Author
: Grachev Ilya Illarionovich
Editor
: Efremov Mikhail Mikhailovich
Date of publication: 09/24/2018 Date of update: 06/08/2020
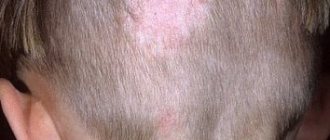
Regular psoriatic plaques can be seen not only on the elbows. No less often they are located on the skin of the anterior (extensor) surface of the knee joint. In some patients they remain unchanged for years, while in others they spread to neighboring and distant parts of the body. There are other manifestations of psoriasis on the legs. When should they be treated and is it worth doing if the disease does not progress? The answer to this question will be given by the specialists of the Paramita clinic.
What are mycosis and ringworm?
The content of the article
Fungi are the cause of many infections in humans and animals. Ringworm, also classified as mycoses, is a fairly common disease.
Among all mycoses, the most common is athlete's foot, which is estimated to account for 15-30% of all cases. Yeast infections (candidiasis) are also on the rise due to the widespread use of antibiotics, corticosteroids, immunosuppressants and the spread of immune-killing HIV infection.
Mycosis of the feet
Ringworm
Lichen planus
The term “lichen planus” was introduced in 1860 by the Austrian physician F. Gebra. Nine years later, English dermatologist E. Wilson first described this disease. But, despite the fact that the history of studying this disease goes back more than 100 years, there is no single theory about the causes of lichen planus.
Portrait of this skin disease
Lichen planus is a fairly common disease of the skin, mucous membranes and nails. Lichen planus can rarely be acute; subacute and chronic forms of the disease are more common.
In 20% of cases, the patient experiences relapses. The danger of lichen planus lies in the ability of its erosive-ulcerative foci to degenerate into squamous cell carcinoma.
Signs of lichen planus disease
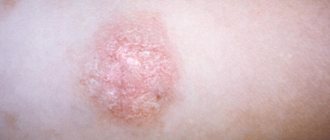
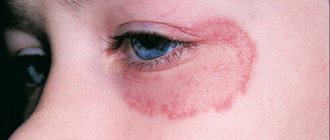
On the skin, lichen planus is characterized by a homogeneous rash consisting of small shiny reddish nodules with a purple tint with a small depression in the middle. In case of larger rashes, a mesh pattern of the rash becomes noticeable. The nodules can occur individually, can be arranged linearly, or can form plaques or rings.
The rash with lichen planus is sometimes accompanied by severe itching, and after the papules disappear, hyperpigmentation of the affected areas occurs.
Favorite habitats of lichen planus are the flexor surfaces of joints, forearms, anterior surfaces of the legs, and the sacral area.
On the mucous membranes, lichen planus often affects the mucous membranes of the mouth and genitals. It is expressed as whitish nodules and appears at the same level as the skin. Rashes on the mucous membranes are much more difficult to treat than on the skin.
Pits, longitudinal grooves, depressions, spots, splits appear on the nails
Causes of this skin disease
Lichen planus is one of those diseases whose causes have not yet been precisely elucidated by science. Among the causes that influence the occurrence of the disease are neurogenic, viral and infectious-allergic.
To date, information has been accumulated about hereditary predisposition to lichen planus, and the role of changes in the immune system characteristic of autoimmune processes has been proven.
Risk factors
Among the impulses that can serve to initiate the development of the disease are the following:
• age (35-60 years); • genetic predisposition; • diseases of the gastrointestinal tract; •diabetes; •stress; • injuries to the oral mucosa and the presence of various metals in it.
Symptoms of ringworm
Ringworm can affect smooth skin, scalp and nail beds. On smooth skin, round lesions are observed with large inflammation at the periphery.
Infection often occurs as a result of contact with animals, especially cats and dogs. Lesions are most often localized on exposed parts of the body - face, arms, neck, and also occur in the groin area. These changes are accompanied by constant itching, which is the most common reason for patients to visit a dermatologist.
How to recognize lichen in a child?
Since there are different types of the disease, differential diagnosis is carried out, usually including:
- examination of skin scrapings under a microscope;
- luminescent tests (characteristic fluorescence of affected areas);
- serological test (blood test for the presence of antibodies to the pathogen);
- bacterial culture for microflora;
- skin biopsy;
- examination under Wood's lamp;
- study of cell morphology, etc.
Under the guidance of a doctor, recovery occurs quite quickly, and compliance with all his recommendations minimizes the likelihood of relapse of the disease.
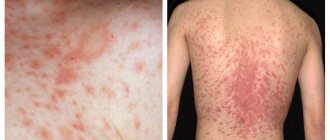
Various forms of lichen have similar clinical signs. Usually the first symptom of the disease is the appearance of a predominantly pink spot on the child's skin. Subsequently, the next spot appears on an adjacent area of skin, which can merge. In addition to the formation of spots, the infected skin begins to peel and itch; in some cases, the child’s body temperature rises and the lymph nodes become enlarged.
Among the most likely locations of lichen spots are:
- upper limbs;
- scalp;
- stomach;
- localization of sweat glands, etc.
Thrush is also a fungal infection
Characterized by inflammatory changes in the mucous membranes, skin and nails. Often accompanies:
- diabetes;
- gastrointestinal disorders;
- pregnancy;
- obesity;
- nutritional deficiencies;
- antibiotic therapy;
- AIDS;
- general cachexia;
- immunosuppressive treatment and corticosteroid treatment.
The development of these infections is facilitated by microtraumas and skin burns associated with getting wet or excessive sweating. Lesions on the mucous membranes resemble curdled milk and have the character of white spots. Then the mucous membranes show acute inflammation, accompanied by pain and burning.
The most common sites for thrush are the mouth, vulva, and vagina. Yeast infection is also the cause of jams - consisting of cracks with the formation of erosions in the corners of the mouth. They are usually bilateral and, if left untreated, can persist for a long time. Such changes cause pain when eating.
Thrush
Infection can occur at any age and is not associated with sexual intercourse (not sexually transmitted). Yeast lesions can occur in the folds - the armpits, groin, subjunctival and intermaxillary areas, as well as in the interdigital areas. In newborns and infants, yeast infections can occur as a result of diaper rash.
Mycosis of the feet
Fungal infection is a very common problem. Infection occurs through socks, shoes, wooden liners in bathtubs and swimming pools. Often found in athletes. In addition, athlete's foot is very common in people who work in very damp and warm environments, especially in rubber shoes.
The lesions are located in the interdigital spaces - between the fourth and fifth fingers and the third and fourth. However, they can spread to other toes. Skin peeling and cracks, sometimes painful, are diagnosed in the interdigital spaces. The changes are often accompanied by itching.
There is a certain genetic predisposition to interdigital mycosis, then these changes can be repeated for many years.
Onychomycosis
Onychomycosis is one of the most common infections. Patients often do not realize that changes in the color and structure of the nail beds are a symptom of infection. They often turn to a dermatologist too late, when large areas are affected.
Infection is promoted by: mechanical pressure, trauma and systemic diseases, such as diabetes.
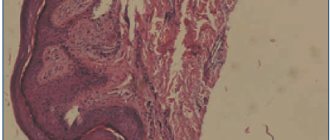
The first changes usually occur on the free edge of the nail plate or on the side of the lateral shafts. The plates become yellow-brown or greenish, brittle, gradually thicken, and delaminate. The diagnosis of mycosis must be confirmed by mycological examination.
Onychomycosis
How to cure lichen in a child?
In order to effectively get rid of lichen, you need to consult a doctor. Self-medication and uncontrolled use of medications and traditional medicine can significantly harm the child’s health, and contagious forms of the disease necessarily require ceasing contact with other children and isolating the child.
The duration and composition of the course of therapy depends on the type of pathology and its severity.
Typically, systemic antifungal drugs, local therapy with antimycotic gels/ointments, multivitamin complexes and immunomodulators are used to treat lichen of mycotic origin. After the course of treatment, a fungal test is performed (microscopic analysis for pathogenic fungi); a triple negative test serves as an indicator of complete recovery.
Lichen of viral etiology involves the use of antiviral agents and drugs to detoxify the body.
To reduce itching in pathologies of both fungal and viral origin, antihistamines and anti-inflammatory (corticosteroid ointments) drugs are effective.
Thus, for the treatment of pityriasis rosea, it is often sufficient to use UV therapy, follow a hypoallergenic diet (excluding animal protein) and wear clothes made from natural fabrics. To reduce skin itching, ointments that reduce its sensitivity are recommended. Measures to prevent deprivation of Zhiber include timely treatment of acute respiratory infections, acute respiratory viral infections, as well as comprehensive oral care (treatment of caries, gum and throat diseases). It is important to prevent hypothermia of the child’s body and take vitamin complexes on time.
Therapy for herpes zoster involves taking drugs that activate immunogenesis, antivirals and sedatives. Local exposure to ultrasound, ultraviolet irradiation or laser on the affected areas of the skin is also effective; if necessary, reflexology or novocaine blockade is performed (for intense pain).
To consolidate the effect of treatment, it is recommended to change the diet and include foods containing bioflavonoids and antioxidants (cherries, apples, blueberries, etc.) and enriched with vitamin E (fatty fish, walnuts, etc.). It is also important to prevent scratching of lichen plaques and maintain hygiene.
To eliminate pityriasis versicolor, local and systemic antifungal agents are effective. It is advisable to enrich the diet with foods containing iron (apples, lentils, etc.), as well as dairy and vegetable dishes.
Ringworm responds well to treatment with local antifungal and iodine-containing drugs, but for severe inflammation, oral antimycotics are recommended. Also, to treat this pathology, you need to take vitamin complexes and immunomodulators. Hair on affected areas should be shaved or trimmed.
Lichen planus is treated with PUVA therapy (photosensitizers), corticosteroids, and antimalarial drugs.
There are a number of foods that should be limited if you have any type of lichen, namely:
- tangerines;
- smoked meats;
- canned food;
- sweets (especially cream cakes);
- tea and cocoa.
Among the foods that alleviate the symptoms of the disease and speed up recovery are green vegetables, dairy products and cereals.
However, any actions must be carried out under the supervision and approval of the attending physician. Timely contact with a specialist significantly speeds up recovery and helps prevent the risk of relapse of the pathology.
0
0
7
Article rating:
3.86 out of 5 based on 7 ratings
Author: Mangusheva Victoria Yurievna
Dermatovenerologist, trichologist. Candidate of Medical Sciences, doctor of the highest category. Work experience more than 10 years.
Treatment of ringworm
When treating ringworm, as with most diseases, it is imperative that the patient reacts early and sees a dermatologist immediately. The sooner ringworm is diagnosed and the sooner treatment is started, the greater the chance of a full recovery.
- In the case of ringworm of smooth skin, local treatment is usually sufficient, but if there are many changes, then oral treatment should be included.
- When treating tinea capitis of the head, both topical and oral medications should usually be used. In the case of onychomycosis of the toes, the choice of treatment depends on the area of the lesion. If the lesions are not too extensive, then topical medications are antifungal varnish. Although when occupying a large area, oral medications should be included along with external medications.
Oral treatment for ringworm
Do not take breaks during therapy, as the fungi become more resistant, which does not lead to further treatment effects.
How is lichen transmitted?
The main sources of the disease are street cats and dogs, or objects containing flakes of their skin affected by the pathogen - a zoonotic form. However, lichen can be transmitted from person to person - an anthroponotic form of transmission, as well as with the help of fungi living in the soil - a geophilic transmission route. Viruses, as a cause of deprivation, can remain in the body of humans and animals for a long time, and only when the child’s immunity decreases can they provoke a disease.
Ringworm is not always contagious. Thus, children's weeping eczema occurs due to infection of microcracks in the skin, dermatoses, or the presence of allergic reactivity in the child's parents. According to the observations of experts, allergic diseases of the mother (asthma, rhinitis or neurodermatitis) increase the likelihood of eczema in the child by 40%. And Zhiber's pityriasis rosea is often a consequence of ARVI and is not transmitted to other people.
The period of high risk of contracting lichen is spring-summer, since the child spends most of his time outdoors and in contact with other children.
Contagious (infectious) types of lichen are pink, ringworm and herpes zoster. They require mandatory isolation of the child to prevent the rapid spread of the disease.
Lichen planus and pityriasis versicolor, as well as psoriasis and weeping eczema are not transmitted.
Prevention of ringworm and other mycoses
- Never touch other people's animals.
- Avoid tactile communication with sick people and animals.
- Do not allow your pets to interact with other people's animals.
- Do not use other people's combs or towels.
- Do not touch common furniture or curbs with your naked body.
After diagnosing mycosis of the feet and nail plates, disinfect shoes and wash socks at a higher temperature (min. 60 degrees). In summer, you should wear light, breathable shoes so as not to create favorable conditions for mycosis.
Finally, it is worth mentioning that foot hygiene is an important element of prevention. Avoid overheating your feet by wearing shoes only and drying your toes thoroughly after swimming. In addition, you must use only disinfected nippers and files.
ONLINE REGISTRATION at the DIANA clinic
You can sign up by calling the toll-free phone number 8-800-707-15-60 or filling out the contact form. In this case, we will contact you ourselves.
Complete information about fungal infections of the skin and nails
Types of mycoses
Doctors distinguish three types of fungal nail disease (onychomycosis): normotrophic, hypertrophic and atrophic.
Subscribe to our INSTAGRAM account!
- In the first case, only the color of the nails changes. White or yellow spots and stripes appear on them. But the shine and normal thickness remain.
- In the second case, the shine also disappears. The nail gradually thickens and becomes deformed. There is pain in the legs when walking.
- The third type is characterized by a dull brown color of the nail plate, its thinning and rejection from the bed, and the exposed area is covered with loose layers.
Ways of infection by fungus
Mycoses are caused by pathogenic fungi. Infection usually occurs from a sick person or animal, or through household means: through objects that were used by the patient. The skin of the feet, palms and nails is most often affected. Moreover, infection of the nail plates (onychomycosis) on the feet occurs mainly in public baths or swimming pools. Infected flakes of skin from a sick person flake off and end up on the floor, benches, grates, and rugs. In conditions of high humidity, microorganisms persist for a long time and actively reproduce.
Intra-family transmission of infection also occurs. This occurs when using shared shoes, towels, washcloths, or due to not thoroughly cleaning the bath after washing.
The development of onychomycosis on the hands is facilitated by injuries Onychomycosis often develops in individuals receiving long-term antibacterial, corticosteroid and immunosuppressive therapy.
Self-diagnosis will deceive
Many people are confident that they can recognize nail fungus on their own. But that's not true. Despite the fact that most nail changes turn out to be a fungus, the other nature of these changes should also be taken into account. Here we need to highlight, first of all, chronic nail injury, psoriasis and eczema . Also, changes in nails can occur with some common skin diseases, internal infectious diseases, damage to the nervous, endocrine, cardiovascular systems, various types of intoxication, as well as dystrophy. Finally, nail changes may be congenital . And although they look similar to a fungal infection, they are not.
The fungus will not go away on its own
Once it starts, a fungal infection will not go away until the fungus is destroyed. Fungi are very tenacious and can survive for months in fallen skin scales. Over time, the fungus affects all parts of the nail and spreads to other nails or skin. Nail fungus is a source of infection for infecting other parts of the body. If it is not cured completely, re-infection will occur due to the remaining focus of infection.
Why is fungus dangerous?
A neglected fungus is a “gateway” to infectious diseases ( for example, erysipelas). In addition, allergization of the human body with a fungal infection is possible, development or worsening of diseases such as bronchial asthma, allergic dermatitis, various skin rashes and reactions. In addition, fungal infection of the nails significantly complicates the course of diabetes mellitus.
Treatment strategy
For onychomycosis, it is imperative to take antifungal drugs in combination with topical agents and removal of the affected nails. Before treating a diseased nail with special ointments, solutions or varnishes, you need to cut or file down the affected area. You can use a keratolytic patch.
For the treatment of fungal diseases of the skin and nail plates, the selection of comfortable shoes is of great importance. It should not injure or put pressure on the leg. In this case, there will be no reason for the disease to worsen. After defeating the fungus, you should not calm down. This disease does not let go of its victims for a long time.
In addition to medications, local treatment also helps in the fight against fungal diseases. People have accumulated many effective recipes.
Measures to prevent fungal diseases
- When visiting a bathhouse, swimming pool or beach, do not forget to wear rubber slippers.
- Never use other people's towels or washcloths.
- Wearing or even trying on someone else's shoes is also not recommended.
- Before going to bed, your feet should be washed and then wiped dry.
Mycosis is mainly affected by people with weak immune systems, so it is necessary to constantly improve your health: take vitamin complexes, stop drinking alcohol and cigarettes, and do gymnastics
Traditional recipes for fungal diseases
GARLIC COMPRESSES. Mix equal parts garlic juice, 90-degree alcohol and distilled water. The resulting mixture is a very strong antiseptic. You need to moisten a cotton napkin in it and apply a compress to the affected area in the usual way.
GARLIC TEA. In addition to local treatment, garlic preparations should also be taken orally. You can make garlic tea, decoction or tincture. To prepare tea, take 2-3 cloves of garlic, mash them and pour a glass of boiling water. Let it brew for 5-7 minutes and take 3-4 times a day.
PROPOLIS SOLUTION. It is good to lubricate the areas affected by the fungus with an alcohol solution of propolis: dissolve 10 g of propolis in 50 ml of 30% alcohol.
MINT WITH SALT. Crush peppermint leaves and mix them with the same amount of table salt. Place the mixture between your toes for about 1 hour, then rinse your feet with cool water and dry with a cotton napkin. Repeat the procedure until complete healing.
LILAC TINCTURE. Take 10 g of common lilac flowers, pour 100 ml of 70% alcohol. Leave for 10-15 days in a dark place, shaking regularly. Wipe the fungus-affected areas with the resulting tincture.
POTATO JUICE. Massage the fungus-affected areas with fresh potato juice or a slice of raw potato. The course of treatment is 1 month. A noticeable improvement occurs already on the 10th day.
For fungal infections of the skin, Veronica officinalis is useful: take baths or make lotions from a decoction of its herbs, and also drink an infusion. The healing tea is especially effective when combined: 2 teaspoons of veronica, tricolor violet and string per 0.5 liters of boiling water - drink in divided portions per day. Veronica officinalis juice is prepared for future use, preserving it with an equal amount of alcohol - also for lubricating fungal skin lesions.
Toadflax has a reliable fungicidal and ceratolic, that is, cauterizing effect , especially for fungal infections of the oral cavity. For rinsing, use a water decoction of the herb: 1-2 tbsp. Leave spoons of flaxseed in 1 cup of boiling water for 2 hours in a warm place.
Creeping thyme, the herb Bogorodskaya , has a strong bactericidal effect, especially against pathogenic fungi For washing 2 tbsp. Brew spoons in 1 glass of boiling water, leave for at least 1 hour. An ointment is prepared from the powder: 1 part dried herb to 4 parts fat base.
blackhead plant has antifungal activity. Ointments with its extract are especially effective in the treatment of fungal diseases. An infusion of the herb - 2 teaspoons per 1 glass of boiling water - is taken in fractional portions for fungus on the skin.