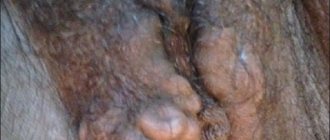
Perineal varicose veins are varicose veins in the perineal area (varicose veins of the labia, varicose veins of the perineum), developing due to obstruction of venous outflow. Varicose veins of the labia are a manifestation of impaired outflow through the system of internal iliac veins due to their blockage or compression. The mere presence of signs of varicose veins of the labia does not pose a threat to the patient’s life, but is aesthetically unacceptable for young women, complicates sexual life and may indicate serious circulatory disorders in the pelvis.
Symptoms of inflammation of the labia
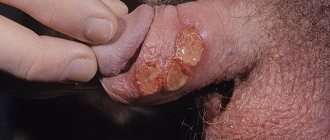
The inflammatory process in the area of a woman’s external genitalia (vulva) is referred to in gynecology as “vulvitis.” This condition has characteristic symptoms, such as redness, itching, swelling of the labia, painful symptoms when urinating, and copious natural female discharge. A woman may also experience a number of additional symptoms:
- the appearance of roughness of the labia minora, which is nodules of enlarged sebaceous glands;
- the appearance of a whitish coating, plaques reminiscent of psoriasis rashes;
- feeling of general malaise and fever.
Like any other inflammatory process, vaginitis is divided into acute and chronic. The acute form is characterized by pronounced symptoms, while the chronic process is more sluggish and unnoticeable.
Expert opinion
You should be especially careful about the development of vulvitis in little girls, since children tend to hush up problems associated with discomfort in the intimate area. For this reason, it is necessary to make it clear to the child that if he experiences any unpleasant sensations, he must inform his elders about their occurrence.
Obstetrician-gynecologist of the highest category Oksana Anatolyevna Gartleb
Gynecologist appointment
Acne in pregnant women: is this normal?
During pregnancy, a woman experiences enormous stress, and the change in hormones alone is worth it. Acne forms on the face, décolleté, back, and genital area. If you maintain daily hygiene, everything will go away on its own. The threat of miscarriage and taking strong medications increases the risk of strange lumps appearing in the delicate area.
The 2nd and 3rd trimester also provokes rashes on the genitals, this is due to the rapidly growing tummy, which prevents the penetration of air to the genitals. It is recommended to choose loose cotton clothing. During gestation, the work of the sweat and sebaceous glands is overloaded several times, so you should rinse more than once so that the pores do not become clogged with dirt. Continue taking vitamins to avoid the risk of vitamin deficiency, and as a result, a decrease in the protective functions of female microflora. By following all these tricks for 9 months, be sure that pimples will not affect the happy course of bearing a child.
You can ask your question to our author:
Causes of vulvitis
In order to clearly understand the causes of vulvitis, it is worth dividing this disease into 2 types: primary and secondary. Primary vulvitis develops in the case of:
- Failure to comply with the rules of intimate hygiene (irregular washing, rarely changing tampons and pads during menstruation, rarely changing underwear, wearing tight and synthetic underwear).
- Sudden hypothermia or overheating of the body.
- Mechanical damage to the vulvar mucosa during sexual intercourse, constant use of tight clothing made of coarse fabrics, removal of hair, and combing.
- Chemical exposure to various drugs.
- Hormonal imbalance and metabolic disorders (obesity, diabetes, insufficient ovarian function, lack of vitamins and minerals in the body);
- Allergic reactions.
Secondary vulvitis, vulvovaginitis (Vulvovaginitis) occurs due to infection of the external genitalia by pathogenic microorganisms contained in vaginal discharge.
Vulvitis - causes
Irritation of the labia can be caused by thrush, colpitis (Vaginitis), endometritis (Endometritis) and other diseases of various organs, not necessarily directly related to the mucous membranes and skin of the genitals. It is worth noting that long-term or frequent use of antibiotics can cause disruption of the vaginal microflora and subsequent vulvitis.
Inflammation of the labia - vulvitis
As medical statistics show, secondary vulvitis most often occurs in women of reproductive age, while primary inflammation is more often diagnosed in childhood. This is facilitated by the tendency of children to diathesis, helminthiasis (Helminthosis) (pinworms with improper hygiene can get into the labia area, causing an inflammatory process).
In this case, vulvitis in girls can be complicated by the appearance of synechiae, which are adhesions connecting the labia minora.
Vulvitis can occur during pregnancy, especially if a woman does not follow the rules of intimate hygiene or wears inappropriate underwear. Vulvitis can occur after childbirth. As the fetus passes, the vagina and labia are injured, which can cause subsequent inflammation.
Diagnosis of vulvitis
To diagnose vulvitis, in most cases, a simple manual examination by a doctor is sufficient, as well as taking a smear for bacteriological, bacterioscopic and cytological examination. The results obtained allow us not only to determine the presence of inflammation, but also to exclude malignant tumors and identify the causative agent of the infection. Additionally, the doctor may prescribe a stool test to detect helminthiasis.
Appointment with a doctor for the treatment of vulvitis
A detailed description of the symptoms and the initial stage of the disease will also have diagnostic value for the doctor. This will simplify the diagnosis and make it possible to exclude any concomitant infections. After all, the itching that vulvitis causes leads (especially often in girls) to the appearance of scratching in the area of the external genitalia, which may also indicate the presence of diseases such as pediculosis, dermatitis or lichen. Also, the cause of itching in the labia area can be any sexually transmitted disease, which sometimes may require consultation with a dermatovenerologist or additional diagnostics.
How to treat vulvitis in women
The gynecologist will answer this question after making a diagnosis. The pathology is detected during a gynecological examination, the cause is determined after additional examinations.
Treatment for vulvitis includes:
- Intravaginal irrigations and baths to alleviate the patient’s condition;
- Drug therapy - antibacterial, hormonal, homeopathic, immunostimulating, antifungal, anthelmintic drugs, depending on the causes of the disease. Medicines are prescribed in the form of tablets, ointments, suppositories;
- A diet excluding sweet, salty, spicy and alcohol.
Vulvitis during menopause requires careful selection of hormonal medications. It is necessary to compensate for the deficiency of estrogen in the body with pills in order to relieve a woman of vaginal dryness and other unpleasant symptoms.
In some cases, gynecologists decide how to treat vulvitis, together with an infectious disease specialist, nephrologist, urologist and other doctors of related specialties.
Treatment of vulvitis
If you notice any alarming symptoms, you should immediately consult a doctor. Only a specialist can diagnose the cause and prescribe correct and quick treatment, including a set of measures: relieving inflammation, eliminating factors that are catalysts for the process.
The basis of treatment for vulvitis is the elimination of the causes of the inflammatory process and treatment of concomitant diseases, which may include diabetes mellitus (Diabetes mellītus), gonorrhea (Gonorrhoea), diphtheria (Diphtheria), helminthiasis. After receiving smear test data and checking the sensitivity of the infectious agent, the doctor can prescribe medication, most often antibacterial drugs. Vulvitis responds well to treatment with local remedies, which include all kinds of ointments, gels and suppositories.
In parallel, in the course of treatment of vaginitis, vitamin complexes can be prescribed, including vitamin A to effectively protect the epithelial layer, as well as vitamins E and C, known for their antioxidant properties.
To combat severe symptoms, other drugs may be prescribed:
- Antihistamines that help relieve itching.
- Hormonal, occurring in atrophic vulvitis in the postmenopausal period.
- Anesthetics that relieve pain.
In addition to the medications prescribed by your doctor, you can use Gynocomfort Restoring Gel. This product was created by specialists from the pharmaceutical company VERTEX and underwent clinical trials at the Department of Dermatovenerology with the clinic of the St. Petersburg State Medical University. During testing of the gel, it was proven that it is a very effective additional agent as part of the complex therapy of inflammatory processes of the female genital tract.
As additional therapeutic measures that can be used at home, it is worth mentioning warm baths with herbal infusion.
Chamomile, calendula, string, and comfrey have excellent anti-inflammatory properties.
Baths will help not only reduce inflammation, but also relieve symptoms such as itching, burning and pain.
Prevention of inflammation of the labia
To prevent vulvitis, it is necessary, first of all, to maintain intimate hygiene. It is recommended to use products designed specifically for caring for intimate areas. Ginocomfort washing gels for intimate hygiene, which were developed by specialists of the pharmaceutical company VERTEX, taking into account the characteristics of the microflora of the genital organs, are well suited for this purpose. They do not dry out the mucous membrane and do not disturb the acid-base balance. These products have a package of necessary documents and quality certificates.
Other measures to prevent inflammatory processes in the labia area include the following:
- Proper drying of the genitals after hygiene procedures. It should be carried out with a clean towel or napkin in the direction from front to back or with gentle blotting movements.
- Careful selection of underwear. It is optimal if it is underwear made of natural and soft material that will not squeeze or rub the perineum.
- General maintenance of immunity, which will allow the body to independently fight infection and suppress the proliferation of pathogens.
Prevention
To protect yourself from unpleasant seals and suppurations, you must follow simple recommendations:
- Stop wearing thongs.
- Take care of intimate hygiene - wash, use wet bactericidal wipes, especially after being in a public toilet.
- If you have hypersensitive skin and your bikini area gets irritated every time, there are gentle depilation methods and creams.
- Follow the timing of changing pads and tampons, use soap without perfumed fragrances.
- Wash yourself properly, wash the outer part of the genitals, there is no need to clean the vagina, this disrupts the natural microflora, which can cause infection in the genital tract.
- After purchasing new linen, be sure to pre-wash it and change it for new ones every day.
- Do not overheat in a bathhouse, sauna, or in the sun, and dress warmly in winter.
- Get enough sleep, eat the right foods, drink plenty of water, avoid stress.
- Avoid uncontrolled sexual intercourse.
- Take immunomodulators and multivitamins that will strengthen the body's defenses.
- Do not self-medicate, make an appointment with a doctor immediately, only a professional examination will help you understand the severity of the rash and choose the right treatment.
These simple tips can not only improve your well-being, but also save you a lot of money on visiting a gynecologist, venereologist, virologist and dermatologist.
Inflammation of the labia in women, video
Gynecologist Irina Vladimirovna Garyaeva about vulvitis in women.
Source - KVD - dermatovenerological dispensary Sources:
- ROLE OF INFECTIONS IN THE GENESIS OF VULVA DISEASES. Reutskaya M.A., Kulinich S.I. // Siberian Medical Journal (Irkutsk). – 2010. – No. 6. – pp. 239-242.
- CLINICAL AND MORPHOLOGICAL PRINCIPLES OF TREATMENT OF CHRONIC VULVITIS. Kulinich S.I., Reutskaya M.A., Pokinchereda T.V., Ezhova I.V. // Acta Biomedica Scientifica. – 2013. – No. 5 (93). – P.42-48.
- Diseases of the cervix, vagina and vulva: Clinical lectures. Ed. V.N. Prilepskaya. // M.: MEDpress. - 1999. - P. 432.
- Recurrent vulvovaginal candidiasis: etiology, pathogenesis, treatment. Levonchuk E.A. // Med. news. - 2001. - No. 4. — P. 40-43.
- Dystrophic diseases of the vulva. Diseases of the cervix, vagina and vulva. Ed. V.N. Prilepskaya. // M.: MEDpress. - 1999. - pp. 326-336.
- https://simptom-lechenie.ru/en/vulvit-u-zhenshhin-i-devochek-simptomy-i-lechenie.html
- https://www.thenakedscientists.com/science-articles
- https://woman-centre.com/vlagalische-i-vulva/vulvit/vulvit-u-zhenshhin.html
- https://simptomer.ru/bolezni/zhenskie-zabolevaniya/864-vulvit-simptomy
Popular questions
I suspect inflammation and cysts.
The doctor prescribed IV thiosulfate, IM ceftriaxone, and Diclovit suppositories. I just didn’t explain, is it necessary to apply everything at the same time or what? Hello! Most often, this complex of treatment is carried out simultaneously, but it is better to check with your doctor.
Hello. My labia and clitoris are swollen, there is a burning sensation and a cheesy discharge with something in it, the color is unclear. What could it be and how to treat it? Before that I had inflammation and treatment, and after that it all started. Hello! This is how vulvovaginitis manifests itself. I recommend that you contact an obstetrician-gynecologist and conduct an examination to find out the cause of the inflammation. This will allow you to correctly prescribe therapy. At this stage, you can use Gynocomfort gel with tea tree oil, 1 dose once a day, which will limit the spread of inflammation and improve your well-being.
Hello! Severe itching on the labia, irritation. There is nothing to worry about in the vagina itself. What could it be?
Hello! This may result in an allergic reaction or inflammation. I recommend using Ginocomfort gel with mallow extract, applying it once a day to the discomfort zone for 7 days. If you do not notice relief, consult a doctor.
Good morning, I have vulvitis on my labia minora, I don’t know what to do or how to treat it.
Hello!
If inflammation occurs in the labia minora area, you can use Gynocomfort gel with tea tree oil. The gel is applied in a thin layer once a day for 1 week. If complaints persist, you should consult a specialist. For an accurate diagnosis, contact a specialist
Expert opinion
Often women hesitate to visit a doctor and try to cope with vulvitis on their own. They find folk remedies on the Internet or learn from friends, buy and take medications on their own. You can suppress the symptoms, but you cannot completely cure the inflammation. An integrated approach is needed.
Moreover, taking pills for vulvitis without a doctor’s prescription can complicate the course of the disease. Pathogenic microflora becomes resistant to drugs. It is extremely difficult to treat such patients in the future. If to this is added a burn to the mucous membrane, an allergy, or other “surprises” from folk remedies, then a whole consultation has to be involved in drawing up a treatment regimen.
There is no need to be embarrassed by the symptoms and waste time. The doctor will help you get rid of the disease in just a few days if you start treatment at an early stage.