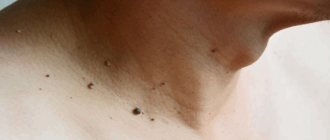
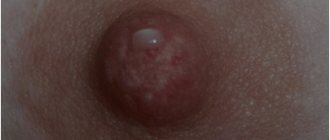
Postpartum papillomas are benign neoplasms that appear on the body of women after childbirth. They usually form no earlier than a month after delivery. They come in different shapes, sizes and colors, and are localized on various parts of the body and internal organs. They are less treatable than papillomas that arise independently of the reproductive process, since treatment of papillomas after childbirth is limited by a number of factors related to the need for lactation.
Causes of papillomas, their types and location
The cause of skin papillomas is the human papillomavirus (HPV). Science knows more than 150 types of HPV, they are divided into three groups:
- Non-oncogenic papillomaviruses - types 1, 2, 3, 5.
- Papillomaviruses of low oncogenic risk (6, 11, 42, 43, 44).
- Papillomaviruses of high oncogenic risk (16, 18, 31, 33, 35, 39, 51, etc.).
Viruses of the last two groups, with varying degrees of probability, can cause the development of malignant neoplasms.
Depending on the type of HPV, papillomas are divided into the following types: ordinary papillomas - also known as vulgar warts, filamentous growths, flat papillomas, genital papillomas - also known as condylomas, plantar warts, juvenile warts and papillomatosis.
The most common are vulgar, filiform and genital papillomas.
- Thread-like forms of papillomas are more common in people aged 40+ and are localized in areas with thin skin - on the chest, armpits, neck, etc.
- Vulgar warts most often “attack” the skin of the feet, palms, fingers and toes, but can appear on any other parts of the body. Often recur in conditions of decreased immunity.
- Condylomas appear only on the mucous membranes. They can affect the glans penis, foreskin, vagina, and labia minora.
- Plantar warts appear on the rough skin of the feet and on the balls of the toes.
- Papillomatosis is a generalized form of the disease, manifested by the formation of growths throughout the body.
What are the consequences of HPV during pregnancy?
To date, there is no reliable evidence of a pronounced negative impact of infection on the course of pregnancy.
Pregnancy pathologies such as miscarriage, premature birth, etc., which are characteristic of other sexually transmitted infections, have not found unconditional confirmation of the connection with HPV.
However, if a woman’s primary infection occurs during pregnancy, there is a risk of developing various complications.
Anogenital warts in the mother caused by HPV types 6 and 11, localized in the area of the labia minora and the vestibule of the vagina, have some consequences for the fetus during pregnancy.
Such genital warts carry a small risk of infection of the fetus during childbirth, leading to the development of respiratory papillomatosis in the latter.
Respiratory, or otherwise laryngeal, papillomatosis (also called laryngeal papillomatosis) most often develops in children 2 to 3 years old.
As a result of infection from a sick mother during the latter’s pregnancy or immediately at birth.
The route of transmission during pregnancy through the placenta, during childbirth or immediately after it is not yet entirely clear.
The main symptoms of the disease are hoarseness, up to the complete disappearance of the voice, and difficulty swallowing.
As the disease progresses, shortness of breath and cough appear.
In severe situations, blockage of the upper respiratory tract and asphyxia are possible, especially in the case of formations with a long thin stalk.
During examination using a laryngoscope (sometimes a bronchoscope is also used), typical growths - condylomas - are found on the laryngeal mucosa.
This pathology has a rather aggressive course: after removal of the formations, relapses often occur, requiring repeated surgical interventions.
If pregnancy occurs due to infection with highly oncogenic papillomaviruses (especially HPV 16, 18), the woman must inform her obstetrician-gynecologist about the presence of infection.
The fact is that changes in a pregnant woman’s body can provoke more intense cell transformation.
Actually, such viruses do not affect the course of pregnancy itself or the child, but they pose a certain threat to the woman’s health.
In a situation where no infection was detected in the past, a cytological Papanicolaou smear (Pap test) is taken, among others, when registering.
If the analysis shows abnormalities, the doctor prescribes additional tests (for example, colposcopy).
Also, situations when pregnancy occurs in women with erosion require special attention.
PCR diagnostics are required to exclude infection with high-oncogenic risk HPV.
As a rule, in the routine practice of an obstetrician-gynecologist, such a combination as HPV and pregnancy is not specifically examined.
Tests for the virus are recommended only if pathological abnormalities are detected.
At the same time, there are research studies demonstrating the effect of the virus on pregnancy.
Thus, it has been shown that infection of women with HPV slightly reduces the likelihood of embryo implantation, and in men it reduces sperm motility.
And since in a married couple, as a rule, both partners are infected, the onset of pregnancy is associated with some difficulties.
As a result, when planning a pregnancy against the background of an infection caused by HPV, planning an IVF procedure, this factor should also be taken into account.
How does HPV infection occur?
The mechanism of transmission of the virus is contact; the source of infection is the patient or the virus carrier. HPV can be released not only from growths on the skin, but also circulate in the blood, saliva and urine. In this case, infection can occur in 4 main ways:
- through contact and everyday life;
- sexually;
- during childbirth from mother to child (which may be the cause of laryngeal papillomatosis);
- during autoinoculation (self-infection or dispersion of the pathogen from existing foci during combing, shaving, or using a hard washcloth).
The risk of HPV infection usually depends on the state of the human body’s immune system, viral load and the presence of microtraumas and other inflammations on the skin and mucous membranes.
Even when infected with the HPV virus, papillomas do not always form on the skin and mucous membranes. The virus is localized in the basal layer of the epithelium and can remain inactive for a long time. Only under certain conditions (weakening of the immune system, stress, exposure to unfavorable environmental factors) do the processes of its replication start, which leads to cell proliferation and the appearance of tumors.
Indications for removal
The only way to treat already “formed” papillomas is to remove them. Indications for removal of tumors primarily include:
- Aesthetic problems. Papillomas are skin growths that are perceived as an aesthetic defect, especially when they are localized in open areas of the face and body.
- Papillomas can be constantly injured, cling to clothes, combs, etc. and due to this, quickly spread throughout the skin, soreness, inflammation, cracks and even bleeding may appear in the area of the tumors.
- Considering that some types of papillomaviruses have a high risk of oncogenicity, large papillomas (more than 6-10 mm) may be prone to degeneration, so timely removal of such tumors will prevent a serious illness in the patient.
How is HPV diagnosed in pregnant women?
First of all, the diagnosis of infection begins with a clinical examination.
Genital warts, like other types of formations, are easily identified by their appearance.
If condylomas are present, examination of the cervix is also required.
In most cases, HPV infection is diagnosed on the basis of a Pap test, which is the primary screening for precancerous changes and cervical cancer caused by the virus.
Papanicolaou cytological examination is a variant of microscopic examination using various groups of dyes.
There are characteristic signs of cell changes detected in this study that support infection with the papilloma virus.
These signs include:
- koilocytosis - a change in the shape and color of the nucleus, an increase in the number of nuclei, the appearance of vacuoles in the cell;
- the appearance of dyskeracites - small cells with colored nuclei and altered cytoplasm.
Another test for HPV during pregnancy is papillomavirus typing using the polymerase chain reaction (PCR).
However, due to its high sensitivity, such a study often leads to overdiagnosis of diseases, since in most cases the infection is short-term.
This method is important when HPV is detected against the background of a characteristic clinical picture.
As a result, global medical guidelines do not recommend the use of PCR as a prognostic test in women under 30 years of age.
At an older age, such a study, especially in the case of determining the group affiliation of the virus, is more significant.
If necessary, additionally resort to instrumental diagnostic methods, such as colposcopy and urethroscopy.
Colposcopy and biopsy with histological examination are performed for all women with neoplasia detected during the Pap test.
During colposcopy, a test with acetic acid and Lugol's solution is also performed.
A colposcopic sign of HPV infection is uneven staining with iodine solution, blanching of areas after treatment with acid.
Methods for removing papillomas
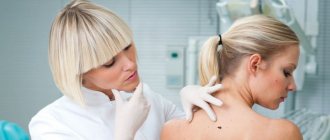
In our medical center, before removing a tumor, a dermatologist examines it and, if necessary, performs dermatoscopy in order to differentiate the type of papilloma and select the optimal method of removal.
It is possible to get rid of papillomas in our clinic without surgery using the destruction of formations using a laser, radio knife and plasma. Removal of papillomas with a laser, especially removal of papillomas on the face, is not carried out so often due to the high traumatic nature of the method and the possibility of hypopigmentation and scarring. Preference is given to radio wave destruction, as well as diathermocoagulation. These methods are highly effective and low traumatic.
- The radio wave method is one of the most effective and least traumatic ways to remove almost all types of papillomas. It is performed on the Surgitron DF-120 device (Ellman International Inc, USA). Removal of the tumor occurs due to local evaporation of cells under the influence of heat generated in the tissues in response to the penetration of radio frequency waves. The cells evaporate and the tissues move apart as if cut with a scalpel. In addition, instant coagulation of blood vessels occurs in the treatment area, so there is no bleeding and no damage to surrounding healthy tissue. In this aspect, laser removal of papillomas is significantly inferior to the radio wave method.
- Diathermocoagulation using the Plasmaskin device (Ultramed, Russia) is a non-contact effect on the affected tissue with a plasma beam. The high temperature of the plasma (up to 2000-2500 C) is combined with the bactericidal effect of an air flow containing a high concentration of ozone and has a virus-destructive effect, destroying HPV DNA, which prevents its spread.
The use of radio wave energy on the SURGITRON DF-120 device (Ellman International, Inc., USA) is the method of choice for removing most forms of papillomas, regardless of their location (face/body), and here’s why:
- Radical - no relapses;
- Rapid epithelization - healing;
- Atraumatic - no complications, no marks or scars remain on the skin;
- Painless - anesthesia is required only in cases of large tumor sizes.
- Complete safety of procedures.
During the destruction of papillomas, anesthesia is usually used. Application anesthesia with the application of lidocaine cream can be used, or infiltration anesthesia, when the site of papilloma localization is injected with an anesthetic solution (Ultracaine). The choice of pain relief method is determined by the size and location of the papilloma.
If the patient has no contraindications, removal of papillomas in Moscow in our clinic can be carried out on the day of treatment, immediately after an appointment and examination by our specialist. In this case, no additional tests are required.
In order to prevent relapses after removing a large number of tumors, our experts recommend taking immunomodulatory drugs. Immunomodulatory therapy is selected individually.
Methods for treating papillomas after childbirth
If papillomas appear after childbirth, their treatment should begin with a consultation with a dermatologist, surgeon or oncologist and always a gynecologist. First, you should make sure that these are papillomas and not moles or melanomas. Secondly, choose a method that is suitable specifically for your current health condition.
Since after childbirth a woman’s immunity is significantly reduced and the secretion of hormones undergoes a transformation, the body will react more sharply to possible irritants found in therapeutic drugs. But at the same time, the virus itself will be more difficult to eliminate. Therefore, an integrated approach will be needed in the treatment of papillomas after childbirth. It will consist of the use of vitamin complexes, antiviral agents or external cauterizing drugs. They can be both medical and folk.
This task is complicated by the fact that, due to the need to feed the child with mother's milk, the entire possible range of medical products in the arsenal of a modern dermatologist cannot be used. Only gentle drugs are used here. If none of them suits the patient, surgical removal must be performed.
Vitamins for papillomas after childbirth
The first thing you need to do to fight papillomas after childbirth is to help the body boost its immunity. To do this, it is necessary to use special vitamin complexes containing a number of useful components. Here it is better to resort to the help of those remedies that are recommended during pregnancy. They are selected in such a way that they will not harm the baby if they enter his body through breast milk.
Pay attention to the following drugs:
- Vitrum Prenatal Forte . Contains B vitamins, as well as A, E, D, C, calcium, magnesium, iron, copper, zinc, iodine, manganese, molybdenum, selenium and chromium. You need to take 1 tablet per day. The price of this drug is from 651 rubles in Russia, from 425 hryvnia in Ukraine.
- Elevit Pronatal . It contains 12 vitamins and 7 minerals. A distinctive feature of this complex is the fact that it does not contain iodine. This is a disadvantage for residents of those regions where, due to poor ecology, additional consumption of this component is necessary, but a big plus for patients suffering from a fairly common allergy to this substance. It is also necessary to use this remedy for papillomas after childbirth, 1 tablet, 1 time per day. The price of the product is from 576 rubles in Russia, from 204 hryvnia in Ukraine.
- Multi-Tabs Perinatal . It contains 11 vitamins and 9 minerals. Manufacturers note that the drug contains sucrose, but there is no gluten or preservatives - allergy sufferers should especially pay attention to this information. One tablet a day during or immediately after meals will provide the body with the necessary resources to boost immunity and fight viruses. The price of vitamins is from 557 rubles in Russia, from 404 hryvnia in Ukraine.
Analogs of these drugs are Complivit Trimesterum, Pregnavit, Doppelherz and other complexes for expectant mothers and nursing women.
Antiviral drugs for the treatment of papillomas after childbirth
Photos of antiviral drugs for papillomas after childbirth
To suppress HPV, the use of antiviral drugs is necessary. As a rule, doctors recommend using the oral form of these drugs together, and not just using external ones. However, the lactation period is not the best time for such therapy, since it is not comparable to breastfeeding. After the end of lactation, general recommendations for the treatment of papillomas that appear after childbirth are applied, and during breastfeeding - limited.
Antiviral agents:
- Papilight . The drug is based on the extract of rhododendron Adams, caragana, garlic, propolis, diatoms, red pepper, Jerusalem artichoke and other more than 50 active ingredients. When applying externally with nozzle No. 1, you need to take a drop from the middle phase and apply it to the new formation, without rubbing or massaging. After 15 minutes, apply a drop from the lower phase using nozzle No. 2 and rub in for 2 minutes. After another 15 minutes, nozzle No. 3 removes liquid from the top layer and, also when applied to a papilloma after childbirth, rubs it in thoroughly. This procedure must be performed twice a day until the growths disappear. Papilight price - from 990 rubles. in Russia, from 339 UAH. in Ukraine.
- Papiderm . The product contains extracts of black walnut, shiitake mushrooms, maclura, Canadian goldenseal, cordyceps and potato shoots. The scheme and frequency of use of this product is the same as the previous one. Price - from 359 rub. in Russia, from 248 UAH. in Ukraine.
- Viferon . This is an interferon-based ointment. It is applied in a thin layer to the papilloma 3-4 times a day for a week. The price of the drug is from 120 rubles. in Russia, from 141 UAH. in Ukraine.
Also, in the treatment of papillomas after childbirth, women resort to the help of Salicylic ointment, Virogel, Panavir cream and other means.
Cauterizing agents for postpartum papillomas
If previous drugs fought papillomas after childbirth by affecting the virus, then these data have a destructive effect on cells mutated by the virus.
Cauterizing agents:
- Sleigh Skin. This product is based on salicylic acid, castor oil and tea tree essential oil. External treatments should be carried out three times a day for 2 weeks until the papillomas disappear. The price of Sani Skin is from 2490 rubles in Russia, not for sale in Ukraine.
- Papilovir . A product based on carbolic acid, sodium and potassium hydroxide, perlite oil, red pepper, garlic extract and propolis. The regimen for use of this drug is the same as for other drugs that have a three-phase structure. The price of Papilovir is from 990 rubles in Russia, from 339 hryvnia in Ukraine.
Traditional recipes against papillomas after childbirth
Traditional medicine recipes include two types of methods for treating papillomas after childbirth: internal use of tinctures and external treatment of tumors. During breastfeeding, only applications are allowed. And this must be done with great care so as not to cause an allergic reaction.
Let's consider folk remedies for postpartum papillomas:
- Oil mixture . Mix equal amounts of eucalyptus, lemon and tea tree essential oils. Rub the resulting liquid into the tumors every day before bed.
- Castor oil . Daily use of castor oil will help to achieve cleansing of the skin. Rub it into the papillomas after childbirth, then cover the treatment areas with a plaster.
- Celandine . For this recipe, it is better to use not pharmaceutical concentrate, but freshly cut shoots of the plant. Lubricate the papillomas with the juice released from the stems once a day.
- Rowan and wormwood . Mix the rowan fruits and wormwood stems in a blender in equal parts. Squeeze the resulting pulp through cheesecloth. Treat new growths with this juice several times a day.
- Garlic . In order to use this product as a remedy for papillomas after childbirth, you need to peel the clove, grind it into a paste, and rub it on the new growths several times a day.
What will happen to the skin after papillomas are removed?
The next day after the procedure, a brown crust forms at the site of the removed tumor. Healing takes from 2 to 7 days, it all depends on the size of the removed papilloma. After healing, the crust will come off on its own. The main thing at this time is not to wet or injure this area.
After the procedure, the doctor gives some simple recommendations for further skin care.
In our clinic, it is carried out using modern equipment by highly qualified doctors, which allows us to solve problems of papillomas removal quickly, efficiently and safely. We use disposable consumables, which guarantees maximum patient safety.