. Papules in children do not hurt and very rarely cause itching. It is important to ensure that the child does not scratch or rub the affected areas. Otherwise, secondary infection with the virus will occur.
Important! In children, rashes are extremely rarely observed in the genital area. If a child has papules on the genitals, pubis, buttocks or inner thighs, the circumstances of possible infection should be especially carefully examined, since sexual abuse cannot be ruled out.
General information
Molluscum on the skin is often called "contagious molluscum."
This is a kind of special form of viral infection that affects the skin.
The virus quickly penetrates the basal layer of the epidermis and provokes excessively rapid division of cellular structures, as a result of which growths-nodules of a roundish shape and small size with an umbilical depression in the center are formed on the surface of the skin.
In this case, a certain number of epidermal cells are destroyed.
It is worth noting that this is a benign disease. This is due to the fact that the growth of nodules occurs in a small place. At the same time, no inflammatory process is observed in the layers of the epidermis.
This disease affects people of different age groups, regardless of gender. But this problem is especially relevant in childhood. Namely for preschool children and the elderly (after 60 years).
Babies under one year of age almost never become infected with this virus. Doctors explain this by saying that a large amount of maternal antibodies were transferred to them through the placenta.
This especially affects individuals with a weakened immune system, those suffering from rheumatoid arthritis and taking cytostatics or glucocorticoid hormones.
But those who come into contact with other people’s skin should also be careful. For example, massage therapists. In addition, the infection factor does not depend on the location and characteristics of the climate zone.
Each mollusk looks like a small tubercle. Pale pink or slightly transparent shade (sometimes with a pearlescent tint).
Types of molluscum contagiosum
There is no generally accepted classification for molluscum contagiosum. At the same time, in addition to the “classical” papules, atypical forms of rashes are distinguished. These include:
- giant clams, the size of which is 3 cm or more;
- cystic molluscs - the appearance of cysts (cavities, with a wall and contents) instead of papules of the same size;
- ulcerated mollusks - instead of nodules, small areas of erosion appear, which subsequently turn into bleeding ulcers;
- molluscs in the form of eels or warts;
- pendicular mollusks - neoplasms are located on a thin stalk above the skin.
Depending on the prevalence of lesions, two forms of the disease are distinguished:
- Localized - affects only a specific area of the body, such as the face, genital area, upper or lower extremities.
- Generalized - rashes are observed over a large surface of the body. In some cases, neoplasms are noted throughout the body.
Forms
The main form of molluscum contagiosum in children or adults is typical. It has the symptoms described above.
There are also atypical (very rare) forms, for example:
- Keratinizing molluscs. In this case, the skin on the rash is very flaky and comes off the surface in scales.
- Cystic molluscs. Where a nodule immediately forms, cysts subsequently grow.
- Giant clams. Such rashes can grow up to three centimeters in diameter or even more.
These are not all forms of atypical molluscum contagiosum, but the risks of encountering them are minimal.
Treatment of molluscum contagiosum
Source: Fantasy Children's Clinic
Before starting treatment, a diagnosis is carried out, which is not difficult for molluscum contagiosum. The diagnosis is made based on the external manifestations of the disease. For atypical forms, specific laboratory tests are used to identify viral particles. This is staining of the contents of nodules according to Romanovsky-Giemsa, Papanicolaou or Wright. Instrumental diagnostics for molluscum contagiosum are not used.
There is no specific treatment for molluscum contagiosum. Treatment is aimed at eliminating skin lesions as quickly as possible. The disease is treated on an outpatient basis by a dermatologist.
Treatment for molluscum contagiosum is not always carried out, since within 6-18 months the papules “go away” on their own. Treatment measures are resorted to based on aesthetic considerations, as well as in severe cases of the disease (when a significant part of the body is affected by rashes) and when patients at risk are infected (people with HIV and a weakened immune system).
Drug treatment
Drug therapy is ineffective. However, to eliminate papules, salicylic acid is used as an external agent. The healing of rashes in this disease is also facilitated by topical preparations with retinoids (in particular, tretinoin).
To eliminate rashes, cantharidin is used, a poison contained in the hemolymph of some types of beetles. Currently, cantharidin is used as a blister agent. In particular, one drop of cantharidin is applied to the papule of molluscum contagiosum. In this case, blisters may appear at the application site. Cantharidin has not yet been registered in the Russian Federation and cannot be used.
Cytostatic drugs (podophyllotoxin) and potassium hydroxide are also used for medicinal purposes. However, the effectiveness of these drugs, as well as the above, for molluscum contagiosum is extremely low.
Antiviral drugs
Since molluscum contagiosum is a viral disease, it is logical to assume that antiviral drugs can help in treatment. Unfortunately, here too the existing arsenal of antiviral drugs turned out to be powerless against the molluscum contagiosum virus. Some doctors prescribe acyclovir and oxolinic ointment to such patients, but these drugs are ineffective against the molluscum contagiosum virus. Currently, antiviral drugs acting directly against the molluscum contagiosum virus have not yet been developed.
Immunomodulators
Some doctors may prescribe immunomodulatory and immunostimulating drugs to patients. For example, this is imiquimod, a drug that enhances local immunity; Local drugs with inducers of interferons, proteins that have antiviral activity, are also prescribed. However, there are no studies confirming the effectiveness of such drugs for molluscum contagiosum.
Thus, in the treatment of molluscum contagiosum, medications and folk remedies are either ineffective or useless. An effective way to eliminate rashes are methods of direct papule removal.
Surgery
The following surgical techniques are used to remove molluscum contagiosum papules:
- Cryosurgery is treatment using liquid nitrogen. The papule is exposed to liquid nitrogen for a few seconds, which leads to its deep freezing and destruction. Since new papules may form over time, the patient will have to undergo several cryotherapy sessions. Among the disadvantages of this treatment is the painfulness of the procedure. Therefore, it is not used to treat young children. In addition, after exposure to liquid nitrogen, blisters may form, and then barely noticeable scars.
- Evisceration is the removal of a papule using thin tweezers. The advantage of the method is that the removed papule is not destroyed, which means it can be sent for laboratory testing.
- Curettage is the removal of lesions using a curette. This is a tool that resembles a long metal fork with a loop instead of teeth. This technique is painful, and after removal scars may form. As a rule, curettage is used for a small number of papules. If there are a lot of rashes, then curettage is ineffective, since after the procedure there is a high risk of new rashes appearing.
- Laser therapy - laser exposure to molluscum contagiosum papules. As a rule, one session is enough for laser removal of papules, but in some patients the rash may persist, which requires re-treatment after 2-3 weeks.
- Electrocoagulation is the removal of skin lesions using electrical cauterization. For this purpose, an electrocoagulator is used - a device that supplies high-frequency current. Under the influence of current, the proteins of the papules are destroyed, which leads to its destruction.
Prevention of molluscum contagiosum
Source: Jesselton Medical Center
There is no specific prevention against molluscum contagiosum (a vaccine against the pathogen has not yet been developed). Basic preventive measures involve isolating patients to avoid infecting other people. To minimize the spread of infection, doctors recommend:
- isolate the sick person until complete recovery;
- observe the rules of hygiene;
- conduct preventive examinations for children of preschool and school age;
- be more attentive to your sexual partners - a quick examination of the person can help you avoid infection, and motivate your partner to undergo examination.