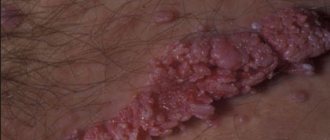
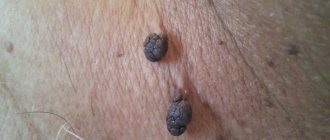
Consequences of the formation of growths
If the growth process of condylomas is not controlled, they will rapidly spread to healthy parts of the skin and mucous membranes. In addition, the patient risks facing the following consequences:
- difficulty urinating and defecating;
- increased likelihood of developing a malignant tumor;
- the formation of bleeding cracks that cause pain;
- a complication of childbirth if the disease is observed in a pregnant woman.
A favorable prognosis can be expected only with timely and correct treatment.
Features of removal of papillomas in intimate places
The choice of method for removing papillomas in intimate places is made based on the number and size of tumors. The condition of the patient’s body and the severity of the disease are also taken into account. The most effective are hardware methods for removing condylomas. If there are a large number of growths, a surgical operation is performed, during which the diseased tissue is removed along with healthy tissue. This solution allows us to avoid further spread of the disease. It is noteworthy that minimally invasive methods are no less effective, and we will talk about them further.
Advantages of radio wave surgery using the Surgitron device
Doctors at the ProfMedLab clinic remove genital warts using the modern Surgitron radio wave surgery device. The principle of the method is that the device generates high frequency radio waves. Coming into contact with tissues, they evaporate liquid from cells, that is, they actually destroy them. Radio wave surgery has some advantages:
- Purposeful action. Only affected tissues are destroyed, while surrounding healthy tissues remain untouched. In this regard, radio wave surgery is a more gentle method compared to laser.
- Good cosmetic effect. After removal of tumors using the Surgitron apparatus, barely noticeable scars remain.
- Full control over the process. The surgeon can precisely control the area and depth of tissue removed.
- Bloodless intervention. There is no bleeding during genital wart removal.
- Fast recovery. The wound heals completely within a few days. There is virtually no pain or swelling.
The procedure for removing growths
The procedure for removing papillomas is very painful, and this is due to the presence of a large number of nerve endings in the intimate area. In most cases, a surgical operation is performed, during which local anesthesia or intravenous anesthesia is used.
Quite often, growths are removed using a laser or radio wave method, which do not cause significant discomfort. You can also get rid of growths with the help of medication, which is prescribed when you visit a doctor. We recommend contacting the Estelia innovative medicine clinic - this solution will help get rid of the pathology in a short time.
Diagnostics
If a condyloma has formed on the genitals, then this is a reason to immediately go to an appointment with a gynecologist.
Using a colposcope, which magnifies the image, the affected area is determined. A study is carried out using an iodine solution. The procedure is absolutely painless, but is considered one of the most informative.
In women, scrapings must be taken from the mucous membrane of the cervix and cervical canal. Using this type of study, the development of oncology can be detected.
In some cases, a biopsy is indicated. To do this, a small piece of tissue from the area affected by condyloma is sent to the laboratory. Cytology can detect the presence of cancer cells.
We often insist on conducting a PCR test. To do this, a scraping is taken from the mucous membrane of the cervix. The test determines the presence and strain of HPV.
Laser removal of warts
Laser removal of papillomas takes no more than half an hour. This procedure is quite simple, and it is performed in 2 stages:
- pain relief using a special cream or injection that prevents pain during the process of removing growths;
- removal, before which the specialist adjusts the equipment, setting the power and diameter of the beam. By acting on tissue, the laser burns out the affected tissue and “seals” blood vessels, preventing internal bleeding.
Laser removal of condylomas is only appropriate if it is necessary to get rid of external signs of the disease. To avoid the recurrence of tumors, you should consult a doctor to select antiviral drugs.
Bartholinitis
It is also a cyst formed due to a blockage of the Bartholin gland. It is necessary to open the cyst before the process of infection and breakthrough begins. This procedure occurs simply on an outpatient basis under local anesthesia. If measures are not taken in time, the inflammatory process can spread to the internal genital organs and lead to serious complications.
Heratsi Medical Center provides paid medical assistance in the removal of papillomas, condylomas, warts and lipomas, as well as the opening of cystic formations of various etiologies.
In our clinic, specialists work only with extensive experience, constantly improving their qualifications, are the authors of scientific works, and have an academic degree. When removing, a Fotek radio knife is used, which is highly accurate and narrows the area of impact as much as possible.
The cost of services can be viewed in the “Price” section or by calling the 24-hour hotline.
Removal of condylomas in the vagina
Removal of papillomas in the vagina is also carried out using hardware methods, for example, laser therapy. However, drug treatment carried out according to the following rules is quite effective:
- The drugs are prescribed in the form of tablets that strengthen the patient’s immunity and help get rid of the virus.
- In addition to tablets, doctors prescribe suppositories for vaginal use.
- Several different medications are taken in combination.
- After getting rid of condylomas, the microflora is restored.
Surgery or laser removal helps to quickly get rid of external signs of the disease, which can cause physical and psychological discomfort to the patient.
Removal of condylomas on the labia minora
Treatment of condylomas on the labia minora is prescribed based on the characteristics of the patient’s body and test results. Unlike growths in the vagina, such neoplasms can be detected with the naked eye.
It is noteworthy that in this case the laser technique is also used, since it does not cause pain in the perineum and does not harm nulliparous women. Laser removal is contraindicated if the patient has herpes in the genital area. In this case, experts select another method of getting rid of papillomas.
Lipomas
Lipomas are formations in the subcutaneous fat layer. Their origin is still not fully understood. There is a possibility of a genetic, hereditary predisposition, but this process cannot be predicted. The size of lipomas ranges from 1 to 15 cm. They do not cause any unpleasant sensations: itching, pain, but they cause inconvenience and cosmetic negatives. They pose a threat to health only if they are damaged by clothing or other mechanical means, which will lead to inflammation.
When treating lipomas up to 3 cm, drug therapy is provided. For larger sizes, lipomas are removed surgically using a radio knife.
Is it necessary to treat a partner for this disease in a woman?
Since perineal condylomas can occur in both sexes, patients are advised to go to a health care facility with a partner. Infection occurs by touching condylomas, so intimacy with a woman who has the human papillomavirus in her body can lead to the development of the disease in a man. In rare cases, infection can occur through household contact. For detailed advice and qualified assistance, you can contact the Estelia Innovative Medicine Clinic.
What is the prevention of diseases caused by HPV?
Examination of sexual partners of patients with diseases caused by HPV has no proven value in terms of preventing their occurrence/recurrence. However, theoretically, timely and complete removal of OCs and intraepithelial lesions can reduce the risk of these diseases, including cervical cancer. It has not been proven that condoms can protect against HPV transmission, but their use reduces the risk of developing OCs and cervical cancer. The most promising method of preventing and treating the early stages of diseases caused by HPV are specific polyvalent (for HPV types 6, 11, 16 and 18) vaccines, which are currently in clinical trials. In summarizing the known information about diseases caused by HPV, the US Center for Disease Control (CDC) draws attention to the public's knowledge of the following key points:
- HPV is an extremely common STD
- It is rarely possible to identify the source of infection due to the highly variable incubation period
- The natural progression of diseases caused by HPV is often benign, and treatment sometimes requires several months. Relapses often occur (up to 50% of cases).
- OCs are most often caused by HPV types that do not cause cervical cancer
- Infectiousness of sexual partners decreases over time
- The effectiveness of condoms in protecting against HPV has not been proven. However, the use of condoms by patients with HPV for new sexual contacts is considered mandatory.
- You should tell new sexual partners that you have previously been infected with HPV
Women, especially those of sexually active age, need to know that the basis for the prevention of cervical cancer is mandatory annual preventive examinations by a gynecologist with a cytological examination of the cervical epithelium according to Papanicolaou, as well as, if necessary, HPV typing, colposcopy and cervical biopsy.
Prevention
The only sure way to prevent perineal condylomas is a vaccination that protects against the papilloma virus. It is recommended to receive it before the first sexual contact - otherwise it will be ineffective if the virus has already entered the body. Prevention measures also include:
- personal hygiene;
- use of barrier contraceptives;
- regular visits to a urologist or gynecologist;
- exclusion of sexual contacts with casual partners.
By taking precautions and treating your health with care, you can avoid the occurrence of such an unpleasant disease.
Condylomas acuminata - symptoms and treatment
The key point in the pathogenesis of the disease is the penetration of HPV into the host body. With a single sexual contact, the probability of infection is 80%, then, with a good state of the immune system, infectious agents are eliminated (destroyed).
Viruses of various types are adapted to a specific host. There are hundreds of types of viruses, many of them are not dangerous to humans, since they are tropic to the tissues of mammals, reptiles and birds and cause benign tumors in them (formation of papillomas).[3]
When studying HPV, three types of viruses were identified - alpha, beta, gamma. Of these, anogenital lesions are caused by papillomaviruses of the first group (α). Infectious agents belonging to the Beta and Gamma genera are more often found with papillomas of the keratinizing epithelium [3] - plantar and palmar warts appear.
In genera, when classifying viruses, types (genotypes) were identified. They are indicated by Arabic numerals. Of the hundreds of virion genotypes, particles with a high carcinogenic risk are isolated - these are α 16, 18, 31, 33, 35, 39, 45, 51, 52, 56, 58, 59. They are detected in 90-95% of cases with malignant processes of the cervix , vagina and vulva. Types 16 and 18 are especially significant. Such oncogenic types of HPV, containing E6 and E7 proteins in their DNA, are able to suppress the activity of the tumor suppressor proteins p53 and pRb, leading to the rapid malignant transformation of papillomas into carcinomas.
About 90% of cases of anogenital warts are caused by HPV α 6 and 11. These are pathogens of low carcinogenic risk.[5] This same low-risk group includes HPV 40, 42, 43, 44, 54, 61, 72, 81.
Penetration
Virions penetrate the basal layer of the epithelium through microscopic damage and then attach to cell membrane proteins. Next, they engage the mechanism of receptor endocytosis (with the participation of integrin and L1 protein from the viral capsid) and enter the cytoplasm. The L2 protein from the viral capsid promotes the release of viral DNA and its entry into the nucleus.[5]
Reproduction
Proteins E1 and E2 from the DNA of the virus are involved in the replication of the foreign genome in the nucleus of the affected cell. At the same time, the cell retains the ability to divide and reproduce its own DNA. By multiplying its DNA, the virus ensures its presence in the form of episomes in the cytoplasm (about 100 per cell). This joint “work” of the virus and the host cell leads to a failure in the processes of proliferation (cell reproduction) and differentiation in the basal layer, leading to visual manifestations.
Manifestations
Abnormal endophytic or exophytic growths of the epithelium appear - papillomas, spots or condylomas. Loose mucous membrane or atypical epithelium of outgrowths are prone to rapid traumatization and maceration (softening). Against this background, a secondary infection quickly develops, pain, discomfort, copious discharge, inflammation, swelling, unpleasant odor, and ulceration of condylomas appear.[2][3]
In the cells of the basal layer, active replication of the virus occurs; as condyloma cells differentiate, their blood supply is sharply depleted, and the central vessels are reduced. But, remaining in the upper layers of the epithelium in an inactive form, this is where the virus is dangerous in terms of contact infection.
During histoanalysis of biopsy materials, the epithelium is thickened, areas of acanthosis and papillomatosis are revealed. Koilocytes are detected (changed in size cells with light cytoplasm, many vacuoles, and a perinuclear light rim). Their nuclei are hyperchromatic. Cells with two or more nuclei are often found.[8]
From the above we can conclude: viruses that cause the formation of anogenital warts, in 90% of cases, belong to types α 6 and 11 HPV.[6][7] They have a low probability of causing malignancy (cancerous degeneration). However, there are frequent cases of joint persistence (residence) of viruses of different types in one carrier. This obliges the patient and doctor to be especially attentive to preventive examinations, their quality and regularity to prevent anorectal cancer .