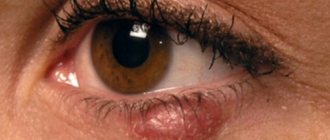
Oral dermatitis is a local skin lesion, which consists of small papules (pimples), usually localized around the mouth, which determines the name of the disease. Another name for this disease is perioral dermatitis. Most often, this type of dermatitis is diagnosed in young women, less often in older women, but can also occur in children and teenage boys. Oral (perioral) dermatitis is an unpleasant cosmetic problem, which can still be eliminated if the cause of its occurrence is correctly identified and an effective treatment regimen is selected.
Medical is a clinic that diagnoses and treats many diseases, including dermatological ones. The treatment regimen in each specific case is selected individually, taking into account the characteristics of the patient’s body.
Clinical manifestations
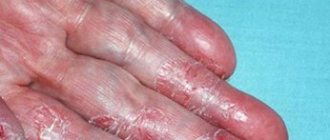
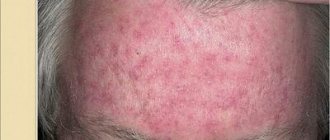
Localization : has a characteristic location of the rashes, these are the perioral zone, nasolabial folds, skin of the chin and cheeks. The affected areas are characterized by symmetry.
Characteristic sign : a strip of healthy skin around the lips measuring 2-4 mm (characteristic in most cases, however, the case shown in the photo is a rare exception).
Rashes : pinkish-red papules, papulo-vesicles and papulo-pustules measuring 1-2 mm are located on an erythematous (red) background. Rashes are resolved by the appearance of crusts in place of the papules. The skin is dry, swollen.
Subjective sensations: characterized by a feeling of skin tightness, itching and burning.
Outbreaks of erythema with temperature changes, alcohol intake, spicy and hot foods. These manifestations are also characteristic of rosacea, which complicates the diagnosis of perioral dermatitis.
pigmentation may develop .
In what cases does perioral dermatitis occur?
The causes of perioral dermatitis are varied. During a detailed interview, the doctor tries to establish the cause of this condition in a particular patient, since further treatment depends on this. Most often, the development of the disease is associated with the following factors:
- prolonged and uncontrolled use of creams and ointments containing corticosteroids;
- the use of fluoride-containing products, for example the use of toothpaste with a high fluoride content;
- prolonged and uncontrolled use of products containing antibiotics;
- prolonged exposure to aggressive components included in some cosmetics and foundations;
- hormonal disorders.
Perioral dermatitis is similar to seborrheic dermatitis, rosacea and other skin diseases, so only a doctor can prescribe an accurate diagnosis and correct treatment. Therefore, only by seeking advice can you understand for sure that this is perioral dermatitis and receive the correct treatment regimen.
Manifestations of the disease
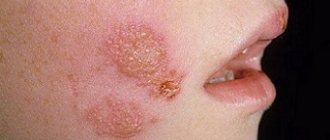
Perioral dermatitis can manifest itself in the chin, eyelids, corners of the lips, nasolabial and nasobuccal folds in the form of single papules, as well as in the form of extensive lesions. Papules are round, convex formations of red or pink color. There is itching and burning in the area of the rash. But there are also cases when papules do not cause any inconvenience other than aesthetic ones.
The affected areas of the skin feel uneven to the touch. In the area of papules, weeping may occur and crusts may subsequently form.
It is worth noting that most often papules form in the chin area and around the mouth rather than on the eyelids. There are also cases of mixed lesions, when papules spread over the entire face.
Possible negative consequences
If you do not seek medical help in time, wounds with pus may form in place of the papules. In this case, the percentage of affected skin will be much greater than at the beginning of the disease. Patients at particular risk are:
- with weakened immunity;
- with hormonal imbalance;
- childhood;
- with concomitant skin diseases.
The course of dermatitis can worsen with the concomitant use of various medications, for example, hormonal contraceptives, as well as during pregnancy, when the skin is exposed to ultraviolet radiation, cold, wind, and dry indoor air.
Diagnosis of the disease
To accurately diagnose this type of dermatitis, you may need not only a doctor’s examination, but also additional manipulations, for example, scraping from the affected area of skin for microscopic examination, bacterial culture. Laboratory diagnostics may reveal:
- presence of demodex mite;
- increased microbial contamination of the skin;
- thinning of the skin with signs of inflammation based on biopsy results.
The difficulty can be considered the absence of a specific causative agent of perioral dermatitis, common for all patients, as well as nonspecific skin changes that may be present in other diseases.
Causes
The exact causes of the development of perioral dermatitis are not known, but trigger factors have been identified, i.e. provoking:
- Deterioration, weakening of immunity;
- Climate change;
- Exposure to ultraviolet rays;
- Use of corticosteroids;
- Fluoridated toothpaste;
- Genetic predisposition;
- The use of low-quality cosmetics against the background of a tendency to allergic reactions to cosmetics;
- Emotional stress.
The most reliable seems to be the development of perioral dermatitis in connection with long-term local use of corticosteroid ointments against the background of other provoking factors. There is a decrease in local immunity, which gives impetus to the development of the inflammatory process.
Risk factors for the development of rosacea
The incidence of rosacea is approximately the same in both sexes, but women during menopause are more susceptible to rosacea, as hormonal levels and vascular properties change. Blondes and redheads with thin, sensitive skin prone to redness are at risk for rosacea. Allergic and contact dermatitis can provoke rosacea, since the blood vessels are often dilated and subsequently their return to their previous state is no longer possible.
Genetically, residents of northern peoples are more predisposed to rosacea; living in extreme continental climates and in northern countries also increases the risk of rosacea.
Diseases and disorders of the endocrine system, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and disorders of the immune system, especially when combined with each other, lead to rosacea. The pathogenesis of rosacea is not fully understood, but most dermatologists agree that exposure to hot or cold areas, wind, and consumption of excessively burning foods, alcohol and spices provoke rosacea.
Principles of therapy
For a pronounced therapeutic effect, an integrated approach is required in the correction of perioral dermatitis.
It is important to understand that the duration of therapy is quite long and takes from 6 to 8 weeks .
STAGE 1 – strict adherence to these recommendations
- Using fluoride-free toothpastes.
- If a course of external corticosteroids (hormonal ointments) was prescribed, complete use.
- Avoid the use of decorative cosmetics, especially in the rash area.
- Cleansing the skin only with specialized hypoallergenic products. For example, DermaQuest Cleansing Milk for Delicate Skin is designed for daily cleansing of dry, irritated, sensitive and dehydrated skin.
Heals dry and sensitive facial skin, giving the skin a feeling of comfort, cleanliness, and velvety.
- Compliance with a special dietary regimen that excludes the intake of hot, spicy foods and alcohol.
STAGE 2 – dermatological treatment
It is prescribed by a dermatologist after diagnosis and includes individual prescription of antihistamines, diuretics, sedatives, and sometimes antibiotic therapy.
Treatment of perioral dermatitis
Treatment of perioral dermatitis includes several stages.
Before treating perioral dermatitis , your doctor may recommend a complete detox of your skin and body. First of all, it is necessary to avoid the use of products that cause inflammation. Most often these are hormonal ointments, antibiotic creams or toothpaste with a high fluoride content. When you stop taking these medications, so-called “withdrawal dermatitis” may occur—burning and itching intensify, swelling and redness increase, and rashes literally “spread” all over the face. Such inconveniences can cause the patient to panic and desire to return the medications used to eliminate symptoms. However, this is the wrong path and will only make the situation worse. It is important to fully follow the doctor's instructions.
Since the skin is inflamed, during treatment it is necessary to avoid any products that could increase irritation. In particular, this applies to masking creams, powders, as well as cosmetics that are applied next to or directly on the area where perioral dermatitis appears.
Dietary instructions must also be followed. A diet for perioral dermatitis involves the complete exclusion of foods such as:
- alcohol;
- fast carbohydrates (industrial sweets, confectionery);
- smoked meats;
- hot spices, sauces;
- nuts;
- some types of fruits and vegetables.
Preference should be given to light vegetable dishes and light protein foods. When processing foods, preference should be given to steaming, boiling, stewing or baking.
To relieve the feeling of itching and burning on the skin, the doctor may prescribe antihistamines, and in particularly difficult cases, sedatives.
Skin-cap cream containing activated zinc pyrithione has shown effectiveness as a means for external treatment of dermatitis. The active substance (activated zinc pyrithione) helps eliminate inflammation, rashes, itching and excessive growth of microorganisms that increase inflammation. Skin-cap cream also contains neutral components that additionally moisturize the skin. The cream has a pleasant texture and helps eliminate the feeling of dryness and tightness of the skin.
In addition to the Skin-Cap medicinal cream, the doctor may recommend neutral skin cleansers and frequent irrigation of the affected areas with thermal water.
What to do with acne* on the chin?
Let's start with what you shouldn't do if you have acne - squeeze out blackheads*. Painful subcutaneous pimples* often appear in this part of the face. Their extraction can lead to rupture of the follicle and spread of the inflammatory process into the deeper layers of the skin. To prevent this, you need to properly care for your face and contact a specialist to select a treatment method.
Here's what skin care should be like if acne appears on it:
- use only gentle care products, forget about scrubs for a while;
- do not try to dry your skin with alcohol-containing cosmetics, it does not need it;
- don’t forget about moisturizing, even oily skin needs it;
- be sure to wash off your makeup at night, especially if you used a large amount of it to mask rashes;
- use cosmetics that do not contain comedogenic elements;
- review your diet, exclude potentially dangerous foods (milk, sweets, alcohol, fatty foods, etc.)
If you often experience a chin rash, but the disease is now in remission, you can try to reduce the risk of relapse. To do this, follow these recommendations:
- check the expiration date of your cosmetics and its composition, it may contain comedogenic components;
- change tools for applying cosmetics more often or use products to clean them;
- change bed linen every 1-2 weeks;
- use different towels for hands, body and face;
- get rid of the habit of propping your face with your hand, and generally try not to touch it unless necessary.
These tips do not protect you 100% from acne, but they can reduce the likelihood of acne.
Prevention of rosacea
Since rosacea is a chronic disease, after removing the excess capillary network, it will reappear after some time. Therefore, the prevention of rosacea consists of periodic visits to the cosmetologist’s office to eliminate newly appeared hypertrophied blood vessels. But, if between procedures you avoid overheating and hypothermia of the skin, spend as little time in the open sun as possible, adjust your diet and use cosmetics that contain horse chestnut extract and other substances that strengthen the vascular wall, then you will need to repeat the procedures no more than once every 2 -3 years.
Perioral dermatitis
Perioral dermatitis
- chronic inflammatory lesion of the skin around the mouth in the form of individual or grouped red papules located against the background of normal or reddened skin.
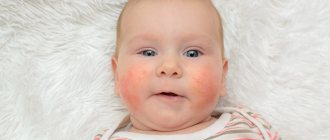
Perioral dermatitis is most often observed in women aged 20 to 40 years. Recently, there has been an increase in the incidence of this type of dermatitis among children.
Symptoms of the disease
At the beginning of its course, the disease goes through a latent (hidden) stage, the duration of which ranges from a couple of weeks to several months. At this time, the pathology does not reveal itself in any way, and it is difficult to find out about its presence. After the incubation period has passed, red spots (erythema) appear on the body of a sick person, which then turn into papules and plaques. They can be single in nature or gather in colonies, increasing the affected area.
Skin rashes are accompanied by:
- dry dermis in areas of localization of foci of dermatitis;
- pain, tingling and peeling of the skin;
- the appearance of a crust;
- the formation of a visible border between the mouth and the adjacent affected area.
Causes of appearance in adults and children
Pathology occurs in both adults and children under the influence of opportunistic microorganisms that reach the surface of the epithelium. In the presence of favorable conditions (decreased immune function of the body), bacteria begin to actively multiply, which causes irritation and the formation of painful lesions - papules.
Among the main causes of oral dermatitis on the face:
- increased sensitivity and individual intolerance to the constituent ingredients used for the preparation of cosmetics (develops from frequent use);
- strong influence of environmental conditions: high humidity, cold weather, wind, ultraviolet rays.
Do not despair! See “Results” “BEFORE” and “AFTER” therapy.
Attention! It is very important for the patient to follow a hypoallergenic diet (see the corresponding article in the “Patient’s School”: “The role of diet in the treatment of patients with psoriasis”). The diet for rosacea-like (perioral) dermatitis is the same.
Attention! Very often, in order to eliminate acne (pimples), gynecologists and doctors of other specialties prescribe hormonal oral or other contraceptives to adolescents and young girls. If you do not want to join the list of patients with fatal consequences associated with the use of hormonal contraceptives, watch the documentary: “Contraceptives. Killer business."
Treatment information cannot be used for self-medication. Consultation with a physician before undertaking any treatment is absolutely necessary.
Types of dermatitis and diagnosis
Depending on the causes of manifestation and the nature of the course, the following types of dermatitis are distinguished:
- simple contact;
- allergic;
- allergic contact;
- seborrheic;
- atopic.[1]
Diagnosis of dermatitis is based on examination of the patient and laboratory tests, including a general blood and urine test, a biochemical blood test, an immunological blood test to determine the level of Ig E, which makes it possible to determine the allergic nature of the disease, and allergy skin tests. Based on the research results, the doctor will be able to assess the picture of the disease and select an effective treatment regimen. In some cases, allergists, infectious disease specialists, and immunologists are invited for consultation.[2]