Exudative otitis media (ESO) is called a chronic form of otitis media, in which pathological fluid (exudate) accumulates in the middle ear as a result of damage to its mucous membrane. With ESO, the integrity of the eardrum is not compromised and in the absence of an inflammatory process in the nasal cavity, nasopharynx and oropharynx, infection of the middle ear does not occur, despite the fact that the formed exudate is a favorable environment for the development of viruses and bacteria, since it is a protein environment.
It is precisely because the exudate contains a large amount of protein that over time it changes its physical properties (thickens, becomes viscous), which leads to a long and severe course of the disease.
Pain is one of the signs of inflammation. The absence of inflammatory changes in the middle ear explains the fact that ESO is painless. This is the insidiousness of this pathology.
In the medical literature you can find other names for this common disease, namely: “ exudative otitis media ”, “ secretory ”, “ mucosal otitis ”, “ effusive otitis media ”, “gleu ear” - “sticky ear”.
Causes of exudative otitis media in children
The main reasons contributing to the development of ESO are:
- changes in the mucous membrane of the auditory tube against the background of acute and chronic inflammatory diseases of the nose, paranasal sinuses and nasopharynx as a result of decreased immunity,
- dysfunction of the auditory tube, due to dysfunction of the muscles that open it,
— obstruction of the mouth of the auditory tube by adenoid vegetations (growths), hyperplastic (enlarged) tubal tonsil, cicatricial changes, benign and malignant neoplasms of the nasopharynx,
- ineffective treatment of acute otitis media,
— anatomical and physiological features of the development of the auditory tube in childhood.
It should be noted that one of the predisposing factors to the occurrence of ESO is visiting a children's day care center. At the age of 2 to 7 years, the development of this pathology may be preceded by an acute viral infection, chronic adenoiditis, and acute catarrhal otitis media. In children aged 8 to 15 years, the development of exudative otitis media occurs against the background of vasomotor rhinitis or chronic rhinosinusitis.
What is the auditory tube?
The auditory tube is an organ that belongs to the middle ear system, connecting it to the nasopharynx. In the literature, its three main functions are distinguished:
- Regulating or equalizing pressure in the middle ear.
- Isolation and evacuation of fluid constantly forming in the middle ear.
- Protection of the middle ear from contents (viruses and bacteria, allergic substances, food) in the nasopharynx.
Unfortunately, these functions work very poorly in children.
Types of exudative otitis media in children
According to their duration, ESO is divided into three forms : acute (up to 3 weeks), subacute (3 to 8 weeks) and chronic (more than 8 weeks).
According to the nature of the changes occurring in the mucous membrane of the middle ear, four forms of ESO : initial exudative, secretory, productive secretory, degenerative-secretory (with a predominance of the fibrosclerotic process).
There is another classification of ESO, which is based on similar principles (physical parameters of the contents of the tympanic cavity: viscosity, transparency, color, density and duration of the pathological process). It distinguishes four stages of ESO: catarrhal (up to 1 month), secretory (from 1 to 12 months), mucosal (from 12 to 24 months), fibrous (more than 24 months).
Treatment
How to treat pemphigus in a child? The main drugs today are hormones from the group of glucosteroids. In this case, systemic therapy is carried out without age restrictions.
Treatment of pemphigus has several main directions:
- preventing the appearance of new blisters and erosions;
- healing of affected areas of the skin.
Glucosteroids are administered in increased dosages. Due to this technique, the intensity of the formation of new foci decreases and the restoration process begins in existing erosions. This process takes about 2 weeks. Subsequently, the patient is transferred to maintenance hormonal therapy. The drug does not change, but the dosage is significantly reduced.
Viral pemphigus in children treatment is aimed at suppressing the virus. Pemphigus vulgaris requires the administration of a larger volume of drugs than foliaceus. The transition to maintenance therapy is carried out gradually. Moreover, the vast majority of patients are forced to take daily injections of maintenance doses of glucosteroid drugs throughout their lives.
Children should take hormonal medications simultaneously with calcium and vitamin D. The effectiveness of treatment increases due to the use of immunosuppressive drugs from the first days of treatment. These drugs have a depressing effect on the activity of the body's immune system.
Early stages of treatment often involve the use of procedures aimed at clearing the blood of aggressive antibodies. Such procedures include hemodialysis and plasmapheresis. The skin must be treated with antiseptics and special ointments to reduce the risk of infection.
Treatment of pathology is daily and lifelong. Sometimes there may be breaks between relapses of the disease.
Baby care
The diagnosis of pemphigus requires special, attentive and daily care for the child. The organization of a baby’s life directly affects his life expectancy. The initial stage of treatment takes place within the walls of the hospital. After discharge, the child should receive all necessary medications in the prescribed volume and time of administration. Parents must learn how to give injections, because the daily services of a hired nurse will negatively affect the family budget.
Every day your child needs to treat blisters and eczema on the skin. Processing is carried out using aniline dyes. This group of agents has the widest spectrum of action on various microbes, including staphylococcus. Erosion and crusts formed are treated with corticosteroid-based ointments.
The presence of infectious signs in the form of pus, inflammation, swelling means the start of using antibiotic ointments. Large affected areas require the use of sterile dressings to help avoid further injury. Dressings are changed at least 2 times a day. For small affected areas, the relevance of bandages is associated with the child’s high motor activity.
The appearance of pain requires taking painkillers and consulting a specialist. The presence of damaged areas in the oral cavity is associated with mandatory rinsing of the mouth with antiseptic agents. A useful and effective means of care is taking baths with antiseptic agents. It is mandatory to take vitamin and mineral complexes consisting of vitamin E, calcium, magnesium and folic acid.
The diet also requires enrichment with vitamins and minerals. Meals are provided on a fractional and frequent basis, at least 6 times a day. This diet plan is especially important when the esophagus and mucous membranes in the mouth are affected. Diet therapy is based on the complete exclusion of salt and increasing the amount of protein. Registration at a dispensary and systematic visits to a dermatologist are required - at least twice a year and urgently in case of relapse. The use of immunosuppressive therapy imposes restrictions on vaccinations.
Exudative otitis media in children.
Both adults and young patients suffer from exudative otitis media. But diagnosing exudative otitis in a child can be more difficult than in adults, not only due to insufficiently clear symptoms, but also due to the difficulties that arise during the collection of complaints and anamnesis (young patients do not complain). Complaints and clinical picture directly depend on the stage of the disease. The initial stage of ESO is characterized by scant complaints and clinical manifestations.
In most cases, parents seek medical help for their child only when they notice a decrease in his hearing, that is, the child begins to speak loudly, does not immediately respond to calls, asks to increase the volume when watching children's television programs, which already corresponds to the productive secretory form of the disease. It is the absence of pain that leads to late detection of ESO. But sometimes young patients are able to describe their feelings. Adults consult a doctor with complaints of a sensation of fluid in the ear (“gurgling”), a feeling of fullness, autophony, and changes in hearing depending on the tilt of the head.
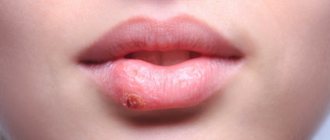
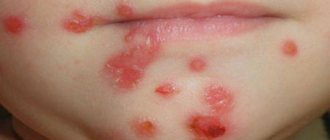
Causes of blisters on and behind the ear
Blisters on the ears can be either independent formations on the skin or symptoms of serious diseases. The causes of blisters (single or multiple) can be:
- allergic reaction of the body;
- insect bites;
- burns (including sunburn);
- taking individually inappropriate medications or non-compliance with their dosage;
- failure to comply with personal hygiene rules;
- skin fungus;
- viral infection;
- inflammatory processes in the body.
Blisters from sunburn or insect bites are not particularly dangerous, except that in rare cases they can lead to skin infections.
Bubbles that appear as a result of infection with viruses or the formation of a focus of inflammation in the body carry a much greater danger and require special attention from the sick person.
The appearance of blisters, just like any other neoplasm on the body, is a reason to seek medical help, especially in cases where it is impossible to determine the cause of their occurrence on your own.
If you know for sure that you could not be bitten by any insect or you have not eaten anything that could cause an allergy,
Is it okay to scratch blisters?
If you want to scratch an itchy blister, it is worth remembering that such a mechanical effect on the blister can lead to its rupture. In this case, a scar may remain after healing, and in the worst case, an infection can be introduced into the resulting wound or the process of suppuration can begin.
What to do if you find a blister on your ear
The first step is to contact a qualified dermatologist to find out the causes of the formation and prescribe treatment. Self-medication, especially when it comes to a child, is not recommended.
If you cannot go to the doctor, and the pain from the blister does not give you peace, you can alleviate the condition by following these steps:
- Wash the affected area of skin with warm water and soap.
- Disinfect the area with the blister with alcohol or iodine.
- Using a sterilized needle, make punctures along the edges of the bladder and thus open it.
- Completely remove fluid from the blister.
- Apply a bandage with antibacterial ointment.
What not to do with blisters on and behind the ear
Whatever the root cause of the blister, it should never be:
- press;
- rub;
- allow moisture (sweat) to accumulate behind the ear, thereby creating favorable conditions there for the development of pathogenic bacteria.
Prevention is the best cure
To avoid the recurrence of blisters on the ear, you must:
- watch your diet;
- maintain a healthy lifestyle;
- observe the temperature regime (do not overheat or overcool);
- avoid unprotected sex (in case of herpes);
- promptly and completely treat viral diseases.
This video will tell you how to get rid of fungus without causing blisters:
And do not forget about observing the rules of personal hygiene
- wash your ears every day;
- When taking a shower or washing your hair, do not forget to rinse your ears, the area behind the ears;
- get rid of the habit of picking your ears with dirty hands and objects not intended for this (matches, hairpins, pins);
- When using cotton swabs to clean the ear, be careful not to damage the eardrum and ear walls.
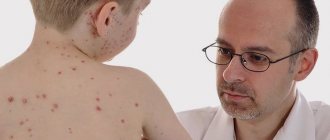
Of course, maintaining hygiene will not prevent the appearance of blisters, which are symptoms of allergies or viral and infectious diseases, such as chicken pox, erysipelas, shingles or herpes and others
Hygiene is quite capable of preventing the appearance of acne on the auricles, in the ears and behind them.
Diagnosis of exudative otitis media in children
To diagnose EOS, an audiological examination is carried out at the Federal State Budgetary Institution National Medical Research Center of the Federal Medical and Biological Agency of Russia in the Department of Pediatric ENT Pathology, which consists of acoustic impedance testing and tone threshold audiometry. For patients with this pathology, acoustic impedansometry is characterized by a tympanometric curve of type “B” and the absence of ipsi-reflexes, which reflects a violation of the transmission of the sound signal along the chain of auditory ossicles due to the pathological contents of the middle ear (exudate); on the audiogram - an increase in air conduction thresholds to 30-40 dB, mainly at low frequencies, bone conduction is not changed. In the case of a recurrent course of exudative otitis media, specialists from the Department of Pediatric ENT Pathology necessarily prescribe the patient a computed tomography (CT) scan of the temporal bones to obtain a reliable picture of the airiness of the middle ear cavity, the condition of its mucous membrane, the chain of auditory ossicles, the windows of the labyrinth and the bony part of the auditory tube, density and localization of pathological contents.
To identify the causes contributing to the occurrence of ESO, the patient in the Department of Pediatric ENT Pathology of the National Medical Research Center of the Federal Medical and Biological Agency of Russia undergoes an endoscopic examination of the nasal cavity and nasopharynx or an X-ray examination of the nasopharynx (in young children if endoscopy is not possible) and paranasal sinuses.
Prevention and prognosis
Medicine has not proposed any specific measures to prevent pemphigus due to the fact that the true causes of its occurrence have not been established. A set of preventive measures is aimed at strengthening the health of a little person:
- formation of strong immunity;
- hardening and walking in the fresh air from the moment of birth;
- proper nutrition;
- avoidance of excessive use of drugs and medications.
Forecasts depend on the speed of contacting a doctor - for symptoms of pemphigus in children, treatment should begin as early as possible. Therefore, you should not self-medicate under any circumstances. In order not to miss the appearance of signs of pathology, it is necessary to examine any skin problems with a dermatologist.
The prognosis of true pemphigus is a priori conditionally unfavorable. Even with adequate and timely treatment, the likelihood of death cannot be eliminated. Any form of pathology is considered chronic.
At the same time, the introduction of hormonal drugs into therapy made it possible to reduce the mortality rate from 65% to 7%. The disease requires constant maintenance therapy. Otherwise, 91% of cases experience acute exacerbations and sudden progression, and consequently an increase in the likelihood of death.