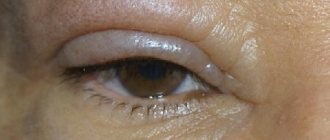
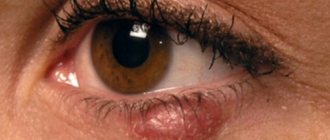
A convex formation on the eyelid in the form of a lump is not uncommon. The causes of this pathology may be different, but in any case, a lump on the eyelid should not be ignored. The formation can develop on both the lower and upper eyelids. It may not cause any inconvenience other than aesthetic discomfort, but it may hurt and fester. The bulge usually has a round or elongated shape. It may not change in size for a long time, and sometimes, on the contrary, it increases rapidly. Let's look at the reasons for the formation of lumps on the eyelid and how to treat them.
Table of contents:
Causes of cyst manifestation
Where are eye cysts located?
Types of cysts Clinical symptoms Diagnosis of the disease Methods for removing an eye cyst Treatment of an eye cyst with a laser Procedure for laser removal Contraindications A benign tumor on the eyelid or mucous membrane containing fluid inside is called a cyst. Translated from Greek - “bubble”. It occurs in representatives of both sexes and all age categories. Quite often this formation is diagnosed in children. When it appears, you should definitely see a specialist to develop further treatment tactics. If left unattended, it can have a bad effect on the quality of vision.
If you do not contact the clinic to solve the problem, then:
- visual acuity decreases;
- eye mobility worsens;
- profuse lacrimation appears;
- frequent headaches occur;
- there is a possibility of developing into a malignant formation.
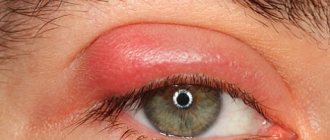
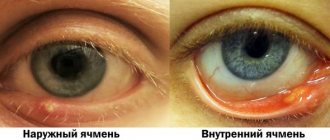
Barley
Styes are more common than chalazions. This type of lump on the lower or upper eyelid is caused by inflammation of the follicle (bulb) of the eyelash. This also clogs the sebaceous gland duct. Styes develop over several days or even hours and can occur in both adults and children. More often, the systematic appearance of barley is observed in people with weakened immune systems or who have changed their place of residence to an area with a more severe climate, as well as in people exposed to constant stress factors.
Based on their origin, there are two types of barley. Inflammation can be external (when the sebaceous gland suppurates) and internal (when the source of inflammation is located in the membolic gland).
The development of external styes is characterized by subjective sensations similar to a foreign body entering the eye. The initial stage may also be accompanied by stabbing pain. External stye visually manifests itself as redness and swelling of the eyelid. The internal one is usually not so noticeable, but it causes even more discomfort and pain.
Without treatment, barley develops within a few days into an abscess, which opens with the release of purulent contents. This brings relief, but an open wound is dangerous due to the possibility of re-infection.
It is better to start treating barley without waiting for the abscess to spontaneously break through. This allows you to get rid of the painful lump faster and with less risk of complications. If you still don’t have the courage or time to visit an ophthalmologist, you should remember that prolonged suppuration of the eyelid is very dangerous. If the stye does not open for more than two weeks, surgical treatment is necessary. An ophthalmic surgeon will remove the abscess under local anesthesia and give recommendations for further treatment of the eyelid. Most often, therapy for developing or already opened barley includes drops and ointments that contain antibiotics (albucid, gentamicin, erythromycin, tetracycline ointment).
Causes of cyst manifestation
- infections;
- parasites;
- injuries, burns;
- consequence of glaucoma;
- genetics;
- eye inflammation;
- reaction to medications;
- congenital iris dissection;
- allergic manifestations;
- dystrophic age-related changes;
- consequences of the operation.
A product of disruption of the activity of the membranes of the eye: iris, cornea, conjunctiva, caused by the above reasons, requires mandatory ophthalmological care and is an unpleasant cosmetic defect. Treatment or removal is necessary to avoid serious consequences.
Types of cysts
Depending on the source of occurrence, there are different types of eyeball cysts:
- congenital, associated with iris dissection;
- spontaneous ones affect people of different ages, the cause has not yet been identified; with serous, the ball is transparent, with pearl, its walls are dense;
- traumatic ones occur as a result of damage to the eyeball or after an unsuccessful operation;
- exudative are the result of glaucoma;
- due to infection, the ocular conjunctiva gives rise to a retention conjunctiva or, after intervention, an implantation conjunctiva grows;
- stromal is detected and disappeared unpredictably;
- dermoid is formed due to displacement of the epithelium.
The latter originates in utero due to the adverse effects on the mother of medications, radiation, and infection. Dermoid leads to edema, strabismus, amblyopia, astigmatism, and optic nerve atrophy. It cannot be cured, it must be eliminated.
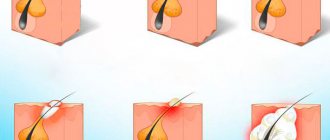
Is it possible to remove whiteheads at home?
Never try to get rid of acne on your own by piercing or squeezing it. Firstly, this way you won’t be able to remove them anyway, and secondly, a very painful redness will form at the site of the squeezed pimple, and the appearance will become even worse. In addition, there is a high probability of infection under the skin. Scars may also remain at this location.
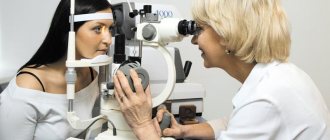
Diagnosis of the disease
- Visual inspection;
- control of intraocular pressure;
- assessment of visual fields and visual acuity;
- determining the state of the optic nerve and the state of the retinal vessels;
- establishing the exact location;
- establishing the composition of the liquid inside the bubble.
The ophthalmologist uses methods such as tonometry, perimetry, biomicroscopy, ultrasound, computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging to make a diagnosis. The cyst is visible to the naked eye; additional studies are required to establish the general picture of the disease and exclude the malignancy of the tumor.
Methods for removing eye cysts
If you are diagnosed with an eye cyst, surgery will help radically solve the problem. Removing an eyeball cyst within healthy tissue is the most effective method of combating the formation.
- Cauterization with a laser beam is associated with the complete destruction of pathological cells. As a result, the likelihood of relapse is guaranteed to be low. The laser has a disinfecting and anti-inflammatory effect. Due to its undeniable advantages, if there are no contraindications, preference is given to this method. But if the formation is large, a significant number of laser pulses will be required, which will injure the surrounding tissue. Therefore, lasers with a shallow penetration depth are chosen, which makes it possible to remove only small formations, less than three millimeters in diameter.
- Surgical method.
Indications for surgical removal:
- medications do not have an effective effect;
- type of cyst;
- complicated neoplasms;
- pediatric dermoid cysts;
- a large or rapidly growing cyst.
Dermoid cysts do not respond to traditional treatment. This is a purely surgical diagnosis.
A cyst is a filled cavity measuring up to three millimeters or more. May consist of one or more chambers. When removing it, it is important not to disturb the integrity of the capsular bag, otherwise it will collapse, and this will complicate its excision. To clearly indicate its boundaries, markings were made on the outside. But the tear fluid blurs the designated boundaries. In addition, the tissues adjacent to the cyst swell under the influence of the anesthetic fluid, which also interferes with clear recognition of the boundaries. Therefore, to improve the visualization of boundaries, the following surgical technologies are used:
- Perform sequential aspiration of the cyst; based on the area of the collapsed section, it is determined whether it is single-chamber or multi-chamber;
- then the colored preparation is injected inside, giving the formation its previous shape;
- Local anesthesia is administered and the cyst is excised along clearly defined external boundaries.
With all the variety of existing types of neoplasms, only a specialist can choose the right treatment tactics if the patient is treated in a timely manner.
Chalazion in children
Chalazion is rare in children unless there is a congenital predisposition. The composition of fat secretion is different for everyone, as are the properties of the skin. If you have a predisposition to eye diseases and gland blockage, then there is a high probability that your child may inherit this feature.
Children aged 5 to 10 years are at risk. The difficulty is that the child is inattentive to eye hygiene. Pay attention if your child rubs his eyes frequently. Find out if he is bothered by itching or burning.
Treatment of chalazion in children is no different from treatment in adults. The only difference is that surgery cannot be performed using a laser if the child is under 14 years old.
Treatment of eye cysts with laser
The first signs of an eyeball cyst may not be alarming, especially since the small lump may disappear. If it turns into a painful pea, the image becomes clouded and distorted, black flickering spots appear, the field of vision narrows, a visit to the hospital is necessary. The doctor will examine the eye, prescribe tests and make a diagnosis.
Afterwards, either drug treatment or surgical removal will be prescribed. Folk remedies can be used only after consultation with an ophthalmologist. When drawing up an action plan, the origin, size, location are taken into account. Treatment of eye cysts caused by infection occurs with the help of anti-inflammatory, antihistamine drops and ointments. The course usually lasts no more than two weeks.
If medications do not help, then the formation is removed using a scalpel, radio wave knife or laser beam. Previously, fluid was sucked out of the bubble, but after this procedure the formation grew again.
The equipment of modern ophthalmology clinics with advanced equipment and the level of training of specialists make it possible to carry out these difficult manipulations on an outpatient basis. It is very important to remove or destroy the capsule completely to prevent regrowth.
The use of a laser to eliminate a tumor helps to effectively cope with the task and has undoubted advantages:
- precisely directed action;
- destruction completely, without a trace;
- exclusion of infection;
- low likelihood of complications;
- fast recovery;
- absence of swelling and scars;
- healthy tissue is not affected.
Prevention of chalazion
Prevention of chalazion includes:
- Proper nutrition;
- Maintaining personal hygiene;
- Strengthening immunity;
- Compliance with the terms of wearing lenses and timely replacement of the solution for their storage;
- Timely treatment of tonsillitis and caries;
- Maintaining a sleep schedule;
- Getting rid of bad habits (smoking, alcohol);
- Eyelid massage.
Also, to prevent chalazion, girls should pay special attention to cosmetic procedures. Before getting eyelash extensions or eyelid tattooing, consult an ophthalmologist.
Laser removal procedure
- Local anesthesia in the affected area;
- an incision measuring 2 mm;
- a specialist inserts a laser source through the hole;
- the beam directionally evaporates the affected area and seals the blood vessels.
If the eyeball cyst is large or an abscess has appeared, then surgical removal under anesthesia is recommended. It takes place in several stages:
- limiting the surgical area with sterile materials;
- introduction of a staining solution to clearly define the boundaries of the lesion;
- fixation of the capsule;
- removal with a scalpel;
- rinsing the cavity with an antibacterial solution;
- connecting the incision using a continuous absorbable suture.
Rehabilitation is long and relapse is possible, unpleasant consequences such as hemorrhage, infection, suture dehiscence. In the postoperative period, antibiotics are prescribed, it is advised to reduce the load, and avoid contact with water. The applied bandage is not removed from the eye for five days. It serves as a barrier to dirt and bacteria. There are a number of restrictions on operations.
Clindovit® - a drug to combat acne
Clindovit® is a gel of clindamycin that exhibits antibacterial activity against a large number of strains of propionibacteria6. The drug helps reduce free fatty acids on the skin from 14 to 2%6.
The base contains additional components - allantoin with a regenerating and anti-inflammatory effect and an emollient that softens and moisturizes the skin4,5.
Contraindications
- Inflammation in the body;
- cold;
- diabetes;
- poor blood clotting;
- venous diseases;
- oncology;
- mental disorder in the acute stage;
- pathologies of the heart and blood vessels;
- pregnancy is considered on an individual basis.
Possible complications after surgery:
- hemorrhages due to tissue injury;
- infection due to exposure to microbes;
- seam instability;
- corneal erosion.
Relapses are rare and are possible when the capsule is not completely removed.
The following are suggested as preventive measures:
- apply makeup carefully;
- monitor the expiration date of products that come into contact with your face;
- do not use lenses;
- observe eye hygiene requirements;
- Healthy food;
- systematically undergo ophthalmological examinations.
The chance that the cyst will self-destruct is negligible, so you should not expose yourself to undue risk. Under certain circumstances, these formations can develop into malignant ones. If alarm bells appear, immediately make an appointment with a doctor at our clinic. We have all the technical and professional resources to remove an eye cyst and solve the problem in full.
Causes of chalazion
- Chalazion on the eyelids develops as a pathological process. It can be triggered by various factors:
- Unsanitary conditions in the premises, poor hygiene;
- Weakened immune system;
- Incorrect use of contact lenses;
- Stress, depression, disturbed psycho-emotional state;
- Hypothermia of the body;
- Vitamin deficiency as a consequence of improper diet;
- Untreated barley;
- Excess cosmetics on eyelids and eyelashes. For example, upper eyelid chalazion can occur in women who wear false eyelashes;
- Chronic forms of blepharitis;
- Skin diseases;
- Oncology;
- Hormonal imbalances and metabolic disorders, including diabetes;
- Blockage of the excretory ducts of the meibomian glands