HPV occurs in men at approximately the same frequency as in women.
It is a mistake to believe that the fair sex, for some reason, becomes infected with the pathogen more often.
Infection occurs with the same frequency, it’s just that symptoms of the disease develop more often in women.
When patients see a dermatologist, they wonder what kind of disease it is, HPV, and what its features are.
How does the disease manifest itself, and how to get rid of it?
What kind of disease is this
HPV is a widely accepted abbreviation for the human papillomavirus.
The disease is easily transmitted from a sick patient to a healthy one.
It is distinguished by the ability to exist in the body for a long time without reminding itself of anything.
Actually, the last fact is the main feature of the virus.
It can live in a person’s body for years, and that person will not even suspect that he is infected.
Once in the body under a certain set of circumstances, the virus begins to negatively affect the processes of cell division.
As a result, small neoplasms appear on the skin and mucous membranes.
Most of them are benign.
Doctors draw patients' attention to the fact that the greatest danger is posed by pathological formations located on internal organs.
The virus is transmitted quite easily.
This explains its wide distribution in the human population.
Some varieties of the pathogen have oncogenic activity, but not all strains have it.
If infection occurs, the patient is advised to take control of the disease.
Today, unfortunately, it is impossible to completely get rid of the disease, but you can effectively take control of it.
To do this, it is enough to follow the doctor’s recommendations regarding the treatment of the pathogen.
It is worth remembering that the presence of even oncogenic strains in the body is in no way a death sentence or a reason to despair.
After all, there are effective ways to control the disease, which also help prevent the development of cancer.
Development and localization
To begin with, it is important to note that there are more than 600 strains of this virus. That is, there is not one diagnosis, one version of the consequences and one version of the manifestations. There are many different situations involving infection.
If the immune system is strong, it can easily cope with the virus on its own and within a few years “displace” it from the body. But at the same time, re-infection or illness with a different strain is also possible.
Papillomas and other symptoms of HPV in the form of formations that develop as a result of infection can appear in different places:
- on the skin anywhere;
- in the anogenital area;
- in the oral cavity, bronchi and upper respiratory tract;
- in the rectum, etc.
Formations can grow and form entire groups, or they can gradually dry out and disappear - it all depends on the specific situation.
Infection options
Human papillomavirus in patients is naturally associated with sexually transmitted diseases.
There is nothing surprising.
After all, the main way the virus spreads is sexually.
In sexual transmission, the pathogen is found in semen in men and in vaginal secretions in women.
Naturally, if you ignore basic recommendations for protected sex, it turns out to be quite easy to become infected.
A single sexual contact is enough.
Doctors emphasize that the pathogen can spread not only through classic sexual contact.
Infection can also occur if partners have unprotected anal or oral contact.
After all, the microorganism can infect not only the mucous membranes of the genital tract, but also the mucous membranes of the oropharynx and anus.
However, HPV can be transmitted from person to person not only through sexual contact.
A man can easily become infected through contact and household contact.
This happens if shared washcloths, towels, toothbrushes and other hygiene items are used, which normally should be exclusively individual.
The microorganism survives well in the environment, and therefore contact and household spread is not excluded.
HPV can also be passed from mother to child during childbirth.
The likelihood of virus penetration transplacentally is minimal.
But passing through an infected birth canal will inevitably introduce infection into the child’s body.
Moreover, not only a little girl, but also a boy can become infected.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of human papillomavirus includes a doctor’s examination, enzyme-linked immunosorbent test, PCR diagnostics, as well as special tests to determine the oncogenicity of the strain. Women undergo a Pap test, that is, a cytological examination, for which a smear is taken from the vagina. A colposcopy is required - a thorough examination of the cervix using a special device.
Varieties
Doctors have developed several classifications of the virus that help navigate all its diversity.
To date, more than 100 strains are known, differing from each other in oncogenicity and a number of other indicators.
HPV classification makes the doctor's work easier.
First of all, viruses are divided into groups:
- low risk, provoking pathological tissue degeneration in exceptional cases
- medium risk, which can, under certain circumstances, lead to the development of oncological processes
- high risk, differing ability to cause cancer in a significant number of cases
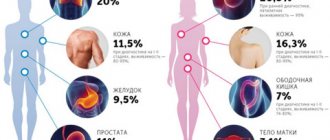
HPV 18 in men, along with strain 18, poses the greatest oncological danger, causing tumors in 85% of cases.
In addition to the risk of oncogenicity, it is customary to classify the disease based on the severity of symptoms.
There are:
- latent form, characterized by the presence of the virus in the body, but the absence of symptoms of its manifestation
- subclinical form, characterized by vague symptoms
- clinical form with typical symptoms, characterized by the ability to greatly reduce the patient’s quality of life
Most often in medical practice, the latent form of the disease occurs.
Vivid clinical symptoms are in most cases a consequence of an exacerbation of the disease, provoked by external factors.
HPV strains
There are strains of the virus that have a high oncogenic potential. They are designated by numbers 16, 18, 39, 45, 56, 68, 73 and 82. There are also options with medium (26, 31, 33, 35, 51, 52, 53, 58 and 66) and low (6.11, 40, 42, 43, 44, 54, 61, 70, 72, 81) oncogenicity. Cervical cancer is most often associated with infection with strains 16 and 18, therefore, when such a virus is detected, maximum monitoring of the patient’s condition is required.
Important clarification! Highly oncogenic viruses detected in the body do not mean that a person will necessarily have cancer. This increases the risk of developing cancer, but is not a 100% determining cause. Moreover, oncology is usually preceded by so-called precancerous conditions. With regular monitoring, doctors have a very high chance of “catching” the disease at an early stage and preventing it from developing into cancer. And cancer itself at the first stage is treated quite successfully. If you have been diagnosed with a virus, do not panic - with proper control, this is not a death sentence for your health and life.
How to get rid of HPV
So far, scientists have not been able to develop HPV treatment that would be aimed specifically at eliminating the papillomavirus infection. Official medical guidelines point to destructive methods of destroying external manifestations of the virus - cryodestruction, radiodestruction, electrocoagulation, laser destruction. If the disease is cyclical, it is necessary to repeat the destruction of genital warts, while simultaneously taking nonspecific antiviral drugs.
Chemical destructive methods involve the use of a 1.5% solution of zinc chloropropionate, a combination of several acids and a copper nitrate trihydrate solution, which is applied to the affected area.
In order to strengthen mucosal immunity, the patient takes immunomodulatory drugs.
Where to go for diagnosis and treatment of HPV
The doctor’s specialization depends on the location of warts, papillomas and other formations:
- It is necessary to contact an obstetrician-gynecologist during pregnancy to diagnose dysplastic and underlying diseases of the genital organs.
- If genital warts occur inside the urethra, you need to make an appointment with a urologist, if in the anus - with a coloproctologist.
- You should contact an oncologist and surgeon if you have Buschke-Levenshtein condyloma.
- If the patient has an immunodeficiency or the disease is recurrent, a consultation with an allergist-immunologist is necessary.
Diagnostic measures
Early detection of HPV type 16 infection is only possible using molecular diagnostics.
It allows you to establish unique DNA sequences that are unique to the desired papillomaviruses.
For this, three types of techniques are used:
- non-amplification
- amplification (PCR)
- signal amplification (hybrid trap system - Digene Hybrid Capture System II)
Tests of the first type are not used in practical medicine due to the high cost and complexity of their implementation.
Amplification methods, among which PCR is the most studied, are used quite widely and are well studied.
Allows you to establish the fact of infection with HPV 16.
They detect viruses of other types (it is quite possible to become infected with several representatives of papillomaviruses at the same time).
The real-time PCR technique also determines the DNA concentration of oncogenic viruses.
This indicator has important prognostic value in dynamics.
Initially large numbers at the start of treatment should gradually fall under the influence of special therapy.
And completely disappear after any destructive treatment or surgery.
If the concentration of viral DNA in the diagnostic material is initially low, the doctor may recommend a wait-and-see approach.
Sometimes there is a 20% chance that HPV type 16 with a low DNA concentration will spontaneously clear from the lesion.
Digene (or Daijin test) differs from PCR in its unprecedented accuracy and high speed of testing (within one day).
Daijin also allows you to perform a quantitative analysis (calculate the concentration) of viral DNA.
The only thing holding us back from introducing this technique into widespread clinical practice is the significant cost of research.
To conduct such rather complex and high-tech tests, a man should contact doctors with access to modern laboratory centers.
The use of oncocytology, the most well-known method for diagnosing tumor processes, is justified only for developing treatment tactics for a man.
The method allows you to determine whether the tumor cells have degenerated into a malignant process or whether the papilloma still remains benign.
This information, provided by oncocytological examination of a tissue sample from a suspicious lesion, is decisive for the development of treatment tactics.
An immunogram in its classical concept is of little value for diagnosing HPV type 16 infection in men.
With its help, you can only establish the approximate duration of infection - based on the types of immunoglobulins identified.
IgA and IgM are detected with recent infection, and IgG - when infection is several months old.
If you ignore HPV 16 in men: complications
If a man ignores the initially benign process caused by HPV 16, then very serious consequences are expected.
Oncology – it’s better not to joke with it.
The surface of the papilloma begins to peel off (on the skin) or transforms into an ulcer (on the skin and mucous membranes).
The process begins to actively increase in size.
It spreads to adjacent areas of the penis and scrotum, grows deeper into the organs, and begins to bleed.
Already at this stage, erection, ejaculation, and therefore conception and pregnancy become painful or impossible.
During the first 3-6 months, in 50% of men, regional lymph nodes are affected by metastases.
After 10-12 months, there is an almost 100% guarantee that metastasis will occur in other pelvic organs.
If you respond in time, the initial stages of squamous cell carcinoma can be eliminated with high efficiency.
Only the volume of surgical intervention will be required much more extensive than when removing a benign papilloma.
These are removal of the penis, castration, pelvic lymphadenectomy and others.
Chemotherapy will also be different; you will have to use drugs with very pronounced side reactions.
Naturally, this will require treatment from an oncologist in a surgical hospital.
Is human papillomavirus (HPV) a sexually transmitted disease?
HPV can be deciphered as a virus that causes a benign tumor of epithelial origin in the form of a papilla. Papilloma is classified as a sexually transmitted disease (STD). Unfortunately, today this concept has expanded significantly. If previously only a few, as it seemed then, “frightening” classical diseases of Venus were known, which in fact are easily treated and detected quickly (gonorrhea, syphilis, trichomoniasis, chancroid), today the list of STDs includes many dangerous, severe detectable, and sometimes difficult to treat and completely incurable (HIV) diseases. Moreover, their number is constantly growing.
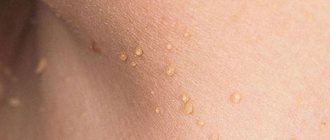
Today, the list of “new” STDs includes mycoplasmosis, chlamydia, gardnerellosis, ureaplasmosis, candidiasis, genital herpes and human papillomavirus. Growths from papillomavirus identified in the genital or perianal areas are called genital warts. In fact, both condyloma and papillomavirus are the same virus, just different strains (varieties).
Genital condylomas in the perineal area can appear either one at a time or as whole growths that look similar to cauliflower. In some cases, such formations cause itching, irritation when touched, and bleeding.
Laryngeal papillomatosis
You can also distinguish papillomatosis of the respiratory tract. With this disease, the tissue that lines the nasopharynx grows from the nose to the lungs. The larynx is also often affected. Respiratory tract papillomatosis is also a type of disease caused by the papilloma virus. In this case, formations are classified as benign. Local and ENT doctors cannot always identify this disease. More often they simply shrug their shoulders and prescribe rinses. In this regard, we recommend that you contact a private clinic.
For whom is the papilloma virus most dangerous?
The constant occurrence, disappearance, and then recurrence of condylomas and papillomas are due to the fact that they are manifestations of a viral infection, and their presence is influenced by the state of the immune system. Those who smoke, abuse alcohol or are promiscuous are more likely to become infected.
Women who have been using oral contraceptives (COCs) for a long period of time are also at risk of contracting the virus. As for age, it does not affect the likelihood of infection: both a young and a mature woman can catch the virus with equal ease.
The risk of infection seriously increases if the body has suffered internal stress, regardless of its origin: a person has had the flu or ARVI, gastrointestinal problems have worsened, the body has had a hard time with prolonged medication use - all this leads to a weakening of the body’s defenses, and therefore to papillomavirus .
Close contact, a long stay near a person carrying the virus, swimming in a “contaminated” pool or shower in a public bath, even a simple walk on the beach - this is enough for the virus to enter the body in case of weakened immunity. It is easiest to catch the papilloma virus in hot weather and high humidity, when the skin is not covered in clothing. In this case, the pathogen quickly finds refuge on the hot skin.
Treatment
Treatment of HPV does not imply the presence of any specific program that would completely destroy the pathogen. But patients are prescribed therapy that helps strengthen the immune system and self-heal. The assignments come down to several points:
- taking special medications. These are vitamins, antiviral medications and immunomodulators;
- removal of tumors. For this purpose, cryodestruction, laser, and electrocoagulation are used. Removal is possible using the classical surgical method;
- all kinds of strengthening of the immune system. A healthy lifestyle, giving up bad habits, giving up promiscuity - all this helps maintain immunity.
There are now vaccines for some types of HPV that are optimally used at 11-12 years of age (but can be used up to 26 years of age). Patients over 12 years of age are prescribed the vaccine if the doctor sees indications for this. The vaccine is not able to destroy the virus, but it can protect against other dangerous strains.