Dermatovenerologist
Khasanova
Alina Rashidovna
9 years experience
Make an appointment
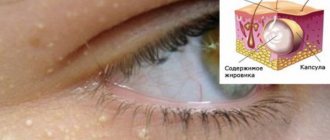
Fibroids are a group of benign neoplasms that affect various tissues of the human body. Tumors are formed from collagen fibers with varying densities and elasticity. Foci of pathology can be located on the skin, bones and walls of internal organs of children and adults. Oncologists consider fibromatosis as a precancerous condition.
General information
Single or multiple fibromas can affect the lungs, mammary glands, liver, skin, oral mucosa, etc. The proliferation of connective tissue occurs under the influence of various factors: unfavorable environmental conditions, severe injuries, bacterial or viral infections. When making a diagnosis and developing a treatment strategy for a patient, dermatologists, oncologists and surgeons take into account laboratory data. Information about the morphology of the tumor allows doctors to assess the risk of its malignant degeneration.
Possible complications
Fibroma turns into a malignant form, therefore low-risk. The exception is location in the friction zone of clothing, or traumatically dangerous places, since the likelihood of violating the integrity of the cover and twisting of the growth can lead to swelling, inflammation, bleeding and the addition of a secondary infection.
After surgery, in 97% of cases, the problem is completely eliminated without the risk of relapse. But, if the wound is not properly cared for, infection and blood poisoning can develop. Therefore, you should strictly adhere to all the recommendations of our specialists.
Reasons for the development of pathology
The causes of fibroids are varied. Doctors identify several factors that contribute to the formation of connective tissue tumors in patients’ bodies:
- systematic use of alcohol and tobacco;
- repeated injuries to the skin, muscles, bones;
- unfavorable environmental conditions in the region of residence;
- the predominance of fatty, spicy and sweet foods in the diet of children and adults;
- viral and bacterial infections;
- immunosuppression due to the use of immunosuppressants.
Doctors often diagnose fibromatosis in people working in chemical production. Benign skin tumors can develop under the influence of excessive sun exposure. Damage to internal organs is often a consequence of endocrine disorders.
Doctors surgeons
Dzhadzhiev Andrey Borisovich Surgeon
Cost of admission 1500
₽
Make an appointment
Marynich Alexander Alexandrovich Vascular surgeon, phlebologist, angiologist
Cost of admission 1500
₽
Make an appointment
Myshlyaev Anton Vsevolodovich Surgeon coloproctologist
Cost of admission 2000
₽
Make an appointment
Kinds
Doctors use several typologies of fibroids. The most common classification takes into account the localization of the tumor focus: the pathological process can affect the skin (for example, desmoid fibromatosis), internal organs (fibrosis of the uterus, mammary gland, lungs), mucous membranes of body cavities (gingival fibroma), bone tissue (non-osteogenic fibromatosis).
Desmoid tumors form on the skin of the back, limbs and chest. Externally, the tumor looks like a growth with a bumpy surface up to 50 millimeters in diameter. About 5% of patients experience malignant transformation of tumors - a small fibroma on the skin of the shoulder or thigh can lead to the development of skin cancer.
Fibrous lesions of the uterus and other internal organs of the human body can affect various tissues: muscle, epithelial, glandular. Often the diseases are asymptomatic; the focus of the pathology is discovered by chance - during ultrasound, magnetic resonance imaging or radiography.
Odontogenic neoplasms form in the oral cavity. The pathological process develops slowly, the patient does not experience pain. If left untreated, the tumor can reach significant sizes and lead to jaw deformation.
Non-osteogenic tumors form in the femur and provoke the destruction of the tubular bones of the skeleton. In an advanced stage, the disease causes a pathological bone fracture. Rarely (3–5% of clinically diagnosed cases) the tumor decreases in size without surgical intervention. Other types of bone tumors grow aggressively. Thus, desmoplastic fibroma can double in volume in 2–3 weeks.
How does the procedure work?
The doctor works in a treatment room. All manipulations are carried out using disposable gloves. Disinfection of a wound with an ultraviolet ray does not eliminate the requirements for sterile conditions.
The cost of removing fibroids on the face with a laser is around 1000 rubles. In other areas of the body, you will have to pay for the size and number of tumors. Most clinics indicate an area of 1 cm2 in the price list. The average price depends on the area:
- Intimate - 1000 rub.
- Heads - 1000 rub.
- Eye - 2000 rub.
- Mouth and mucous membranes - 2500 rub.
- Bodies - 700 rub.
Anesthesia and doctor's consultation are not included in the cost of the procedure.
Symptoms
The development of the tumor process is accompanied by moderate pain and a feeling of fullness. In 55–60% of cases, the pathology is asymptomatic. The likelihood of developing specific signs of fibromatosis depends on the type and location of the tumor. Fibromatosis of cartilaginous tissue is characterized by increasing symptoms - from mild pain when performing movements to complete loss of mobility of the upper or lower limb.
Specific symptoms develop when fibroma affects the patient’s internal organs. Thus, fibrosis of the uterus can cause bleeding that is not related to a girl’s menstrual cycle. Fibrous lesions of the lungs provoke difficulty breathing and shortness of breath in a child or adult after short physical activity.
Indications for laser removal
Regardless of the type and location, the dermatological defect must be benign.
Using a laser, tumors of various types are eliminated:
- moles;
- lipomas;
- warts;
- papillomas;
- condylomas;
- adenomas of the sebaceous glands;
- angiomas;
- keratomas, etc.
Indications for laser fibroid removal:
- uncontrolled growth;
- persistent swelling of nearby skin areas;
- soreness;
- severe peeling;
- itching;
- the formation is located in a place where it creates inconvenience and/or is often injured.
The reason for removal may be purely cosmetic when the formation:
- spoils appearance;
- just do not like.
Fibroma is strongly recommended to be eliminated if there are suspicious changes in its shape or color. Just before this you need to consult a doctor and undergo at least a minimal examination.
Diagnostic measures
Diagnosis of fibroids is performed by doctors of various specializations - dermatologists, oncologists, surgeons, gynecologists, etc. Methods for confirming the primary diagnosis are determined by the location of the benign neoplasm. At the first stage of the examination, patients receive a referral for radiography. Computed tomography allows you to determine the exact size of the tumor and identify signs of its invasion into adjacent organs.
Fibrous formations in bone and cartilage tissue are detected during scintigraphy. If necessary, the doctor can take a biopsy sample for laboratory tests. Microscopy of the obtained biomaterials will allow doctors to assess the morphological structure of tumor cells and the likelihood of their malignant degeneration.
Benign neoplasms of the female reproductive system are often detected during ultrasound examinations. The focus of the pathological process has less echogenicity compared to adjacent tissues.
Features of the rehabilitation period
The healing process takes a matter of days - about 3-5 days. A specific crust forms at the site of the intervention, which peels off after a few days and falls off on its own. It should not be forcibly removed, as there is a risk of infection. To ensure healing goes as quickly and smoothly as possible, follow these recommendations:
- do not wet the intervention area;
- for 2 weeks, refuse to visit baths, saunas, swimming pools, ponds;
- Do not sunbathe until the wound is completely healed.
Immediately after the manipulation, you can return to your usual activities; no special regime is required. If you want to quickly, painlessly and safely get rid of an unwanted tumor, sign up for a consultation with a GMS Hospital surgeon!
Treatment
The treatment strategy for fibroids is determined by the doctor after the patient undergoes diagnostic procedures. For small tumor sizes and localization of the pathological focus on the skin, a conservative approach is used. Dermatofibromas can dissolve with steroid injections. Surgery is performed in cases of high risk of tumor malignancy.
Fibroids are removed in several ways. Small tumors on the skin are excised using a laser. The advantages of this method are minimal rehabilitation time and high efficiency.
Removing fibrous formations using an electric knife minimizes the risk of bleeding (small vessels are sealed under the influence of current). As an alternative method for removing overgrown collagen fibers, the surgeon may choose a radio wave knife. The use of this equipment reduces trauma to the patient’s healthy tissue.
Predictions of why fibroids are dangerous
Dermatofibroma has no serious complications. Complications of plantar fibroids usually occur as a result of surgical interventions. These include flattening of the arch of the foot, postoperative nerve entrapment, and postoperative growth of larger and recurrent fibromas.
Article sources:
- Desmoid fibroma. Staged, organ-preserving surgical treatment. Khvastunov R.A., Mozgovoy P.V., Lukovskova A.A., Yusifova A.A. Volgograd scientific and medical journal No. 2, 2022. p. 54-57
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2927520/ Central odontogenic fibroma: a case report with long-term follow-up. Marco T Brazão-Silva, Alexandre V Fernandes, Antônio F Durighetto-Júnior, Sérgio V Cardoso, Adriano M Loyolacorresponding
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3351722/ Literature survey on epidemiology and pathology of cardiac fibroma. SuguruTorimitsu, Tetsuo Nemoto, Megumi Wakayama, Yoichiro Okubo, Tomoyuki Yokose, Kanako Kitahara, Tsukasa Ozawa, Haruo Nakayama, Minoru Shinozaki, Daisuke Sasai, Takao Ishiwatari, Kensuke Takuma, Kazutoshi Shibuya
The information in this article is provided for reference purposes and does not replace advice from a qualified professional. Don't self-medicate! At the first signs of illness, you should consult a doctor.
Prognosis and prevention
When patients seek medical help in a timely manner, doctors can formulate a favorable prognosis in 75–80% of cases. The likelihood of a complete recovery of a child or adult is reduced when fibromatosis is advanced or secondary pathologies are attached to the disease.
Preventive measures are simple - patients are advised to avoid repetitive trauma to the skin, soft tissue and bones. Persons working in hazardous industries must undergo regular preventive examinations. Children and adults should eat a healthy diet and include adequate amounts of vitamins and minerals.
Preparatory stage
Laser removal of skin tumors does not require special preparation. The only thing is that you cannot get into the procedure without a preliminary examination of the fibroid.
You need an in-person consultation, where a cosmetologist:
- conduct a visual examination and dermatoscopy;
- clarifies the contraindications;
- will prescribe tests to clarify the diagnosis.
The presence of any diseases or medications can seriously affect the quality of the procedure. Equally important is the identification of the fibroma itself, including testing the tumor for benignity. It is impossible to confirm this without biopsy results. The patient may also be asked to take a general blood test and go for an ultrasound.
Classification of fibroids
Pathology is divided into several types according to criteria. This includes the density of the benign neoplasm, the nature of its origin, as well as the severity of clinical manifestations.
Dense fibroma
Characterized by a solid consistency. This is due to the fact that the contents are quite hard fibers of connective tissue. They include a small number of cores. Formations of this type are most often found on the gingival surfaces and palate.
Soft fibroma
The fibrous structures are thin and freely located, so their clusters are characterized by a high degree of softness. This type is most often observed on the tongue and the inside of both cheeks. Benign neoplasms of a mixed type, combining the signs of all the varieties listed above, can be found on the sublingual part and on the mucous membranes of the floor of the oral cavity. For example it could be:
- Fibrolipoma. It is hard to the touch because it contains fibrous fibers. It can be eliminated surgically, with laser, or radio waves.
- Fibrohemangioma. As a rule, it is provoked by infectious processes occurring in the child’s body. It is extremely rare in adults. It never degenerates into malignant tumors. Most often it is treated surgically, in some cases it can resolve on its own.
Fibroma from irritation
This is not a tumor formation in its usual form, but the result of reactive hyperplasia. Chronic pathology is characterized by the development of focal lesions, which are caused by systematic mechanical action and subsequent injury.
The most common cause is installed crowns, fillings, and dentures. In the latter case, the disease is called prosthetic granuloma. The orthopedic structure exerts continuous pressure on the alveolar process, leads to its resorption, moves forward and contributes to the formation of compactions, which are associated with the inflammatory process.
The risk group includes not only patients who have undergone prosthetics, but also people with untimely cured caries, in adulthood, with foreign objects in the oral cavity (for example, with piercings). Studies have shown that women are more prone to such hypertrophic transformations than men.
Symmetrical fibromas
Doctors diagnose such tumors in the area of the third molars in the areas between the gums and the roof of the mouth. The tumor is hard to the touch and resembles a bean in shape.
It should be noted that this type of compaction does not apply to true fibromatosis. These are just overgrown tissues in the gingival membranes, accompanied by the process of scarring and other changes of a similar nature.
Lobular fibroma
It occurs as a result of reactive hyperplasia with systematic trauma to delicate sensory fibers with prostheses or other orthopedic structures. The main distinguishing feature of such formations is their rough, textured surface. When palpated, tubercles are felt.
Fibrous epulis
This is a dense growth of pinkish tissue that does not cause pain or other discomfort. The edges are often hyperemic, have clear boundaries and irregular shape. The base is quite wide.
The vestibular part of the gums is usually affected. There are cases of neoplasms occurring in the interdental spaces in the form of a saddle with spread to the intraoral surface.
Quite often, a dental unit located in a pathological area has a poorly fitted metal crown, extensive carious lesions, or a prosthetic clasp. It is these structures that are the provoking factor in the occurrence of a chronic inflammatory process with the formation of granules, which over time are transformed into mature connective fibrous fibers.
In dentistry, there are also angiomatous epulis. They are brighter in color, somewhat softer to the touch and bleed. In this case, blood appears not only at those moments when the surface is affected mechanically, but regardless of the presence or absence of a traumatic factor. When conducting diagnostic studies, many vascular branches are detected in the pathological area.