Structure of the area under the tongue
Everything that is located under the tongue is called the floor of the mouth. This:
- nerve endings;
- hyoid bone;
- hypoglossal muscles;
- salivary gland;
- connecting folds called frenulums;
- vessels.
Each element of the floor of the mouth serves its own purpose and is irreplaceable. Only if all muscles, tissues, glands and nerves are healthy does the tongue function normally. If there is pain under the tongue, then we are talking about pathology.
Treatment and removal methods
The treatment regimen is drawn up depending on what factors caused the anomaly. But treatment is necessary so that the acute stage of the disease does not develop into the chronic phase. If this happens, the exacerbation will recur from time to time. This form of the disease is more difficult to treat. If necessary, laser treatment of gums should be carried out on time. A healthy oral cavity is the key to the overall well-being of the body.
- The doctor selects medications based on the underlying pathology. The initial manifestations of the disease are successfully eliminated with medications and local applications. According to indications, medications are recommended that stimulate saliva production. This may be Galantamine, Pilocarpine, Potassium Iodide. To maintain general condition, the doctor selects means to stimulate the immune system.
- Serious blockage of the salivary glands is eliminated by mechanical cleaning of the ducts. Today, sialoscopy, a minimally invasive procedure for grinding mineral deposits, is widely used.
- Purulent papules are opened, after which the exudate is removed. Surgical technologies such as galvanocaustics, electrocoagulation, cryodestruction, laser beams, and radio waves are used.
- Sanitation of the oral cavity to accelerate the regeneration of damaged tissue includes rinsing with Chlorhexidine, Furacilin, Rotokan, Miramistin.
To prevent pathology, you need to regularly carry out hygiene procedures with a brush and toothpaste. In addition, floss and irrigator should be used. It is necessary to visit the dentist every six months, and other doctors when the initial symptoms of the disease appear.
Causes of pain under the tongue
- Allergic reactions cause tissue swelling and pain.
- Harmful microorganisms that appear in the mouth during a sore throat cause acute inflammation. Often, it affects the floor of the mouth.
- Mechanical injuries from a bruise or a fall damage blood vessels, nerves, and soft tissues. Vessels may rupture, which will lead to the accumulation of blood between the muscle fibers.
- Some untreated diseases lead to phlegmon, inflammation with pus inside. In most cases, phlegmon appears under the tongue.
- Ordinary caries, if left untreated, causes inflammation that reaches the sublingual area.
- There are many ducts in the salivary gland, and if an infection gets into it, then through these ducts it can easily enter the gland tissue.
- Injury to the frenulum of the tongue. In people with a congenital short frenulum, injuries occur more often. Even a normal conversation can cause a breakup. However, people with a normal frenulum size also suffer. Inflammatory diseases and allergic reactions often lead to injury, leading to swelling of the tongue and the appearance of ulcers. But also improper oral hygiene leads to damage to the frenulum - the so-called dangerous brushing.
Some people have asymmetry of the hyoid bone from birth, and sometimes this anomaly is formed due to injury. Asymmetry prevents the organs of the floor of the mouth from functioning properly.
Causes and diagnosis of cancer
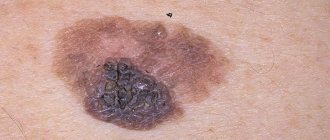
There are different forms and stages of tongue cancer
Tongue cancer occurs in women 6 times less frequently than in men. It is difficult to say what is the reason for such statistics. Perhaps men are more often susceptible to addiction to bad habits or to occupations that are hazardous to health. It would seem that detecting pathology is not difficult, because it is on the surface and is clearly visible. But unfortunately, when it is already quite clearly visible and palpable, this is far from the initial stage.
A person does not always go to the doctor with mild pain, lumps and ulcers. Sometimes a doctor may make an incorrect diagnosis because a cancerous tumor looks like an inflammatory process from mechanical damage or a symptom of a purulent sore throat. The doctor is obliged to identify the presence of hereditary burden, collect anamnesis, and also conduct an instrumental examination using mirrors, if required. The presence of metastases is determined using a lymph node biopsy, CT scan, and MRI of the brain. The ultrasound result will tell you how much the tumor has grown. It is also necessary to conduct a cytological analysis of the tumor. What can lead to such a terrible disease as tongue cancer?
- Systematic smoking and alcohol abuse. Many people do not believe that smoking can lead to tongue cancer; they believe that this is a myth to intimidate teenagers who smoke. However, the reality is that it is the carcinogens released with cigarette smoke that provoke the development of this disease. And alcohol significantly worsens their effect and increases the risk of cancer by 2 times.
- Permanent injury to the mucous membrane. A place that is constantly injured becomes potentially dangerous and also accessible to bacteria and infections. This applies to constant biting of an organ in the same place, damage to the mucous membrane by the edge of a tooth or a low-quality denture.
- Chronic viral infection caused by human papillomavirus, herpes virus, HIV. All of the above affects the development of cancer cells and requires special attention and observation, as well as systematic examination.
- Hereditary predisposition. Of course, this does not mean that if one of your relatives suffered from cancer, then now you cannot avoid it either. You just need to remember that there is a potential danger, so it is important to avoid provoking factors and keep the body in shape.
How is the sublingual area treated?
Considering the above reasons, if you have the slightest pain in the sublingual space, you should immediately consult a doctor. The doctor will find out the source of the pain and determine a treatment regimen. In some cases, allergists and therapists provide treatment. But more often, pain in the floor of the mouth is treated by dentists.
In case of injury to the frenulum or the tissues of the area under the tongue, rinsing will be prescribed: with a solution of soda, romazulan, stomatophyte, hexoral, chlorophyllipt or iodinol. You should rinse your mouth according to the following schedule:
- morning and evening before bedtime;
- after meal.
The doctor also treats the area of injury with an antiseptic and anti-inflammatory drugs.
Inflammations caused by dental problems require immediate treatment - the specialists at Family Dentistry will get rid of caries, pulpitis or periodontitis and prescribe a course of anti-inflammatory drugs to cope with sublingual inflammation.
But one of the most dangerous diseases in the floor of the mouth is inflammation of the salivary glands. It is important to begin treatment before an abscess appears and complications develop. In this case, the doctor prescribes:
- antibacterial therapy - the doctor injects medicine into the gland and also prescribes a broader-spectrum antibiotic;
- drugs to activate saliva secretion - either a solution of potassium iodide or pilocarpine is used, sometimes regular lemon is used;
- hot dry compresses;
- physiotherapy course.
If the inflammation is advanced and pus appears or a stone has formed, the patient is sent to a surgeon, who cleans the gland cavity of pus and removes the stone.
Symptoms of tongue cancer
Examination of the tongue and oral cavity
Let's look at the main symptoms of cancer:
- Pain in the tongue and oral cavity as a whole. This symptom can occur both at the last stage of the disease and at the initial stage. At first the pain is not severe, but at stages 3-4 of cancer the pain becomes very noticeable. It hurts not only when swallowing and speaking, but also when at rest. If metastases have already reached the lymph nodes, pain may also be in the neck, ears, and areas of the head.
- Ulcers. Quite often, with tongue cancer, patients complain of the presence of a painful ulcer on the tongue. Even before contacting a doctor, patients begin to treat it on their own with various ointments and lotions, mistaking the dangerous disease for simple inflammation from the bite (or as people say, pip). However, despite this, the ulcer does not heal. Usually the ulcers are small, no more than 1 cm, but during the course of the disease they can grow.
- Compaction of part of the tongue. This symptom is detected by palpation and examination by a dentist. Part of the tongue becomes hard to the touch and loses sensitivity. The mucous membrane in this area may become thinner.
- Pungent odor from the mouth. If the disease is at a fairly advanced stage, tissue death occurs in the place where the cancerous tumor (ulcer) is located. In this case, the smell from the mouth is even more than unpleasant.
- Difficulty opening the mouth. If the cancerous node is located on the back, this will especially make it difficult to speak, swallow food, saliva, and generally manipulate the tongue and jaw in any way. Cancer, as is known, promotes the growth of metastases to other organs of the body, and the throat, palate, and lymph nodes may also suffer. Muscles, skin, teeth are destroyed.
- Difficulty eating. The tumor can reach a large size, cause tissue swelling, as well as painful sensations when swallowing. At an advanced stage, eating becomes completely impossible.
- Swelling of the neck and face. This is a sign of tissue swelling, inflammatory processes provoked by cancer cells. Lymph nodes in the neck area may also become hard and painful.
Prevention of inflammation of the floor of the mouth
To prevent diseases of the sublingual area, dentists give recommendations on proper oral care:
- take care of your gums;
- avoid the accumulation of bacterial plaque;
- visit the dentist 2 times a year;
- prevent the occurrence of caries;
- brush your teeth 2 times a day.
But if the patient has congenital or acquired anomalies in the development of the floor of the oral cavity, such as a shortened frenulum or structural asymmetry, then you will have to be more careful to prevent injury. Some abnormalities can be treated. Come to an appointment at Family Dentistry and experienced specialists will tell you how to get rid of defects, tumors and inflammations.
Course of the disease
The disease may have different symptoms, but the progression of the disease is always approximately the same. There are three stages during the course of the disease:
- Initial stage. It can occur in three different forms: ulcerative, nodular and papillary. The ulcerative form is more common than others and proceeds more slowly. The nodular form manifests itself in the form of compactions on the body of the tongue, the so-called cancerous nodules. The papillary form is characterized by the presence of outgrowths on the tongue. They are usually dense and light in color. The initial stage is sometimes completely asymptomatic and may be accompanied by the appearance of light spots on the tongue, which can be confused with plaque, thickening or redness. The lymph nodes under the jaw may become enlarged and sometimes become painful when touched.
- Stage of cancer development. At this stage, numerous symptoms begin to appear, such as intense pain radiating to the temporal region and ears, bad breath, and drooling. There may be no pain even with a fairly large tumor. They manifest themselves individually. Ulcers can be either flat or in the form of cracks. The crevice form of the tumor, as a rule, has a more malignant nature. At the same stage, there is difficulty swallowing, partial numbness of the tissues of the tongue, a sore throat, as with a sore throat, the inability to clearly pronounce sounds, and the tongue may bleed.
- Advanced stage of cancer. At this stage, the cancer has already spread sufficiently and has begun to actively destroy nearby tissues. Cancer of the rear part of the organ is more malignant than cancer of the front part, and it is much more difficult to cure. Cancer cells multiply quickly, and there are distant metastases in the bones, brain, and lungs.
In some cases, the disease progresses quickly; tongue cancer is generally characterized by rapid growth, so it is important to undergo a timely examination, make a correct diagnosis and begin treatment. The earlier the disease is detected, the greater the chances of achieving a positive result. Moreover, you should not diagnose yourself via the Internet by comparing yourself with pictures. It is better to trust a professional; only he can make a correct and accurate diagnosis.
Often tongue cancer is preceded by various diseases that cause thinning of the mucous membrane, such as leukokeratoses, ulcers, fissures, hemangiomas.
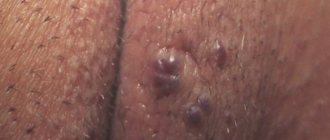
Cyst (wound)
A cyst under the tongue appears as a growth in the form of a ball with liquid inside. It is localized on the tip of the tongue, in the sublingual area and on the root. Most often, a cyst forms in the area of the frenulum of the tongue.
The cyst progresses slowly, but as its size increases, it causes a sensation of a foreign body in the oral cavity; there is no pain. A large growth is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- swelling of the lower jaw;
- rupture of the growth shell.
In case of the first manifestations, it is necessary to seek the help of a doctor, since ranula can become infected and cause complications of the following nature:
- displacement ;
- disorder ;
- breathing and swallowing problems
- development of an abscess.
The cyst itself is not dangerous, but additional research is required to establish a diagnosis.
Diagnostics
In the early stages, the disease is difficult to detect, since the lump is small and does not show symptoms. A preliminary diagnosis is established based on the patient's complaints and visible signs. The doctor carefully examines the tumor to determine its characteristics.
For confirmation, a histological examination is prescribed. To do this, cells from the tissue of the cone are collected with a special instrument, and then the sample is sent to the laboratory.
In some cases, consultation with other specialists, such as an oncologist, may be necessary.
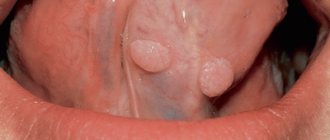
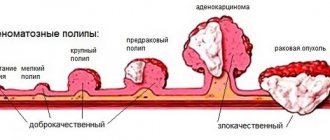
Polyp
A benign neoplasm of a flat or convex shape that grows over the mucous membrane of the root of the tongue. Formed from areas of ectopic gastric mucosa.
Unlike other tumors, tongue polyps are quite rare and appear as a lump on the base of the tongue. The polyp itself is painless. Discomfort occurs only in the event of an accidental injury or when a polyp grows.
The formation of such a lump does not exclude its ability to develop into a malignant tumor. As a rule, surgery is used to remove a polyp.
Lymphangioma
Lymphangioma is a congenital benign tumor localized in the lymph nodes. The tumor can affect either one side or the entire tongue. In this case, the organ takes on an enlarged shape, which makes it difficult to close the mouth.
Such a disorder causes the formation of small bubbles on the cavity of the tongue, which can grow at high speed.
The main causes are considered to be:
- congenital pathology;
- infectious diseases;
- hereditary factor;
- previous surgical operations;
- the presence of other neoplasms of any form.
Signs of the disease:
- bubbles of different sizes with a glassy surface;
- opening and bleeding due to injury;
- white coating on the mucous membrane of the tongue;
- malocclusion ;
- disorder .
The presence of signs indicates immediate treatment, which involves complete removal of the tumor. Minimally invasive methods are considered effective removal methods.
What is a blood blister on the tongue?
What does it look like?
It is an accumulation of coagulated blood in an organic cavity under the mucous membrane
A blood blister is also called a hematoma, blood blister, or lump.
It is an accumulation of coagulated blood in an organic cavity under the mucous membrane.
On the tongue, a hematoma looks like a swelling, the color of the tongue changes and becomes bluish, and swelling appears.
The patient feels pain and discomfort while eating and talking.
In addition, pinpoint hemorrhages are often observed on the mucous membrane.
The appearance of bloody bumps is a kind of hemorrhage that occurs as a result of injury to the capillaries and thin vessels of the oral mucosa.
Inside the bladder there may be a clear serous fluid without blood impurities, which indicates that the vessels are not intact and have not been damaged. Such hematomas are superficial in nature and the healing process occurs very quickly.
If a hematoma on the tongue contains blood inside, then the injury is deep and its healing period will be much longer until the blood resolves.
How does a blood blister form?
At the moment of microtrauma, harmful microorganisms begin to attack the damaged area
Bloody blisters in the mouth often do not pose a serious threat to human health.
They arise as a result of mechanical damage to the mucosa.
At the moment of microtrauma, harmful microorganisms begin to attack the damaged area.
To destroy them in the body, immune forces begin to activate.
Leukocytes and monocytes, macrophages are immediately sent to the injured area, which suppress the vital activity of microbes and eliminate them.
Important! Considering that a blood lump in the mouth is only part of the body’s defense reaction, it goes away quite independently after 7 days. If this does not happen, then it is recommended to visit a qualified specialist who can establish the correct diagnosis and prescribe the appropriate treatment regimen. This measure is necessary to exclude serious diseases in the body and neoplasms.
The level of health of the body is assessed according to the general condition and integrity of the oral mucosa, and only upon examination can a final diagnosis be made.
Since the clinical manifestations of many pathological conditions, including infectious, chronic, bacterial, occur along with a change in the color and integrity of the oral mucosa (tongue, gums). Here it is important to identify the true cause of the blood ball.
Localization
Appearing hematomas indicate microtrauma that has occurred.
Blood blisters are distinguished by their location. They can be on the surface of the tongue, under it and on the cheeks.
The appearance of hematomas indicates that microtrauma has occurred or the presence of a serious pathological condition.
A large number of blisters on the oral mucosa, filled with blood, can form due to diseases of the gastrointestinal canal, dental problems, and disturbances in the functioning of the endocrine system.
So, with stomatitis, blisters and ulcers appear on the mucous membrane of the cheeks, on the gums, and on the palate, as well as on the tongue.
With syphilis, blood bumps are located on the tip, back of the tongue or on its lateral surfaces. With tuberculosis, hematomas are localized on the tongue, lips, cheeks, gums, and palate.
Lipoma
Lipoma (wen), a benign connective tissue fatty tumor. The fatty tissue is located on the mucous membrane of the tongue. Divided into two types:
- Patchwork. Flat in shape, has the ability to grow deep into tissues.
- Vulgar. Normal bulge on the tongue.
Lipoma is a soft lump that is completely painless. Slow growth and small size do not cause discomfort in humans. The reasons for education are:
- Heredity.
- Injuries.
- Metabolic disease .
- Unfavorable environmental conditions.
- Bad habits.
If such a formation appears in the mouth, you need to consult a dentist to diagnose the disease.