SPECIALISTS Gynecologist Gynecologist-endocrinologist Pediatric gynecologist Mammologist-oncologist Dermatologist Hirudotherapist Intimate plastic surgery Doctor Contour plastic doctor Ultrasound doctor SERVICES AND PRICES Gynecology Mammology Ultrasound diagnostics Paid tests Intimate surgery Contour plastic Treatment for women PROMOTIONS AND DISCOUNTS Students Teams Friends and subscribers am For residents of the region For pensioners Promotions in clinic
HPV is a viral infection that is transmitted between people through skin-to-skin or mucous-to-mucous contact. There are more than 100 varieties of this virus, 40 of which are sexually transmitted and can affect the genitals, anus, mouth or throat in women.
Some types of HPV, so-called. “high risk” are responsible for cancer of the cervix, anal canal, vagina and vulva. Other types of papillomavirus cause genital warts. About half of the new infections are people aged 16 to 25 years. In most people infected with HPV, the body clears it of it on its own. But for others who are not cleared of the virus, it can cause cancer of the cervix, vagina and external genitalia in women, and cancer of the anus and rectum in men and women.
And at present, medicine and, in particular, gynecology, has no way to predict who will or will not be cleared of papilloma viruses. After all, HPV usually has no visible signs or symptoms, so HPV carriers can transmit it to other people without knowing it.
Types of papilloma virus
Research scientists have divided the types of HPV in women into those that are more likely to develop into cancer and those that are less likely. So-called “high-risk” HPV types are more likely to lead to cancer, while “low-risk” viruses rarely develop into cancer. High-risk sexually transmitted HPV types include the following types: 16, 18, 31, 33, 35, 39, 45, 51, 52, 56-59, 68/69.
Low-risk types of papillomavirus do not cause cancer in humans. Warts or papillomas may grow weeks, months, or even years after exposure to infection, or may never appear. In fact, most people with low-risk HPV types never know they are infected without testing because they do not have any other symptoms.
Oncogenic HPV type
There are more than 40 types of HPV that can affect the genital area, but 9 of them are known to cause the majority of HPV-related cancers and diseases. Against their background, changes in the cervix that lead to cancer often develop over 10 or more years, and non-oncogenic types of HPV often resolve on their own within one or two years without causing cancer.
⚠ High-risk HPV types are 6, 11, 16, 18, 31, 33, 45, 52, 58 and some others. But these 9 main oncogenic types are responsible for approximately: ☛ 90% of cases of cervical cancer, ☛ 85% of anal cancer in men and women,* ☛ 90% of vulvar cancer cases,* ☛ 85% of vaginal cancer detections,* ☛ 90% of cases genital warts.
* - Not all cases of cancer of the vagina, external genitalia and anus are caused by high-risk HPV. About 70% to 75% of cases of vaginal cancer, 30% of cases of vulvar cancer, and 85% to 90% of cases of anal and rectal cancer are associated with the complex influence of individual risk factors in combination with these highly oncogenic types of HPV.
The main cause of HPV of the anus, including the high oncogenic type in a woman or man, is the practice of anal sex and the introduction of objects contaminated with viruses into the rectum (dildos, anal toys, etc.).
HOW IS THE PAPILLOMA VIRUS TRANSMITTED?
Most people get HPV through direct sexual contact in the vagina or rectum, or through oral sex. Since HPV is a skin-to-skin infection, sexual intercourse is not a requirement for infection. Up to 30% of cases of PVI transmission occur through contact at home. This may be one of the explanations for the presence of both genital warts and the detection of HPV in girls and virgin girls who have never had intimate contact.
In rare cases, a mother with HPV can pass the virus to her baby during childbirth. Often the virus is hidden in the body of the infected person. As a result, that person may unknowingly transmit HPV to their sexual partners. The virus is also more likely to be transmitted if there is an opening in the skin, such as a cut, abrasion or tear. These holes can be microscopic in size and not noticeable to the naked eye. Thus, any contact of these areas with a person who has the infection can transmit the virus.
HPV symptoms
The papillomavirus is one of the most common types of sexually transmitted infections (STIs). Almost all sexually active people will have HPV at some point in their lives, and they may not even know it. Most people never experience any symptoms of HPV. According to various estimates, up to 8 out of 10 cases of infection go away without treatment, often within two years. However, there are cases when the papilloma virus persists in the human body and symptoms appear.
Signs of infection depend on the type of HPV you were given. Some can cause genital warts, such as HPV types 6 and 11. Other types, such as HPV 16 and 18, do not cause warts or papillomas in women, but can lead to certain types of cancer.
Ⅰ WARTS.
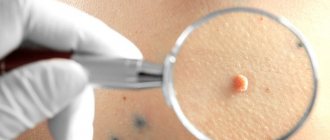
They are a common symptom of HPV infection. They may appear weeks, months or even years after exposure to the virus. How warts look and where they are located on the body is determined by the type of HPV. Here is their list:
- Common warts. These rough, red bumps usually appear on the elbows, fingers, and hands. Common warts may be painful or bleed easily.
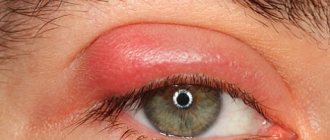
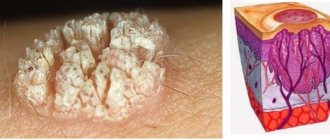
- Genital and anal warts. Condylomas and papillomas of intimate places, or genital warts, as their name indicates, most often appear near the anus and on the external genitalia of women and men. They may also appear near the anus, in the vagina, or on the cervix. These warts resemble irritated, cauliflower-like clumps, fringes, grapes, tiny raised bumps, or flat bruises. In men, genital warts most often affect the tip of the penis, the opening of the urethra, and the skin around the anus (especially in men who have anal sex). They usually have no symptoms and may be slightly itchy, but rarely cause pain. Genital condylomatosis is the most common manifestation of HPV infection in gynecology.
- Flat warts. They appear as darkened areas of skin with slightly raised flat tops. They can appear anywhere on the body.
- Plantar warts. These are thick, painful growths of skin on the soles of the feet. They are often mistaken for simple calluses. They may appear irritated, hard, and grainy (called a callus).
- HPV of the mouth and throat. The same types of HPV that can cause genital warts can also cause warts in the mouth and throat. This is called oral HPV. With this localization of HPV, symptoms may include: ear pain, hoarseness, sore throat that does not go away, difficulty swallowing, swollen lymph nodes.
Ⅱ HPV AND CANCER.
Certain types of HPV, most commonly 16, 18, 31, 33, 51 and 52, 45 and 49, can also lead to certain types of cancer. Cervical cancer is the most common HPV-related cancer. Symptoms of cervical cancer may include:
- irregular vaginal bleeding,
- unusual vaginal discharge,
- difficulty urinating or bowel movements,
- fatigue, weight loss.
Other types of cancer that are possible due to HPV include diseases of the vagina and vulva, cancer of the penis and scrotum, anus and rectum, and the back of the throat (oropharynx).
Table 1. “Manifestations of papillomavirus infection on the human body depending on the type of virus”
| Localization of education | Culprit |
| Skin warts | Types 2 and 7 |
| Plantar warts | Types 1, 2, 4 and 63 |
| Genital and anal papillomas | Type 6, 11, 42, 44, etc. |
| Cancer of the mouth, throat | Type 16, 33, 52 |
| Cervical tumors | Types 16, 18, 31, 45, etc. |
| Precancerous changes in the vulva | HPV 16, 18, 34, 39, 42, 55 |
HPV in girls, adolescents and virgins
As mentioned earlier, the spread of HPV in up to 80% of cases occurs through sexual contact. But this virus is also transmitted non-sexually. In children, it spreads from skin to skin through close contact. This leads to warts on the hands and face.
Genital papillomas are rare in childhood and are observed less frequently than in adults. However, there is an increase in the incidence of HPV in adolescents during puberty. In girls of primary and secondary school age, gynecologists often find warts in intimate places in the vaginal, vulvar and perianal area. Virgin girls get condylomas and HPV either as a result of surrogate sex without mechanical damage to the hymen, or sexual intercourse in the rectum or blowjob, as well as through contact and household contact.
Manifestations of HPV in children
Skin warts: At least 10 percent of children suffer from skin warts. These can be ordinary warts, plantar and flat. They are more common in girls than in boys. They are usually visible on the hands, fingers and nails. Genital warts, although rare in children, can appear as multi-colored cabbage-like growths in and around the genital and anal area. Genital condylomas are usually painless. Plantar warts are painful and cause discomfort.
In many children and adolescents, the infection remains latent and symptoms go unnoticed. It is believed that many women with cervical cancer were likely exposed to oncogenic types of HPV during adolescence or before the age of 20–25 years.
Photo of HPV
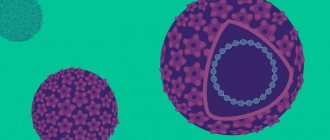
In the photographs below you can see what the mucous membrane and skin of the genitals affected by the papilloma virus look like. Some photos show manifestations of different types of HPV (high and low oncogenic risk) in women and men, taken under an electron microscope with high magnification.
Table No. 1.
HPV types
| Photo of HPV 16 | Photo of HPV 18 | Photo of HPV 6 |
| HPV 31/33 | HPV 42/45 | HPV 51/59 |
Table No. 2.
Photos of HPV in women
| HPV in the uterus | HPV on lip |
HPV DNA
International guidelines updated in 2014 recommend that girls undergo their first PAP and HPV testing at age 21, regardless of sexual activity.
After that, young women aged 21 to 29 should have a Pap smear every two years. Regular examination will help identify abnormal cells. They may signal cervical neoplasia or other problems associated with viral carriage.
Then, if previous test results are favorable, patients aged 30 to 65 years should be screened every three years with PAP and HPV tests simultaneously.
How to effectively detect human papillomavirus?
Donating DNA for HPV types is the main method for diagnosing this infection. This analysis can help identify the types of HPV that can cause cancer, and an expanded list of indicators will establish not only the genotype of the virus, but also its amount in the tissue. The gynecologist usually combines DNA testing for the papilloma virus with a Pap test. Next we will talk about these studies.
- "HPV DNA." The most common diagnostic method that allows one to detect the presence of infection even in a minimal sample of biological material. Most often, HPV DNA tests in women identify types 6, 16, 18, 31, 11, 33, 35, 39, 45, 51 and 52.
- “HPV DNA + PAP” liquid. Combined diagnosis of carriage of human papillomavirus infection and the degree of its possible influence on the epithelium of the cervix.
- "DNA for HPV types extended." The genotyping method allows you to both find out the type of HPV and determine its quantity. This has important prognostic significance in gynecology.
✔ You can donate HPV DNA to women and men in Moscow at reasonable prices from the specialists of our clinic. Gynecologists (for ♀) and a treatment room (for ♂) work daily, from 10-00, seven days a week. The clinic staff will tell you what types of HPV to test for. At the following link you can see all prices for analysis for the papilloma virus and advanced Digene tests.
Questions - answers on the topic
What types of HPV cause condylomas? There are 30-40 strains of the virus that specifically affect the genitals, but only some of them can cause genital warts in women and men. HPV types 6 and 11 cause the growth of condylomas and papillomas in the intimate area in 80% of cases.
What are the most dangerous types of HPV (for women)? Low-risk types cannot cause cervical cancer and are treatable. High-risk types 16 and 18 are dangerous because they can cause a woman to develop abnormal cells on her cervix, which often turn into cancer if left untreated.
What to do if a woman has HPV? During the examination, did the doctor find condylomas or did testing for the virus give a positive result? First of all, you need to get advice from a good gynecologist, a specialist in this pathology. After discussing the test data, conducting a colposcopy and a full examination to identify possible foci of condylomatosis, you can plan further tactics. In the future, after recovery from the virus and removal of condylomas, women are advised to “watchful waiting” with regular repeat HPV tests and colposcopy.
How to find out if you have HPV? Getting tested is the only and correct way to clarify your health status. A possible list of services and prices are presented in the table above. The status of a virgin does not prevent you from undergoing examination and knowing about the presence or absence of the human papillomavirus in the body.
Preparation for the procedure
It is advisable to conduct examinations of women in the first half of the menstrual cycle, but not earlier than the 5th day. Examination in the second half of the cycle is acceptable, but no later than 5 days before the expected start of menstruation.
If there are pathological changes, material is taken on the day of treatment.
The day before and on the day of the examination, the patient is not recommended to douche the vagina. Biomaterial collection should not be carried out earlier than 24-48 hours after sexual intercourse, intravaginal ultrasound and colposcopy.
A scraping from the urethra is carried out before or 2-3 hours after urination.
Men need to avoid sexual intercourse 1-2 days before taking a smear (scraping). You cannot urinate for 1.5-2 hours before the procedure.
How to treat HPV
How to treat the papilloma virus in women is a question often faced by patients who have received positive test results. As a rule, in the absence of cancer risk and clinical signs, HPV treatment is not required. For many people, the body clears the virus on its own.
When is HPV treatment needed:
- Detection of high-risk types (16, 18, etc.);
- Abnormal colposcopic picture;
- Unsatisfactory result of oncocytology.
☑ For information:
The doctor who treats HPV in women is a gynecologist. If questions or problems arose at a young age, under 16 years of age, then pediatric or adolescent gynecologists work with the patient.
Which doctor treats HPV in men? Typically, young people with this disease turn to a urologist or dermatovenerologist. This specialist will prescribe treatment for the infection and, if necessary, will be able to remove formations in the anogenital area.
HPV vaccine
At what age are girls vaccinated, can it be given to boys, as well as women after 30 years of age and older? Reviews from doctors about the effectiveness after infection, where to get vaccinated against papillomavirus in Moscow and is it given in clinics or antenatal clinics for free? We will try to answer these and other questions in more detail below.
As far as we know, cervical cancer is closely related to the human papillomavirus, which is present in almost 90% of the world's population. At the same time, articles have been periodically published on the Internet for several years now stating that the HPV vaccine, the Gardasil vaccine, leads to infertility. How correct is this information? Is it possible to get infertility due to the HPV vaccine?
The WHO Global Advisory Committee on Vaccine Safety regularly reviews the evidence on the safety of HPV vaccines. Clinical testing and monitoring of the drug has consistently demonstrated that it is safe and effective in preventing infections caused by human papillomavirus and also protects against the development of dysplastic phenomena and cervical cancer. There is no evidence that this vaccine causes infertility.
Many people are diagnosed with HPV at some point in their lives. Most infestations do not develop into cancer. But in a small number of women, HPV can become a chronic condition and lead to the development of invasive cervical cancer. There are certain negative factors in which HPV infection will lead to such consequences. These are, in particular, a certain type of HPV with a high cancer risk, the immune status of the woman herself, the presence of any concomitant sexually transmitted infection, the number of children born, as well as tobacco smoking.
The HPV vaccine is recommended for boys and girls aged 11-12 years. Women and men can be vaccinated with Gardasil up to age 26. People ages 27 to 45 who have not previously been vaccinated against HPV are now also eligible for Gardasil (Gardasil 9 in the US for women over 30).
According to the instructions, the vaccine protects against types of PVI that are associated with malignant diseases of the anogenital zone, and also prevents certain types of HPV that cause condylomas and papillomas in intimate places in both women and men.
Those wishing to get vaccinated against the human papillomavirus for free should know that this is not possible. Clinics and antenatal clinics in Moscow do not provide vaccinations against HPV and cancer free of charge - it is not included in the list of services under compulsory medical insurance and is not covered by government guarantees and subsidies.
PRICES FOR HPV VACCINATION
Vaccination against human papillomavirus, the price of which in commercial clinics starts from 11,000 and reaches 19,000 rubles per course injection. Having started the vaccination course, experts recommend completing it completely and completing it with the third injection 6 months after the first injection.
Girls and teenagers in Moscow can be vaccinated against papillomavirus in our clinic at the patient’s (or his legal representative’s) own request. However, doctors recommend undergoing a preliminary examination by a pediatric/adolescent gynecologist and passing HPV tests.
HPV treatment in Moscow
Doctors who treat HPV, including women and teenage girls, effectively and with good results, according to patient reviews, work at the Gynecology Clinic on Kutuzovsky! Effective regimens, courses and drugs that help get rid of papillomavirus types 6, 11, 16, 18, 31, 33, 45, 51, 52, 56 and other types of high and low oncogenic risk.
Reasonable prices, good results and 20 years of experience in gynecological treatment! HPV is not scary if precious time is not lost - make an appointment with a gynecologist right now! Phone number of the clinic in Moscow ☎
Additional examination in case of deviation from the norm
The doctor interprets the result of the analysis taking into account data about the patient and the disease, examination findings, cytological and histological studies.
A gynecologist, urologist or proctologist may prescribe additional tests:
- cytological examination of biomaterial from scrapings of the vulva and vagina, except the cervix (Papanicolaou staining, Pap test);
- cervical cancer screening - determination of HPV DNA and cytological examination of scrapings of the cervix and cervical canal using liquid cytology;
- cytological and immunocytochemical study of the expression of proteins p16INK4a and Ki-67 in smears of the cervical mucosa (Cytology and p16 and Ki-67 immunocytochemistry test in cervical mucosa smears);
- determination of antibodies to HIV 1 and 2 and HIV antigen 1 and 2 (HIV Ag/Ab Combo).
Antibodies to HIV 1 and 2 and HIV antigen 1 and 2 (HIV Ag/Ab Combo)
Synonyms: Antibodies to HIV 1, 2, antibodies to human immunodeficiency virus, HIV-1 p24, HIV-1 antigen, p24 antigen. Anti-HIV, HIV antibodies, human immunodeficiency virus antibodies, HIV-1 p24, HIV-1 Ag, p24-antigen. Attention! In case of positive and questionable reactions, the issuance period...
510 rub.
A consultation with an immunologist, surgeon, or oncologist may be recommended.
Sources:
- Bakhtiyarov K.R., Shchukina A.S. Human papillomavirus - a modern view of the problem. Medical and pharmaceutical journal "Pulse". No. 12 (Vol. 19), 2022. pp. 37-42.
- Laboratory diagnosis of infectious diseases: a reference book / ed. IN AND. Pokrovsky, M.G. Tvorogova, G.A. Shipulina. - M. - Binom, 2013. - 648 p.
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment. In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor.
Information verified by an expert
Lishova Ekaterina Alexandrovna
Higher medical education, work experience - 19 years
Share this article now
An example of a form with test results for papillomavirus
HPV test form
Absolute viral load is the amount of virus found in a sample. If HPV is absent or its concentration does not exceed clinically significant levels, the form is marked “virus absent” or “not detected.” Such a record does not mean that the pathogen is not in the body at all. This is unlikely, since papillomavirus occurs in 80% of the population. Its concentration is simply not sufficient for the development of cervical cancer and other diseases.
If the absolute content of HPV exceeds the clinically significant value, its concentration (viral load) is indicated opposite the virus strain. The higher it is, the worse the result.