Causes of growths under the tongue
Formations on the tissues of the tongue and oral mucosa appear when the growth mechanism of epithelial cells fails. This process is provoked mainly by condylomatosis or the so-called papilloma virus. The disease is considered insidious due to hidden symptoms at an early stage of development, which complicates early diagnosis. In addition, it is contagious, the virus is transmitted even through kisses and shared household items, not to mention closer contacts of partners (sex of different types).
Children can become infected with condylomatosis at birth from an infected mother, therefore, when the disease is detected in a pregnant woman, it is recommended to allow labor by cesarean section.
Types of benign tumors of the tongue
Papilloma
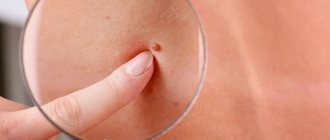
Focal skin growth caused by activation of the human papillomavirus in the body. The virus is transmitted when the tongue comes into contact with the mucous membrane or skin of an infected person. In the rarest cases, transmission of the virus occurs through household contact. The virus can remain dormant for a long time and appear when the immune system is weakened.
Externally, papillomas look like small pink, flesh-colored or white papillae of various shapes. Their size usually does not exceed two centimeters. You can detect these tumors yourself. They are usually localized on the back, surface and tip of the tongue. These small tumors pose a serious threat to human health because they are very often damaged and susceptible to malignancy.
Adenoma
The occurrence of this tumor is caused by the proliferation of glandular epithelium. As a rule, neoplasms are single. The following types of tongue adenoma are distinguished:
- polymorphic;
- basal cell;
- canalicular;
- sebaceous;
- adenolymphomas;
- monoform.
The pathology is usually accompanied by the formation of polyps on the tip of the tongue.
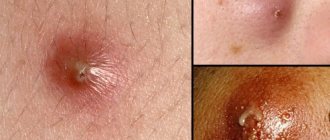
Botriomyxoma
A benign tumor of the tongue, the occurrence of which is caused by traumatic injuries - burns, cuts, injections. A couple of months after the injury, a red tumor-like formation with a lobulated or smooth surface may appear in its place. Botriomyxoma has a dense elastic consistency, sits on a stalk, and with minor damage begins to bleed.
Fibroma
A neoplasm that is formed from connective tissues covered with mucous membrane. Usually appears as small nodules, but can also look like branched polyps. The main causes of the disease are traumatic and inflammatory processes in the oral cavity. Most often, a tumor forms against the background of advanced inflammatory dental diseases - stomatitis, glossitis, periodontitis, gingivitis.
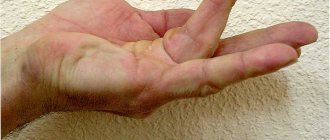
Retention cyst
The tumor occurs due to problems with the outflow of secretion from the gland, which causes blockage of the duct. Because of this, the secretion gradually accumulates in the gland, stretches it and fills it with new contents. This type of tumor is removed surgically.
Lipoma
A tumor that is predominantly localized in the back of the tongue. A lipoma forms in the submucosal layer of the tongue and has a soft and elastic consistency. Often the process of lipoma formation occurs without symptoms, so diagnosing it at an early stage is extremely difficult.
Myoma
A tumor in the tongue that occurs due to the growth of muscle tissue. Myoma has a fairly dense consistency, is covered with a mucous membrane, and small papillary outgrowths can form on it. This tumor usually reaches a centimeter in size.
Neurofibroma
A tumor develops from the sheaths of peripheral nerves. Doctors associate its formation with a defect of the facial or trigeminal nerve. This tumor is extremely rare.
Hemangioma
This is a vascular neoplasm that occurs in the tissues of blood vessels. The tumor is benign - it grows quite slowly and does not penetrate other organs. However, hemangioma is completely unpredictable, as it can suddenly increase in size and begin to interfere with the functioning of the tongue. Depending on the structure of the tumor, it can be of two types: simple (looks like a tangle of capillaries located on the mucous membrane of the tongue) and cavernous (a tangle of large vessels under the mucous membrane of the tongue).
Lymphangioma
The tumor usually grows in the walls of the lymphatic vessels, which then leads to a significant increase in the size of the tongue. Tumors often form on the tip of the tongue and its surface.
Struma of the tongue
A congenital pathology that occurs due to a violation of the location of fragments of the thyroid gland. It looks like a small organic node. After surgical removal of the tumor, the prognosis for the patient is favorable.
Symptoms
You can recognize a problem in the oral cavity by the following signs:
- seals, tubercles, small antennae or outgrowths form under the tongue, which are clearly visible upon visual inspection;
- the shape of the formation is filamentous or elliptical;
- the texture is soft and smooth, no peeling is observed;
- the color of the growth may be the same as the mucous membrane, or have a reddish, whitish tint;
- the formation is 2-20 mm in diameter.
What could be the cause of the problem?
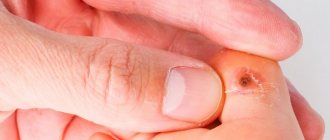
- Damage to the frenulum. This is a common cause of the problem. The mucous membrane is very vulnerable. There is a very delicate structure here that can be damaged during hygiene procedures or eating. If you have a shortened frenulum, then it can be injured while talking or eating. In childhood, stomatitis often occurs, which is accompanied by erosion throughout the entire oral cavity. This can also cause swelling in the mouth;
- Acute sore throat can cause inflammation of the area under the tongue;
- Teeth with caries are a source of infections. As a result, the mucous membrane may be affected; the area under the tongue is no exception;
- Formation of phlegmon or abscess. Swelling under the tongue is associated with purulent inflammation. This is a very dangerous disease that requires immediate specialist intervention. Cellulitis develops due to untreated periodontitis or periostitis;
- Inflammatory process of the salivary gland;
- Anomalies in the development of the hyoid bone or mechanical trauma that made its shape asymmetrical;
- Allergic reaction to irritants;
- Mechanical injury to muscle fibers, nerve endings, and blood vessels located in the oral cavity.
During treatment, you cannot do without consulting a doctor, as self-medication can lead to unpleasant consequences. It is necessary to choose medications taking into account the cause of the problem. Otherwise, it will be possible to remove only the consequence, which means that after a while it will make itself felt again.
At the first manifestations of negative sensations, you can independently check the oral cavity for the presence of ulcers, plaque, abscesses, pus and rashes. This way you will roughly understand what the problem is and how to solve it.
External manifestations (+photo)
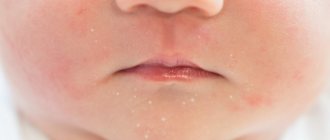
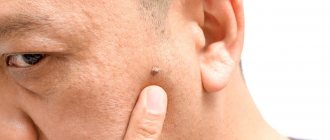
Growths under the tongue in humans form in the form of warts, papillomas, and condylomas. All varieties are signs of the presence of VPI in the body. Their differences lie in the type of epithelium and external manifestation. Papillomas can be either protruding above the surface of the mucous membrane or flat with rough tissue. And condylomas always rise above the surface of the skin or mucous membrane with the help of a fairly high stalk.
Types of growths under the tongue:
Depending on the type and causes of formation, condylomas come in different colors:
- red;
- white;
- light with a yellow tint;
- pink;
- gray;
- from light to dark brown.
Growths in the oral cavity are most often localized in the following areas:
- on the mucous membrane under the tongue;
- on the bridle;
- on the gum under the tongue;
- on the inside of the tongue;
- along the rim of the tongue and other areas of the mucous membrane.
Reasons for the appearance of a lump
A tumor can appear for various reasons. If the pain is not severe, temporary, and goes away on its own within a day, there is nothing to worry about. And when the appearance of a growth causes significant discomfort and lasts for several days, you should be alarmed. A growth under the tongue near the frenulum can be caused by the following factors:
- Condylomatosis, that is, papilloma virus. In this situation, the cell growth mechanism is disrupted. The early phases of the disease have no obvious symptoms. The virus is actively transmitted through household and sexual contact, especially with weak immunity. The nature of warts is such that they act selectively. HPV is distinguished by genotypes. There are benign and life-threatening strains. Warts may rise above the muscular organ. Keratin, which is produced in such cells, gives the balls rigidity.
- Inflammation often appears when the frenulum is short from birth. It is better to correct the problem in childhood.
- The process of inflammation appears with vitamin deficiency, gastrointestinal diseases, allergies, abscesses in the oral cavity, and injuries.
- A pimple on the frenulum under the tongue is formed during tonsillitis, when streptococci and staphylococci are activated and the lymph nodes are affected.
- The problem occurs when the salivary duct is blocked. Mineral or mucus plugs can become an obstacle. This interferes with patency. In this situation, a ranula is formed, which contains liquid exudate. The bubble may be clear or cloudy. It can burst, then build up again. Provoking factors include stomatitis, herpes, candidiasis, and lichen planus.
Since the mucous tissues of the oral cavity are sensitive, they can be damaged by hot food or drink. In the burn area, bacterial microflora feels comfortable, which contributes to the formation of salivary plugs in the ducts.
Diagnostics
Examination by an otolaryngologist
If characteristic growths are detected in the oral cavity, you should contact one of the recommended specialists (depending on the location of the focal zone):
- dentist;
- otolaryngologist;
- dermatovenerologist.
It would also be a good idea to visit an oncologist to rule out the possibility of developing a tumor of malignant origin.
Diagnosis of condylomatosis and other diseases associated with the formation of growths under the tongue consists of the following steps:
- visual examination by a doctor;
- taking anamnesis;
- laboratory research;
- histology.
Which doctor should I contact?
If a lump appears under the tongue on the frenulum, you need to find out what factors provoked its formation. Only a doctor can correctly determine the cause. After all, the ball can be filled with liquid or consist of epithelial cells. The degree of discomfort depends on the size of the formation. When papillomas are soft, the patient may not feel them, but large inflammatory growths interfere and begin to hurt. Contact your doctor if you experience any of the following symptoms:
- The mucous tissues of the oral cavity constantly dry out;
- The deficiency of saliva and its composition is clearly expressed;
- The taste sensations have changed a lot;
- Increasing pain appeared;
- Swelling on the face increases;
The affected tissue around the lesion may become red and begin to bleed. First of all, you should consult with your local therapist. To confirm the suspected diagnosis, it is most often necessary to visit a dermatologist, dentist, otolaryngologist, venereologist, or gastroenterologist. If the need arises, the patient is referred to a surgeon or oncologist. During the examination, the doctor collects anamnesis, conducts a thorough examination, and performs laboratory diagnostics and histology. In complex cases with abscesses, patients are referred for ultrasound examination, as well as computed tomography. The pathogen is detected using a cytological analysis of saliva.
Types of processes
Most often, flat or pointed warts form in the oral cavity:
- Flat formations have a small protrusion above the mucous membrane and tissues, their shape is predominantly round. Condyloma differs in color from the general background in a brighter shade, so identifying it is quite simple. It is quite dense to the touch and is localized on the lower part of the tongue and oral mucosa.
Flat build-up
- Pointed papillomas form individually in the form of nodules or as a whole family, which makes them similar to cauliflower. They are moderately soft and elastic to the touch.
Pointed growth
Another type of growth is condylomas lata, which are localized not only on the tongue, but also on other parts of the oral mucosa. The reason for their appearance is syphilis.
Pain due to inflammation of the salivary glands
In cases where a person feels pain on both sides of the tongue, the cause may be inflammation of the sublingual salivary gland. It arises as a result of:
- Complications of another disease (inflammation of the tonsils, acute respiratory viral infections, anemia, vitamin deficiency, dental diseases);
- Insufficient hygiene;
- Obstruction of salivary flow caused by stones or pathogens.
The main symptoms indicating inflammation of the salivary gland:
- Dry mouth – it always seems like there is not enough saliva;
- Pain that is observed not only under the tongue, but also in the ear area;
- Redness of the mucous membrane, thickening or swelling under the tongue;
- Putrid taste.
If you observe such signs in yourself, you should immediately go to the dentist and undergo a course of therapy. Otherwise, an abscess may develop or the disease may become chronic.
If you have a problem similar to that described in this article, be sure to contact our specialists. Don't diagnose yourself!
Why you should call us now:
- We will answer all your questions in 3 minutes
- Free consultation
- The average work experience of doctors is 12 years
- Convenient location of clinics
Single contact phone number: +7
Make an appointment
Drug treatment
A mandatory part of treatment is sanitation of the oral cavity.
To eliminate growths under the tongue with condylomatosis, complex treatment is used, which includes:
- taking antiviral drugs;
- the use of antiseptic solutions and ointments for local treatment of the affected area;
- carrying out complete sanitation of the oral cavity at the dentist (treatment of caries, inflammation of dentin, and other problems);
- consumption of a vitamin complex to strengthen the body’s protective functions;
- taking immunomodulatory drugs;
- removal of growths using surgery, a laser beam or radio waves.
During the period of therapy, it is important to reconsider your usual lifestyle and make adjustments to it, getting rid of bad habits and casual relationships. To speed up the healing process, you need to avoid irritating the mucous membranes with hot or too cold drinks and dishes. Hygiene procedures should be carried out regularly, at least 2 times a day, using high-quality cleaning products.
Popular antiviral drugs include:
- Acyclovir (tablets);
- Panavir (solution for intravenous injection);
- Isoprinosine (tablets);
- Allokin-Alpha;
- Alpizarin (tablets).
The following are considered effective immunomodulators: Derinat, Likopid, Immunomax, Polyoxidonium.
For local impact on the lesion, the following means are used:
- Podophyllin;
- Cryopharma;
- Lapis pencil;
- Solcoderm;
- Verrukacid et al.
When using local preparations, you need to carefully read the instructions so that during the treatment of papillomas you do not burn healthy mucosal tissue.
Removal methods
There are several ways to remove growths under the tongue. In each individual case, the specialist selects the best option, taking into account the localization of the formation and the extent of the affected area. Whatever method is used, it is complemented by antiviral therapy to prevent relapses. Only an integrated approach, including taking medications, will help get rid of the problem in the oral cavity.
| Treatment of growths under the tongue | |
| Method name | Process description |
| Surgical removal | An effective way to remove growth by cutting it off from soft tissue using surgical instruments: scalpel, scissors, electric knife, conchot. Sutures are subsequently placed on the wound. |
| Cryodestruction | The growths are removed using liquid nitrogen. The method copes with the task, but this type of influence can provoke malignancy of the formation, that is, have the opposite effect. |
| Laser removal | The essence of the method is to cut off the growth with a laser beam. The advantages of the method: quick and effective elimination of formations, absence of pain for the patient and bleeding, which prevents infection. The likelihood of relapse is very low; after the procedure, the process of cell regeneration is stimulated. |
| Radio wave therapy | The method is low-traumatic and painless; the procedure does not even require the use of a local anesthetic. Removal of growths occurs under the influence of high frequency radio waves. The specialist directs them to the base of the growth and cuts off the affected tissue. The rehabilitation period lasts 7-10 days. |
| Electrocoagulation | This method efficiently and quickly removes pedunculated growths on the tongue. The essence of the method is to throw a loop of special fiber over the formation and apply high-frequency current to the material. The hot fiber cuts off the growth, simultaneously soldering the microvessels, which prevents bleeding and infection of the wound. Electrocoagulation prevents further development of the virus. At the site of the removed growth, a crust forms, which after some time comes off on its own. |
| Galvanocaustics | The location of the small growth is cauterized with platinum wire heated under the influence of current. The method is fast, eliminating bleeding and infection of the wound. |
What to do at home if a growth appears - folk methods
In addition to traditional treatment of growths under the tongue, many patients use traditional recipes. It is impossible to replace treatment with a completely unconventional method, but nothing prevents you from trying it.
Popular folk recipes for growths under the tongue:
- daily rubbing of the formations with garlic juice or applying cloves of spice;
- lubricating newly appeared growths with egg white;
- treating affected areas with castor oil (using cotton swabs);
- rinse the mouth twice a day with decoctions of medicinal herbs (medicinal chamomile, string, sage, echinacea, etc.);
- ingesting rosehip decoction, freshly squeezed potato or carrot juice.
Any infections and viruses developing in the body signal a decrease in immunity, so during the treatment period you should take care of taking fresh vegetables and fruits. A good vitamin complex is also suitable for these purposes.
Before using an unconventional approach, you should consult your doctor to rule out contraindications.
Preventive measures
Use mouthwash after meals.
Preventing the development of a disease is always easier than fighting harmful microorganisms and the results of their vital activity. To prevent the formation of growths in the oral cavity, the following measures are recommended:
- perform hygienic cleaning of the mouth at least 2 times a day;
- after eating, use a mouthwash;
- develop a diet so that it contains mainly fresh vegetables and fruits (to strengthen the immune system);
- regularly visit the dentist for preventive examinations;
- do not borrow other people’s household items (dishes, towels, cosmetics);
- undergo an annual examination with an oncologist;
- lead an active lifestyle (if you work sedentarily, include morning exercises and twice-a-day workouts on simulators in your daily routine).
Treatment
Having established the causes of inflammation of the tongue, the specialist prescribes treatment. In case of inflammation of the salivary glands, the purulent contents are initially removed, then antibacterial agents are injected into the ducts, and the patient is also prescribed antibiotics or sulfonamide drugs orally.
As a rule, therapy is accompanied by rinsing (in each case the doctor selects the optimal solution) and physiotherapy: UHF, Sollux and others. For fever and general malaise, paracetamol or ibuprofen is prescribed.
Surgical treatment methods are used extremely rarely. The operation is performed if there are stones in the duct and they cannot be removed in any other way.
If you experience unpleasant symptoms or discover inflammation or swelling under your tongue, do not look for what it might be. Go to a qualified dentist, he will examine the oral cavity, make a diagnosis, and prescribe adequate therapy. Perhaps pain in the sublingual space is a symptom of another serious disease and consultation with an appropriate specialist will be required.
Monitor the condition of your teeth and mucous membranes, visit the dentist regularly, promptly treat inflammation of the ENT organs and ARVI - such preventive measures will minimize the possibility of inflammation and pain.
HPV vaccinations
HPV vaccine
You can protect yourself from the formation of growths in the oral cavity by getting vaccinated against the papilloma virus. There are many different rumors around this vaccine, but they have no basis in terms of effectiveness.
The product contains substances of organic origin that promote the production of cells in the body that resist the development of condylomatosis.
Effective means are used for vaccination:
- Cervarix;
- Gardasil.
These vaccines are not used in the treatment process; they are intended solely for preventive purposes. The procedure must be performed before sexual activity begins; the maximum age of the patient is 26 years. When using the product at an older age, the effectiveness decreases significantly.
One vaccine protects the body from the papilloma virus for 8 years.
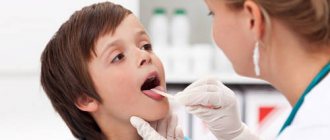
Features of child treatment
The treatment strategy for growths under the tongue in children includes two main stages: improving the immune system and eliminating formations in the mouth.
There are difficulties in selecting agents for local action on papillomas due to the constant contact of the drug with saliva. Therefore, the first recommendation for children is to change their usual toothpaste to a professional product that has a bactericidal effect.
When choosing antiviral drugs, the priority is not effectiveness, but safety. The ideal option is a drug that contains a combination of ascorbic and rutic acids (for example, Ascorutin). Recommended immunomodulators include: Amiksin, Viferon.
When determining the most suitable method for removing papillomas, the accuracy and speed of the procedure, as well as the low level of risks, are taken into account.