Tinea versicolor can be transmitted through personal hygiene products, contacts and clothing. At the same time, the most favorable time for the development of lichen will be the summer period, when high temperatures and air humidity are combined. The peculiarity of the course of the disease, which causes the formation of colored spots on the skin, is a wave-like nature, which subsides in the cool season and intensifies at elevated ambient temperatures.
Tinea versicolor most often affects people with reduced immunity, increased sweating, disruption of the physiological processes of the skin and a genetic predisposition to the development of skin diseases. In this case, lichen affects people who have been diagnosed with tuberculosis, diabetes mellitus, metabolic disorders or vegetative neurosis. The development of lichen can be provoked by excessive use of antibacterial hygiene products, excess weight, and long-term use of medications.
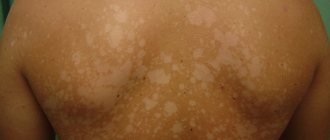
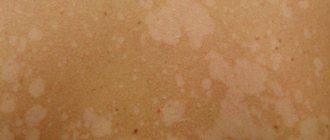
Only a dermatologist can make a correct diagnosis, since the symptoms of pityriasis versicolor are similar to other skin diseases: vitiligo, pityriasis alba and rosea, psoriasis, dermatophytosis, seborrheic dermatitis and others. The main sign of the appearance of tinea versicolor is the presence on the body of colored spots from yellow to brown, which have uneven edges and are not symmetrically located. In this case, colored spots are localized in the back, chest, shoulders, abdomen, and can sometimes be found on the neck, face and scalp.
How to diagnose lichen
Diagnosis of tinea versicolor consists of conducting a visual examination by a dermatologist and ordering a study of the affected area of the epidermis. When examining the patient, it is necessary to identify: for what reason the lichen occurred, the duration of the process and the degree of damage to the skin by colored spots.
To identify lichen, the following research methods can be used:
- Skin scraping. The study reveals round fungal spores with a double contour.
- Culture method. It is based on placing a sample of cells in a nutrient medium in order to develop colonies of the fungus lichen cauliflower.
- Balser's test (iodine test). The affected area of skin is covered with iodine solution (or 1-2% aniline solution) to change the color of the epithelium. At the same time, the cells that have been affected by tinea versicolor acquire a loose structure and are painted in a rich dark color, while healthy cells are painted in a light shade. After the examination, the skin is cleansed with an alcohol solution.
- Using a Wood's lamp. Examination of skin areas under an ultraviolet lamp. In this case, the areas that are affected by lichen give off a greenish-blue or red-yellow glow.
- Use of mercury-quartz lamps. The study is used to identify areas of skin that are affected by the fungus, but have no visual manifestation. Under the light of a lamp, these areas acquire noticeable color pigmentation.
Symptoms of tinea versicolor
In those places where skin manifestations of the disease are observed, the number of corneocytes is three times higher. Changes in the skin color of a person infected with tinea versicolor can also be explained by the fact that the fungi colonize unevenly on the skin.
The primary site of occurrence of tinea versicolor is the mouth of the pilosebaceous follicles. Here, fungi, under the influence of provoking factors, begin to multiply, forming colonies. They use the fatty secretion produced by the sebaceous glands for their own nutrition. It contains all the fatty acids necessary for fungi.
The disease debuts with the appearance of yellowish dots on the skin, which are located near the mouths of the hair follicles. Then pinkish-yellow spots form around these points. As the disease progresses, they darken, becoming brown. Pityriasis-like scales appear on their surface. If you just look at the stain, the peeling is almost invisible. However, as soon as you scrape it, the scales immediately come off. This sign is called Besnier's sign.
So, the following symptoms will indicate tinea versicolor:
- The spots that appear on the skin can have different colors: yellow, pink, brown. As the pathology progresses, they merge together, forming large lesions with uneven contours. The initial size of the spot is 3-5 cm in diameter.
- The spots can cause itching in humans. It is rarely intense.
- If a person has been in the sun for a long time and gets a tan, the color of the spots will change. They become lighter and therefore more noticeable. In winter, the spots, on the contrary, darken. This feature of the course of the disease is also one of the reasons why this ringworm is called tinea versicolor.
- The favorite places for the fungus to localize are the shoulders, back, and stomach. Less commonly, spots appear on the neck and scalp. At the same time, a person does not lose hair on his head. They can only fall out on the body.
- Although the pathology is quite amenable to correction, sometimes it can bother a person for years, either subsiding or exacerbating again.
- As a rule, a person does not indicate any subjective symptoms. A burning sensation and pain in the affected area can be a signal of a secondary infection.
Depending on how deeply the dermis is affected and where exactly the spots are located, the following types of tinea versicolor are distinguished:
- Erythematosquamous form. The spots are located in the upper part of the body, there are no symptoms of inflammation.
- Follicular form. The spots are accompanied by the appearance of papules and pustules, which have an average size of 2-3 cm. This form of the disease is typical for people suffering from severe concomitant disorders.
- Inverted form. The spots are located in the folds of the human body.
Regardless of the form of the disease, its treatment is carried out according to the same type of scheme.
It is important to compare the symptoms of tinea versicolor with the symptoms of other diseases:
- Lichen Zhibera is characterized by the appearance of pink oblong spots on the skin. In the center of these lesions, the dermis peels off. The spots are located along Langer's lines; they themselves are surrounded by a collar of scales.
- Syphilitic roseola is characterized by pinkish spots on the skin, which become discolored when pressed on them. There is no peeling of the dermis, the spots do not merge or grow.
- It is necessary to distinguish tinea versicolor from vitiligo.
Sometimes tinea versicolor has an atypical course. In this case, the spots are located on the skin of the soles. This form of the disease is difficult to treat, and after the acute phase is eliminated, brown spots with an irregular shape remain on the feet. They are located on the heels and on the transitional fold from the sole to the toes.
In people with AIDS, tinea versicolor spots reach a size of 5 cm, while in a person with a normal immune system their diameter rarely exceeds 1 cm.
Rules of conduct when treating ringworm
Treatment of tinea versicolor is a long process that requires a person to comply with prevention. If the basic principles of treatment are not followed, the patient may become infected again.
For successful treatment, the following criteria must be adhered to:
- take baths with antifungal soap to activate the process of exfoliation of skin cells in the area where the colored spots are located;
- treat affected skin areas with salicylic alcohol;
- After swimming in ponds, sunbathing is prohibited, as tinea versicolor increases the impact on the skin due to high humidity and high ambient temperatures;
- take sunbathing in warm periods, as ultraviolet radiation promotes self-healing of the skin;
- it is necessary to refuse to visit public baths, saunas, swimming pools;
- use only your own personal hygiene products, having previously replaced them with new ones (towels, washcloths);
- disinfect clothes, things, bed linen using high temperature;
- treat rooms in which the patient is constantly present;
- be sure to iron the laundry on both sides to increase the degree of disinfection;
- strengthen the body’s immunity through hardening and physical exercise;
- follow a strict diet - exclude fatty and sweet foods, alcoholic beverages, yeast bread and kvass;
- maintain a daily routine;
- Avoid synthetic fabrics if possible;
- provide fresh air access to the premises where the patient is located.
Pityriasis versicolor during pregnancy
During pregnancy, women may experience various diseases, including skin inflammation. The causes of lichen, like many ailments, in pregnant women are often a decrease in immunity or hormonal changes.
As a rule, pityriasis versicolor is not treated during pregnancy, or a gentle course with carefully selected components is prescribed so as not to harm the fetus, but to improve the quality of life of the expectant mother. Treatment is always strictly individual.
Pityriasis versicolor in children
This is a common disease in children. It usually affects the scalp, but can appear on the face and body. For young children and adolescents, as well as for pregnant women, treatment can only be prescribed externally (in particularly difficult cases, the use of medications and drugs is possible). Parents of infected children need to monitor the child’s hygiene and not allow the baby to scratch the spots in order to prevent the spread of the disease and not create a favorable background for the occurrence of other diseases.
How dangerous is solar lichen? Is pityriasis versicolor contagious or not?
If the disease does not have complications and does not occur in parallel with other diseases, then it does not pose a danger to human health, except for the psychological discomfort mentioned above, especially if spots appear on the face.
The disease can be called conditionally contagious, since the fungus (causative agent) of skin inflammation is present on the skin of any person (it is part of the microflora) or can be transmitted from person to person, but the disease itself will occur only in the event of an external “irritant”.
Infection is possible:
- during personal contacts;
- through personal and hygiene items;
- in public changing rooms or fitting rooms.
How and how to treat pityriasis versicolor in humans (colored, multi-colored, etc.)?
If you notice signs of this disease, it is important to remember three simple rules:
- do not self-medicate, because the wrong medicine can only worsen the condition;
- do not wait until everything goes away on its own (the disease has a wave-like nature, that is, it can be repeated at different intervals and does not always return in a mild form);
- Do not use dubious, suggested by someone, or self-selected remedies for pityriasis versicolor.
Seeing a doctor is a sure way to not only get cured, but also strengthen your immune system, as well as get rid of annoying aesthetic skin defects that bring psychological discomfort.
General provisions of therapeutic measures for tinea versicolor
The main condition for eliminating tinea versicolor is to contact a dermatologist, since self-prescription of drugs or the use of folk remedies is irrational. Incorrect selection of a course of medications during treatment or non-compliance with the dosage of medications can cause complications or relapse of the disease (repeated skin damage by the pathogen). The use of infusions, ointments, lotions and sprays, which are prepared according to folk recipes, is allowed to a person only after consultation with the attending physician and under his strict supervision.
Treatment of tinea versicolor is carried out strictly under the supervision of a specialist and consists of the use of medications, various ointments, special diets and physiotherapeutic procedures. Medicines are selected for each patient individually, depending on the cause of the fungal infection, the area of development of color pigmentation and the individual characteristics of the patient.
Depending on the degree of infection of the patient by the colored fungus, the method of therapeutic treatment is selected - outpatient (in the absence of a bacterial infection) or inpatient. Specialists use an integrated approach to treatment using local and systemic drugs. Ointments and creams cannot completely remove the causative agent of the disease, since they only have a superficial effect.
Treatment of tinea versicolor requires the dermatologist to prescribe medications and vitamin-mineral complexes to the patient that support the immune system and increase the body’s defenses. To enhance the healing effect of skin affected by lichen, physiotherapeutic techniques are used, which are carried out in the form of ultraviolet irradiation.
Causes of tinea versicolor
Tinea versicolor is caused by fungi called Malassezia furfur and Pityrpsporum orbiculare. They parasitize in the upper layer of the epidermis. Therefore, to detect a mycotic microorganism, a simple examination of skin particles under a microscope is sufficient. The fungi gather in clusters that look like curved threads.
Lipophilic yeast-like fungi Malassezia furfur have unique properties. They are able to exhibit their pathogenic activity depending on environmental changes, as well as depending on the host immunity. In addition, this is the only fungus from the human microflora that requires fats for its existence. This quality is called obligate lipophilicity.
Malassezia furfur and Pityrpsporum orbiculare are able to exist in both aerobic and anaerobic conditions. In addition to the fact that these microorganisms can cause lichen versicolor, in some cases they cause systemic pathology. This occurs when the infected person has severe immune deficiency. For example, there is evidence that a fungus of this species and genus has led to sepsis in premature newborns and sepsis in HIV-infected people.
Most people have a firm belief that it is impossible to get infected with tinea versicolor. In fact, the fungus can be transmitted from one person to another. However, clinical symptoms of the disease do not appear in every patient. Therefore, dermatologists classify causative agents of tinea versicolor as opportunistic flora.
This means that it can exist on the skin, but will not manifest itself in any way. So, many people are infected with pathogenic fungi, but the symptoms of the disease develop only when the body’s defenses are weakened. It has been established that the causative agent of tinea versicolor is isolated from 10-12% of the population; it is found 2 times more often in men. The disease develops in people aged 15-40 years. This type of mycosis worsens in the summer, and spontaneous recovery is also possible. In some people, tinea versicolor develops a recurrent, chronic course.
The fungus is transmitted in the following ways:
- During personal contact with a person. Therefore, the pathogen is most often found in all family members.
- Through the use of personal hygiene items. This could be items of clothing, a towel, a washcloth, etc.
- While using public changing rooms or fitting booths in stores.
Sometimes a fungus can exist on the skin for many years without a person knowing about it. However, if provoking factors appear that contribute to its reproduction, the pathogenic flora will begin to actively increase its numbers. The incubation period is equal to 2 weeks.
Causes (provoking factors) that can lead to the development of tinea versicolor:
- Increased sweating. In particular, hyperhidrosis, in which sweat changes its chemical composition, is dangerous. This promotes the proliferation of mycotic microorganisms.
- Human predisposition to various skin diseases. It can be inherited, or be a feature of a particular organism. In this case, an increased level of cortisol in the blood plasma is observed.
- Too oily skin. Thus, in 15-year-old patients with lichen colorus, lipophilic fungi are found in 93% of cases. While in children under 5-7 years of age these mycotic microorganisms are absent on the skin.
- Disruption of metabolic processes in the upper layer of the epidermis.
- Weakening the body's defenses. This can occur due to many reasons: chronic inflammation of the tonsils, caries, or pyelonephritis. Often tinea versicolor is a companion to tuberculosis. Moreover, the bacillus is capable of parasitizing not only in lung tissue, but also in the kidneys, genital system, bones, etc. Tuberculosis often has a hidden course and is discovered by chance. Therefore, all patients diagnosed with lichen colorus should be tested for tuberculosis.
- Living in countries with high humidity. A high prevalence of tinea versicolor is observed in cities and towns with tropical and subtropical climates. The incidence rate in them is 40%, while in residents of countries with temperate climates it does not exceed 5-10%.
- Presence of seborrhea.
- Tinea versicolor can accompany diseases such as AIDS, rheumatism and diabetes. If a patient has one or more of the listed pathologies, then the probability of developing tinea versicolor is 63%.
- Vegetative-vascular dystonia. In addition to tinea versicolor, a person will suffer from weakness, frequent dizziness, panic attacks, etc.
- Pathologies of the digestive and hepatobiliary systems always affect the condition of the skin. Disturbances in their work can be manifested by tinea versicolor.
- Middle-aged people are at risk. Tinea versicolor is extremely rarely diagnosed in children under 7 years of age, only if the child has a serious illness.
- Diseases of the respiratory system can provoke the development of tinea versicolor. In this case we are talking about asthma, pneumonia or chronic bronchitis.
- Itsenko-Cushing syndrome and obesity.
- Long-term local or systemic treatment with corticosteroids.
- Hormonal imbalance is another factor that contributes to the symptoms of ringworm. As a rule, this happens in pregnant women, as well as in people suffering from pathologies of the adrenal glands and ovaries.
- The next risk factor for the development of tinea versicolor is the use of shower gels that have an antibacterial effect. Of course, after a single use of such a remedy, the disease will not develop. However, if a person uses them on a regular basis, the likelihood of this dermatomycosis occurring increases significantly.
- Chemotherapy that cancer patients undergo can provoke the development of a persistent form of tinea versicolor. After completion of treatment, spontaneous recovery is most often observed.
What does pityriasis versicolor look like?
The first symptom of the disease is the appearance of small spots, most often localized on the torso, arms, scalp or external genitalia. The rash may be accompanied by mild itching or may not cause the patient any noticeable discomfort.
The rashes do not have a sharp outline, are not inflamed and do not swell. Initially they are pink in color, but gradually change shade: from pink-yellow to brown and red-brown. The number of spots increases: the fungus spreads across the skin, occupying more and more surface area of the body. The rash may appear on the hands, legs, face, but never affects the mucous membranes, palms or feet, which is due to the special structure of the epithelium in these areas.
The rashes can increase in diameter (up to several centimeters) and merge with each other. Peeling zones appear in the center - when you touch the spot, the scales easily peel off. An atypical form of pityriasis versicolor includes pityriasis alba, in which the affected areas completely lose their pigment (become white). In this case, there may be no peeling.
A distinctive feature of pityriasis versicolor is a disorder of skin pigmentation. Fungal colonies damage melanocytes, which are responsible for the production of melanin, the substance responsible for the color of the skin. Areas of hypopigmentation are especially noticeable during tanning: the epithelium damaged by yeast remains white. This effect can persist for a long time even after recovery.
Pityriasis versicolor is prone to a chronic course and frequent relapses.
To quickly recover and avoid the unpleasant consequences of the infection, it is recommended to consult a dermatologist at the first symptoms of the disease:
- the appearance of a pink or reddish rash;
- mild itching of the skin;
- a feeling of tightness and flaking in certain areas of the skin of the torso and arms.
Is it possible to sunbathe with pityriasis versicolor?
This dermatosis is popularly called “sun fungus”: during the beach season, the yeast is activated and the disease is diagnosed most often. At the same time, the areas of the skin affected by the colonies do not tan and remain white - the patient is covered with light spots, which bring him to the dermatologist’s office.
Since pityriasis versicolor can be diagnosed during rest, patients are often interested in: is it possible to sunbathe with pityriasis versicolor? Opinions differ on this matter. Previously, quartz treatment was prescribed for the treatment of lichen versicolor: under the targeted influence of ultraviolet light, colonies of the fungus died. But now many dermatologists dispute this method of treatment.
UV radiation can be dangerous for an organism weakened by infection. In addition, the occurrence of pityriasis versicolor indicates a decrease in immune strength. Therefore, experts do not recommend exposing the skin to additional stress.
If the patient doubts whether it is possible to sunbathe with pityriasis versicolor, he is recommended to consult a dermatologist. The doctor will give recommendations taking into account the individual characteristics of the body, the severity of the disease, its form and location. If you follow medical prescriptions, the patient will avoid the complications of lichen and will be able to recover in a short time.
It should also be remembered that if the patient decides to sunbathe with pityriasis versicolor, the areas of the skin affected by the colonies will remain light: it will not be possible to get an even and beautiful tan. Therefore, it is better to first get rid of the disease, and only after that return to the beach.
Method of infection
Mushrooms can come into contact with the skin of a healthy person, but with strong immunity, the body uses protective functions and the disease does not occur.
Main routes of transmission:
- Skin contact with the carrier.
- In public places: shower, fitting room.
- Use of a person’s personal belongings: towel, washcloth.
When infected with this microorganism, symptoms do not appear for 2 weeks to several months. They may not appear at all unless a situation arises when the immune system weakens.
Contraindications and features of the use of shampoos
Therapeutic shampoos for lichen contain antifungal substances, many of which are highly allergenic. Therefore, they are used in accordance with the instructions and recommendations of a dermatologist or trichologist. Frequently washing your hair with preparations is fraught with itching, burning, redness and peeling of the skin.
Features of using shampoos:
- a small amount of product (5-7 ml) is applied to damp hair;
- rub into the scalp in a circular motion for 1 minute;
- After 3-5 minutes, remove with running water.
The use of drugs is contraindicated for:
- hypersensitivity to components;
- purulent inflammation of the skin;
- burns;
- abrasions.
In the first days of treatment, a third of patients complain of hair loss. It is possible that the natural shade of the hair will change.
When is deprivation shampoo treatment effective?
Medicinal shampoos are topical preparations that affect the pathogen directly at the sites of inflammation. Their use is justified in cases where the disease is caused by a scalp fungus. Dermatologists include shampoos in complex therapy for the following types of lichen:
- pityriasis (colored);
- shearer;
- pink.
Topical fungicidal preparations are suitable for the treatment of seborrheic dermatitis and candidiasis of the scalp. Medicinal shampoos alleviate scaly and weeping lichen, which are also called psoriasis and eczema, respectively.