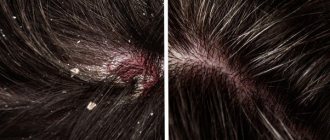
Seborrhea develops in the so-called seborrheic zones - areas of the skin in which there are especially many sebaceous glands, about 400-600 per 1 cm2 1. These include:
- scalp;
- T-shaped area of the face (forehead, nasolabial folds, chin);
- the central part of the chest and the upper part of the back between the shoulder blades.
Seborrheic dermatitis is a chronic inflammatory disease that develops when the yeast-like fungus Malassezia furfur begins to actively multiply in the affected areas. About 3% of the population suffers from manifestations of this disease, and young people are more susceptible to them, among whom the number of patients increases to 5%.2
The disease is considered quite common. It manifests itself especially often in the first years of a child’s life, as well as in people after 40 years of age. This age-related feature of the occurrence of seborrheic dermatitis is explained by the fact that it is during these periods of a person’s life that the sebaceous glands on the body work with high intensity.
Causes of occurrence and development
The development of seborrhea and seborrheic dermatitis is based on dysfunction of the sebaceous glands of the skin, which manifests itself in the fact that the glands begin to produce either too little secretion (sebum) or too much, in addition, the composition and consistency of the secretion also changes. Excess secretions are mixed with dust, dead skin cells and can serve as a substrate for the active reproduction of opportunistic microorganisms, most often fungi of the genus Malassezia, which are normally present on the skin of 90% of the population3. The metabolic products of this pathogen cause skin irritation and its inflammatory reaction, manifested in the form of redness and the appearance of papules covered with greasy crusts.
Why does the functioning of the sebaceous glands malfunction? Doctors identify many factors that can play a role in dysfunction of the sebaceous glands. Among them:
- genetic predisposition;
- changes in hormonal levels (increased levels of progesterone and androgens, decreased levels of estrogen - therefore, the disorder is often found in men), including in infancy, puberty, pregnancy, and chronic diseases;
- decreased immunity due to chronic or infectious diseases, taking potent medications;
- a lot others.
The ducts of the sebaceous glands open into the mouth of the hair follicle, so with seborrhea and seborrheic dermatitis, not only the skin, but also the patient’s hair suffers.
The problem may worsen as a result of prolonged exposure to heat or due to increased sensitivity of the skin to external irritants. At the same time, seborrheic dermatitis in children and adults can be severe, regardless of the number of active fungi on the skin.
Seborrhea: causes of appearance
The main causes of seborrhea of the scalp and face include:
- — Hormonal changes in the body in adolescents.
- — Yeast-like fungi (Malassezia).
- — Imbalance of estrogen and andogens in both men and women.
- - Testicular tumor.
- - Pakinson's disease.
- — Violation of the psycho-emotional state.
- - Mental illnesses.
- — Long-term use of testosterone, progesterone, etc.
The true cause of seborrhea of the scalp and face can only be identified by a doctor after all the research results have been received. The most important thing is to correctly identify the source in order to avoid further relapses and protect yourself from the appearance of seborrhea in the future.
For the treatment of oily seborrhea and its other forms, it is important to select modern techniques aimed at people of the 21st century.
How does seborrheic dermatitis manifest?
The disease affects certain parts of the human body. Typically this is:
- scalp skin;
- face;
- behind-the-ear areas;
- upper body (most often the area of the chest, shoulder blades);
- large skin folds on the body (for example, groin area, armpits).
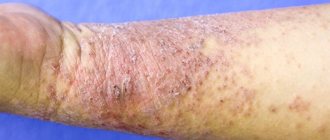
Seborrheic dermatitis in adults and children manifests itself in the form of local redness and papules covered with greasy scales.
The disease can also be recognized at an early stage in adults by the appearance of a sign such as dandruff. As the situation worsens, the scalp gradually begins to become covered with red spots; later they can merge, forming lesions with characteristic peeling of the skin. In advanced cases, when oily crusts peel away from the surface of the skin, a moist secretion is discovered underneath. If you do not take any measures to treat seborrheic dermatitis, then this problem may be complicated by the addition of an infection.
In addition to external signs of seborrheic dermatitis, patients often complain of itchy skin. As a result of constant scratching of the inflammation, even greater tissue injury occurs with a high risk of further infection.
The disease not only causes serious discomfort, but also worsens a person’s quality of life as a whole, provokes self-doubt, makes it difficult to establish contacts with other people, and prevents them from building close relationships with the opposite sex.
What is the difference between dandruff and seborrhea?
Ordinary dandruff is a mild form of seborrhea, which, as a rule, does not require treatment, just proper care - using a mild detergent that does not irritate the skin.
In the case of dry seborrhea, skin flakes (dandruff) easily flake off and settle in large quantities on the hair and shoulders. Hair may become thinner and break easily.
If seborrhea is oily, the skin flakes (dandruff) stick together, often sticking to the hair and forming yellowish, greasy crusts. With oily seborrhea, the hair quickly gets dirty, becomes greasy, and often thins.
Manifestations of seborrhea are noted in those places where the sebaceous glands are located: the face, mustache, eyebrows, upper chest, interscapular area and, in fact, the scalp.
Hair also changes with seborrhea, becoming greasy and shiny, it quickly becomes dirty, sticking together in strands.
Symptoms and forms/Types of seborrheic dermatitis
If we consider seborrhea and seborrheic dermatitis in children and adults, we can distinguish the following varieties:
- Dry seborrhea. With this nature of the disease, the sebaceous glands produce an insufficient amount of secretion. As a result, the skin does not receive enough moisturizing components, dries out, and microcracks appear on its surface. Typically, dry seborrhea occurs without the formation of acute inflammatory foci. Instead, the patient is concerned about the separation of dry dandruff particles. Most often, this form of the disease is observed in adolescent children.
- Oily seborrhea. The form differs from the previous one in that the sebaceous glands, on the contrary, work too actively and secrete a large amount of thick secretion. The substance glues together dead skin cells and is deposited on the hair, causing it to take on an unkempt appearance. The problem often affects young women.
- Combined type. It is characterized by the presence of signs of both dry and oily seborrhea. The disease develops in various parts of the body and therefore causes serious discomfort. In most cases, this form is diagnosed in males.
Depending on the location of the foci of inflammation, seborrheic dermatitis of the scalp, face and torso is distinguished.
The first sign of damage to the scalp is the appearance of dandruff. In this case, the scalp can be either excessively dry or oily, and the scales can range from silvery-white in mild cases to dense fatty crusts in severe cases.
In patients with seborrheic dermatitis of the scalp, over time, the hair becomes sparse, thin, brittle and often falls out.
Focal inflammation on the face is considered no less common. This form of the disease mainly affects teenagers and young people under the age of 25. The cause of seborrheic dermatitis in this case is the high activity of the sebaceous glands in the facial area. During puberty, they begin to work more actively, which can provoke the development of the disease. On the face, rashes are often symmetrical, located in the forehead, nasolabial folds, wings of the nose, and eyebrows.
At the initial stage, the disease manifests itself in limited areas of inflammation, the surface of which is covered with white-yellow scales. The rash is accompanied by itching and constantly peels off. As the disease progresses, areas of inflammation may merge. In some cases, inflammation is aggravated by the addition of a secondary infection.
Sometimes the inflammation spreads to the skin of the eyelids. This leads to the development of seborrheic blepharitis. It is characterized by the formation of severe swelling of the eyelids, redness of the eyes, and the formation of cracks in the delicate skin in this area. At the eyelash growth line, inflammatory foci gradually begin to form with a characteristic separation of small scales and crusts. Because of this, patients have to literally “pry” their eyes out in the morning, since the eyelids stick together so much.
On the torso, seborrheic dermatitis is usually localized in the area of the sternum and shoulder blades. The disease occurs with the formation of foci of inflammation with clear boundaries, covered with yellowish scales.
The severity of seborrheic dermatitis varies from mild to severe and depends on the extent of skin lesions, severity of inflammation and intensity of itching.
Infantile seborrheic dermatitis is one of the first skin diseases that a child encounters. It develops against the background of immature functions of the skin and sebaceous glands in infants and manifests itself in the form of fatty yellow crusts covering the head (the so-called “baby cap”), sometimes the area of the eyebrows and cheeks.
What is seborrhea?
Seborrhea is a common skin disease characterized by overactive sebaceous glands.
Typically, oily seborrhea develops during puberty, but older people can also experience the disease. Seborrhea is a serious cosmetic problem that all sufferers want to get rid of. Because of dandruff, a person cannot wear dark clothes; he has to constantly wash his hair and make masks. In addition, you may experience itching and pain.
To get rid of seborrhea on the face, oily seborrhea of the scalp and other forms of the disease, it is important to consult a professional dermatologist or trichologist. The specialist will suggest a way to eliminate seborrhea, the causes of which will be determined after the examination.
Treatment of seborrheic dermatitis: basic approaches and methods
The tactics and treatment regimen for seborrheic skin dermatitis are selected by the doctor based on the form in which the disease occurs and in which area the inflammation is localized.
If the disease is mild, then this form is characterized by the presence of a small amount of dry or greasy scales, moderate redness of the skin, and occasional mild itching. With this course of the disease, the doctor, as a rule, limits himself to external therapy. For example, with mild damage to the scalp, or dandruff, the doctor may recommend the use of Skin-cap shampoo. Apply shampoo to damp hair, then massage the scalp until foam forms and rinse thoroughly. After this, you need to reapply the shampoo, leave for 5 minutes, and rinse thoroughly with plenty of water. Skin-cap shampoo can be used both for exacerbation of seborrheic dermatitis according to the scheme 2-3 times a week, and for the prevention of further relapses 1-2 times a week.
When the disease occurs in moderate to severe form, the symptoms of seborrheic dermatitis become more pronounced. At this stage, brighter red spots appear on the skin, sometimes noticeable swelling forms on the skin, and the surface is covered with dense gray-yellow crusts. All this occurs against the background of severe itching, which is present almost constantly. Due to discomfort, the patient cannot work fully, it is difficult for him to concentrate on anything, and often in the acute phase of the disease a person experiences problems with sleep.
In this case, there are also generally accepted recommendations on how to treat seborrheic dermatitis. The measures taken are comprehensive; patients may be prescribed hormonal medications. Treatment of seborrheic dermatitis is prescribed by a doctor, based on the severity of the disease and the individual characteristics of the patient. One of the non-hormonal drugs for the treatment of seborrheic dermatitis is the drug Skin-cap. It inhibits the activity of the Malassezia fungus and helps reduce signs of inflammation and also helps reduce flaking. Depending on the location of the inflammatory foci, Skin-cap shampoo, cream or aerosol may be prescribed. Skin-cap aerosol, for example, is suitable for treating the scalp, and the cream is convenient to apply to the face. The duration of treatment for an exacerbation varies, usually it takes from two weeks to 1 month to completely eliminate the symptoms of the disease.
The use of shampoo, cream and aerosol Skin-cap helps to significantly alleviate the condition of seborrheic dermatitis. The active ingredient of the drug Skin-cap has the following effects:
- provides anti-inflammatory effect;
- suppresses the growth and reproduction of pathogenic fungi, which are the main cause of exacerbation of the disease;
- inhibits the activity of bacteria that can increase inflammation.
The drug can be recommended to patients with any form of seborrheic dermatitis; treatment is possible for both adults and children over the age of one year. Products from the Skin-Cap line do not just eliminate the signs of the disease, they help keep the disease under control, preventing relapses.
Shampoos with zinc against seborrhea
Today, shampoos with zinc are very popular. More than a hundred brands produce shampoos with zinc to eliminate dandruff and seborrhea.
- SKIN-CAP shampoo is an original treatment based on activated zinc pyrithione, a substance with pronounced antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory and antifungal activity. The skin cap contains activated zinc pyrithione in a proportion of 1 g per 100 ml of the drug. Suitable for combating dry and oily seborrhea, dandruff and seborrheic dermatitis.
- Friederm Zinc is a cosmetic product based on zinc pyrithione. Contains a suspension of zinc pyrithione at the rate of 20 mg of active substance per 1 ml of shampoo. Helps eliminate dandruff, but is not therapeutic.
- Keto plus Keto plus is a medicinal antifungal shampoo. 1 ml of the drug contains two active components: pyrithione zinc (10 mg) and ketoconazole (20 mg). Keto plus is used for the treatment and prevention of scalp skin diseases such as pityriasis versicolor, seborrheic dermatitis, and dandruff.
- Cynovit Shampoo Cynovit is a cosmetic product used to combat dandruff on the head. It is recommended to wash your hair up to 2-3 times a week. The duration of the course is 1 month.
Features of SKIN-CAP release forms
The cream is quickly absorbed and softens and moisturizes the skin well and does not leave greasy marks on it. It is suitable for facial skin and affected surfaces that require moisturization.
The aerosol can be applied even to the scalp using a special nozzle, which is included in the kit, without touching the hair. It helps eliminate itching and dries out wet rashes.
Seborrhea shampoo effectively7 fights its manifestations on the scalp. Actively helps eliminate dandruff and itching, fights the root cause of the disease - pathogenic microorganisms. Ideal for preventing relapses.
Skin-cap shower gel is a cosmetic product that is indispensable for daily hygiene in cases where seborrhea affects the skin of the chest and back. It cleanses, soothes and moisturizes the skin, helps eliminate inflammation and restores the protective properties of the skin.
Prevention of seborrheic dermatitis
Patients with this disease need to know not only how to treat seborrheic dermatitis, but also learn the basic rules for preventing exacerbation of the disease. The main task in this case is to exclude those factors that can trigger the triggering of pathology development mechanisms.
Thus, as part of the prevention of seborrheic dermatitis, it is worth paying attention to several aspects:
- following a certain diet;
- compliance with personal hygiene rules;
- quality skin care;
- maintaining an active and healthy lifestyle;
- timely treatment of concomitant diseases.
Treatment
Treatment for oily scalp seborrhea can take a long time, so it is important to be patient and not give up. Due to the fact that dandruff is only a symptom, it is not easy to eliminate it: you need to overcome the disease itself.
The basic course includes drugs such as selenium disulfide, lithium succinate and ketoconazole. Special medicated shampoos (for example, Sulsena) may be prescribed. The patient should carefully monitor personal hygiene and not neglect washing his hair.
Doctors recommend adjusting the nutrition system, eating more vegetables, lean meat containing protein. Moderate fasting will be beneficial. It is also important to protect yourself from stress and try to improve your emotional state.
It is important for women to understand their menstrual cycle; if it is disrupted, visit a gynecologist. If a man exercises and takes supplements, it is important to completely limit their use.
The quality of the water remains an important factor: if you are unhappy with the composition, you can install a household filter that will soften and remove metals.
Diet for dermatitis
The diet for seborrheic dermatitis should be based on healthy foods containing a small amount of fat. These include a variety of cereals, lean meats and fish, and always fresh vegetables and fruits.
It is important not only to eat well and properly, but also to follow some recommendations for cooking. Thus, the most preferred options for heat treatment of products are boiling, baking, steaming or grilling without adding oil.
Maintaining personal hygiene
Patients with seborrheic dermatitis are recommended to injure the inflammation as little as possible. Personal hygiene rules include cleansing the skin twice a day using special products with a low pH. To cleanse the skin, it is prohibited to use aggressive agents such as laundry or tar soap.
General recommendations for maintaining personal hygiene:
- the use of washcloths or sponges with hard fibers is excluded;
- For a while, you should avoid cleansing your skin with scrubs and peels containing abrasive particles and aggressive chemical compounds;
- During water procedures, it is recommended to use dechlorinated water; for this purpose, it is recommended to first settle or filter it;
- the duration of water procedures should be reduced to 10-15 minutes;
- when choosing shower products, choose products without dyes and fragrances, with a low pH;
- use towels with soft bristles, and it is better to blot your skin with them rather than rub them;
- to reduce the likelihood of skin injury when combing, try to cut your nails as short as possible;
- Avoid using other people's personal hygiene items.
Skin care rules
Skin care prone to symptoms of seborrheic dermatitis is primarily focused on normalizing the functions of the sebaceous glands. It is important not only to reduce sebum production, but also to ensure skin hydration.
General care recommendations:
- Try to reduce the use of comedogenic makeup, as it can cause clogged pores.
- Use care products that do not contain alcohol. It irritates the skin, dries it out, causing the sebaceous glands to work more actively.
- For care, choose special cosmetic products designed for seborrheic skin.
Diagnostics
Oily seborrhea is distinguished by characteristic symptoms. Despite this, the process of diagnosing seborrhea includes a set of measures.
First, the doctor gets acquainted with the patient's medical history. This allows you to determine what led to seborrhea. After this, he collects and analyzes his life history. This makes it possible to find out against what factors the pathology of the epidermis of the head developed. Then a thorough examination of the affected segments of the head is carried out and a complete clinical picture of the course of seborrhea is compiled.
Also, before treatment, comprehensive instrumental diagnostics are carried out. The doctor examines both skin and hair.
The main methods of examining the head and hair include:
- Skin scrapings and microscopic examination of hair.
- X-ray of the abdominal cavity.
- Ultrasound of the thyroid gland.
- CT and MRI.
Patients also undergo laboratory diagnostics. It includes a general and biochemical blood test, as well as hormonal tests. If necessary, a gynecologist and andrologist, a neurologist, an endocrinologist and other specialized doctors are involved in the examination, diagnosis and further treatment.