It’s good to be healthy, but unfortunately, we cannot always boast of an excellent state of mind and body. Everyone has heard about hives. This is a fairly common allergic disease that can occur at any age. Ruthless statistics say that 15-20% of the population of our planet have observed at least one case of urticaria throughout their lives.
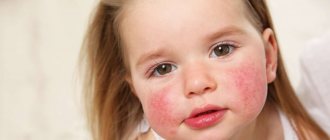
Urticaria is a widespread disease that manifests itself in the form of characteristic rashes, similar to nettle burns, on the skin and mucous membranes and is very rarely accompanied by itching.
In childhood, each of us was inadvertently burned by nettles, so it is quite easy to remember the symptoms of this disease. Hippocrates was one of the first to talk about this seemingly simple disease: he drew an analogy between urticarial rashes in people suffering from urticaria and problems of the gastrointestinal tract.
Causes of urticaria
Very often, the cause of hives is an allergic reaction of the body to certain substances or allergens. There are different ways that allergens enter the body, depending on which urticaria occurs:
- food (citrus fruits, seafood, pork, nuts, eggs, tomatoes, berries are the culprits),
- insect (as a result of insect bites), including those resulting from infection with parasites (helminths, ticks),
- medication (for penicillin, aspirin, codeine),
- result of stress
- toxic allergies (to dust, pollen),
- as an individual reaction to cold, heat, prolonged ultraviolet irradiation.
In all of the above cases, you need to consult an allergist.
Urticaria and its treatment: you can’t do without a doctor!
Let us remind you that, although urticaria itself is safe and goes away without a trace, the “companion” of this disease - Quincke's edema - can lead to serious consequences.
That is why you should pay utmost attention to the first signs of nettle fever and consult a doctor who will determine the causes of the disease and give the necessary recommendations. This is especially important if the rash appears in children.
If symptoms of anaphylactic shock appear (difficulty breathing and swallowing, in women - spasms and pain in the uterine area), you must immediately call an ambulance.
To determine the nature of the pathology, an allergist-immunologist will examine the patient and conduct the necessary tests and tests for allergens.
Having made conclusions about the causes of urticaria, the doctor will begin treatment. Patients with acute urticaria are prescribed antihistamines, and patients suffering from chronic urticaria also take immunomodulators.
It is important to remember that the treatment process will be quite long, but it will be most effective if you follow the correct lifestyle: you need to remove everything that can cause an allergic reaction, adhere to the diet recommended by your doctor, stop smoking and drinking alcohol.
Never take antihistamines unless prescribed by a specialist. By doing this you can only harm yourself and your body.
Classification of the disease
There are two forms of urticaria:
- acute (duration is about 6 weeks),
- chronic (over 6 weeks).
- There are different types of immunological urticaria:
- Urticarial vasculitis.
- Allergic
- Compliment addict.
- Autoimmune.
- Physical is divided into:
- mechanical: vibration, dermographic;
- temperature: thermal or cold contact;
- allergies that develop under the influence of other extraneous factors.
- There are also the following forms of urticaria:
- Contact.
- Aquagenic.
- Adrenergic.
- Idiopathic.
- Urticaria caused by non-IgE-mediated mast cell degranulation.
- Cholinergic.
- Drug-induced urticaria with development mechanisms different from those previously described.
Symptoms of urticaria
- Blisters can appear as pinpoint or large-focal, sometimes they merge with each other.
- A blister, the primary element in the manifestation of a skin rash, is a local swelling of the papillary dermis, which occurs as a result of accelerated blood flow, vasodilation, and increased vascular permeability.
- Blisters may also appear as cavityless exudative ephemeral elements. Dense, swollen, bright pink in color, they can rise above the skin level and have different shapes (large scalloped, rounded, etc.), different sizes (diameter - from 0.5 to 10-15 cm) and often a pale area in the center. Blisters may disappear without a trace (even after a few minutes).
- Sometimes there may be a burning sensation or a blister may be accompanied by unpleasant itching of the skin.
- Inflammation can occur anywhere. But most of all skin rashes appear in places where skin and clothing come into close contact: under straps, belts, and suspenders.
- The duration of the visual presence of the rash can range from several minutes to a day.
- In half of the patients, urticaria is accompanied by angioedema (Quincke's edema).
If swelling and rash have spread to the surface of the mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract, nausea and vomiting have appeared, this indicates a possible threat to human life and requires immediate intervention by a specialist.
Very often, urticaria is not treated and the disease is not given due importance. However, it is important to know that hives can be a signal of the appearance of diseases of the internal organs or some other serious infection in the body.
Do not forget about the predisposition to urticaria. This will be indicated by increased sensitivity of the skin and white stripes that remain after light scratching (white dermographism). If hidden infections are detected in time, the immune system will be able to function normally. It is important to assess the condition of the internal organs, being aware that if their functioning is disrupted, skin diseases may occur.
Symptoms
What are the main signs of a nettle rash?
- Skin redness
- The appearance of blisters
- Weakness
- Dizziness
- Itchy skin
- Joint pain
- Temperature increase
- Nausea
- Vomit
- Chills
- Diarrhea
- Insomnia
- Swelling of the skin and mucous membranes.
Urticaria is one of the most common diseases. In general, the definition refers to a number of individual ailments, characterized by different specific natures of occurrence, but manifesting themselves in the same way.
Make an appointment online
Sign up
For what indications is specialist consultation necessary?
Consultation with an allergist is necessary in case of exacerbation of chronic recurrent urticaria, as well as in intermittent acute form of the disease. The causes of diseases associated with urticaria can be determined by an allergist. It is also necessary to consult a dermatologist, rheumatologist, parasitologist, endocrinologist and, possibly, an oncologist.
Brief description of some clinical forms of urticaria
Allergic urticaria
- Most often acute or episodic
- The most common allergens are food, medications, insect poison, latex
- Patients also have other manifestations of allergy pathology, allergic heredity
- Positive results of allergological examination
- Elimination measures are effective
Autoimmune urticaria
- Current type of chronic idiopathic urticaria
- Frequent presence of autoimmune thyroiditis and thyroid diseases in the family
- Severe general symptoms (weakness, malaise, gastrointestinal dysfunction)
- Presence of histamine-releasing anti-Fcε-RI antibodies and anti-IgE antibodies
- Positive test with autoserum
Cold urticaria
- It can be acquired (idiopathic and arising against the background of an underlying disease, for example, viral hepatitis, lymphoproliferative disease, etc.) and congenital.
- The appearance of itching, burning, hyperemia, urticarial rash, angioedema in areas of the skin exposed to low temperatures
- Symptoms persist for 20-30 minutes and disappear without a trace after the patient warms up
- exposed
Delayed pressure urticaria
- Characterized by the appearance of swelling and blisters in pressure areas 4-6 hours after exposure.
- Characterized by resistance to treatment
Heat urticaria
- Occurs from exposure to heat.
- Hereditary local thermal urticaria has been described, characterized by a delayed (4-6 hours) appearance of elements after local thermal exposure.
- May be accompanied by systemic circulatory disorders and convulsions
Solar urticaria
- Occurs under the influence of ultraviolet radiation
- Blisters appear on exposed areas of the body after exposure to the sun; there may be fixed light urticaria
- The disease can be primary (idiopathic photic urticaria) and
- Secondary light urticaria may be associated with the action of drugs (tetracyclines, sulfonamides, quinolones) or associated with an underlying disease (SLE, thyroiditis, gastrointestinal dysfunction).
Dermographic urticaria
- The appearance of blisters due to mechanical irritation of the skin
- Itching precedes the appearance of rashes
- The phenomenon of dermographism is reproduced by intense line irritation of the skin with a blunt object (spatula)
Vibration urticaria/angioedema
- There are hereditary (autosmal dominant type) and acquired forms
- Characterized by the appearance of a rash and swelling in areas exposed to vibration
- Rash and swelling appear 4-6 hours after exposure to vibration and persist for up to 24 hours.
- The disease is caused by nonspecific degranulation of mast cells
Aquagenic urticaria
- The rash occurs only after contact with water of any temperature
- A rash with severe itching occurs immediately after contact with water
- Characterized by the appearance of small blisters surrounded by erythematous spots
Cholinergic urticaria
- Occurs more often in young people
- Characterized by the appearance of pale pink blisters with a diameter of 1-5 mm, often surrounded by erythema, the rash is generalized
- Provocative factors include exercise, stress, sweating, and hot showers.
- May be accompanied by systemic manifestations (hot flashes, weakness, rapid heartbeat, headache, abdominal pain, shortness of breath
- Can be reproduced by subcutaneous administration of acetylcholine
Adrenergic urticaria
- Rarely seen
- Characterized by the appearance of small papules with a white halo
- Triggered by stress
- Can be reproduced by intradermal injection of epinephrine
Anaphylaxis/urticaria caused by physical exertion
- Characterized by the appearance of skin itching, rashes, angioedema during or immediately after physical activity
- May be accompanied by systemic manifestations, including bronchospasm, laryngeal edema, vascular collapse
- A provoking factor may be the consumption of certain foods (alcohol, apples, shrimp, tomatoes, nuts, celery) before physical activity.
Additional research:
- skin test when using autologous serum;
- rheumatological tests;
- nasal swab for the presence of eosinophils;
- TSH, T3, T4, antibodies to thyroid peroxidase and thyroglobulin;
- culture of throat flora, throat culture for sensitivity to antibiotics and bacteriophages;
- stool analysis for sensitivity to bacteriophages and dysbacteriosis;
- antibodies to helminths, as well as roundworms and lamblia;
- coprogram;
- HBsAg, AT to hepatitis C, RW, AT to HIV;
- ultrasound examination of the thyroid gland;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity;
- consultation with a gastroenterologist to identify H. pylori, endoscopy, consultation with a neurologist, ENT specialist (VSD);
- ECG;
- if urticarial vasculitis is suspected, a dermatovenerologist performs a skin biopsy.
Diagnostics
When visiting a medical office, the doctor prescribes a number of measures:
- General blood and urine analysis.
- Blood for HIV and syphilis;
- research on parasites.
Making a diagnosis is usually not difficult. Sometimes it is difficult to identify the allergen. This requires additional laboratory tests - tests to determine the presence of antibodies to possible irritants in the blood.
If the rash is periodic, then you should not hesitate to visit a doctor. The doctor determines the need for diagnostics and nuances individually. Subsequently, the patient is registered with a dispensary so that the specialist monitors the course of the pathology over time, identifies provoking factors and promptly adjusts the treatment tactics.
Recommended drugs that are used to treat urticaria
- Antihistamines. The Gorbakov Clinic uses new drugs that do not have side effects.
- Leukotriene receptor antagonists.
- Histamine H2 receptor blockers.
- Immunosuppressants.
- Glucocorticoids.
- Slow calcium channel blockers.
- Androgens.
- Combination drugs that include M-anticholinergic drugs.
- Antidepressants.
- Medicines that are used in rheumatology.
- Plasmapheresis.
- Intravenous immunoglobulins.
Specialists at the Gorbakov Clinic individually determine the patient’s treatment tactics in each individual case. A systematic approach to treatment will help the patient get rid of the problem for a long time or forever.
How is allergic urticaria treated?
First of all, when allergic urticaria develops, the effect of the allergen should be eliminated. In case of contact allergies, remove the irritating substance from the surface of the skin; in case of an insect bite, remove the sting, stop eating or taking medication, take enterosorbent (activated carbon, Enterosgel), and, if possible, rinse the stomach.
Before seeking medical help, you can take an antihistamine and use an ointment that does not contain hormones. There is no need to try to treat yourself; further prescriptions should be made by a doctor, since uncontrolled use of hormonal and other potent drugs can lead to negative consequences.
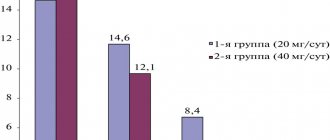
Medical care consists of a more precise selection of allergy medications that have minimal side effects, the prescription (in severe cases, with chronic urticaria) of systemic corticosteroids, and in some cases, immunosuppressants. Source: Modern principles of treatment of acute and chronic urticaria. Skorokhodkina O.V., Klyucharova A.R. Practical medicine No. 7, 2012. p. 45-49.
Emergency care for a patient with allergic urticaria is required when Quincke's edema develops. If it occurs, you should immediately call an ambulance. In order to alleviate the patient’s condition before the ambulance arrives, you need to calm him down, provide an influx of fresh air, and unfasten clothing that is restricting breathing. To relieve swelling, doctors provide the necessary assistance on site, including adrenaline injections and tracheal intubation, then the patient is taken to the hospital, where further treatment is carried out.
Features of the treatment of urticaria at the Gorbakov Clinic:
- Individual patient training at the immuno-school and asthma school.
- Treatment begins on the first day of treatment.
- A comprehensive examination is carried out on the day of treatment.
- Return to normal life.
- Rapid relief of a serious condition occurs within 1-3 days.
Urticaria is an extremely common allergic disease, affecting one in five people worldwide. Most often, people do not attach importance to the symptoms and rarely consult a doctor if they notice characteristic rashes. However, urticaria is often a signal of the presence of serious diseases in the body. Contact a specialist at the first symptoms of allergic urticaria and undergo the recommended comprehensive examination.
It’s good to be healthy, but unfortunately, we can’t always boast of an excellent state of mind and body. Everyone has heard about hives. This is a fairly common allergic disease that can be acquired at any age. Ruthless statistics say that 15-20% of the population of our planet have observed at least one case of urticaria throughout their lives.
Urticaria is a widespread disease that manifests itself in the form of characteristic rashes, similar to nettle burns, on the skin and mucous membranes. Rarely accompanied by itching.
In childhood, each of us was inadvertently burned by nettles, so it is quite easy to imagine the symptoms of this disease. Hippocrates was one of the first to talk about this seemingly simple disease. He drew an analogy between urticarial rashes in people suffering from hives and problems of the gastrointestinal tract.
Causes of urticaria
Very often, the cause of hives is an allergic reaction of the body to certain substances (allergens). There are different ways that allergens enter the body, depending on which urticaria occurs:
- food (citrus fruits, seafood, pork, nuts, eggs, tomatoes, berries or other products are the culprits);
- insect (as a result of insect bites), including those resulting from infection with parasites (helminths, ticks);
- medication (for penicillin, aspirin, codeine and other drugs);
- result of stress;
- toxic allergy;
- as an individual reaction to cold, heat, prolonged ultraviolet irradiation.
In all of the above cases, you need to consult an allergist.
Classification of the disease
There are two forms of urticaria:
- acute (duration is about 6 weeks);
- chronic (over 6 weeks).
There are different types of immunological urticaria:
- urticarial vasculitis;
- allergic;
- compliment dependent;
- autoimmune.
Physical urticaria is divided into:
- mechanical urticaria:
- vibration;
- dermographic;
- temperature urticaria:
- thermal;
- cold contact;
- allergies that develop under the influence of other extraneous factors.
There are also such forms of the disease:
- contact;
- aquagenic;
- adrenergic;
- urticaria, which is caused by non-IgE-mediated degranulation of mast cells;
- cholinergic;
- drug-induced urticaria with development mechanisms different from those previously described;
- idiopathic (if the cause of urticaria is not established);
Symptoms of urticaria
A blister is the primary element in the manifestation of a skin rash. It is a local swelling of the papillary dermis, which occurs due to accelerated blood flow, vasodilation and increased vascular permeability.
Blisters can be either pinpoint or large-focal, sometimes they merge with each other.
Blisters may also appear as cavityless exudative ephemeral elements. Dense, swollen, bright pink in color, they can rise above the skin level and have different shapes (large scalloped, rounded, etc.), different sizes (diameter - from 0.5 to 10-15 cm) and often a pale area in the center. Blisters may disappear without a trace (even after a few minutes).
There may be a burning sensation or an unpleasant itching sensation.
The duration of the visual presence of the rash can range from several minutes to a day.
In half of the patients, urticaria is accompanied by angioedema (Quincke's edema).
If swelling and rash have spread to the surface of the mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract, nausea and vomiting have appeared, this indicates a possible threat to human life and requires immediate intervention by a specialist.
Very often, urticaria is not treated and the disease is not given due importance. However, it is important to know that hives can be a signal of an infection in the body.
Do not forget about the predisposition to urticaria. This will be indicated by increased sensitivity of the skin and white stripes that remain after light scratching (white dermographism). If hidden infections are detected in time, the immune system will be able to function normally. It is important to assess the condition of the internal organs, being aware that if their functioning is disrupted, skin diseases may occur.
Brief description of some clinical forms of urticaria
Allergic urticaria:
- often occurs acutely or episodically;
- the most common allergens are food, medications, insect poison, latex;
- Patients also have other manifestations of allergopathology, the so-called allergic heredity;
- the results of the allergy examination are positive;
- Elimination measures are effective.
Autoimmune urticaria:
- characterized by a course of chronic idiopathic urticaria;
- frequent presence of autoimmune thyroiditis and thyroid disease in the family;
- severe general symptoms (weakness, malaise, gastrointestinal dysfunction);
- the presence of histamine-releasing anti-Fcε-RI antibodies and anti-IgE antibodies;
- the autoserum test is positive.
Cold urticaria:
- can be acquired or arising against the background of an underlying disease (for example, viral hepatitis, lymphoproliferative disease and others) and congenital;
- the appearance of itching, burning, hyperemia, urticarial rash, angioedema in areas of the skin exposed to low temperatures;
- symptoms persist for 20-30 minutes and disappear without a trace after the patient warms up.
Delayed pressure urticaria:
- characterized by the appearance of swelling and blisters in pressure areas 4-6 hours after exposure; Inflammation can occur anywhere. But most often, skin rashes appear in places where skin and clothing come into close contact: under straps, belts, and suspenders.
- characterized by resistance to treatment.
Heat urticaria:
- occurs from exposure to heat;
- hereditary local thermal urticaria has been described, characterized by a delayed (4-6 hours) appearance of elements after local thermal exposure;
- may be accompanied by systemic circulatory disorders and convulsive syndrome.
Solar urticaria:
- occurs under the influence of ultraviolet radiation;
- blisters appear on exposed areas of the body after exposure to the sun, there may be fixed light urticaria;
- the disease can be primary (idiopathic light urticaria) and secondary;
- secondary light urticaria can be associated with the action of drugs (tetracyclines, sulfonamides, quinolones) or with an underlying disease (systemic lupus erythematosus, thyroiditis, gastrointestinal dysfunction).
Dermographic urticaria:
- the appearance of blisters due to mechanical irritation of the skin;
- itching precedes the appearance of rashes;
- the phenomenon of dermographism is reproduced by intense line irritation of the skin with a blunt object (spatula).
Vibration urticaria/angioedema:
- there are hereditary (autosomal dominant type) and acquired forms;
- characterized by the appearance of a rash and swelling in areas exposed to vibration;
- rash and swelling appear 4-6 hours after exposure to vibration and persist for up to 24 hours;
- the disease is caused by nonspecific degranulation of mast cells.
Aquagenic urticaria:
- the rash occurs only after contact with water of any temperature;
- the rash appears instantly;
- presents as small blisters surrounded by erythematous spots.
Cholinergic urticaria:
- occurs more often in young people;
- characterized by the appearance of pale pink blisters with a diameter of 1-5 mm, often surrounded by erythema;
- the rashes are generalized;
- provocative factors are physical exercise, stress, sweating, hot shower;
- may be accompanied by systemic manifestations (hot flashes, weakness, rapid heartbeat, headache, abdominal pain, shortness of breath);
- can be reproduced by subcutaneous administration of acetylcholine.
Adrenergic urticaria:
- rare;
- characterized by the appearance of small papules with a white halo;
- triggered by stress;
- can be reproduced by intradermal injection of adrenaline.
Diet
Diet is very important to prevent the occurrence of both acute and chronic allergic urticaria and its treatment. To determine what exactly triggered the allergic reaction, either the method of introducing a single product or allergy tests are used.
If it is not possible to identify a specific product, general recommendations should be followed:
- exclude products with a high and moderate degree of allergenic activity: chocolate, citrus fruits, eggs, nuts, fish, red fruits and berries, poultry, mushrooms, spices, vinegar, honey;
- exclude tonic drinks – tea, coffee, alcohol;
- exclude products with dyes and preservatives from the menu.
It is recommended to include water porridge (oatmeal, rice, buckwheat), vegetable soups, baked goods made from soft dough, and fermented milk products into the diet. Food processing helps reduce the allergenicity of food: peeling, heat treatment, freezing.
To speed up the removal of the allergen from the body, you need to drink a sufficient amount of water - up to 2-2.5 liters per day.