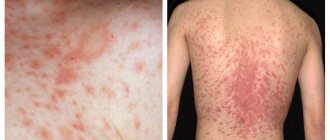
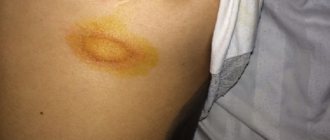
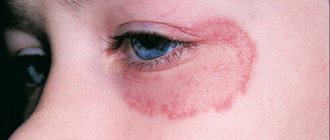
The most common dermatological diseases include lichen - an infectious lesion of skin areas caused by the action of microscopic fungi or viruses. The danger of lichen is that it is easily transmitted by contact from person to person or from sick animal to person and has several varieties that require a special approach to treatment.
What kind of lichen occurs, what type of therapy is more effective in each specific case, how to avoid complications - this will be discussed further.
Pathogens and carriers of lichen
The content of the article
Dermatologists distinguish several types of lichen, caused by different pathogens.
Most often, the appearance of lichen on human skin is initiated by fungi:
- zooanthropophilic - transmitted to humans from an infected animal, including from pets;
- anthropophilic - live only on human skin;
- geophilic - live in the soil and come into contact with human skin upon contact with the ground.
In addition to fungi, viruses are often the causative agent of lichen. Their cunning lies in the fact that they can live asymptomatically in the human body for a number of years and become more active when the immune system is weakened. This is exactly how, for example, those familiar to many with herpes or shingles behave.
Epidemiology of microsporia
Microsporia affects mainly children of primary and school age. The high incidence of ringworm in children is associated with an imbalance of cellular-humoral immunity, a reduced concentration of bactericidal components of the blood serum and a reduced level of enzymes in the hair follicles that destroy pathogens. Upon reaching puberty, the disease disappears.
Zoophilic microsporia
In our latitudes, among all species, zoophilic microsporia accounts for 90 - 97%. The cause of the disease is the fungus Microsporum canis, which is transmitted from sick kittens, cats, dogs (through contaminated wool), less often - from humans, as well as through objects containing pathogen spores (combs, toys, bedding and hats). Children often become infected when playing in the sandbox. The source of infection in most cases is stray animals.
The causative agents of ringworm are highly resistant in the external environment. From 7 to 10 years they remain viable on skin scales and hair. They can be stored in soil (sandboxes) for more than 1 month. The incubation period is 5 - 7 days.
Rice. 3. Ringworm in a dog.
Rice. 4. Ringworm in cats and kittens.
Anthropophilic microsporia
In our latitudes, among all types of microsporia, anthropophilic microsporia accounts for about 2% of cases. The cause of the disease is Microsporum ferrugineum (more often) and Microsporum audouinii (less often). The infection is transmitted only from a sick person and his personal belongings infected with fungi - hats, combs, clothes, towels, bed linen and hairdresser's tools.
Rusty microsporum (Microsporum ferrugineum) is the most infectious and virulent of all pathogenic fungi known today. The spread of the disease in children's groups is rapid and requires immediate implementation of intensive anti-epidemic measures.
Children aged 5 to 14 years old, mostly boys, are most often affected, which is associated with transmission of infection during haircuts. The disease disappears upon reaching puberty. The incubation period for Microsporum ferrugineum infection is 4 - 6 weeks.
Microsporum audouinii is most common on the African continent. The pathogen may be brought into the Russian Federation by tourists and migrants. Mostly children of preschool age are affected.
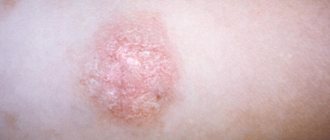
Rice. 5. A focus of microsporia on the skin of a person’s hand.
Geophilic microsporia
This type of disease develops when persons cultivating the soil become infected with the soil saprophyte fungus Microsporum gypseum.
Rice. 6. Microsporia in adults.
Types of lichen
In order to cure lichen, it is not enough to make a general diagnosis. It is equally important to promptly determine the type of lichen, since each is characterized by its own symptoms and requires its own treatment.
Dermatologists distinguish the following types of lichen:
- shearer;
- encircling;
- pityriasis;
- pink;
- red flat;
- tubular;
- solar;
- scaly.
Only a competent dermatologist can draw a line between them and correctly prescribe a set of therapeutic measures. Therefore, under no circumstances should you self-medicate. The surest way is to go to the clinic at the first sign of deprivation.
Now about what changes in the skin should alert a person.
Ringworm
The source of trichophytosis - this is the second name for ringworm - can be any of the fungi that primarily affects the hairy parts of the body (head and beard), neck, shoulders, face. The symptoms of this type of lichen are usually as follows: first, swollen pink or red spots with clearly defined edges appear, then the edges of the spots become covered with bursting blisters and an itchy crust, and finally, the center of the spot begins to peel off, and the hair in the affected area breaks off and thins.
Ringworm is diagnosed using a Wood's lamp. If the disease is confirmed, the patient - children often suffer from ringworm - is protected from contact with others and is prescribed complex therapy, including taking special tablets (for example, Terbinafine) and the use of antifungal ointments. In particularly difficult cases, it is possible to take hormone-containing agents that help stop the inflammatory process on the skin.
Symptoms
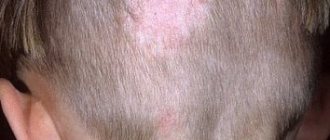
What does ringworm look like in the initial stage, how to recognize it in time and prevent hair loss? Unfortunately, a person may not notice the first signs of the disease immediately. Any area of the scalp begins to lose its vegetation. The hairs gradually thin out, fall out and break, changing their length to 1 - 2 mm. Peeling of the skin adds to the problem. As the disease progresses, the lesion acquires clear outlines.
Symptoms of ringworm (see photo) are more noticeable on the chest, back, lower and upper extremities. A person may notice such deviations as:
- burning and itching spots;
- redness and swelling of the skin;
- framing the hearth with a solid roller;
- blistering of the lesion with subsequent leakage of contents and the formation of crusts.
If nails are affected by trichophytosis, the plates become brittle and dull. Their structure thickens and coarsens. Subsequently, the nails crumble and change color. Dents on the plates, grooves and a dirty gray color are a characteristic sign of lichen.
In addition to ringworm patches on the head, problem areas can also appear on the body. The disease manifests itself as a rash, the elements of which are similar to round red spots. Since the fungus feeds on keratin taken from the upper epidermal layers, the skin elements gradually acquire the contours of a ring. Having “eaten” the keratin in one area, parasitic microorganisms move on. This is why plaques grow in diameter and change the boundaries of their edges.
The accumulation of dermatophytes leads to the formation of a bright border. Its bubbly and scaly appearance indicates increased fungal activity in this area. Sometimes the parasites return to the center of the ring and again use it as a source of nutrition. But this is only possible when keratin reserves are restored. The so-called “ring within a ring” is a clear sign of increased dermatophyte activity.
Herpes zoster
It is caused by a virus that remains “dormant” in the human body for the time being. It appears in the form of fluid-filled blisters, usually located in the intercostal part of the body. Associated symptoms of herpes zoster: pain (caused by damage to the intercostal nerve endings) and itching of the skin in the affected area; sometimes fever with chills, headaches.
Treatment of herpes zoster is complex. Since the blisters of shingles burst, they are initially treated with brilliant green. And to lubricate the crust that forms in their place, use dermatol ointment. In parallel, the doctor may prescribe antipyretic, painkillers and antiviral drugs, quartz and laser therapy.
Forecast
If you follow all the recommendations prescribed by your dermatologist, the prognosis is favorable . To confirm the success of treatment, skin particles are scraped from the lesions and examined for the presence of fungal flora.
This procedure is carried out the next day after completion of the treatment cycle, after 7 days and for the last time - after 60 days, to confirm the absence of an infectious agent. Upon receipt of the first negative result for flora, the dose of the drug is adjusted (as a rule, the number of doses is reduced by 2 times).
Pityriasis versicolor
It is also called multi-colored, because the small pink - and sometimes greenish - rash that appears on the back, stomach, shoulders, and chest changes color and turns brown as the disease develops. Moreover, on tanned skin (in summer) these spots appear discolored, but on white skin (in winter), on the contrary, they look quite dark.
Diagnosis of pityriasis versicolor can be carried out by a specialist who has resorted to microscopic examination of the dermis, Balzer iodine test, and Wood's lamp. He will also prescribe a special drug treatment (with the help of Orungal, Mycozolon, etc.) that can kill the fungus that causes the disease.
With proper therapy, pityriasis versicolor can be eliminated quite quickly (although without treatment, the disease drags on for many years). Additionally, the patient is recommended to adjust their lifestyle (a concomitant cause of this type of lichen may be increased humidity or air temperature), and carry out a complete treatment of clothing and linen.
Routes of infection
How can you get lichen?
The source of the infectious agent is hair, skin flakes or particles of nails of an infected person, which come into contact with healthy skin through household items (towels, bed linen, clothing, comb) or through direct contact.
Predisposing factors for active proliferation of fungi are:
- decreased immunity due to recent infectious, general somatic diseases, stress;
- increased body temperature;
- increased environmental humidity;
- skin injuries, which are the entrance gates of infection;
- endocrine diseases.
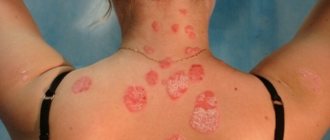
Lichen rosea (or Zhibera)
A little-studied type of disease that usually develops against the background of a weakened immune system in the autumn or spring season. The risk group in this case consists of girls who have a hormonal imbalance in their body.
The manifestation of lichen is the appearance of round or oval pink and light brown spots on the chest, shoulders, back, sides, and skin folds. Dermatological changes, accompanied by itching and flaking of the skin, may go away on their own within a few weeks, however, when the first signs of the disease appear, it is recommended to consult a doctor to rule out the presence of syphilis similar in symptoms.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis is based on a visual examination of the patient, as well as collecting a medical history and questioning about possible sources of infection. If in doubt, the doctor will scrape the affected area.
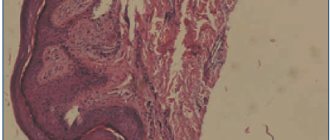
The collected materials are examined under a microscope or placed in a nutrient medium for three days, during which rapid growth of fungal colonies is observed. When filaments of mycelium and spores of a fungal pathogen are detected, its identification is made.
Lichen ruber planus
Flat multi-colored (from pale pink to purple) nodules of lichen red often appear on the mucous membranes, nails (they crumble), and delicate skin of the chest and abdomen. Their appearance is accompanied by severe itching, which, as a result of scratching, leads to the rapid growth of foci of skin damage.
Dermatologists find it difficult to determine the cause of the appearance of lichen red, but note that it is quite common in patients with diabetes, as well as those suffering from diseases of the stomach, liver, and biliary tract. Moreover, women over 40 years of age are primarily at risk.
Tinea tubularis
Malasezzia is the name of the fungus that causes tubular lichen. This fungus can live in the human sebaceous glands for a long time without revealing itself in any way. Under certain conditions: for example, a decrease in immunity or an imbalance in the acid balance of the skin, severe hypothermia or excessive sweating, endocrine disorders or the development of certain chronic diseases - it begins to multiply intensively.
As a result, small flaky spots appear on the skin, which gradually grow and merge into one large spot. And although the victim practically does not feel itching or pain, he should not postpone a visit to the doctor.
After diagnosing the disease (methods used - scraping test, iodine test, use of a Wood's lamp, etc.), the dermatologist prescribes local or complex antifungal drugs.
Treatment
To make a diagnosis and prescribe adequate therapy, a laboratory examination of skin flakes or nail plates and isolation of a fungal culture are necessary.
Differential diagnosis of trichophytosis is carried out with:
- microsporia;
- rubrophytia;
- favus;
- seborrheic eczema;
- pityriasis rosea;
- athlete's foot inguinal.
The infectious-suppurative form is differentiated from:
- microsporia;
- pyoderma. Here you can read in detail about pyoderma in children.
- psoriasis.
Treatment is a combination of drugs for general and local use. Medications should only be taken as prescribed by a specialist. For single lesions located on the surface of the ugly skin, only external medications can be used.
Systemic drugs
Antifungal drugs are used orally, such as:
- griseofulvin;
- levorin;
- nystatin in an individual dose.
To increase the activity of the immune system, general strengthening drugs are prescribed:
- adaptogens (ginseng, eleutherococcus, lemongrass, roseola rosea, ginger);
- vitamins A and E (which are keratoplastics).
The most preferred antifungal drugs are:
- Orungal (based on itraconazole) and exifin (based on terbinafine). The presented medications are most effective, which allows them to be taken for a minimum period of time 1-2 times a day. Moreover, these products are low-toxic, which means they can be used in childhood.
- Griseofulvin. It is not inferior in effectiveness to the analogues presented above, has a much lower cost, but the number of daily doses increases up to 3 times and the course duration increases up to 6 weeks. In addition, griseofulvin has an inhibitory effect on the immune system and can interfere with the absorption of B vitamins, so its use must be combined with vitamin therapy and immunocorrective drugs (Immudon, Thymalin, Taktivin).
Local treatment
Hair needs to be shaved. This recommendation applies to hair on the head, eyebrows, mustache, beard, and vellus hair located on other surfaces of the body. If the eyelid is affected, it is necessary to manually remove the eyelashes (using tweezers).
Applications with 3% salicylic ointment, tar ointment, Wilkinson's ointment or 2% alcohol solution of iodine are applied to the affected area. Shampoos containing antifungal agents (mycoseptin, fluconazole, ketoconazole) are very effective.
There is a huge selection of different antifungal ointments:
- funginal (3 times a day for 20 days);
- mycogel (2 times a day for 20 days);
- exoderil (2 times within 14 days);
- Lamisil (1 time for 7 days);
- exifin (1-2 times for 7 days).
Personal hygiene
Hygiene is one of the most important steps in both the prevention and elimination of ringworm.
Necessary measures to be taken after contact with an infected person or animal:
- treat hands and contacted areas of skin with soap and antiseptic or other antiseptic agents (chlorhexyline, miramistin);
- apply a cream with a fungicidal or fungistatic effect (amiclon, afitin, binafine, canison and others);
- in case of possible damage to the scalp, it is necessary to wash it with shampoo with an antifungal effect (keto-plus, mycozoral, nizoral);
- for preventive purposes, it is very convenient to use fungicidal sprays, which can be used to treat not only your own skin surface, but also other surfaces, to prevent contact and household transmission of infection (Lamitel, Lamisil, Canesten);
- exclude mutual use of objects (combs, clothes, etc.).
Ringworm solar
Under the influence of sunlight, excessive sweating, abuse of solariums and antibacterial agents, uneven, flaky dark spots may appear on the skin. Their occurrence is provoked by a fungus that multiplies on the dermis as a result of a violation of its acidity. Gradually, the spots grow to significant sizes, which causes aesthetic discomfort to a person: they clearly stand out against the tan. And although solar lichen is rarely accompanied by itching and pain, it requires mandatory therapy.
As a rule, solar lichen is diagnosed quickly: it is often enough to conduct an iodine test or use a Wood's lamp. At the initial stage of the disease, local antimicrobial drugs help well; in cases where the disease is advanced, the doctor prescribes complex therapy.
Ringworm scaly
The causes and treatment of this lichen, better known as psoriasis, are not fully understood. However, it is noted that it appears more often in people suffering from diseases of the endocrine and nervous systems and prone to alcoholism.
Psoriasis is a chronic disease, often occurring latently, i.e. is hidden. First, small reddish spots appear on the skin - most often the bends of the legs and arms, lower back and buttocks, causing severe itching due to dryness. Gradually, the spots grow and turn into a lesion that affects a large area of the skin. The peculiarity of psoriasis is that when the plaque is removed, the lichen begins to bleed.
It is necessary to treat scaly lichen under the supervision of a doctor, who will select the necessary topical medications (when applying them, you must strictly follow the instructions), and, if necessary, prescribe antibiotics.
Preventive measures and skin care during illness
To exclude re-infection or recurrence of lichen in the groin, the patient needs to change his lifestyle:
- follow a diet, exclude allergenic foods from the diet;
- treat colds in a timely manner;
- lichen in the groin in women becomes a consequence of hypothermia, so it is necessary to dress warmly in cold weather;
- observe the rules of personal hygiene;
- take medications to improve immunity;
- spend more time outdoors;
- avoid contact with an infected person;
- do not pet street animals, do not allow pets to walk independently;
- take care of your oral cavity;
- keep the groin area clean.
Such measures significantly reduce the risk of contracting inguinal lichen again.
Are all types of lichen contagious?
Many people believe that absolutely all types of lichen are dangerous to others. Meanwhile, this is not entirely true. So, with pink, ringworm or shingles, the patient will really need to be isolated. But, for example, pityriasis or scaly ones are not dangerous for others.
And this is another reason why any change in the skin should be the reason for going to a specialist - only he will be able to correctly determine the type of lichen, assess the degree of its danger, give recommendations for treatment, and finally select a set of medications and therapeutic measures aimed at including general strengthening of the body.
Onychomycosis
Onychomycosis is one of the most common infections. Patients often do not realize that changes in the color and structure of the nail beds are a symptom of infection. They often turn to a dermatologist too late, when large areas are affected.
Infection is promoted by: mechanical pressure, trauma and systemic diseases, such as diabetes.
The first changes usually occur on the free edge of the nail plate or on the side of the lateral shafts. The plates become yellow-brown or greenish, brittle, gradually thicken, and delaminate. The diagnosis of mycosis must be confirmed by mycological examination.
Onychomycosis