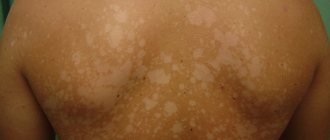
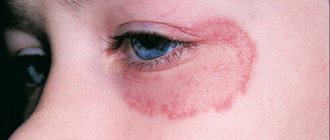
Pityriasis versicolor or pityriasis versicolor is a superficial skin lesion caused by a yeast-like fungus of the genus Malassezia.
These microorganisms are representatives of typical skin microflora, are found in most people and do not cause the development of the disease. But under the influence of external or internal factors, the pathogen can transform from a non-pathogenic form into a pathogenic one: the fungus penetrates the upper layers of the skin and damages melanocytes - the cellular structures responsible for the pigmentation of the skin.
As a result, the patient develops small spots of different colors: from pale pink to red-brown, with noticeable peeling in the center. When touched, the scabs flake off easily and resemble flakes, which is what gives pityriasis versicolor its name.
What is lichen?
Ringworm is a group of dermatological polyetiological diseases, which is characterized by the appearance of a rash and itchy dry/weeping elements. There are several varieties of lichen, which differ from each other in:
- the type of rash present;
- pathogen;
- contagiousness;
- localization.
Among the most common types of lichen in humans:
- multi-colored (pityriasis);
- encircling;
- red flat;
- ringworm (trichophytosis);
- pink (pityriasis).
The course of the disease is long. There is always a danger of secondary infection.
Differential diagnosis of pityriasis versicolor with other diseases
To make a diagnosis, the doctor performs the following procedures:
- Conducting an examination under a microscope to determine the scraping. The specialist scrapes the scales from the skin area, processes it and examines it. Using a microscope, it is possible to detect spores and fungi that are round in shape. The mycelium threads are white in color and long in shape, like a thread.
- Balzer test. A 5% iodine solution is used, which is applied to or near the infected areas. This study will take time; the affected skin gradually acquires a different color.
Causes of lichen in humans
Ringworm is usually caused by a fungal or viral infection. The mechanism of infection is not fully understood, since not all people, even those at risk, suffer from lichen. Presumably, fungal infection of the skin is promoted by the simultaneous influence of the following factors:
- stress;
- reduced immunity;
- hereditary predisposition;
- emotional/physical fatigue;
- infectious diseases.
The incidence of different types of lichen may vary depending on gender and age.
Causes of pink lichen Zhibera
Pityriasis rosea is of an infectious-allergic nature.
Causes of herpes zoster
Shingles develops through secondary contact with the Herpes zoster virus. It can also be caused by activation of a latent herpetic infection. Its causative agent is a virus of the Herpesviridae family.
Causes of tinea versicolor
Pityriasis versicolor or pityriasis versicolor affects the stratum corneum of the epidermis. Its appearance is promoted by sweating, seborrheic skin condition, and hot climate. Infection occurs through household contact, that is, through the use of common household items, through direct contact with a sick person. The causative agents of lichen versicolor are fungi:
- Pityrpsporum orbiculare;
- Malassezia furfur;
- Pityrosporum ovale.
Causes of ringworm
Infection with ringworm occurs as a result of contact of a child or adult with a person or animal infected with trichophytosis, as well as household items on the surface of which the fungal spores have fallen.
Causes of lichen planus
Lichen planus belongs to the category of a multi-cause disease that develops under the influence of internal/external factors that cause disruption of immune and metabolic processes. There is a hereditary predisposition to the disease. It can also occur as a result of contact with certain medications and chemicals.
Description of the disease
Pityriasis versicolor is a disease of the upper layer of the epidermis, caused by a fungus of the genus Malassezia. For a long time it can be asymptomatic, and subsequently affects only the stratum corneum of the skin and the hair cuticle. It affects mainly young people aged 14 to 40 years, and is practically not diagnosed in children under 7 years of age. Treatment of pathology is systematic and includes the use of antifungal agents for internal and external use. Otherwise, the lichen begins to grow, spreading to increasingly large surfaces of the epidermis.
What does lichen look like in humans - symptoms
Symptoms of pityriasis rosea
Pityriasis rosea begins with the appearance of a bright pink plaque on the skin, the diameter of which is up to 5 cm. If you look at a photo of the disease, it will become clear that this is a spot that peels off in the center. Within 1-2 weeks, the lichen begins to peel off more strongly along the periphery, its center becomes like tissue paper.
A week after the first spot appears, round pink spots appear on the back, stomach, and shoulders, located along the lines of skin tension. They can merge with each other. After recovery, dark areas may remain on the body for a long time.
Symptoms of herpes zoster
Symptoms of shingles include:
- soreness of the affected area of the skin and a slight burning sensation that occurs several hours before the first rash appears;
- pain in muscles, joints;
- numbness of the affected tissues;
- the appearance of bubbles of different sizes, the formation of edema in places where they are localized;
- enlarged lymph nodes.
In the photo, shingles is usually shown as a unilateral rash that is located on the scalp, along the intercostal nerves, on the abdomen or chest in the direction from the spine to the sternum. Shingles seems to encircle the torso, which is why it is called that.
A few days after the bubbles appear, the liquid contained in them becomes cloudy. They dry out and become crusty. After the latter falls off, pigmentation remains in place of the lichen. A second wave of rashes may then follow. The incubation period for shingles is about 2 weeks.
Symptoms of pityriasis versicolor (lichen versicolor)
Lichen versicolor most often affects the skin of the back, shoulders, neck, chest, and rarely - the head, thighs, groin, forearms, hands, shins, and behind-the-ear folds. First, the patient notices small pink spots, which gradually enlarge, merge, turn brown and turn white after the fungus dies. This creates:
- itching;
- burning;
- peeling of the skin at the site of the lesion.
Tinea versicolor can last for several years.
Symptoms of ringworm
Symptoms of ringworm, which is usually pictured as a bald patch on the scalp, include:
- itching in areas of rash;
- oval and round pink spots without clear boundaries, rising along the periphery like a ridge (may be covered with crusts and blisters).
Ringworm rashes often coalesce to form large lesions. The incubation period is 5-7 days.
Symptoms of lichen planus
Lichen planus in children and adults manifests itself:
- itching;
- skin lesions in the area of the anterior surface of the leg, genitals; torso, flexor surfaces of the forearms;
- the appearance of spots on the nails, oral mucosa, palms, face, soles.
In the photo, lichen planus looks like dark brown bumps. If the fungus infects the nail plates, they darken and become covered with white stripes, along which the nail soon splits.
If you experience similar symptoms, consult your doctor
. It is easier to prevent a disease than to deal with the consequences.
Causes and characteristic symptoms
Normally, a fungus of the genus Malassezia is constantly present on the body and at the mouth of the hair follicles. However, under the influence of a number of unfavorable factors, it begins to multiply intensively, causing characteristic symptoms. These factors include the following:
- increased sweating;
- failure to comply with basic hygiene rules;
- increased skin oiliness;
- concomitant diseases (diabetes, gastrointestinal pathologies, asthma, hormonal imbalance);
- vegetative-vascular disorders;
- immunodeficiency while taking glucocorticoids or cytostatics.
The first symptom of lichen is small, irregularly shaped spots. They can be localized on the back, sternum, neck, head, legs. They have a pinkish or brownish tint. Peeling in the form of small scales appears on the surface of the spots. There is no inflammatory process, suppuration or pain.
Diagnosis of lichen
Diagnosis of all types of lichen includes:
- listening to patient complaints;
- anamnesis analysis;
- inspection of rashes to determine their color, size, shape, location, etc.
Further, the dermatologist’s actions depend on the preliminary diagnosis he made.
Diagnosis of pityriasis rosea
To diagnose pityriasis rosea in a child or adult, in addition to a medical examination, during which the final diagnosis is usually determined, the following is additionally carried out:
- microscopy of scales to exclude syphilis;
- serodiagnosis of syphilis.
A biochemical and general blood test is also taken, and a general urine test is given.
Diagnosis of herpes zoster
Usually, a doctor can accurately determine whether a patient has pityriasis rosea during an examination. But in some situations additional research methods are required:
- detection of viral DNA by polymerase chain reaction in the contents of vesicles and in the blood;
- determining the presence of antibodies to the pathogen;
- identification of the pathogen virus genome in cells/tissue sections using in situ hybridization.
Diagnosis of pityriasis versicolor (lichen)
Diagnosis of versicolor versicolor pumps in:
- Balzer test (iodine test). The affected areas of the skin are treated with iodine and immediately wiped with alcohol. Pityriasis versicolor always turns brown;
- examination under a Wood's lamp (lichen looks like a brown or yellow glow);
- microscopic examination of scales (allows one to identify hyphae (curved short filaments of mycelium), oval and round spores).
Diagnosis of ringworm
To determine ringworm, the following are carried out:
- examination of lesions using a Wood's lamp (lichen becomes green);
- microscopic examination;
- sowing the discharge on various nutrient media (to determine the sensitivity of the pathogen to antibiotics);
- biochemical and general blood tests, urine analysis.
Diagnosis of lichen planus
To diagnose lichen planus in an adult/child, a small affected area of skin is taken for histological examination. The patient is also prescribed a general urine and blood test and biochemistry.
Homeopathy and herbal medicine
For patients with individual hypersensitivity to components in most drugs, doctors often prescribe homeopathic remedies and herbal medicine sessions. This treatment regimen is suitable for women during pregnancy. During this period, the use of many medications is prohibited. A good therapeutic effect is observed from Psorilom tablets.
Their composition is absolutely safe and does not cause side effects. This drug is also available in the form of ointment and gel for external use, shampoo and spray.
Homeopathic tablets, as a rule, are allowed to be taken not only during pregnancy, but also during lactation.
To eliminate the external manifestations of lichen, doctors recommend herbal medicine sessions. Patients are prescribed tinctures based on calendula, propolis and celandine. You can either prepare them yourself at home or purchase them ready-made at any pharmacy chain.
Treatment of lichen
Treatment of pityriasis rosea
Usually, pityriasis rosea does not require drug treatment, as it goes away on its own. During illness you need:
- follow a hypoallergenic diet;
- limit water treatments;
- do not use cosmetics;
- wear underwear made from natural fabrics.
If the patient complains of itchy skin, he is prescribed:
- antihistamines;
- hormonal creams and ointments containing boric acid/zinc;
- hyposensitizing drugs.
Effective methods of non-drug therapy include exposure of the skin to UV radiation with a wavelength of 280-320 nm.
Treatment of herpes zoster
Treatment of herpes zoster in children and adults involves the use of Virolex, Acyclovir, Zovirax. These drugs are effective at the very beginning of the disease. Additionally, Curantil and Furosemide are prescribed. Intravenous administration of immunoglobulin, which activates immunogenesis, helps to achieve good results.
Depending on the severity of the disease, the patient may be recommended symptomatic therapy, which consists of taking:
- general health-improving medications (B vitamins);
- analgesics;
- antipyretic tablets.
Sedatives help with sleep disorders. In some cases, taking antidepressants is indicated. In case of pronounced intoxication of the body, detoxification measures are carried out with forced diuresis.
Locally, lesions of herpes zoster can be treated with a solution of brilliant green, five percent dermatol ointment. For a sluggish form of the disease, metacil ointment and Solcoseryl are used. Areas of skin with rashes can be affected locally using quartz, UV irradiation, and laser.
Treatment of pityriasis versicolor
Treatment of pityriasis versicolor is carried out on an outpatient basis. Antifungal agents are effective against the pathogen:
- salicylic alcohol (3-5%);
- salicylic ointment (5%);
- sulfur ointment (5-10%);
- resorcinol alcohol (3-5%);
- Bifazol;
- Miconazole;
- Cycloperox;
- Naftifin;
- Lamisil et al.
If the lesions are spread throughout the body, oral administration of Orungal, Itraconazole, and Ketonazole is preferable.
Treatment of ringworm
If possible, the treatment of ringworm should be limited to the use of topical medications. If only smooth skin is involved in the pathological process (hair follicles are not affected), you can alternately treat the lesions with an iodine-containing solution and antifungal ointment (Microspor, Lamisil, Exoderil).
For severe skin inflammation, oral antifungal medications are recommended. The optimal triazole derivatives are Itrazyl, Irunin. It is best to shave or trim the hair in the ringworm area.
If suppuration forms on the surface of the lesion, it must be removed by first softening the scabs with salicylic ointment or a solution of potassium permanganate. At the infiltrate stage, ichthyol ointment and Liniment according to Vishnevsky can be used.
Additional methods of treating ringworm include vitamin therapy, as well as taking medications aimed at strengthening the immune system.
Treatment of lichen planus
Treatment of lichen planus is aimed at eliminating itching and burning. The patient may be prescribed:
- Tavegil;
- Suprastin;
- Zyrtec.
Selective phototherapy or PUVA therapy using photosensitizers helps achieve good results. It is also possible to take combined antimalarials (Plaquenil, Delagil) and corticosteroids (Diprospan, Prednisolone).
Local therapy for lichen planus is usually not carried out. If mucous membranes are involved in the pathological process, they should be treated with Rotokan, Solcoseryl, corticosteroid ointments and vegetable oils. If a secondary infection occurs, antibiotics are prescribed.
Ointments and creams
Treatment of pityriasis versicolor with ointments and creams is most often used. Such drugs act directly on the affected area. Preference is usually given to keratolytic and antifungal options. The former quickly soften the surface of the skin and promote exfoliation of the epidermis affected by pathogenic flora. And the latter are intended to destroy the causative agent of the disease.
Ointments and creams necessarily contain wound-healing components. Thanks to them, fungal spots quickly dry out and heal. Sometimes there are antibacterial substances. At the initial stage, it is almost always possible to get rid of lichen through ointments and creams, because the fungus cannot penetrate deep into the epidermis. Another important advantage of such drugs is the almost complete lack of ability to be absorbed into the bloodstream.
Review of popular drugs
Fungoterbin
- an effective cream for pityriasis versicolor, the active substance of which is terbinafine hydrochloride. It is practically not absorbed into the blood and is excreted from the body 20 hours after use. It is recommended to apply the drug to the affected areas twice a day for a week. After use, itching and rash may appear on the skin.
Mycozoral
is another popular remedy that is prescribed to patients diagnosed with pityriasis versicolor. The treatment ointment should not be used if the integrity of the skin is damaged or if you are allergic to the active component (ketoconazole). The drug is applied once a day for 2-3 weeks. After the procedure, allergy symptoms may occur in the form of itching and redness of the skin. The maximum duration of therapy is 6 weeks.
Ciclopirox
also suitable for the treatment of pityriasis versicolor. It can be used in patients over 10 years of age in the absence of allergies to the constituent components. The cream is applied to the skin twice a day for 14 days. Then another 2 weeks as a preventive measure, and after that they definitely take a break. With the simultaneous use of other antifungal drugs, the effectiveness of both only increases.
Diet for lichen
Nutrition during treatment of lichen depends on the type of disease, but there are foods that are equally useful for skin lesions of any type of fungus:
- green vegetables, herbs;
- dairy products;
- breakfast cereals;
- mineral water;
- natural honey;
- foods high in iron.
Pityriasis rosea requires adherence to a dairy-vegetable diet.
For shingles, ringworm, lichen planus and multicolored lichen, it is necessary to enrich the diet:
- foods rich in vitamin E (peanuts, sea buckthorn, rose hips, eel, walnuts, viburnum, sorrel, squid, hazelnuts, prunes, salmon, oatmeal/barley, seeds, vegetable oils);
- products that are sources of antioxidants and bioflavonoids (apples, grapes, apricots, blueberries, cherries, prunes, blueberries, carrots, kiwi, cherries, sweet red peppers, barley, raisins, etc.).
The list of prohibited products for the treatment of any type of lichen includes:
- spices (mustard, pepper, horseradish);
- spicy dishes, pickles;
- alcohol;
- tangerines.
It is necessary to limit consumption:
- offal;
- smoked meats, mushroom and meat broths;
- fatty fish;
- canned food;
- salty and spicy cheeses;
- cream cakes;
- legumes;
- products with preservatives.
Drink coffee, strong black tea and cocoa in small quantities.
Treatment of the scalp
When the scalp is affected by pityriasis versicolor, therapy is carried out using special shampoos. In most cases, they cope well with the task. If there is no effectiveness, treatment is supplemented with systemic drugs in agreement with a dermatologist. One such remedy is Nizoral. The active component is ketoconazole.
The shampoo has no age-related contraindications, but itching may occur when using it. It is recommended to apply the product to all hair, rubbing into the scalp for 5 minutes. The procedure should be repeated every day for 5 days.
Doctors often prescribe Sebozole to their patients. The active ingredient is ketoconazole. Using shampoo may be accompanied by itching or increased oiliness of the scalp. Apply it to clean hair and leave for 5 minutes. The procedure is repeated once a week for one month. Sebozole should not be used while taking potent hormonal drugs.
Why is lichen dangerous?
The harm that lichen can cause to health depends on its type. Pityriasis rosea always occurs without complications. The prognosis of the disease is favorable for ability to work and health.
Shingles is more dangerous. It can lead to:
- decreased motor activity in the limbs;
- partial loss of sensation in the limbs;
- inflammation of the membranes of the spinal cord/brain (encephalitis, meningitis);
- viral damage to the lungs and liver;
- the addition of a secondary infection;
- inflammation of the cornea, eyeball, loss of vision.
The most common consequence of shingles is postherpetic neuralgia. This disease develops after an illness and is manifested by severe pain. Only after a few months the pain goes away.
Pityriasis versicolor and ringworm can lead to a secondary infection. This makes the treatment process more complicated and requires the use of broad-spectrum antibiotics. Trichophytosis can also lead to the formation of bald patches that will last a lifetime.
Complications of lichen planus include:
- addition of bacterial infections;
- inflammation of the oral mucosa.
Pityriasis versicolor during pregnancy
As a result of hormonal changes, the appearance of pathology is possible, but it does not harm the mother and fetus. The disease causes discomfort, but self-medication and folk remedies are unacceptable. If pathology appears, contact a dermatologist, he will choose treatment and, if necessary, prescribe diagnostics. Pregnant women are prescribed therapy for ringworm, taking into account the danger of the situation.
The doctor prescribes drugs that do not enter the bloodstream, does not prescribe anti-fungal tablets, they are toxic and harmful to the unborn child. Nizoral is prescribed; it is not recommended to use the medicine without a prescription.
Many dermatologists advise delaying the full course of treatment until after the baby is born. The fungus is not harmful to the fetus and will not affect its development. Oral medications are prohibited during breastfeeding, as they can pass into the milk and harm the baby's health.
Why should you contact our clinic?
Dermatologists of the highest category
Experienced dermatologists in Moscow. Experience of specialists from 15 years.
Modern equipment
Modern equipment from the world's best manufacturers.
Expert class equipment
Ultrasound is performed using expert-class equipment manufactured by General Electric, SONY, Mindray.
Tests and ultrasound on the day of treatment
Tests, x-rays, ultrasound with interpretation, dressings on the day of treatment in Moscow.
Consultations for adults and children
A network of dermatological clinics in Moscow. Clinics near the metro.
Experienced doctors
Our experienced doctors with over 15 years of experience. Candidates of Medical Sciences.
Are there predisposing factors?
The fungus, which is the causative agent of pityriasis versicolor, can live on the skin for quite a long time without appearing outwardly. In order for its signs to be revealed, a push is needed. Such an impetus for the active development of fungus can be endocrine pathologies, increased sweating, weakened immunity, stressful situations for the skin that disrupt the protective function of the skin - solarium, excessive exposure to the sun, frequent use of antibacterial soaps and shower gels.
IMPORTANT!
The thought of self-medicating pityriasis versicolor is tempting. It seems so simple - I bought antifungal ointment, did it as indicated in the instructions for use, and it’s done. Alas! Without an individual, qualified course of therapy, the fungus will simply adapt to the drugs used, and further treatment will be complicated. Unsystematic or symptomatic self-treatment is highly undesirable.
How does infection occur?
The contagiousness of pityriasis versicolor is believed to be very low. But not all dermatologists-mycologists support this opinion. Pityriasis versicolor can be contracted from a loved one through personal contact or through household contacts through objects used by the infected person, for example, bedding, towels, clothing, washcloths. You can also pick up a fungus in the fitting room of a store. The incubation period for pityriasis versicolor ranges from two weeks to several months.
Make an appointment
Prices for services
Initial appointment with a dermatologist (assessment of patient complaints, history taking, examination, preliminary diagnosis, consultation)
Primary appointment – visiting a doctor of a specific specialty for the first time. Make an appointment
1170 ₽ 1500 ₽
Repeated appointment with a dermatologist
Make an appointment
620 ₽ 800 ₽
Appointment with a dermatologist during removal of tumors (evaluation of complaints, medical history, dermatoscopy if indicated)
Make an appointment
500 ₽
Causes of pathology
Corynebacteria, which are the causative agents of the disease, are normally always present on human skin. Moreover, they provoke the development of pathology only under certain, favorable conditions. Corynebacteria do not penetrate deeper than the epidermis, and also do not affect nails and hair. Since the appearance of erythrasma is directly related to increased sweating, the disease most often manifests itself in the hot summer season.
Among the main reasons for the development of erythrasma are:
- hyperhidrosis;
- deviation of the normal pH of the skin to the alkaline side;
- diaper rash, constant friction and mechanical damage to the skin;
- dermatitis and other skin diseases;
- neglect of personal hygiene rules;
- wearing synthetic, overly warm clothing;
- the use of low-quality care products or the abuse of soap with an antibacterial effect, which destroys the natural protection of the skin.
Erythrasma is transmitted by contact, most often after the use of clothing, bedding and personal hygiene products of the patient. You can also become infected during sexual intercourse, when visiting a pool or bathhouse, and when walking barefoot on the ground or beach. At the same time, it is not always possible to accurately determine the source of infection, because the carrier may not have obvious external manifestations of the disease in the form of characteristic spots and peeling.