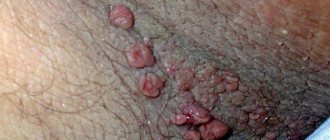
Types of inguinal dermatitis in women and men
Among the possible diseases, the most common diseases in the groin area are those of a fungal nature (the so-called athlete's foot inguinal and candidiasis of the folds). Bacterial diseases (erythrasma) and inflammatory dermatoses (psoriasis, contact dermatitis, benign familial pemphigus) can manifest themselves in a similar way. Children often develop diaper dermatitis in the groin area, which is primarily caused by improper care of the diaper area.
In some cases, it is impossible to make a diagnosis from a photo. In addition to examining the affected skin, a dermatologist will take a scraping to exclude the infectious nature of the disease and conduct an examination using a special ultraviolet lamp - a Wood's lamp.
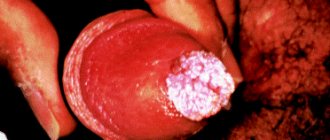
Photo 1. Inguinal dermatitis.
Photo 2. Inguinal dermatitis.
Causes
There is currently no consensus on the causes of seborrheic dermatitis.
However, the development of the disease is usually associated with the functioning of the sebaceous glands. This disease is characterized by changes in the qualitative composition and quantity of sebum, and disruption of the epidermal barrier. Also, with seborrhea, there is a high degree of colonization of fungi of the genus Malassezia - yeast-like lipophilic fungi. Fungi of this genus require a fatty nutrient medium. That is why these microorganisms parasitize in the upper layers of human skin, where the sebaceous glands are most represented. As a result of excessive colonization with Malassezia fungi, the stratum corneum of the skin is damaged, peeling appears, and a local allergic reaction and inflammation develop. Interestingly, an increase in the number of fungi of this genus is not the root cause of the development of seborrheic dermatitis, but a consequence of excessive activity of the sebaceous glands. Also, patients with seborrheic dermatitis often experience an increased level of colonization of fungi of the genus Candida (especially in children of the first year of life). Typically, among the most common causes that provoke the development of seborrheic dermatitis are the following:
- Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Immune and endocrine disorders. Seborrheic dermatitis is often one of the first symptoms of HIV infection. So seborrheic dermatitis may indicate the development of immunosuppression (immune suppression).
- Psycho-emotional stress.
- Obesity.
Causes of inguinal dermatitis in men and women
Factors that cause the disease include:
- reaction to synthetic fabrics from which underwear is made;
- intolerance to any component included in intimate hygiene products;
- the use of low-quality gaskets or their irregular change;
- insufficient attention to hygiene in this area;
- fullness, as a result of which folds form on the skin;
- increased sweating.
- bacterial or fungal infection
Symptoms of seborrheic dermatitis
With seborrheic dermatitis, skin damage is gradual, slowly progressing and is accompanied by itching, often intense. In seborrheic areas, against a background of red spots, plaques with fairly clear boundaries appear, formed as a result of the fusion of small yellowish-pink nodules, covered with fatty scales. The process of skin lesions is often symmetrical in nature and due to peripheral growth and resolution in the center, plaques can acquire garland-like and ring-shaped shapes.
The photo shows the symptoms of seborrheic dermatitis of the face
The pathological process, located in the folds (behind the ear, under the mammary glands, in the groin), is often accompanied by weeping, the appearance of sticky crusts and cracks.
The photo shows the symptoms of seborrheic dermatitis (naso-cheek folds)
When the skin of the scalp is affected, uneven peeling or the formation of dense crusts is noted. Often, upon examination, you can see yellow or white scales attached to the hair shaft, as well as dandruff. The hair usually becomes thinner and thinner, which ultimately leads to diffuse alopecia (baldness).
The photo shows the symptoms of seborrheic dermatitis of the scalp
With a prolonged course of the process, in severe cases, seborrheic dermatitis can progress. In this case, the peeling becomes significant, the scales thicken. Often a secondary infection occurs in the form of honey-yellow crusts. Redness of the skin and peeling can increase in size, up to erythroderma - redness of large areas of the skin. This condition requires mandatory medical monitoring and additional examination.
The photo shows the symptoms of seborrheic dermatitis of the body: erythroderma
In newborns, when seborrheic erythroderma is combined with diarrhea and delayed weight gain, a rather serious skin lesion is diagnosed - Leiner's desquamative erythroderma . This condition is classified as severe and requires urgent medical intervention.
The photo shows the symptoms of seborrheic dermatitis in a child: milk scab
Prevention of groin dermatitis in men and women
To prevent the disease from disturbing your quiet life, get a separate towel for the groin area, which you will wash often. You need to use specialized intimate hygiene products carefully. Doctors repeatedly draw the public's attention to the fact that not all of them meet the standards.
One of the main preventive measures for women is to observe the rules of intimate hygiene during the so-called critical days. Do not forget that the pads need to be changed not only when necessary, but also after a few hours, so that the bacteria accumulated on them do not get on the skin. You need to shower more often than usual.
Treating rashes in the groin area is a difficult task. Modern anti-inflammatory drugs cannot be used in this area for a long time, because the skin is thinner and the development of unwanted reactions is possible. At the same time, it is very important to restore the skin structure after a severe inflammatory process. This task, as well as preventing the development of exacerbations, can be dealt with using Losterin cream. The components of the cream have anti-inflammatory, moisturizing and moderate antimicrobial effects.
Incorrect treatment of atopic dermatitis. 5 main mistakes
Atopic dermatitis is a chronic inflammatory skin disease that causes itchy red patches, rashes, peeling and dryness. This disease is diagnosed in 30% of children and 10% of adults. However, atopic dermatitis is often not given due attention, and incorrect treatment of this disease can slow down the onset of remission and worsen the overall level of health. Dermatologist Anna Trushina talks about the 5 most common mistakes in treatment tactics.
Mistake #1. Excessive diagnostics aimed at identifying “non-skin” causes.
The reasons for the development of atopic dermatitis lie in genetically determined features:
1. From the skin - associated with a violation of the barrier function.
2. From the immune system. In response to the penetration of irritants and allergens through a broken skin barrier, inflammation forms.
Therefore, it is not advisable to look for the cause in helminths, disturbances of intestinal microflora, intoxication, etc. The entire range of examinations prescribed in this regard only because of atopic dermatitis is not justified. Efforts aimed at finding the “root cause” outside the skin are better directed towards competent treatment of the skin itself.
Mistake #2. Search for the causative allergen.
Atopic dermatitis is not an allergic disease in nature. However, allergic reactions can be combined with atopic dermatitis as a concomitant disease. This happens in approximately 20-30% of patients.
Therefore, atopic dermatitis itself is not a reason to undergo expensive panels for specific allergens, and the test should only be taken if a specific allergic reaction is suspected in some patients.
Mistake #3. Following an unreasonable diet.
Often atopic dermatitis becomes the reason for prescribing a strict “hypoallergenic” diet. Children's diet becomes monotonous and boring. However, such dietary restrictions are not scientifically justified and do not bring the desired result, even if there is an allergy at the same time.
In addition to the lack of effect, a strict diet can harm the body. It leads to deficiencies of important nutrients, minerals and vitamins, which can negatively affect the overall health of the child. Therefore, children with atopic dermatitis need to eat a varied and balanced diet. Only those foods whose role has been clearly proven to aggravate the pathological process are excluded from the diet. Similar rules apply to the mother’s diet if the baby is breastfed.
Mistake #4. Irrational skin care.
The basis of the treatment of atopic dermatitis is the restoration of the skin barrier function and the elimination of inflammation. Therefore, products are prescribed that help HYDRATE and soften the skin and retain moisture inside it, and thereby improve the protective properties of the skin. The complex also uses measures that reduce the likelihood of developing an inflammatory process, i.e. skin contact with potential aggressors from the external environment is limited.
To achieve the goals listed above, careful and careful care of the skin of an atopic child using EMOLENTS is required. These are special products, lotions, creams, balms, which, when applied to the skin, soften and moisturize it, help fill the intercellular spaces in the skin, restoring its barrier properties.
It is important to understand that using simple baby creams 1-2 times a day may not be enough. Proper care requires the application of special emollients in sufficient quantities. They are distributed in a thick (!) layer on both problem and visually unchanged areas of the skin. At the same time, the frequency of application directly depends on the condition of the skin. It is necessary to use emollients so many times during the day that the skin remains smooth, soft and without flaking to the touch all day.
Mistake #5. Refusal of “hormones”.
With atopic dermatitis, an inflammatory process occurs inside the skin (the word “dermatitis” itself, literally translated into Russian, means inflammation of the skin). That is why during an exacerbation, anti-inflammatory external agents are used to stop the inflammation. These drugs include external glucocorticosteroids. However, many parents refuse these “hormones” due to steroidophobia (fear of using steroids).
Topical (i.e., used externally: lotions, emulsions, ointments, creams) corticosteroids have been used in the treatment of atopic dermatitis for decades. During this time, they have demonstrated high efficiency and a high safety profile.
If parents do not use corticosteroids in cases where there are indications for this, or do it irrationally (prescribed independently without taking into account the degree and form of skin inflammation, independently cancel the hormone before the required time without the supervision of a doctor), then this can lead to deterioration of the skin condition , the formation of foci of chronic inflammation and other local complications.
Conclusion
Atopic dermatitis is a fairly well-studied disease with established mechanisms of development. Regular skin care, timely relief of inflammation and the elimination of unnecessary aggressive manipulations and diagnostic procedures will help cope with this disease as effectively as possible.
Treatment
For mild seborrheic dermatitis without severe inflammation (usually such dermatitis is called dandruff), it is enough to use special shampoos. Such shampoos contain keratolytic (exfoliating), antifungal and anti-inflammatory components. One of these products is the special dermatological shampoo Belosalik® Salik. Its composition is designed specifically for gentle cleansing of the scalp and hair for problems such as dandruff, seborrheic dermatitis, inflammation of the scalp, accompanied by flaking of the skin. Special shampoo Belosalik® Salik helps remove scales from the skin thanks to the action of 3% salicylic acid, has an antifungal effect due to the presence of piroctone olamine, and also has anti-inflammatory properties because it contains chamomile extract.
For more severe seborrheic dermatitis, external medications are recommended - a combination of an anti-inflammatory agent and a keratolytic (exfoliating component). Such drugs are Belosalik® preparations: lotion - for the treatment of seborrheic dermatitis on scalp areas of smooth skin, spray - for use on the scalp. The liquid form of release does not stain or grease the hair, which makes treatment simple and convenient.
Dermatitis on the labia
In the initial stage, the disease practically does not attract attention and does not cause concern. Small rashes in the groin are attributed to symptoms of an allergic reaction after consuming the product or are compared to prickly heat. Taking antiallergic drugs only relieves itching and burning, but does not improve the condition of the skin, which over time becomes covered with profuse rashes, forming quite large erosive formations.
Based on external signs, a doctor cannot always immediately establish an accurate diagnosis. To exclude lichen and candidiasis, a special ultraviolet lamp with a blue glow is used.
In advanced stages, with inadequate or no treatment at all, the skin in the groin begins to crack severely, in some cases resembling a snake's skin. The affected areas become excessively inflamed, and the disease progresses to the chronic stage.