SPECIALISTS Gynecologist Gynecologist-endocrinologist Pediatric gynecologist Mammologist-oncologist Dermatologist Hirudotherapist Intimate plastic surgery Doctor Contour plastic doctor Ultrasound doctor SERVICES AND PRICES Gynecology Mammology Ultrasound diagnostics Paid tests Intimate surgery Contour plastic Treatment for women PROMOTIONS AND DISCOUNTS Students Teams Friends and subscribers am For residents of the region For pensioners Promotions in clinic
Have growths on the labia, rashes and pimples near the vagina? Maybe there is a feeling of “something extra” near the anus and there is an itching of the anus? What is it, the reasons and how can a woman get rid of genital warts? Cauterization of condylomas is a procedure for eliminating viral skin lesions. Removal is associated with physical discomfort and some nuances, so it should take place in a medical center under the supervision of a gynecologist.
Condylomas in women
For those who do not yet know, intimate condylomas are warty, papillary growths on the mucous membrane and skin of the genitals. Caused by the human papilloma virus - HPV, they are more common in adults, regardless of the presence or absence of sexual intercourse, as well as in children, adolescents and virgin girls.
In women, intimate condylomas are most often seen by the gynecologist during an external examination of the genital organs. Although it is not uncommon for small genital warts to be undetected due to insufficient physician care. When a certain size is reached, the growths on the labia begin to be felt by the woman herself, which manifests itself in the form of a vague feeling of the presence of “something extra” between her legs.
Where do condylomas grow most often in women:
- labia,
- Vaginal walls,
- Hymen,
- Entrance to the vagina
- Cervix,
- Anus (usually during anal intercourse),
- Urethra, clitoral area.
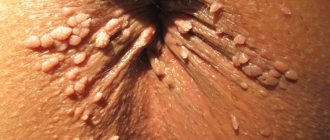
A very common place for intimate condylomas to occur is the skin around the anus. In women, this place is often injured during anal sex, the use of rough toilet paper, and some diseases of the anus, so condylomas from the external opening of the anus quickly spread deep into the anal canal through microtrauma. In a similar way, papillomas can also occur in those girls who, wanting to remain virgins, allow sexual intercourse in the rectum. Using a condom during anal sex cannot always protect against infection - HPV can penetrate through the micropores of the product, and the product itself can break due to excessive stress due to the relative narrowness of the anus. It is best to remove condylomas around the anus using the radio wave method in order to minimize the impact on sensitive areas.
Infection with condylomas
If you have been diagnosed with genital condylomatosis or HPV carrier status, don’t be surprised! The presence of this virus in the body is a more expected thing in gynecology than its absence, since it is quite easily transmitted. The asymptomatic course is the reason that papillomas in many cases are an “accidental finding” during an examination by a gynecologist. In this case, it is difficult to accurately determine the route of HPV infection and the duration of the disease.
The virus that causes condyloma lives and manifests itself on the skin and mucous membranes and is transmitted from these areas by touching them. Thus, HPV and intimate papillomas not a disease transmitted exclusively through sexual contact! Yes, of course, sexual intercourse (vaginal, anal) is also a method of transmission, but not the only one: it could also enter the body through everyday means. Therefore, the lack of experience in sexual relations ☛ does not guarantee virgin girls the absence of HPV and genital warts. Therefore, it is important for all representatives of the fair sex from the age of 16 to regularly undergo preventive examinations with a gynecologist and at least have smears for flora.
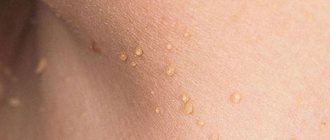
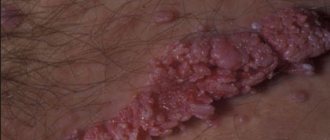
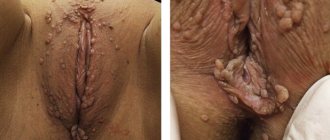
Photos of condylomas in women
| Intimate papillomas | Vaginal condylomas | Condylomas on the labia |
| Papillomas of the hymen and urethra | Papillomas of the labia minora | Growths on the labia |
Do you want to be checked for intimate warts? Do you want to see everything with your own eyes, just as a gynecologist sees it? We invite you to do a video colposcopy!
Do condylomas need to be removed?
Cauterization of condylomas in intimate places (vagina, cervix, urethra, anus and anal canal, labia, etc.) is a mandatory procedure in gynecology. As well as preliminary diagnosis of carriage - tests for HPV infection in the body. If it is detected, simultaneously with the elimination of all formations, it is necessary to treat the virus. Only in this way can one prevent the progression of the process, the spread of papillomas to other parts of the body, transmission to a sexual partner or family members, and infection of the newborn during childbirth.
And, in the end, for a girl to wear and not remove warts on the genitals and various growths on the labia minora is simply unaesthetic.
Reviews about genital wart removal in the clinic
1. Recently discovered HPV and warts on the labia. Growths in the intimate area appeared several weeks ago. Where is the best place to remove condylomas in Moscow, by what method, so as not to hurt and is effective, I knew firsthand, because... two of my friends went to this clinic. I would like to note the high level of service and professionalism of the gynecologist who worked with me, namely Victoria Borisovna Irmiyaeva. I also liked the conditions at the clinic! I made an appointment through their website and was accepted almost on time. They looked at everyone, took tests, and explained my further actions. After receiving the results, I came to the center to have condylomas cauterized, and during colposcopy the doctor also found one on the cervix, and they are known to be the most dangerous... They removed everything at once, with an injection, it didn’t hurt, I only groaned once) In general, very attentive staff, nice nurses. I have already and will continue to recommend your center to all my friends and acquaintances. Thank you! — Maria, 29 years old, Moscow
2. I tried to remove papillomas in intimate places and in the urethra 2 times, each time they grew back. I was tired of self-torture and decided to go to another center. I found positive reviews on the Internet about the removal of condylomas, which is carried out by this specialized clinic on Kutuzovsky Prospekt. I would like to express my deep gratitude to the gynecologist Bezyuk Laura Valentinovna, who devoted a lot of attention and time to solving my problem. It was only from her that I realized that before I had not carried out the treatment quite correctly, i.e. I simply burned out the condylomas, but did not get tested for viruses, and this is important. After all, if you do not get tested for HPV and do not treat it if it is present, then the papillomas will return again. In my case this was the case. But this time we did everything right, underwent treatment for HPV (types 33 and 18), removed condyloma in the urethra and there were many around. The doctor did everything with pain relief, I didn’t feel anything, only then there was slight discomfort for several days. Thanks for your help! — Sabina R., 31 years old, Moscow
3. There were a few condylomas in the intimate area (near the clitoris). Cauterization with Solcoderm, done by the doctor at this clinic, helped the first time. After a week, everything was practically healed and now there is no longer a trace left. Thank you to the doctor and all the staff! — Olga, 21 years old, Moscow. region
Here you can see all reviews about gynecologists.
Treatment methods for condylomas in the labia (vulva) area
If you have condylomas on the vulva, you should immediately consult a gynecologist. Today, there are several approaches to the treatment of this disease, and an experienced professional, having established the correct diagnosis and assessed the extent of damage to the body, will be able to choose the correct treatment regimen.
As a rule, condylomas in the vulvar area are treated in the clinic in the following ways:
· excision with a scalpel;
· cryodestruction – cold treatment;
· the excision procedure is performed using laser or electrosurgical devices (radio wave apparatus with argon-enhanced coagulation).
How and what is the best way to remove condylomas
The gynecologist at our clinic will conduct a comprehensive gynecological examination to identify these formations and begin treatment only after the necessary examination and confirmation of the diagnosis! This will allow you to cauterize condylomas in intimate places quickly and without complications. At the following link you can read about what tests you need to take for condylomas.
PRELIMINARY DIAGNOSTICS
- Examination on the chair,
- Extended colposcopy,
- Flora smears, PCR,
- HPV tests,
- Cytological analysis (according to indications),
- Biopsy of the cervix (if indicated),
- Anoscopy or rectoscopy (according to indications),
- Blood tests - hepatitis B and C, syphilis, HIV.
Radio wave removal of condylomas
Depending on the results of HPV tests and indications, the treating doctor selects the most suitable method for removing intimate papillomas (radio wave surgitron or solcoderm). If you choose a clinic in Moscow where to remove condylomas from intimate places, prices can be found at the bottom of the page. Please note that our gynecologists perform this procedure under modern local anesthesia, absolutely without pain, so even young patients avoid unnecessary anxiety and unnecessary stress!
Removal of condylomas using the radio wave method (Surgitron or Fotek) has such advantages as speed, absence of long-term cosmetic defects and postoperative complications. Gynecologists resort to chemical methods (Solcoderm) mainly in cases of single, few formations of the mucous membrane of the external genitalia.
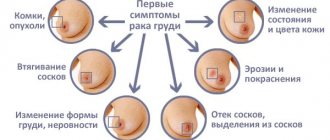
What is the relationship between HPV and human cancer?
The clearest causal role of HPV has been demonstrated in cervical cancer. Thus, high-risk HPV types (see Table 1) were found in 93 - 99% of women with cervical cancer. Previously, it was found that the most susceptible to cervical cancer are women who began sexual activity early, had an STI, and also had a large number of sexual partners, as well as those who were in contact with men whose partners had cervical cancer. It turned out that high-risk HPVs contain regions with high oncogenic activity (E6 and E7) in their genome. When HPV invades the genome of cells in the cervical mucosa, regions of the genome E6 and E7 stimulate the synthesis of corresponding proteins, which in turn interact with proteins that regulate cell division and cell death. The E6 protein suppresses the activity of the P53 gene (and the corresponding protein), and the E7 protein of the retinoblastoma gene, which stimulates the process of apoptosis (programmed cell death). This leads to the predominance of cell reproduction over cell death, which stimulates the uncontrolled malignant growth of cervical epithelial cells and the development of cervical cancer. Thus, the International Agency for Research on Cancer has concluded that high-risk HPV types are the leading cause of cervical cancer.
However, it is known that most women infected with HPV do not develop cervical cancer and the presence of HPV is “necessary” but not “sufficient” for the development of this disease. The development of cervical cancer in people infected with HPV is facilitated by smoking, long-term use of hormonal contraceptives, and the presence of other STIs, such as chlamydia, namely Chlamydia trachomatis, herpes simplex virus type 2. In addition, vitamin A deficiency, genetic predisposition and immunodeficiency contribute to the development of cervical cancer in the presence of HPV. In addition to cervical cancer, the causative role of HPV has been established in cancer of the anal area (especially in homosexuals), and in cancer of the vulva, vagina and penis. Some cases of cancer of the mouth, larynx and esophagus are also possibly related to HPV.
Every year, up to half a million new cases of cervical cancer occur worldwide. Most of these cases are registered in developing countries, where preventive programs of annual screening examinations for HPV, dysplasia and cervical cancer do not work or work poorly. The introduction of similar preventive programs in developed Western countries has reduced the incidence of cervical cancer by 75%. Although the incidence of other HPV-related cancers is much lower, the incidence of anal cancer among gay men is estimated to be 4 times higher than the incidence of cervical cancer in women (35 cases per 100,000 homosexuals per year, versus 8.3 cases per 100,000 women). population per year).
Papillomas on the genitals: causes of pathology development
The most common route of infection is direct contact, in which the skin and mucous membranes of the virus carrier and a healthy person come into contact. As a rule, this is sexual contact. Although there is a risk of infection of the child from the mother, the household method is through personal hygiene items. You can also become infected with HPV in common areas – swimming pools, showers.
Important: With each new sexual partner, the risk of infection for a healthy person increases by 20%. Unfortunately, standard protective equipment used during sexual intercourse does not protect against HPV, since latex products do not protect all parts of the genital organs from contact.
The causes of infection are not as important as methods of combating it. After all, the risk of direct or household infection is very high. The main thing is to start treatment on time to avoid complications. It is noteworthy that Western scientists understand the importance of the problem. Up to 6 billion dollars a year are allocated for HPV research and the development of new treatment protocols in the USA alone. But a medicine that will cure the virus once and for all has not been found. However, today’s methods of combating pathology are quite effective with timely access to a specialized medical institution.