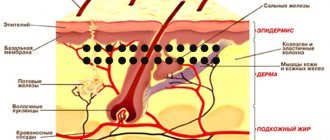
Eyelid melanoma is an aggressive malignant tumor that develops from melanin-producing cells and is located on the upper or lower eyelid. However, this is not the only neoplasm that develops in this area, but it is the most malignant and, fortunately, the rarest. Melanoma of the eyelid is diagnosed in approximately 5-7% of all melanomas. It develops mainly in people of the older age group. The peak incidence occurs at 50-60 years of age.
- Types of eyelid tumors
- Causes of development of melanoma of the eyelid
- How is eyelid melanoma diagnosed?
- Methods for treating eyelid melanoma
- Prognosis for recovery from melanoma of the eyelid
Types and causes of moles
Among the most common nevi that occur near the eyes or on the eyelids themselves, there are four types:
- Intradermal. They form in the deep layers of the skin and visually resemble a small ball. The color is dark (brown or black).
- Vascular. They appear as pinkish or reddish bumps (consisting of a collection of blood vessels). Often appear as a result of abnormalities in the functioning of the capillaries.
- Epidermal (hanging). The most common neoplasms are flesh-colored or dark brown.
- Mixed (flat). They are located between the epidermis and dermis and are light brown or dark brown in color.
A mole near the eye can appear for various reasons. Their growth is facilitated by a number of factors, including: genetic predisposition, hormonal imbalance, puberty, pregnancy, uncontrolled use of certain medications, prolonged exposure to direct sunlight.
Causes of development of melanoma of the eyelid
Why melanoma occurs in the eyelid area is not completely known. As with most cancers, this tumor develops due to mutations that have occurred in melanocytes. As a result, they gain the ability to reproduce uncontrollably and spread to neighboring tissues.
Several risk factors have been identified, the presence of which increases the likelihood of developing eyelid melanoma:
- Belonging to the white race. The risk of developing melanoma is especially high in people with light skin color.
- Age over 50-60 years.
- The presence of dysplastic nevi in the eyelid area.
- Excessive insolation.
- Sunburn.
- The presence of melanoma in close blood relatives (hereditary predisposition).
Advantages of laser technique
The tumor can be removed in different ways: cryodestruction, using a scalpel, radio knife or laser. The latter method is most preferable when working with nevi located on the face. The laser acts on the tumor with high precision, evaporating its cells layer by layer. Its main advantages include:
- minimal trauma;
- complete security;
- eliminating the appearance of new formations in the area of mole removal;
- no risk of bleeding;
- saving time (the procedure lasts about 5-10 minutes);
- short postoperative period;
- absence of scars and cicatrices.
Are there any restrictions after deletion?
When removing small moles on the eyelids, contrary to popular belief, I do not recommend limiting yourself in water procedures. This is due to the fact that the operation is performed without completely cutting the skin and without suturing. In order for patients to understand the scope of the operation more clearly, I usually give an analogy with a small scratch on the skin.
Unfortunately, there is still one limitation. Direct sunlight should be avoided at the extraction site for 2 months from the date of surgery. This is necessary to obtain a good cosmetic result.
Indications and contraindications for tumor removal
A specialist may recommend removing a nevus near the eye if it causes severe discomfort, has uneven edges, bleeds, quickly increases in size, or changes color. Some moles are prone to malignancy, which is also an indication for removal. Doctors often advise getting rid of tumors that can easily be damaged mechanically, for example, with a comb. Patients themselves often resort to surgical intervention due to the unaesthetic appearance.
Despite the safety of the laser technique, its implementation is not always possible. Absolute and relative contraindications include:
- infectious diseases;
- severe cardiovascular diseases;
- abnormalities of the endocrine system (diabetes mellitus);
- pregnancy and lactation;
- exacerbation of chronic pathology.
Also, it is prohibited to remove tumors on the eyelids if there is inflammation and redness. You must first consult an ophthalmologist who will draw up a treatment plan. After recovery, there are no restrictions on the laser technique.
Types of eyelid tumors
Eyelid tumors can be benign or malignant.
Benign neoplasms
Benign eyelid tumors grow slowly, superficially, and do not affect the underlying tissue. Their course is favorable and the reason for visiting a doctor, as a rule, is a cosmetic defect. Most often, benign neoplasms develop from epithelial tissue, but the source can be hair follicles and other skin elements (trichoepithelioma, Malert epithelioma, fibromas, lipomas).
The most common benign eyelid tumors are:
- Papillomas are nodular neoplasms of a dirty yellow or dirty gray color. They can be located on a leg or a wide base. The neoplasm resembles a villous mushroom or cauliflower in appearance. Sometimes it can spread widely throughout the tissue of the eyelid, affecting the tear ducts, conjunctiva of the eyelid and even the paranasal sinuses. May become malignant.
- Senile warts (senile warts) are similar in appearance to papillomatous nevus. It looks like a brown, yellow or grayish nodule, dense to the touch, does not cause pain. Compared to papilloma, they have more pronounced keratinization. Does not malignize.
- Keratoacanthosis - manifests itself as white spots covered with scales. If left untreated, it may become malignant (risk 20%).
- Trichoepithelioma - a neoplasm arises from hair follicles, has the appearance of a dense nodule, 1-3 mm in size, rarely 1 cm. It can be multiple. In some patients, the number of tumors exceeds a dozen. Mostly young people suffer. If left untreated, they can malignize into basal cell carcinoma.
- Syringoadenoma is a tumor growing from the epithelium of the sweat glands. The tumor is a multilocular neoplasm. It grows very slowly.
- Fibroma - has the appearance of a node on a wide base or on a narrow stalk. It grows from mesodermal tissue and can reach several centimeters.
Malignant tumors of the eyelids
Malignant tumors of the eyelids have infiltrative growth and tend to destroy underlying tissues and metastasize. Basal cell carcinoma progresses most favorably. It is also called a semi-malignant tumor. The most aggressive growth is in melanoma. It not only infiltrates the underlying tissues, but also gives distant metastases.
- Basalioma is a type of skin cancer. It looks like a nodule with a ridge-like surrounding. It grows slowly, germinating into the underlying tissue. In advanced cases, it can spread to the structures of the eyeball and even the orbit. Metastases are casuistically rare. Most often, basal cell carcinoma is located on the outer side of the eye, a little less often - on the lower and upper eyelids, and very rarely in the area of the inner corner. When located in the lower eyelid area, the neoplasm proceeds more favorably. The most aggressive growth is in basal cell carcinoma of the inner corner of the eye.
- Skin cancer of the eyelids. Usually this disease is represented by squamous cell skin cancer. At the initial stage, the tumor has the appearance of redness, which eventually thickens and ulcerates. The tumor is prone to infiltrative growth and metastasis.
- Meibomian gland cancer is a very rare type of cancer and has an extremely aggressive course. The tumor is localized in the upper eyelid, looks like a basal cell carcinoma, but grows quickly and metastasizes.
- Melanoma of the eyelids is the most malignant neoplasm localized in this area. The first signs are the formation of a spot with blurry contours, surrounded by an area of increased pigmentation and redness. The stain quickly spreads over the surface of the skin. Also, melanoma of the eyelid can be presented in a nodular form. In this case, it will be a node with vague contours, which is prone to bleeding. It grows rapidly, infiltrating the underlying tissue.
How to remove a mole near the eye using a laser
No special preparation is required for the procedure. In one session it is possible to completely get rid of one or more tumors. The skin is pre-treated with an antiseptic. To prevent the patient from experiencing discomfort, he is injected with an anesthetic substance. Special glasses are used to protect the eyes. If the mole is located on the eyelid itself, during laser technology the eyeball is covered with a soft shield that reliably protects it from external influences.
Next, using the device, the doctor acts on the tumor in a targeted manner. During the procedure, the doctor is able to control the penetration of the laser beam deep into the epidermis (healthy nearby tissues are not injured). Thanks to its sterilizing properties, it is possible to avoid infection or inflammation in the treated areas. After the procedure, a small depression remains, which completely levels out within 10 days.
How to safely and quickly remove a mole on the eyelid?
In my opinion, the simplest and most convenient way to remove small (up to 6mm) moles on the eyelids is the method of radio wave surgery. It allows you to take into account all the features of this anatomical area, perform the removal in 1 visit and achieve an excellent cosmetic result within 1-2 months after the operation:
- The minimal size and shape of the instrument allows you to remove moles of any size, even the smallest, with minimal damage to healthy tissue
- Syringes with a needle thickness of 0.33 mm allow you to inject an anesthetic into the skin without damaging blood vessels
- Special plastic cornea shields reliably protect the eye during surgery
If you follow all the care instructions, you will soon forget about where the mole was that you lived with for so many years.
Thanks to Svetlana for the photographs provided.
Svetlana also liked the result: A pleasant feature of this method of removal is that after the procedure there is no need for repeated examination, dressings and removal of sutures. The operation itself takes no more than 10 minutes.
Where to have the procedure done in Moscow
Due to the thin and delicate skin, the eyelids are recognized as one of the most difficult areas to eliminate tumors. Therefore, you should entrust your health only to an experienced specialist. Certified surgeon Kirill Viktorovich Listratenkov can safely remove a mole using laser technology. Thanks to extensive experience, a positive result is guaranteed. Other advantages of seeking help from Kirill Viktorovich include:
- competitive prices for services provided (the price list is presented on the website);
- confidentiality (patient data never leaves the medical institution);
- individual approach;
- convenient work schedule;
- free online consultations (you can ask a question online, the doctor will give a detailed answer to it in the near future).
To make an appointment for an initial consultation, just call the number provided or fill out a standard form on the website (leaving your contact information).
Why is a nevus on the eye dangerous?
Regardless of its location, a nevus is dangerous due to its ability to degenerate into a malignant tumor - melanoma. A mole that is benign in nature usually practically does not change its color and size, while melanoma is characterized by fairly rapid growth.
But it is practically impossible to determine the malignancy or benignity of a birthmark on the eyeball by this sign, because Nevus of the eye is characterized by changes in both size and color, regardless of the characteristics of the histological structure.
How to remove a nevus on the eye?
Until recently, the only safe treatment for nevus on the eye was its surgical removal. The operation was performed under a special microscope using a radioscalpel or microscalpel.
The use of a laser beam was considered dangerous by many experts, since it could damage neighboring eye tissues.
Currently, the development of modern laser technologies has made it possible to develop new methods of surgical treatment of nevus. And now it is increasingly being removed from the eye using laser radiation.
The main advantages of using laser technologies to remove a nevus are that they are painless, bloodless, and most importantly, the absence of a rough postoperative scar.
↑ Precancerous melanosis
↑ SYNONYMS
Precancerous Dubreuil melanosis, intraepithelial melanosis, Hutchinson's cockerels.
↑ DEFINITION
Flat pigment spots of different shapes, sizes and degrees of pigmentation located on the skin of the face and eyelids.
↑ EPIDEMIOLOGY
The disease is more often found in older women and men against the background of atrophic, wrinkled skin.
↑ PREVENTION
The use of creams with a high content of vitamins A and E, the prevention of excess ultraviolet radiation.
↑ CLINICAL PICTURE AND DIAGNOSTICS
↑ History
The disease progresses slowly, over years and decades, in combination with similar changes in other (especially sun-exposed) areas of the skin.
Clinically, the appearance in the outer or inner half of the eyelid of a flat pigment spot of irregular shape with scalloped edges, slightly rising above the skin level, around which satellite freckle-like spots are found, the pigmentation of which increases with insolation in the summer and decreases in winter. Over the years, the spots thicken slightly, and scales and flat papillary growths appear on their surface. Malignization occurs extremely rarely (in cases where pigmentation borders the mucous membrane of the eye and moves to the conjunctiva). Melanomas arising from melanosis are more benign than those arising from nevi.
↑ Biomicroscopy
The study reveals atrophic changes in the skin of the eyelids, combined with blepharochalasis, folding, which is associated with circulatory failure and aging of collagen and muscle tissue.
↑ Laboratory research
When excision of age spots on the skin of the eyelids for cosmetic purposes, microscopic examination is indicated. A characteristic sign of Dubreuil's melanosis is the proliferation of melanocytes in the border dermoepidermal space, pigmentation of the basal epithelium and the accumulation of foci of lymphoplasmatic proliferation and pigmented macrophages in the dermis. The initial sign of malignancy of Dubreuil's melanosis is a change in pigmentation, the appearance of hemorrhagic crusts and ulcerations in the central part of the spot.
—
Article from the book: Ophthalmology. National leadership | Avetisov S.E.
Content:
- 1 SYNONYMS
- 2 DEFINITION
- 3 DIAGNOSTICS 3.1 History
Description
↑ SYNONYMS
Melanocytic tumors of the eyelids.
↑ DEFINITION
The skin of the eyelids is a common location for tumors that synthesize melanin. Histologically, they are related to the human melanocytic system, which develops from the neural crest (neuroectoderm). Neoplasms are divided into benign (nevi and melanoses) and malignant (melanomas).
↑ DIAGNOSTICS
↑ History
Anamnesis data are important in recognizing benign nevi and malignant melanomas.
The human melanogenic system is not fully formed at the time of birth; it goes through a cycle of postnatal development. Pigmented nevi in newborns are observed with a frequency of 1:40. In the second and third decades of life, the number of nevi reaches a maximum (20-40 neoplasms per person). This is the time of greatest activity in the biological cycle of the nevus, followed by a period of rest, then almost complete involution.