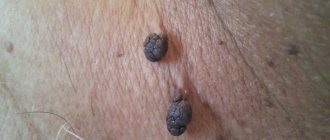
Vulvar neoplasms are tumor diseases of the external genitalia. The formation of foreign bodies may be asymptomatic. If the tumor develops rapidly, it increases in size, the woman feels discomfort and pain. Accompanied by bloody or purulent discharge from the perineum. Causes itching and irritation of the vulva. Diagnosed during examination by a gynecologist. Various studies are being carried out. Vulvar neoplasms are recognized by smears and biopsies.
The type of tumor is determined and treatment is prescribed. Benign ones are excised or enucleated. Special technologies and individual therapy are used to treat malignant tumors.
The collection of external female genitalia is called the vulva. This includes the pubis, clitoris, labia, and vestibule of the vagina. The organs serve as a protective barrier for the genitourinary system. The hymen is the boundary between the reproductive system and the vulva. The vulva has a sensitive function. Her external organs are responsible for arousal during sexual intercourse. The signal is transmitted to the secretion of the glands, thereby moisturizing the vaginal slit. Congenital defects of the vulva include a violation of the development of any organ, for example, hermaphroditism. A visual examination of the vulva can be performed by a gynecologist. You can do this yourself with the help of a mirror or a sexual partner.
Damage to the organs of the vulva is possible during childbirth and injury. The process is accompanied by pain, swelling, and wounds. Bleeding is observed, the area of the clitoris and vestibule suffers. The vulva is subject to a number of inflammatory diseases, such as gonorrhea, vulvovaginitis, vulvitis, trichomoniasis, and candidiasis. There are growths: papilloma, condyloma, kraurosis, leukoplakia. These diseases are frequent precursors to cancer. Treatment includes surgical radiation or medication.
Vulvar neoplasms are found in the following places:
- Pubic area.
- Labia majora and labia minora.
- Cliteral part.
- Perineum and posterior commissure.
- The opening of the urethra.
Types of rashes on the genitals
The rash on the genitals usually has the appearance of certain skin elements and may appear in the patient suddenly or after an incubation period.
In this case the following appears:
- blisters - they have a short-term course and disappear on their own without treatment;
- pustules are yellow or green in color, contain purulent discharge and appear when the disease is in an advanced stage;
- blisters - they are filled with liquid, located in groups or singly, without treatment they turn into ulcers;
- chancre – has a red color, hard edges and an ulcerated bottom;
- erythema - a very reddened area of the skin that rises above healthy tissue;
- condylomas - they are round lumps above the surface of the skin, they can be either flesh-colored or brown.
- nodes are rashes with a dense structure that lie in the dermal layer of the skin.
- plaques are a rash that consists of grouped small blisters.
These are the most common types of genital rash, but there may be others.
Women's problems: micropapillomatosis
Often the external manifestations of many diseases are confused with a common anatomical feature. However, any pimple that appears, any new spot in an unusual place on a person’s body should be alarming. Especially if the genital and perineal areas are bothering you.
Some women noticed red rashes symmetrically located on the labia. Of course, something that suddenly appears does not lead to anything good. However, there are phenomena in nature whose occurrence does not in any way affect human health. For example, micropapillomatosis in women. Is this your first time hearing this? - here is detailed information about such a manifestation.
be careful
Papillomas and warts can at any time become melanoma - skin cancer, which leads to death in 89% of cases in the first 2 years!
Moreover, in most cases, it all starts with harmless papillomas and warts, which do not interfere with everyday life.
The more papillomas and warts on your body, the more likely it is that one of them will develop into a malignant tumor. The spread of papillomas in the armpits and groin area is especially dangerous.
Infections
Some types of sexually transmitted infections have the natural ability to masquerade as micropapillomatosis. In the first stages of the development of an infectious disease, only external symptoms of damage to the skin of the labia are observed.
Subsequently, the symptoms worsen and, in addition to small benign neoplasms, an acute inflammatory process with damage to the vaginal mucosa occurs.
What is micropapillomatosis
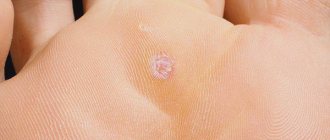
Micropapillomatosis is a multitude of small, light pink or flesh-colored rashes on the labia minora. The shape of the elements resembles papules. Less commonly, the rash appears on the labia majora. The photo below shows micropapillomatosis of the labia minora, located on their inner surface.
What does micropapillomatosis look like? The photo shows a clear example of flesh-colored rashes on the midline of the vulva. Usually the elements appear symmetrically on the labia, most often they are localized along two parallel lines. When you touch them, you feel a soft structure. The formations are painless.
The development of the elements occurs during puberty, but the specific causes of the appearance of the rash have not yet been identified. Possible factors in the development of the disease, according to medical scientists, include:
- strong hormonal changes in the body, especially during the maturation of a teenage girl;
- systematic irritation of the genital organs when wearing uncomfortable underwear;
- chronic inflammatory diseases of the reproductive system in the fair sex.
Micropapillomatosis of the labia
Micropapillomatosis of the labia is a fairly rare phenomenon, occurring in only 4% of patients. The origin of the pathology is explained by the anatomical features of the woman. Treatment of micropapillomatosis in women does not require taking special medications.
According to research, micropapillomatosis in women has nothing to do with human papillomavirus infection. Although some medical institutes are still looking for a connection between these pathological processes. The relationship of the disease with the HPV virus is determined during histological and cytological studies for the diagnosis of coycelotosis. This phenomenon is characteristic of the presence of HPV in the body.
Despite similar names, micropapillomatosis has nothing in common with human papillomas and is not viral in nature. Its etiology has not yet been studied, but most experts consider such manifestations to be a variant of the anatomical norm.
To finally verify the correctness of this judgment, we propose to consider the differences between viral papillomas and micropapillomatosis:
- Genital warts (condylomas) are hard and rough to the touch. Micropapillomas are soft formations. They resemble small skin elevations of a similar structure.
- The nature of localization. Condylomas are scattered chaotically and are characterized by unilateral lesions. Micropapillomas are arranged in symmetrical rows along a line.
- The vinegar test for warts gives a positive result. Upon contact with acetic acid, the initially pinkish rashes begin to fade. Micropapillomas remain unchanged.
So, micropapillomatosis is a symmetrically located small rash on the labia minora, more precisely on their inner surface along the midline. In rare cases, papules appear on the labia majora. Their color blends with the skin tone, sometimes acquiring a pinkish tint.
Typically, nodular rashes appear during puberty and pregnancy, when hormonal disruption and disruption of the endocrine system occur. However, cases of occurrence after wearing tight synthetic underwear cannot be ruled out. Micropapillomatosis in women is not a disease. It is not sexually transmitted and does not affect conception or pregnancy. Unusual rashes on the labia do not cause discomfort, except psychologically.
Definition and description of the disease
Micropapillomatosis is a collection of rashes that form on the inner and outer areas of the labia minora of women.
It practically does not occur on large lips, and is also not diagnosed in men. There is also vestibular micropapillomatosis (micropapillomatosis of the ulva) located in the vestibule of the vagina. The rash is localized on the mucous membrane of the labia minora and may not be visible to the eye.
Most often, the occurrence of rashes does not cause serious discomfort, but the phenomenon is a cosmetic defect and in rare cases causes pain. In addition, when such dermatological problems are detected, it is important to establish the cause of their occurrence and make a prognosis regarding the progression of micropapillomatosis and possible consequences.
Important: The disease has nothing to do with papillomavirus and is not transmitted through direct contact.
Manifestations of micropapillomatosis
About 5% of healthy women may notice rows of small pale pink nodules on their labia minora. They appear most often during puberty, which suggests their hormonal etiology. These nodules, called papules, are soft to the touch and do not cause discomfort or pain to the woman.
The color of the formations can vary from pinkish to flesh-colored. Most often they are located on the inner surface or midline of the labia minora (rarely major) in symmetrical rows.
Micropapillomatosis is not an infectious disease, so it cannot be contracted through sexual or household contact. Unusual changes in the labia do not limit a woman in the sexual sphere, sports or other areas of life. The reproductive system is not endangered, there is no threat to successful conception and pregnancy.
The only inconvenience that micropapillomatous rashes can bring is psychological. Women may consider micropapillomatous pimples a serious cosmetic defect. This problem can be solved: formations can be removed using simple modern procedures.
Reasonable restrictions for leukoplakia
For leukoplakia of the vulva, vagina and cervix, it is extremely UNADVANTABLE to take hot general baths, stay in the sun for a long time and sunbathe (regardless of the activity of the Sun, the presence/absence and type of bathing suit).
HEAT TREATMENTS and insolation (sunbathing in natural conditions and solariums) increases the production of estrogens (female sex hormones), the excess of which stimulates oncological processes.
- Reviews about the treatment of vulvar leukoplakia in our Clinic
- About the Clinic
- Clinic team
- Prevention of female diseases
- What is homeopathy?
- How to prepare for an appointment with a gynecologist?
Our specialized clinic for the treatment of leukoplakia is open 7 days a week and on holidays:
Monday - Friday from 8.00 to 20.00, Saturday, Sunday, holidays from 8.00 to 17.00.
Treatment of vulvar leukoplakia in Pyatigorsk by appointment no later than 3 days in advance by multi-channel phone number 8 (calls within Russia are free), or (for foreign calls).
| ONLINE about the treatment of leukoplakia in Pyatigorsk at BOOK ONLINE for leukoplakia treatment here. BOOK online for leukoplakia treatment here. Buy coursework for treatment by phone or here. |
Booking
Subsections
- Program No. 1. Treatment of inflammatory and infectious diseases of the pelvis
- Program No. 2. Treatment of urinary incontinence, prolapse and prolapse of the uterus and vagina
- Program No. 3. Treatment of female infertility of endocrine (hormonal) and mixed origin
- Program No. 4. Treatment of erosion, endometriosis, leukoplakia, dysplasia, polyps, cervical cysts (uterine cysts)
- Program No. 5. Treatment of uterine fibroids
- Program No. 6. Treatment of cervicitis and endocervicitis
- Program No. 7. Postpartum rehabilitation and wumbling
- Program No. 8. Treatment of chronic cystitis
- Program No. 9. Treatment of severe menopause
- Program No. 10. Treatment of mastopathy
- Program No. 11. Treatment of endometriosis
- Program No. 12. Treatment of hydrosalpinx
- Program No. 14. Comprehensive treatment of polycystic ovary syndrome
- Program No. 15. Preconception preparation for IVF, ICSI
- Program No. 16. How to remove belly fat
- Program No. 17. Treatment of kraurosis
- Program No. 18. Treatment of vulvar leukoplakia
Micropapillomatosis and human papillomavirus
The human papillomavirus (papillomavirus, abbreviated as HPV) is not the cause of such changes in the surface of the labia, despite its similar name. However, it causes another disease, which is sometimes very difficult to distinguish from harmless micropapillomatosis - papillomavirus infection, which affects the external genitalia, perineum and is accompanied by the formation of genital warts (anogenital warts). HPV affects the growth pattern of vulvar tissue, causing pathological changes in the cellular structure - koilocytosis.
The main differences between viral condylomas and micropapillomas:
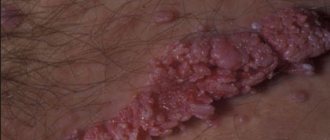
- Micropapillomas are located on the labia mainly linearly, in symmetrical rows. Condylomas are scattered over the surface of the vulva.
- Micropapillomatous formations are soft to the touch, the structure of warts is more dense.
- Condylomas are pink, white or red in color and turn pale during the acetic acid test, unlike micropapillomas.
It is extremely important to make a correct diagnosis in the presence of nodular rashes in the vulvar area.
Causes of growths on the body - condylomatosis in men and women
The human papillomavirus can be present in the body in a dormant state.
It is introduced into the DNA of cells and waits there for favorable conditions for development. Under the influence of certain factors, it is activated and provokes the growth of tumors. Often the virus occurs in conjunction with gynecological diseases. In the presence of infectious or inflammatory diseases, special vigilance should be exercised.
Provoking factors for the development of HPV include:
- taking corticosteroids;
- pregnancy period;
- violation of vaginal microflora;
- Papillomas on the labia;
- early onset of sexual activity;
- diseases accompanied by decreased immunity;
- postoperative period;
- stressful situations;
- lack of vitamins.
Papillomas tend to grow rapidly. As they increase, they cause discomfort.
Condylomatosis is a disease characterized by the appearance of growths in the groin and anogenital area. Less commonly, warts can be localized on the décolleté, chest, armpits, face and oral mucosa.
Today, scientists know more than a hundred strains of HPV that can cause the formation of pathological spiky growths on the body. Since the incubation period can vary from a month to a year or more, it is almost impossible to find out the exact causes of condylomas and the time the virus entered the body.
Condylomas in women - causes
The virus is mainly located in the layers of the dermis, but a small proportion of it is also localized in biological fluids, through which one can also become infected (if the low immunity of a healthy person coincides with a large amount of the virus in the patient’s body).
Micropapillomatosis: norm or pathology
According to medical research, the following clinical characteristics of the rash have been identified:
- such damage to any area of a woman’s reproductive system does not harm her health;
- symptoms of vaginal micropapillomatosis refer to normal variants of the anatomical development of the female body;
- the rash is not sexually transmitted;
- the development of complications caused by papules has not been established.
In some cases, this disease resolves itself without the use of any therapeutic measures. Various methods of removing rashes are not prohibited by medicine. For most women, papules cause shame and moral discomfort, although they do not provoke physical ailments; they are often removed. Next in the photo is micropapillomatosis in women.
Micropapillomatosis: photos, symptoms and signs
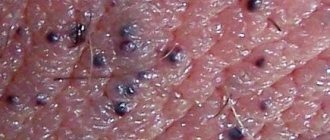
There is a high probability of this disease occurring due to hormonal changes in a young body. The process is marked by the appearance of rashes on the labia or vulva, similar in appearance to papules, light pink or flesh-colored nodules.
These elements are soft to the touch and do not cause any physical discomfort or pain . The nodules are located symmetrically, and their localization in rows is often noted. The same symptoms may be present in adult women suffering from hormonal imbalance due to pathology of the endocrine system or in similar physiological conditions, for example, during pregnancy.
Preventive measures
In order to minimize the likelihood of micropapillomatosis on the labia, it is recommended to adhere to the basic rules of prevention:
- Carry out hygiene procedures daily;
- Wear only soft, breathable underwear with a minimum amount of synthetic fibers in the composition;
- Monitor the state of the endocrine system and promptly eliminate diseases associated with changes in the level of hormone production;
- Systematically visit the gynecologist’s office (at least twice a year);
- Use only pH-neutral mild agents for hygiene procedures;
- Eliminate infectious disorders in a timely manner;
- Use contraception to prevent sexually transmitted infections.
Micropapillomatosis of the vulva: photo
If you experience pain, itching in the area of the rash and an increase in the size of the papules, you should consult a doctor, since other pathologies may appear during the course of this disease.
In medical practice, it is important to correctly distinguish such a disease from the development of HPV in the body. Condylomas are formations that arise as a result of pathogens of a viral nature entering the body. They are characterized by asymmetric localization in the genital area. The color of condylomas is often similar to the rashes associated with this disease, but upon palpation a denser structure is felt. Condylomas are characterized by a group manifestation in the form of multiple growths.
Diagnostics
Often, initially appearing papules can be harbingers of diseases of the reproductive system. Such manifestations resemble the initial stage of syphilis and other sexually transmitted diseases. To clarify the diagnosis, the patient is sent for a serological blood test. The rash can also be confused with genital warts.
External symptoms are not enough to make an accurate diagnosis; differentiated diagnosis is needed. It is performed by a gynecologist. After examining the woman in a gynecological chair, a smear is taken from the affected area, which is subsequently subjected to microscopy.
Cytological examination helps determine the cellular structure of the rash and determine the nature of the phenomenon: whether it is of viral etiology or not. If the causative agent is the human papillomavirus, koilocytosis is detected (specific damage to cellular structures by viral pathogens). The most accurate results will be provided by polymerase chain reaction. Using it, you can determine the nature of formation at the molecular level.
Diagnostic procedures
The vulva is examined during a pelvic examination. A gynecologist performs vaginal examinations. A transvaginal ultrasound is prescribed. If necessary, vulvoscopy and colposcopy. A bacterial smear is examined to exclude infectious diseases. Clarification of the nature of the neoplasm using histological examination. For biological analysis, scrapings and punctures of tumors are taken.
Removing the tumor often causes a new growth to appear. Removing papillomas requires long-term treatment. Surgeries and the postoperative period may occur with complications. Hematomas may form, the urinary system may be disrupted, and severe bleeding may occur.
Differential diagnosis
Micropapillomatosis is completely harmless for a woman, however, papules are easily confused with condylomas caused by human papillomavirus infection or syphilis. Misdiagnosis will lead to the prescription of inadequate treatment. To determine the etiology of changes in the labia, the gynecologist conducts a microscopic examination of a smear taken from the affected area. Cytological examination can detect signs of specific damage (koilocytosis), if present. Such results indicate that the neoplasms are viral condylomas.
Is treatment necessary?
Such rashes are completely harmless. The only problem a woman may encounter is a cosmetic defect. The fair half of humanity can be confused by micropapillomatosis of the labia. However, in modern medicine this problem can be eliminated.
The principle of treatment is the same as for warts:
- Electrocoagulation . New growths are removed under the influence of electric current. Pinpoint tissue dissection is painless and does not require additional anesthesia. The current has a cauterizing effect, the vessels stick together, so bleeding does not occur.
- Cryodestruction is a popular way to eliminate unwanted tumors. Warts and micropapillomas are frozen under the action of liquid nitrogen and destroyed in seconds. Nitrogen itself is safe, however, after such manipulations, bleeding and infection of the wound cannot be ruled out.
- Laser cauterization . This is the fastest and most accessible procedure. Non-contact interaction with affected tissues makes the manipulation safe. Painlessness, rapid healing, anti-inflammatory effect are the main advantages of laser therapy.
Opponents of physical and chemical treatment methods will not dare to undertake such procedures. Lack of knowledge will push desperate women to seek drug therapy, but any attempt will be in vain. No drug can eliminate these anatomical formations. Even topical medications (vaginal suppositories, all kinds of ointments) will not help solve the problem.
There is no need for treatment of micropapillomatosis. It does not cause pain or itching, and does not lead to any complications.
Throughout life, nodular rashes do not change in color or size. There have been cases where the rash went away on its own over time without prior treatment. Do not immediately resort to eliminating this harmless ailment.
There are no consequences from micropapillomatosis, but after trying to eliminate it, there may be complications. The skin of the genitals is very sensitive, and after physical impact its structure becomes thinner. At any time, if the rules during the rehabilitation period are not followed, an infection may occur. The consequences will be more serious than the initial rash.
Treatment of micropapillomatosis
This process does not require specific treatment. However, if the rash makes a woman feel uncomfortable, it is possible to remove papules using the following modern methods:
- exposure to cold nitrogen – cryodestruction;
- destruction of formations by electric current - electrocoagulation;
- laser burning.
Laser treatment is considered the most popular - a painless method that promotes rapid tissue regeneration. It does not leave visible scars in place of the fallen elements. The recovery process takes up to two weeks. To determine the right method, you should consult your doctor.
How to treat micropapillomatosis at home
Treatment of micropapillomatosis at home involves the use of decoctions of medicinal herbs when washing. Herbal decoctions help normalize the vaginal microflora and prevent the occurrence of infection in the intimate area. For the treatment of micropapillomatosis with folk remedies, infusions of oak bark and chamomile are most often used. A concentrated decoction is added to the water before bathing.
This disease can be eliminated on its own; therapeutic treatment is not required, except in cases where a woman wants to remove pathological elements from the genitals due to aesthetic discomfort.
Leading specialists in the treatment of vulvar leukoplakia in the Southern Federal District
Ermolaeva Elvira Kadirovna is a well-known and recognized specialist in the North Caucasus in the treatment of leukoplakia of the vulva, vagina and cervix, diagnosis and treatment of kraurosis, lichen sclerosus, Keir's erythroplasia and other diseases of the vulva. One of the authors of the method of regenerating microinjections for the treatment of leukoplakia. Desperate people turn to her and women exhausted by suffering. Experienced gynecologist, physiotherapist-health resort specialist, ultrasound doctor.
Ermolaev Oleg Yurievich Candidate of Medical Sciences, gynecologist-endocrinologist with 25 years of experience and successful experience in the treatment of dysplasia, kraurosis and leukoplakia of the vulva Able to see relationships that elude others
About the doctors of the Clinic in detail...
| INTERNATIONAL RECOGNITION of the reputation and achievements of the Women's Health Resort Clinic in the development and implementation of effective and safe treatment methods and the quality of medical services provided is the AWARDING of the Women's Health Resort Clinic in Pyatigorsk with the SIQS International QUALITY CERTIFICATE in the field of medicine and healthcare. International Socratic Committee, Oxford, UK and Swiss Institute for Quality Standards, Zurich, SWITZERLAND. |
The resort women's health clinic is open 7 days a week and on holidays:
Monday - Friday from 8.00 to 20.00, Saturday, Sunday, holidays from 8.00 to 17.00.
Treatment of vulvar leukoplakia in Pyatigorsk by appointment no later than 3 days in advance by multi-channel phone number 8 (calls within Russia are free), or (for foreign calls).
| ONLINE information about the treatment of vulvar leukoplakia in Pyatigorsk can be found at REGISTER ONLINE for leukoplakia treatment here. REGISTER online for leukoplakia treatment here. You can buy a COURSE for treatment by phone or here. |
Booking a course
The doctors of the Women's Health Resort Clinic have gained EXTENSIVE EXPERIENCE in treating vulvar leukoplakia, vaginal leukoplakia, cervical leukoplakia using natural medicines and resort factors.
We accept women from all cities of Russia, near and far abroad.
The spa clinic for women's health facilitates the accommodation and accommodation of women, women with children and couples during examination and treatment.
ACCOMMODATION in Pyatigorsk is NOT INCLUDED IN THE PRICE of the treatment course and is paid separately.
About living conditions and transfer from Mineralnye Vody airport and Pyatigorsk railway station in detail in the article “Accommodation”.
If you need to book accommodation, please coordinate your arrival date no later than 7 days in advance.
We are at your complete disposal if you have any doubts or wishes.