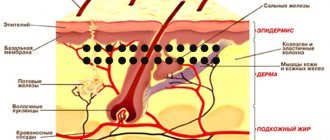
When melanin (coloring pigment) is localized, a birthmark appears on the skin. When there are as few melanocytes as possible, the spot becomes white. Blood vessels collected in a nodule make the mole red or pink.
With an excess of dye, the spots turn brown. You can see various photos of a white mole and its other shades on the Internet.
White moles, their distinctive features
This phenomenon is considered rare, which means it should be under constant surveillance. Only a specialist can determine whether a birthmark is dangerous or not.
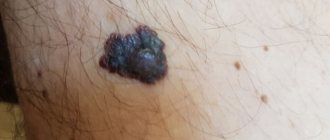
Attention! The nevus suddenly darkened and a light-colored halo formed around it. See a doctor immediately, because... there is a suspicion of degeneration of a benign tumor into a malignant one.
What symptoms should you see a doctor for?
If the mole has decreased or increased in size and lightened, you should pay attention to the presence of symptoms:
- the color of the nevus has changed dramatically: it has become black or white;
- the hanging wart darkened and fell off - the cause could be a break in a thin stalk;
- the skin began to dry out, becoming covered with microcracks;
- the size changed, the spot began to actively grow;
- the mole began to itch, a burning sensation and constant itching appeared;
- the center of the spot has changed, the surface has become lumpy, uneven, and a crust has appeared;
- the edge of the formation has become asymmetrical, losing its clear outline;
- with light pressure, fluid and blood are released from the formation;
- when touching the area, a person experiences pain;
- the appearance of a characteristic halo around the nevus of a dark or light color.
The combination of alarming symptoms is a signal about the development of certain processes in the body that should be identified at an early stage.
The doctor does not always identify the negative consequences of the transformation. To prevent complications, it is recommended to undergo a full examination.
Variety of light nevi
Externally, there are such moles:
- flat;
- melacite;
- non-cellular;
- warty;
- organoid.
To fully understand what white moles mean, you need to undergo an examination.
Methods for diagnosing a lightening mole
The diagnostic complex is prescribed by a doctor after a visual examination and history taking:
- anamnesis specifying the exact time of appearance of the mole, modifications, and the presence of atypical symptoms;
- diagnostics using a dermatoscope (a device with a magnifying glass and a fluorescent lamp for examining human skin);
- blood test for tumor markers (TA90 and SU100c) to exclude malignant processes;
- a smear for examination on a computer microscope in the presence of atypical discharge;
- taking a biopsy from the surface layer for histological and cytological examination of the biopsy in order to establish the nature of the formation, exclude an oncogenic process, and determine the causes of the appearance of a white nevus;
- layer-by-layer computer diagnostics of formation using a special apparatus.
If a light mole or lightening of an existing nevus is detected, it is recommended to seek advice from a medical institution, since only a doctor can thoroughly and fully determine the nature of the process of fading pigmentation and transformation of nevi.
Dimensions
Most often, white moles are small or medium in size. However, you can find giant spots, the diameter of which can exceed 10 cm.
The classification of spots is carried out depending on the depth of their location in the dermis: superficial, borderline and intradermal (deep).
Treatment options
In the absence of signs of unfavorable development of white moles, targeted treatment is not required. You just need to take measures to strengthen your immune system:
- increase the consumption of vegetables, fruits of yellow, orange and red shades;
- reduce the amount of animal proteins in the diet;
- monitor the general condition of the body.
It is better to eliminate white birthmarks with ointments, and if they do not help, with surgery.
Drug therapy is not recommended for children under 5 years of age. But if the pigmentation has not recovered by this time, then a comprehensive examination of the body should be carried out to find the reason for this. For medical reasons, children may be prescribed:
- hormonal ointments;
- B vitamins;
- treatment of affected areas with extracts of medicinal herbs.
Mole removal
The advisability of surgical removal can only be determined by a doctor who can offer the following methods for this purpose:
- surgery using a scalpel;
- laser removal;
- electrocoagulation;
- cryodestructive method, in which freezing occurs with nitrogen or carbonic acid;
- electrocoagulation;
- radiosurgery method.
Parents should remember that if there is no harm to the child’s health, there is no need to resort to surgical intervention. The same applies to adults. The prognosis for such moles is quite favorable if you monitor their condition, shape, and visit a doctor if there is the slightest change. White moles can remain on the skin for a long time without causing noticeable discomfort.
Formation
First of all, it should be noted that moles in which blood vessels have formed are dangerous forms. Particular attention should be paid to those formations that do not have increased melanin density. They can be located on any part of the body. In addition, they can be found on the head and face.
If a birthmark appears in the area of the hands, on the back, feet, neck, chest, then its owner will have to be more careful so as not to accidentally cause damage. The most inconvenient place for a mole is the eyelid; it interferes with movement and full vision.
It is believed that nevi appear at the site of a diseased organ. Experts often predict degeneration into cancer cells based on location.
White spots around moles should be alarming, but those with flat, brown spots can relax. Pale-shaded ones “live with the owner” until old age.
What diseases may this indicate?
Diseases and conditions characterized by white spots on the body:
| Disease (condition) | Peculiarities | Localization location |
| Tinea versicolor | Pathology occurs in the warm season (summer, late spring, early autumn). The reason is increased sweating, hormonal imbalance. Occurs more often in people under 30 years of age. | Chest, back area, limbs, open areas of skin. |
| Lichen vulgaris | The spot is covered with flaky scales. The disease is more common in children. | Whole body. |
| Vitiligo | The disease is genetic in nature. Pigment formations are located symmetrically and can be large in size, up to the size of an independent organ. They do not cause discomfort, the problem is more of an aesthetic nature. | Whole body. |
| Pregnancy | Hormonal imbalance. The pathology will go away on its own. | Whole body. |
| Degeneration into melanoma | The nevus is brown in color, with a white mark formed along the edges. | Whole body. |
| Deficiency of vitamins and minerals (especially calcium, vitamins D and E, iron ions). | Light spots in the form of small dots. | Nails. |
| Pityriasis white | The pathology is typical for children from 3 to 16 years old. Initially, dots are formed that turn into spots. | Whole body. |
| Poikiloderma | The disease is accompanied by peeling of the skin, dilation of subcutaneous vessels, and white pigmentation. | Face (forehead, neck). |
The diagnosis is made by a doctor after collecting an anamnesis, examination, and based on laboratory data. The table is provided for reference purposes.
White spots are harmless and temporary if they occur:
- when squeezing the skin (for example, wearing clothes with tight elastic);
- due to mechanical injuries and burns;
- as a result of sunburn.
Causes of formation of white nevi
Small birthmarks are classified as benign. But this condition for the epidermis is not entirely natural and healthy. If damaged frequently, they can develop into cancer.
Congenital nevi are a rare occurrence; most often they form after 10 years of life during hormonal changes. If the bulge formed before the age of 25, this is a normal process.
Attention! The mole appeared in adulthood. It is worth sounding the alarm and contacting a specialist for an examination.
White Spot Meaning
Astrologers say that the location of moles on the body can say a lot about a person.
| Localization of nevus | Meaning |
| Face, head | The mole adds piquancy and a special “zest” to the image. Indicates the beauty and attractiveness of the owner. |
| Forehead | Hard work. |
| Cheeks | Kindness, good nature. |
| Shoulders | Life wisdom, prudence. |
| Hands | Localized on the right hand - a person will have a start in business, a successful career, on the left - hard work. |
| Breast | For a man – confidence, optimism, focus on success. For a woman, this is a sign that she will be a good mother. |
| Back | Honesty, sincerity, loyalty. |
| Stomach | White birthmarks on the stomach mean wealth. |
| Legs | Difficulties on the path of life. |
Sometimes groups of nevi form a geometric figure.
The meaning of spots when a group of nevi appears:
| Form | Meaning |
| Star | Talent. |
| Triangle | A sign of success in creativity and business. |
| Heart | There is love in the life of the owner of the mole. |
| Constellations | A random event will change your life. |
The data given above does not have a medical basis and is given for general development.
Pigmentless flat nevi
A white mole most often does not grow, does not bother, and does not itch. It is oval and has clear contours. Comes in different sizes. It can be either congenital (in children) or newly formed (in adults), which often indicates the presence of vitiligo.
- Duplex scanning of the vessels of the lower extremities
- Melanoma with metastases: diagnosis, treatment, prognosis
- A sick gastrointestinal tract is a risk zone for Covid-19
Sometimes many small bulges form that are invisible to the naked eye. Up to ten pieces they do not cause any discomfort.
Hanging nevi may also appear, which they try to get rid of immediately (they are more likely to be injured than others).
Complications
The most serious complication of a white mole is malignancy, that is, the transition of a benign pathological process to a malignant one. It is worth noting that the frequency of malignancy of white nevi is minimal, but everything happens.
Removing moles with an electric knife
Situations are often observed when ordinary moles, under the influence of certain circumstances, transform into malignant neoplasms.
People who are at risk and have:
- congenital mole of significant size;
- a mole that appeared after 60 years;
- any mole with a diameter of 3 cm or more;
- number on the body .
Frequent injuries and rubbing of moles can provoke degeneration into cancer. In this case, it is worth paying attention to the frequency of the appearance of new nevi, bleeding and the appearance of crusts on their surface.
If you experience discomfort, pain or itching in the area of the mole, do not delay visiting a doctor. After all, the sooner treatment is carried out, the more favorable the outcome.
Postoperative period
What is needed after removing white moles using electrocoagulation? Everything is quite simple - take care of your skin by treating it with an antiseptic.
It is also important to protect the area from exposure to UV rays, moisture and not to use cosmetics. Do not touch the crust; after a while it will fall off on its own.
Congenital nevi (moles)
Balybina Yulia Gennadievna
Dermatologist
April 24, 2021
Congenital nevi (moles) are considered to be those with which a child is born, or those that appear in the first year of life. They differ from the usual dark spots that appear in all people later, as they are quite active. If the baby has skin lesions, they should be examined by a dermatologist.
The cells of such nevi can be located deep - in the lower third of the reticular layer of the dermis, sometimes in the subcutaneous fat, muscles, and even bones. Or they may have a superficial location. Superficial nevi often have dark shades of brown. This may contribute to the appearance of melanocytic dysplasia (malignancy).
This process occurs due to the influence of internal factors, such as hormonal stimulation, or external ones, for example, under the influence of ultraviolet radiation, due to trauma.
The risk of dangerous behavior of congenital nevi directly depends on:
- size
- heredity, cases of melanoma in family history
- skin phototype (1, 2, 3, 4, 5 or 6)
- harmful environmental factors
- hormonal stimulation
- traumatization
For each child with a congenital nevus, management tactics are selected individually by a dermatologist/dermato-oncologist, taking into account all the data.
The size of the education matters most. Therefore, let’s look at the classification by size and the risks within each group:
— Congenital nevus is small. Has a size of less than 15 mm. The risk of developing a malignant process in this group, according to one data, is less than 1%; according to others, from 1 to 4% throughout life. When present, melanoma most often appears after age 20. In childhood, it is characterized by a calm course, so routine observation by a dermatologist is usually sufficient.
— Congenital nevus averages from 15 to 100 mm. Before the onset of hormonal changes in puberty, on average up to 12 years, the risk of malignancy is low. Further, during life, according to various sources, from values less than 1% to 5%.
The tactics for managing such nevi, removal or observation, are determined by the doctor, taking into account the presence or absence of severe somatic diseases, skin characteristics, for example, a tendency to form scars, and aesthetic goals.
In general, I consider it safer to remove it at the age of 7 to 12 years in the absence of contraindications. Contraindications may be, for example, for the use of general anesthesia or in the form of severe skin pathology.
It is also important to consider the location of the nevus. After removal of the nevus, a scar remains; if it is on the face, you need to make a very balanced decision about the operation. On the scalp, if located deeply, removal may leave a hairless area.
— A special place in the classification is occupied by large formations, from 100 to 200 mm, and giant, more than 200 mm formations. They can occupy an entire anatomical region. They have the greatest risk of malignancy compared to those indicated above. The main distinctive feature of large nevi is that against their background, melanoma can form in the first years of a child’s life. The average risk of developing malignant cells during the first 20 years of life is about 5%. Therefore, I consider the main tactic to be removal.
Such nevi are observed when removal is impossible. This may be due to the complexity of the location, or due to excessively large sizes, when there are not enough skin grafting options.
In cases where the nevus is located on the scalp and spine, it is additionally recommended to do an MRI to exclude nerve damage. In some of these cases, neurocutaneous melanosis must be excluded. This pathology is a separate topic.
It must be borne in mind that even in cases where a difficult decision is made to remove large and giant nevi, this will not be a guaranteed fact that melanoma will not appear in other areas.
The main thing parents need to remember:
- If a newborn baby or a baby under one year old has moles, an examination by a dermatologist/dermato-oncologist is mandatory.
- Small congenital nevi should be observed by a specialist until the age of 20 (unless there are reasons to remove them earlier). In cases where the characteristics of the nevus change after 20 years, it may need to be removed.
- Medium congenital nevi are routinely removed between the ages of 7 and 12 years, in the absence of contraindications. Earlier removal may be recommended based on the results of follow-up examinations.
- Large and giant nevi should be removed, if possible, with the participation of a plastic surgeon under general anesthesia. If removal is impossible - observation and inspection once every 3-6 months. When a suspicious area appears, a fragmentary histological examination is performed.
- For skin with congenital nevi, it is necessary to adhere to general measures of protection from ultraviolet radiation: avoid direct sunlight, do not be in the open sun from 11 am to 5 pm, use photoprotection products with SPF 50+ and mechanical protection with clothing and hats.
- Try not to injure moles.
- When prescribing stimulant medications, discuss with a dermatologist the feasibility and safety of taking them, taking into account the presence of a congenital nevus.
Fortunately, large nevi are rare. Moles can be beautiful and even piquant, giving your appearance a special twist. The main thing is to have information about possible risks and keep them under the supervision of a competent specialist. At our center, doctors are ready to provide qualified assistance and answer all your questions.
Big ones - under the knife!
Melanoma can make itself felt by changing the color of the nail to brown or black, and the appearance of spots on the palms and soles.
To monitor atypical nevi, the patient usually undergoes dermatoscopy every 3–12 months. A biopsy is taken from suspicious lesions and histological examination is performed to establish a diagnosis. All congenital moles larger than 2 cm should be under constant medical supervision; in any case, they will have to be removed. If necessary, the baby will have a skin passport to monitor the number, dynamics of growth and identify any changes in moles. The operation is usually performed shortly before the onset of puberty. Especially often, cells degenerate on a giant congenital nevus (more than 15 cm in diameter) in adolescence.
Published on the portal parents.ru
What are moles?
Every child is unique, and every mole is too. From the name you can easily guess that moles are spots that are on the baby’s skin from birth. There is also a theory that identical “marks” on the body were a sign of the same genus. Some moles form before the baby is born and are immediately visible. Others are present on the skin “in theory,” but only appear some time after birth.
Moles can differ significantly from each other in appearance: some can be flat, others can be convex, some can be regular in shape, others can have uneven edges. Colors can vary from yellowish and brown to red and blue.
Most often, moles on the skin are not dangerous. Some even shrink in size or fade completely over time. In rare cases, moles can be a symptom of an underlying disease. In any case, if your baby's moles cause you concern, consult your pediatrician.