Free consultation with a doctor by phone
Surgeon appointments are available daily by appointment!!!
LLC "Your Doctor"
Chat with the doctor
Addresses of medical centers in Moscow (unified reference) +7 (495) 255-45-59
Make an appointment at the clinic Discount on services Promotions
- +7 (495) 255-45-59
- Surgical centers in Moscow
- Every day from 9.00 to 20.00
- call me back
You can make an appointment with our operators by calling +7 (495) 255-45-59
Prices for services Clinic address Make an appointment Call a surgeon to your home Pediatric surgeon Ligation
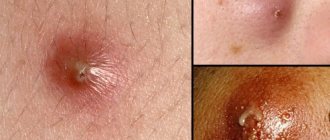
Atheromas, popularly known as wen, are essentially a benign tumor in the subcutaneous tissue. They belong to the group of benign soft tissue tumors or are perceived as a squamous cell cyst.
It occurs most often in the area of large sebaceous glands: the head area (on the face or back, neck area), in the area of the interscapular space, perineum, for example, atheroma in the groin.
Useful information on the topic:
- Treatment of atheroma
- Ear atheroma
- Atheroma on the head
- Atheroma on the face
- Atheroma on the back
- Inflammation of atheroma
- Atheroma on the penis
- Atheroma of the eyelids
- Purulent atheroma
- Breast atheroma
- Laser removal of atheroma
- Removal of atheroma at home
- Atheroma on the neck
- Atheroma on the lips
- Atheroma on the leg
- Atheroma on the labia
What kind of disease
Atheroma is a benign formation, often with a genetic predisposition. An epidermal cyst looks like a thickening of the skin.
It consists of sebum and dead cells. Inside there is a white-yellow liquid with an unpleasant odor.
It is formed due to blockage of the sebaceous duct, then the discharge from it begins to accumulate under the skin and mixes with keratin. Atheroma can grow to large sizes if no measures are taken to eliminate it.
The tumor can be large or small, grow quickly or not change in size. Sometimes it can open on its own, then the liquid contained in it will flow out.
In such cases, it is important to prevent infection from entering the middle of the capsule, which can lead to infection. That's why it's so important to see a doctor.
Causes
The following factors can lead to the occurrence of atheroma:
- heredity;
- general hypertrophy;
- hormonal imbalance , which can cause hypersecretion of lipid substances in the glandular tissue of the skin;
- increased sweating;
- unhealthy diet, where fatty foods and sweets predominate;
- failure to comply with basic hygiene rules;
- metabolic disorders ;
- mechanical damage to the skin.
Treatment of atheroma without surgery
It is possible to cure atheroma without surgery, if it is not inflamed and does not fester.
The development of atheroma largely depends on hormonal disorders in the body. When hormones are imbalanced, the oiliness of the skin increases, which significantly increases the likelihood of skin cysts.
The cause of the appearance of cysts in intimate places in women is often metabolic disorders, in particular the presence of a disease such as diabetes.
Causes and signs of occurrence
The main reason is blockage of the sebaceous glands. Sebum, which is produced by the sebaceous glands, enters the skin and accumulates there. Since the sebaceous glands produce very little sebum per day, therefore, as a rule, atheroma grows very slowly. Although wen is not dangerous to health, it creates a certain discomfort and, when inflamed or suppurated, also causes pain. They may appear and disappear spontaneously. Even if the wen has disappeared, this does not mean that the problem does not exist; it may arise again. So, what provokes their appearance:
- failure to comply with personal hygiene rules;
- genetic predisposition;
- skin diseases, allergies;
- endocrine, hormonal disorders;
- metabolic disorders;
- poor nutrition;
- bad habits.
Atheromas in the groin can be detected during water procedures. Even if there is no pain, you will feel lumps on the skin. At the same time, they are mobile. Often an inflamed red nodule can be painful, especially when touched.
Due to the fact that atheroma in the groin has a high probability of inflammation and infection, since the risk of injury is quite high. This leads to unwanted inflammatory processes.
Conclusion: at the first signs of this disease, be sure to consult a doctor. The sooner you take action, the easier and faster the treatment will be.
Useful information about visiting a surgeon at the clinic:
- How to prepare for a surgeon's appointment
- What diseases does the surgeon treat?
- Calling a surgeon to your home
- Surgical care in the clinic
- Surgical care at home
- What symptoms should you contact a surgeon for?
- Treatment of surgical diseases
- Treatment of intestinal pathologies
- Treatment of skin surgical pathologies
- Treatment of bedsores and necrosis
- Treatment of parasitic diseases
- Treatment of inflammatory processes of soft tissues
- Treatment of diseases of the musculoskeletal system
- Diagnosis of surgical diseases
Symptoms
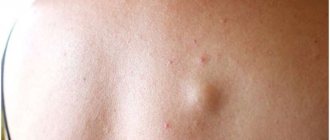
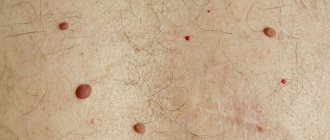
In appearance, atheroma is a small round formation. The cyst is smooth and mobile, has a dense consistency and clear boundaries.
There is no pain when pressing on the tumor, and there is no swelling or redness either.
In the center of the atheroma, the excretory duct of the sebaceous gland is often visible, which is increased in size.
If a tumor appears on the labia with similar symptoms, you should immediately contact a gynecologist.
Removal of formations on the labia - methods and results
A variety of formations can occur on the labia majora, labia minora and nearby – on the pubis, in the groin and in the area of the vaginal opening. They interfere, cause discomfort, spoil the appearance of the genitals, enlarge and can degenerate into malignant tumors. Therefore, such growths and pathological lesions must be removed.
For this purpose, laser and low-traumatic surgical methods are used. All procedures and operations are performed under local anesthesia, and when removing large, multiple, deeply located formations and a woman’s increased pain sensitivity, a light general anesthesia is used. Therefore, the patient does not feel pain or discomfort.
Laser method
Surgical method
Diathermic loop for polyp removal
Removal of tumors on the labia and adjacent areas
| Type of formations | Appearance and characteristics of the neoplasm | Removal method | Forecast |
| Fibromas, angiofibromas, dermatofibromas | Tumors containing connective tissue. Convex nodes of different sizes and shades located on the labia, in their thickness or in the area of the entrance to the vagina | Laser | Favorable, relapses (recurrence of tumor) do not occur |
| Surgical. Used for large fibromas, angiofibromas and dermatofibromas | |||
| Myomas, leiomyomas, rhabdomyomas | Tumors containing muscle tissue. Dense, elastic formations located in the thickness of the labia majora | Laser | Favorable, swelling no longer occurs |
| Surgical. Used for large tumors | |||
| Hydradenomas | Tumors of the sweat glands. Convex nodes of a flesh-colored, reddish or bluish hue, located on the labia, pubis, and groin. Inside they consist of several connected cysts | Laser | Favorable, relapses are practically non-existent |
| Surgical. Used for large hidradenomas | |||
| Lipomas (fat) | Convex soft formations of flesh color, sometimes with a yellowish tint, representing an accumulation of adipose tissue. May be multiple. Located on the labia majora and pubis. Due to the tendency of lipomas to grow, it is better not to delay the operation | Laser method - suitable for smaller wen | Favorable. Wen disappears forever |
| Excision – removal using a surgical instrument. Used for large formations | |||
| Liposuction – pumping out fat from a tumor through an incision in the skin | |||
| Atheromas | Appear due to blockage of the sebaceous gland duct. Formations similar to large acne appear on the labia majora, pubis, and groin. Sometimes they open with the release of purulent and sebaceous contents. After self-opening, an atheroma capsule remains in the tissues, so it often appears again. Due to the increasing accumulation of sebum, atheromas grow. Therefore, they must be removed immediately | Opening with removal of contents. Rarely used, mainly when it is impossible to perform another operation | A relapse may occur because the atheroma capsule remains inside the tissues |
| Surgical removal of the tumor along with the capsule | Favorable, with proper removal, relapses do not occur. | ||
| Laser removal of the tumor along with the capsule | |||
| Hemangiomas | Hemangiomas are blue or red vascular tumors, soft to the touch, appearing on the labia majora and minora, vulva, and vagina. They can have a multi-chamber structure and different shapes. Due to the tendency of hemangiomas to grow, it is better not to delay their removal | Laser | Favorable. The tumor no longer appears |
| Surgical. Used for extensive hemangiomas | |||
| Lymphangiomas | Formations formed from lymphatic vessels, often consisting of several small fragments. They can have a shade from flesh to brown. Lymphangiomas tend to spread to neighboring areas, so they need to be removed as quickly as possible | Laser | Favorable – tumor no longer forms at the site of removal |
| Surgical. Used for large lymphangiomas | |||
| Myxomas | Connective tissue yellowish-white gelatinous tumors that can be felt under the skin of the labia majora or pubis. More common in old age | Laser | Favorable – tumor no longer appears at the site of removal |
| Surgical. Used for large or deeply located formations | |||
| Cysts of the labia minora and majora | Tumor-like formations, which are a capsule filled with liquid or semi-liquid contents. Formed due to blockage of the glands on the labia majora or minora | Piercing the cyst, removing the contents and inserting a rubber drainage inside. The elastic is needed for the outflow of secretions - a substance secreted by the gland | Relapse may occur as the cyst capsule remains inside the tissue |
| Surgical method - opening and removing the cyst along with its contents | Favorable. Cysts do not recur | ||
| Removal of the cyst along with the membrane using a laser | |||
| Marsupialization - used in the treatment of Bartholin gland cysts formed in the labia. The cyst is dissected and emptied. A channel is formed from its tissue for the outflow of mucus secreted by the gland | |||
| Removal of the gland along with the cyst. It is used for Bartholin gland cysts formed in the labia area. The method is undesirable because it reduces the amount of lubricant secreted by the gland to moisturize the mucosa | |||
| Papillomas | Formations caused by papillomavirus. They look like hanging moles on the labia. They are often multiple. Due to the tendency of papillomas to grow and spread, they need to be removed | Laser destruction – tumors are removed using a laser | Papillomas no longer appear at the site of removal. However, without antiviral treatment they may appear in other areas |
| Condylomas – genital warts | Formations caused by papillomavirus. Reminiscent of cauliflower or cockscomb. They are often multiple, spreading over the labia, perineum, vaginal opening and anus. Since condylomas tend to spread and cause cancer, they must be removed as quickly as possible | Laser destruction - growths are removed using a laser | Condylomas no longer appear at the site of removal. However, without antiviral treatment, they may appear in other areas. |
| Molluscum contagiosum | Caused by a pathogen similar to the smallpox virus. Dense light nodules with an umbilical depression in the center appear on the skin of the labia, vestibule of the vagina, in the groin, on the perineum and near the anus. When pressed, a thick cheesy mass emerges from them. The disease is contagious and can be transmitted through any contact, including sexual contact. In the absence of timely treatment, mollusks spread throughout the body | Cauterization with laser | After removal of the mollusks, the patient is prescribed antiviral, antimicrobial treatment, and immunostimulating drugs. This makes it possible to destroy the virus and avoid concomitant bacterial damage. |
| Polyps | Benign formations in the form of a “mushroom” on a stalk. They are found on the labia minora, in the area of the clitoris and the vestibule of the vagina. Prone to growth, bleeding, detachment, and degeneration into cancer. Therefore, they must be removed as quickly as possible. | Surgical. Effective for multiple polyps (polyposis). The pedicle is dissected with an instrument and the polyp is cut off | Polyps will no longer grow at the site of removal, but if they are prone to formation, they may appear in other areas. If there are a large number of polyps in the intimate area, you need to check the condition of all pelvic organs of the uterus - bladder, rectum, since these formations can occur in several places |
| Diathermic - a diathermic loop with a high temperature is placed around the leg of the polyp. Due to heating of the leg, the neoplasm separates | |||
| Laser – polyps are destroyed with a laser | |||
| Moles and nevi (pigment spots) | Formations of various shapes, sizes and colors - from light pink to almost black. They can be found anywhere on the body, including the genitals. They are flat and convex. The labia and other parts of the intimate area are unfavorable places for moles and birthmarks. They can rub, become inflamed, hurt, enlarge, and even degenerate into extremely malignant cancer - vulvar melanoma. Therefore it is recommended to remove them | Laser | Favorable. After removal, age spots and moles no longer appear |
| Surgical. Used to remove large moles and birthmarks |
Atheroma
Hemangioma
Condylomas
Molluscum contagiosum
Pigmented nevus
Papillomas
In our center, you can remove any formations on the labia majora and in neighboring areas - on the pubis, in the groin, on the perineum, near the anus. For this purpose, laser devices are used that completely remove tumors and other growths and have a disinfecting and wound-healing effect. During surgical removal, the most minimally traumatic methods are used, leaving virtually no traces on the body.
Diagnostics
During examination and palpation, the doctor can easily diagnose atheroma. In the center of the formation, the outlet of the sebaceous duct is often visible, and if it is not completely closed, a yellowish liquid with an unpleasant odor will slowly ooze through it.
Through the thin skin of the labia, the doctor will be able to see the yellowish contents of the neoplasm. A dense structure also indicates atheroma.
The inflammatory process can make it difficult to make an accurate diagnosis. It occurs if a woman has ignored the appearance of atheroma for a long period, and the disease progresses.
In addition, diagnostics may include additional methods so that the doctor can make sure that the neoplasm is not malignant.
Diagnosis of atheroma in children
It is relatively easy to identify atheroma.
Even at the stage of the initial conversation with the patient or his parents, the surgeon assesses the general well-being of the child, collects anamnesis and analyzes complaints. When examining a neoplasm, the doctor pays attention to its size, location, pain, and the presence of redness. Before surgery, the surgeon prescribes a number of tests to comprehensively assess the child’s condition:
- general and biochemical blood test;
- general urine analysis;
- blood test for infections (HIV, syphilis, viral hepatitis B, C);
- ECG, fluorography.
The child is also examined by an anesthesiologist and pediatrician before the operation. A mandatory diagnostic method is histological examination of tumor tissue after its removal. At this stage, it is possible to determine whether it was an atheroma or a lipoma (a tumor similar in appearance).
Treatment methods
The most effective method of treating atheroma today is to remove it surgically. Surgery to remove the tumor is performed in almost all cases when it is diagnosed.
Self-medication is dangerous with complications!
Attention
Despite the fact that our articles are based on trusted sources and have been tested by practicing doctors, the same symptoms can be signs of different diseases, and the disease may not proceed according to the textbook.
Pros of seeing a doctor:
- Only a specialist will prescribe suitable medications.
- Recovery will be easier and faster.
- The doctor will monitor the course of the disease and help avoid complications.
find a doctor
Do not try to treat yourself - consult a specialist.
Several types of surgery are possible.
Opening and husking the contents
This is a classic surgical method, during which the doctor makes an incision and removes the atheroma capsule along with the fluid it contains, after which self-absorbing sutures are applied. The disadvantage of this method is the possibility of relapse due to incomplete removal of the cyst contents.
Removal of atheroma and surrounding tissues
The method is used for severe inflammation. This type of operation has a significant drawback: scarring.
Endoscopic method
The operation is performed by inserting an endoscope into a small puncture and sucking out the contents of the atheroma capsule. It is quite difficult to accurately determine whether all the fluid has been removed from the capsule, so the possibility of relapse remains. The advantage of the method is the absence of seams.
Laser removal
This type of atheroma removal can be used when it is small in size. The method has a minimal risk of complications and a short recovery period.
There is another method that can be used to resolve atheromas. It involves the introduction of special drugs and carries certain risks.
The danger of using this method is that there is a high probability of relapse due to the inability to determine whether the tumor has completely reabsorbed or not.
Also, drugs can have a reverse effect on atheroma, accelerating its growth. If the treatment is effective, the result will be noticeable only after two months.
Only the doctor should choose which method will be used to eliminate the problem. The decision is made individually in each case, after the doctor evaluates all the risks and chooses the least traumatic method.
Why can our articles be trusted?
We make health information clear, accessible and relevant.
- All articles are checked by practicing doctors.
- We take scientific literature and the latest research as a basis.
- We publish detailed articles that answer all questions.
Today, it is also practiced to treat cysts in the vaginal area in women without surgery, but only if they are small in size.
Symptoms of atheroma in children
In 80-85% of cases, apart from the visual defect, children do not present any other complaints. Uncomplicated atheroma is characterized by:
- painlessness;
- mobility;
- elasticity upon palpation.
The skin over the surface of the tumor is smooth and does not fold. The clinical picture may change when the contents of the atheroma become inflamed against the background of the addition of bacterial flora. In this case, patients may note:
- pain when pressed;
- redness and increase in size of the tumor itself;
- local increase in body temperature.
If the above symptoms occur, you should immediately seek help.
This situation threatens the penetration of infection into nearby tissues and blood with the spread of microorganisms to distant areas of the body and can cause a deterioration in the general condition of the child. Atheromas occur in areas of the skin that are rich in sebaceous glands. Therefore, they especially often have the following localization:
- scalp;
- face and neck area;
- shoulder girdle, armpit area;
- back.
Neoplasms occur less frequently in the groin area and scrotum (in boys). In these areas they have the appearance of a skin growth and require differential diagnosis with other skin tumors.
Preventive actions
Surgery to remove atheroma on the labia is only part of the treatment. It is very important after surgery to prevent atheroma from forming again.
The following rules will help reduce the risk of relapse of the disease:
- Correct hormonal balance if disturbances occur.
- Select hygiene and cosmetic products with special care.
- Control your weight.
- Wear underwear made from natural fabrics.
- Lead a healthy lifestyle.
- Wear special clothing and a respirator if the profession involves chemicals.
- Visit a gynecologist at least once every six months.
In the prevention of atheroma on the labia, diet plays an important role. Therefore, you need to reconsider the foods that are consumed every day, and minimize the consumption of foods rich in carbohydrates and fats.
If even a small, dense bump appears on the labia, you should not put off visiting a doctor. Only a qualified specialist can determine what kind of formation it is and select the appropriate treatment method.
Diagnosis of pathology
Atheroma on the penis can reach large sizes, which causes discomfort during sexual intercourse and disrupts the aesthetics of the appearance of the penis. To correctly diagnose the pathology, you need to consult a doctor. It differentiates this pathology from other similar diseases. Such as:
- Allergic reactions of the body;
- Peyronie's disease;
- Lesions of the skin of the penis;
- Adenomas;
- Lymphangitis.
Diagnosis is carried out by examining the site where atheroma is detected. Also, neoplasm tissue is taken for histological studies. Atheroma cannot be treated with medication. For diagnosis and the correct choice of treatment method, consultation with a urologist, dermatologist and surgeon is necessary. They will select the treatment method necessary for your health condition.
What symptoms do you see a surgeon for:
- Presence of hernial protrusion
- Daggering pains in the abdomen
- Bloating
- Pain in the right hypochondrium
- Bitterness in the mouth
- Nausea
- Presence of neoplasms on the skin
- Swelling and redness of the skin
- Bone fractures and bruises
- Wounds of any location
- Vomit
- Enlarged and painful lymph nodes