Why does pathology occur?
Stress factors for the development of the pathological process are a number of circumstances:
- injury to toes and hands;
- chemical exposure;
- lack of calcium and vitamins;
- wearing narrow and uncomfortable shoes;
- disruptions of the cardiovascular and endocrine systems;
- gastrointestinal diseases;
- unfavorable environmental conditions;
- decreased immune defense of the body;
- stress, depression;
- infectious diseases;
- fungal infections.
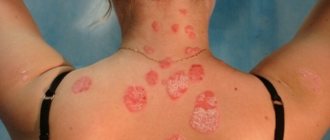
Separately, it is worth noting the fungus, which is a common cause of infection of the nail plate and its subsequent destruction. Fungal infections occur in public places such as baths, swimming pools, gyms, and dormitories. Manicures and pedicures in beauty salons and private practitioners are also a risk factor.
In addition, people who have to come into contact with soap solutions, sugars, antibiotics and dairy products for a long time are at risk of becoming infected with the fungus.
At CELT you can consult a dermatologist.
- Initial consultation – 3,500
- Repeated consultation – 2,300
Make an appointment
Reasons for development
Onychodystrophy can occur against the background of internal and external factors leading to changes in the course of trophic processes in the nails. The first include:
- chronic skin diseases, in particular eczema, atopic dermatitis, lichen planus, psoriasis;
- endocrine diseases, including diabetes mellitus, hypothyroidism, thyrotoxicosis;
- gastrointestinal pathologies, including gastritis, gastric ulcer;
- iron deficiency in the body and resulting anemia;
- decreased immunity due to a lack of vitamins, minerals, the presence of chronic diseases, immunodeficiencies;
- oncological diseases;
- intoxication;
- frequent stress;
- cardiovascular disorders.
However, more often onychodystrophy is caused by external factors, including:
- fungal and bacterial infections of nails;
- nail injuries, improper manicure;
- the influence of chemicals, including those contained in household chemicals, paints and varnishes, etc.;
- frequent exposure to ultraviolet rays on nails;
- living in unfavorable environmental conditions.
Therefore, onychodystrophy is most often diagnosed in women who regularly perform manicures, including in specialized manicure salons, and work with household chemicals without using gloves.
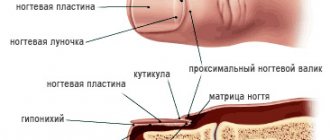
What's happening to your nails?
Experts distinguish three stages of development of the pathological process:
- Central (primary)
Small spots and streaks appear in the center of the nail plate, or on one of the sides.
- Second
The spots and streaks grow, the nail begins to peel.
- Dystrophic (third)
The nail plate is destroyed and cracks form. The surface of the nail exfoliates, and the inflammatory process of nearby epidermal tissue begins.
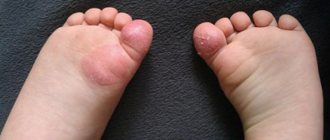
Onychodystrophy is differentiated by different types, and the symptoms of each of them have their own characteristic features:
- Psoriatic
The nail changes in color and thickness, and streaks and dots are observed under the nail plate.
- Onychorexi
A crack appears on the free edge of the nail, which, in the absence of treatment, rises to the root part of the plate.
- Onycholysis
The splitting of the nail starts from the outermost part of the nail and spreads over the entire surface in later stages.
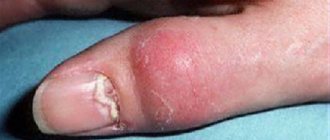
- Onychomadesis
If the hands and toes are injured, then pus accumulates under the nail, which subsequently causes it to peel off the entire nail plate.
- Koilonychia
The nail takes on a saucer shape, and noticeable dents form on the surface.
- Hapolonychia
The nail plate softens and becomes brittle.
- Onychogryphosis
The nail becomes thicker and becomes dull. The surface becomes rough and uneven.
- Scleronychia
The nail thickens and separates from the bed, acquires a brown or yellow tint, and also begins to grow more slowly.
- Trachyonychia
The top layer of the nail becomes rough, the shine is lost, and the plates peel off.
- Anonychia
A congenital disorder in which the nail is completely absent.
- Onychoschisis
A negative chemical or physical effect that causes transverse stripes to appear and the nail to take on a wavy shape.
Isolated acquired onychodystrophies
The category of isolated onychodystrophies includes those that occur independently without connection with other diseases. Most often they are the result of adverse mechanical, chemical and ultraviolet effects. These include increased fragility of nails, the formation of longitudinal grooves, onycholysis and others. In general, they cause only a cosmetic defect and do not pose a danger. To restore the health of the nails (with rare exceptions) in such situations, it is enough to eliminate the cause of the development of onychodystrophy.
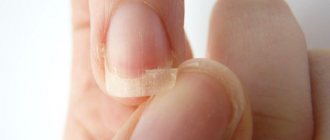
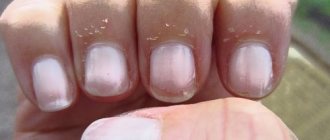
Brittle nails
Increased fragility of nails is the most common type of onychodystrophy, which consists in breaking off the free edge of the nail plate along the entire thickness. In most cases, women face a similar problem due to the depletion of their nails by frequent manicures, especially those carried out in violation of the rules, or frequent contact with hot water or chemicals.
Onychoschisis
This term means transverse separation of the nails without the occurrence of other disorders and signs of inflammation. With onychoschisis, the free edge of the nail splits into 2 or even 3 layers, and no changes are observed in the rest of it. Most often, the nail plates of the index, middle and ring fingers are affected, since they are the ones that are most injured in everyday life. In addition, an addiction to playing stringed musical instruments and improperly performed manicure can provoke splitting of nails.
Furrows Bo
Bo's groove is the formation of a transverse notch on the nail plate, which is a direct consequence of mechanical injury. This is also called manicure onychodystrophy, since the main cause of such dystrophy is a violation of the technique of removing gel polish with a cutter or injury from other manicure tools.
Longitudinal furrows
Longitudinal grooves are faintly defined individual or multiple lines on the surface of the nails, which can be present both in cases of dysfunction of the matrix and in healthy people. The main reason for the formation of longitudinal furrows is considered to be zinc deficiency in the body, which most often affects adherents of a vegetarian diet. Although such a nail defect can also be a consequence of:
- careless manicure with severe injury to the cuticle, which often occurs when the manicure is cut too deep;
- matrix damage;
- decreased immunity due to certain reasons;
- frequent stress.
Onycholysis
Onycholysis is a common type of onychodystrophy, in which there is detachment of part of the nail plate from the bed. As a result, the separated part of the nail may become paler with a grayish tint, although the surface itself remains smooth and has a normal structure. However, when a bacterial or fungal infection is attached, it becomes rough, lumpy, and may thicken and become brittle.
Onycholysis can be a consequence of a variety of factors:
- mechanical trauma or prolonged compression of the nail;
- chronic dermatoses, pathologies of the endocrine, nervous, cardiovascular systems and gastrointestinal tract;
- taking antibiotics, in particular the group of tetracyclines and fluoroquinolones;
- a diet poor in vitamins and minerals, leading to the development of hypovitaminosis;
- use of low quality varnishes for manicure;
- behavioral disorders in the form of the habit of biting and breaking nails, including using various devices.
Onychogryphosis
Onychogryphosis is an onychodystrophy, accompanied by a sharp thickening of the nail plate, a change in their color to dirty yellow or even brown and twisting into a spiral or in the form of a horn. The reasons for the development of this type of disease are still unknown, although it is believed that both exogenous and endogenous factors are simultaneously involved in its occurrence. These may include nail injuries, frostbite, infections, wearing uncomfortable, too-tight shoes, chronic skin diseases, immunodeficiencies, age-related hormonal changes, and even varicose veins of the lower extremities.
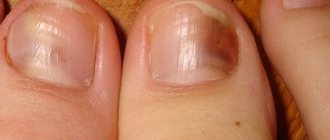
Leukonychia
Leukonychia is one of the most common types of onychodystrophy, which is characterized by the appearance of white spots and stripes of various sizes in the thickness of the nail. Depending on the characteristics of nail damage, the following forms of leukonychia are distinguished:
- dotted or stripe-shaped - white spots that appear in the thickness of the nail move along with the nail and are subsequently cut off and do not form in the future;
- subtotal - white spots are persistent and occupy a significant part of the nail plate;
- total – almost the entire surface of the nail becomes white, the changes are permanent.
There are many reasons for the development of leukonychia. Most often it occurs against the background of a deficiency in the body of vitamins and minerals, in particular calcium, zinc and potassium. White spots can also be caused by violating the rules of manicure, using low-quality varnish, wearing shoes that are too tight, or frequent contact with chemical compounds.
Hyperpigmentation
Hyperpigmentation of nails is onychodystrophy, manifested by yellowing or browning of the nails over the entire surface or only part. This may occur when taking tetracycline and resorcinol when treating bacterial or other infections. In such cases they talk about drug-induced hyperpigmentation. But also a change in the color of the nails can occur with prolonged use of manicure varnishes, then chemical hyperpigmentation is diagnosed.
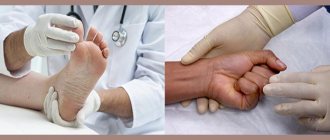
Diagnosis and treatment
Dermatologist
establishes a diagnosis based on the clinical manifestations of the disease, as well as studying the patient’s medical history. Diagnosis involves drawing blood to determine alkaline phosphatase activity.
In addition, methods such as:
- scraping from the nail plate to test for fungus;
- a detailed examination that allows you to track the dynamics and causes of changes in the skin and nails;
- confocal microscopy - examination of biomaterial under a microscope.
The doctor measures the distance from the nail root to the lesion to determine the onset of the disease. The conclusion will be based on the fact that the nail grows no more than 0.15 mm per day.
Treatment of onychodystrophy
requires a lot of time, sometimes therapy can take several years. To prevent the progression of the disease, it is necessary to seek medical advice at the first suspicious symptoms.
Complex therapy
includes taking medications and local application of medications, taking a complex of vitamins, performing medical manicure and pedicure procedures, as well as hand and foot massage to improve blood circulation, iontophoresis, the use of baths and compresses. Sometimes laser treatment of the nail plate is prescribed.
Make an appointment through the application or by calling +7 +7 We work every day:
- Monday—Friday: 8.00—20.00
- Saturday: 8.00–18.00
- Sunday is a day off
The nearest metro and MCC stations to the clinic:
- Highway of Enthusiasts or Perovo
- Partisan
- Enthusiast Highway
Driving directions
What to do in case of onychodystrophy?
Symptoms can be ambiguous, so if you detect the slightest deviation, contact a podologist or dermatologist. It is impossible to independently make a correct diagnosis, identify the type and causes of onychodystrophy based on reviews on forums on the Internet. Knowledge of medicine and understanding of the mechanisms of pathological changes are needed. Sometimes several variants of onychodystrophy are present at the same time, which makes diagnosis difficult.
First, the doctor will examine your nails. Assess the color, transparency, condition of the cuticle, shape of the plate, tightness of fit to the nail bed. Then he will ask about accompanying symptoms, lifestyle, work, nail care, and general diseases.
For onychodystrophy the following is prescribed:
- blood analysis;
- dermatoscopy (examination with magnification);
- scraping the affected area to examine for fungus.
In the presence of any type of onychodystrophy of the hands and feet, the affected areas are analyzed for fungus, since it causes 50% of all nail diseases. In case of doubtful results, the test is repeated 2–3 times at intervals to accurately verify the absence or presence of the pathogen. The treatment tactics depend on this analysis. When a fungal infection is confirmed, the emphasis is on fighting the pathogen; after its destruction, the nail plate itself will recover.
If the diagnosis of onychomycosis is made incorrectly, then medications against the fungus will not work, and the condition of the nail will not improve. In addition, unjustified therapy with fungicidal agents is harmful to health.
Treatment of nail onycholysis
Pathology requires complex therapy. The key task is to treat the underlying disease against which onycholysis of the nails develops. The allergic type of damage to the nail plate requires consultation of the patient with a nutritionist or gastroenterologist to adjust the functioning of the digestive system through diet. Correcting the imbalance of minerals and vitamins will reduce the likelihood of further progression of onycholysis.
The traumatic type of pathology involves daily removal of the growing tissue of the exfoliated area, followed by disinfection of the subungual space and protection of the bed with an antibacterial patch.
Large area detachments are treated surgically. After removing the nail plate, antibacterial and antiseptic dressings are applied to the bed. The operation allows surgeons to remove hyperkeratotic deposits, dirt and the consequences of hematoma development. Nail restoration is carried out using gelatin solutions of various concentrations.
Bacterial and mycotic lesions of the nail are treated with alcohol solutions of aniline paints, antibacterial and antifungal drugs.
Seeing a doctor
Detecting the first symptoms of onycholysis is a good reason to visit the clinic. Any stage of the disease requires consultation with a dermatologist. During the diagnosis and treatment of the disease, the patient may require the opinions of other specialists: an endocrinologist, a surgeon, a therapist.
Ignoring the symptoms of pathology can lead to multiple damage to the nail plates on the patient’s hands and feet, the formation of numerous foci of infection and damage to other tissues and systems of the body.
Are you experiencing symptoms of onycholysis?
Only a doctor can accurately diagnose the disease. Don't delay your consultation - call