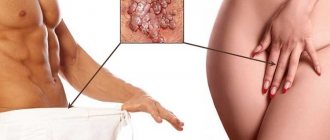
Condylomas in women on the small lips occur for various reasons. The causative agent of this disease is the human papillomavirus. These are growths on the epidermal or epithelial layer in the area of the external genitalia, cervix, anus and groin. Human papillomavirus infection enters the body mainly through sexual contact during unprotected intimate contact. The virus can also be transmitted to the baby during childbirth. The average incubation period is about three months.
Condyloma: what is it?
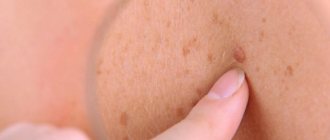
Benign formations that occur on the labia, perineum, clitoris and other intimate places are called vulvar condylomas. They can be brown, pink, flesh-colored. They look like large moles or warts. The size can be quite large: 1-3 centimeters. New growths can appear one by one, although without adequate treatment they can become more and more numerous.
Condylomas in women cause virtually no discomfort. But due to the fact that they constantly touch underwear, injury can occur. Therefore they should be removed.
What can vulvar condylomas be confused with?
With the active development of the process, the shape of condylomas is quite typical for this disease.
But in the early stages, when the pathological elements are still small and there are few of them, other diseases can be assumed:
- herpes infection;
- allergic rashes;
- nonspecific pustular lesions;
- flat warts;
- lipomas;
- manifestations of secondary syphilis.
The most dangerous disease, which is very similar to genital warts, is verrucous invasive squamous cell carcinoma.
Why did the disease occur?
The main cause of condylomas is the human papilloma virus. It enters the body and causes disease. Such an infection may manifest itself years after infection, or perhaps very soon. It depends on the woman's immunity. This virus mainly causes genital warts of the vulva.
Syphilis is often the cause of another type of condylomas, genital warts. Typically, such formations appear in those women who have had syphilis for a long time.
Other causes and factors contributing to the appearance of condylomas are:
- Sexual intercourse without using a condom. The infected person will thus transmit the virus.
- In little girls, condylomas may appear immediately after birth from an infected mother.
- Minor injuries to the skin of the intimate area. For example, when performing hair removal.
- Low immunity.
- Bad habits: alcohol, smoking, drugs.
- Some oral contraceptives.
- Violation of the rules of intimate and personal hygiene.
Condylomas can appear in any woman. The above factors only increase the risk of disease. But by following the rules of safe sex, personal hygiene, and being tested for HIV and syphilis every year, you can significantly reduce the chances of developing vulvar warts.
Vulvar condylomas: how does infection occur?
Papillomavirus enters the body from an infected person, and several types of this virus can be “received” at the same time.
Once in the body, the virus penetrates epithelial cells.
The favorite zone is the junction of the flat and cylindrical layer of cells.
There it can exist in two forms: episomal and introsomal.
- Episomal form - the virus is in the cell, but is not integrated into the genetic material (chromosomes). This is a benign form of the existence of HPV, when there is an incubation period for vulvar condylomas. Its duration is very variable: from several weeks to decades. In addition, the virus can be eliminated from the body on its own without leading to the development of the disease.
- Introsomal form - the virus is located inside the cellular genome; this is a more malignant version of the infection.
With the active reproduction of HPV, a change in the growth and development of epithelial cells begins.
Namely, their uncontrolled division, which leads to tissue proliferation with the formation of genital warts.
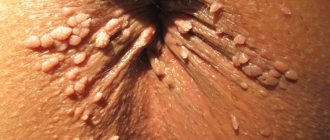
Location of vulvar condylomas in women: labia minora, frenulum and clitoris area of the vulva, anus area.
Less commonly found on the labia majora, in the perineum, inguinal folds, on the walls of the vagina and cervix.
The last two options can only be detected by a doctor during an examination.
What types of condylomas are there?
Neoplasms are of two types. This:
- Genital warts in women,
- Labial or broad condylomas.
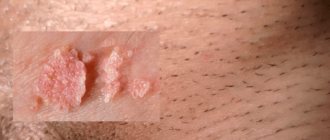
Genital warts are characterized by a cone-shaped shape. The growth has a sharp edge, darker in color than that of wide condylomas. Such formations are quite soft and delicate to the touch. Sometimes, if you press on such a condyloma, you can feel a slight pain. Such neoplasms arise due to the presence of the human papillomavirus in the body.
Wide ones have a flat base. They do not have a characteristic “leg”. When palpated, such condylomas are quite hard, similar to small plaques. The formations may protrude slightly above the skin, approximately 3 mm. Compared to genital warts, such condylomas have a lighter color. Often, condylomas lata in women can also mean that a sexually transmitted disease is present, most likely syphilis.
Complications of vulvar condylomas
The main danger is the possibility of infecting a partner. Condylomas lata contain the causative agent of syphilis in large quantities, and any unprotected sexual contact, including anal or oral, virtually guarantees infection.
Genital warts are not so dangerous in this regard. You can become infected with HPV only at a time when the papilloma virus reaches the surface of the skin; at other times it is in an inactive state, and the risk of transmission to a partner is minimal. On the other hand, the partner himself may already be infected with this virus, and, which is also likely, be the initial source of infection for a woman who has genital warts.
Symptoms of the disease
She can notice that a woman has condylomas when she performs intimate hygiene procedures. For a long time, condylomas may not manifest themselves at all. And the woman may not even suspect the presence of the disease, especially if the formations are located in a hard-to-reach place and not on the external genitalia. But the obvious symptoms of the disease are:
- Neoplasms on the labia, vulva, clitoris. They are similar in appearance to cauliflower.
- Burning sensation, itching and discomfort.
- During sexual intercourse, unpleasant sensations may occur, and if the condylomas are large, they can complicate the process.
- If a woman has a sexually transmitted disease or other concomitant diseases, uncharacteristic, possibly purulent discharge appears.
If such symptoms appear, they should not be ignored. You need to see a doctor immediately.
About vulvar condylomas
Condylomas are multiple peculiar growths of flesh-colored, brownish or pink color that appear on the skin in the genital area.
In appearance they resemble warts or large moles and can grow up to several centimeters (1 - 3 cm). Vulvar condylomas are located on the labia majora and minora, sometimes on the clitoris, in the vestibule of the vagina. This is a fairly common disease that is classified as sexually transmitted. The infections that cause condylomas can be different. Depending on what pathogen causes the appearance of condylomas, they may be a symptom of one or another sexually transmitted disease.
What diagnostic methods should be used?
Treatment of vulvar condylomas should begin with a correct and accurate diagnosis. First of all, it is necessary to identify the reason why the disease occurred, and also to understand what type of condyloma is present. To do this, you need to undergo the following studies:
- Gynecological examination. The doctor will use mirrors to determine where the condylomas are located, their number, and type.
- A blood test for HIV, as well as a test for the Wasserman reaction (or syphilis).
- Taking a smear from the vagina. This will help determine the presence of inflammation and infections.
- Condyloma biopsy. Just a small piece of tissue will help to understand whether cancer cells are forming.
- Test for the presence of human papillomavirus.
- Colposcopy of vulvar condyloma - under a microscope, the doctor will examine the tumors in more detail.
A thorough diagnosis will help you think through treatment tactics and find the optimal way to get rid of the disease.
Symptoms and diagnosis
Vaginal condylomas are usually easy to diagnose. The appearance of a genital wart allows you to diagnose its presence even independently. The severity of the clinical picture is usually determined by the intensity of the immune system. If the virus multiplies intensively and quickly in the body, warts in the vaginal area grow quickly. The key signs of the disease are:
- the presence of itching of varying intensity on the surface of the epithelium of the mucous membrane of the external genitalia;
- feeling of discomfort during sexual intercourse;
- pain during bowel movements or bowel movements;
- if the growth is injured, it may bleed or even bleed.
Diagnosis occurs during a gynecological examination. Additionally, a blood test is required for syphilis, sexually transmitted diseases, and AIDS.
Condylomas in women - treatment
To prevent condylomas from causing trouble, they should be treated rather than ignored. Removal of vulvar condylomas in Kyiv can be performed at the IPF clinic. Modern methods of getting rid of troubles are used here. But it should be remembered that treatment of condylomas must be comprehensive. It should include removing the cause of the disease, and then eliminating the condyloma itself. If the formations are caused by the human papillomavirus, antiviral therapy must be carried out. It is impossible to completely cure this virus, but it can be entered into a latent stage and then it will not cause harm.
If condylomas are caused by sexually transmitted diseases, it is necessary to be treated with appropriate antibiotics and other potent drugs.
To remove condylomas, you can also use the following methods:
- Cryodestruction of vulvar condylomas - with the help of liquid nitrogen, the formations will be “frozen” and removed.
- Electrocoagulation – condylomas are eliminated using electric current.
- Laser removal of vulvar condylomas is a fairly modern method in which formations are removed using a laser.
- Removal of tumors using radio waves.
- Elimination of condylomas using chemicals – condylomas are treated using special medications. Necrosis and rejection occur, after which the formations disappear.
- Interferon therapy is a modern method in which condylomas are treated with a special substance that increases the body’s ability to resist viruses. Condylomas resolve after some time.
All these methods are quite effective, but if you do not follow preventive measures and lead a promiscuous sex life, condylomas can occur again.
Preventive measures
The disease has a very favorable prognosis after removal of vulvar condylomas. They may never appear again if adequate treatment is provided. If you have the human papillomavirus in your body, you should constantly consult with your doctor and undergo preventive treatment so that the virus does not affect your health in any way.
It is also correct to follow basic preventive measures:
- Do not have promiscuous sex life, and in case of casual contacts, always use a condom.
- Boost your immunity with the right foods, fruits, and vitamin complexes.
- Maintain personal hygiene.
- To refuse from bad habits.
- Visit your gynecologist regularly.
- Once a year, undergo an HIV test and the Wasserman reaction (even if there are no signs of the disease).
- You can use pharmaceutical herbs (chamomile, echinacea, calendula) to take baths.
If you follow these simple rules, the disease may never return.
Complications: to be or not to be?
Condylomas are not as harmless as they seem at first glance. They may have the following complications:
- Due to constant contact with underwear, the formations may bleed. This in turn leads to pain, discomfort and even infection of such wounds.
- Spread of condylomas to the walls of the uterus, vagina, and entire intimate area.
- Condylomas can develop into malignant tumors.
- Active syphilis or human papillomavirus reduces the quality of life and negatively affects the body.
- Having sexual intercourse without using a condom can infect your partner.
By removing condylomas and the cause of their occurrence, you can avoid unwanted consequences and complications.
Why IPF
Condylomas should be eliminated only in good clinics that guarantee excellent results. At the IPF clinic, you can undergo a course of treatment for this unpleasant disease, as well as choose a method with which you can remove the formations. In the hospital, you can remove genital warts of the vulva and get rid of other types of formations. Affordable prices and excellent staff will help a woman feel comfortable and safe.
Condylomas can cause discomfort to a woman and also provoke serious illnesses. But by removing them and applying simple preventive measures, you can forget about this trouble forever.
Folk remedies
Folk remedies are not a panacea for warts or condylomas. These are only auxiliary methods in order to reduce the severity of itching, inflammation and other unpleasant symptoms. It is also advisable to use non-traditional methods after radical removal of the tumor:
- chamomile decoction and calendula infusion are used to treat the damaged area;
- applying a paste of grated garlic;
- applying compresses and applications based on alcohol tincture of juniper;
- using a paste of salt and grated horseradish;
- lubrication with iodine;
- oral administration of burdock infusion, decoction from the root part of elecampane, decoction based on lemon balm.
Such methods are not approved by representatives of official medicine. It is believed that only surgery can completely remove the formation and prevent its growth in the future.