July 1, 2021
Warts bother many people and are associated with dirt and uncleanliness. Some people still believe that warts appear because a person touched a toad. And for what reasons do these tumors actually appear? In this article, we will look at why warts appear and also look at their types.
Causes of warts
Viral warts are most common on the face.
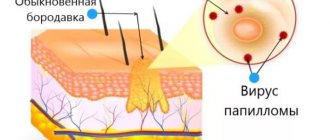
The main reason for their formation is the papillomavirus.
It enters the skin and causes excessive cell division.
As a result, small benign tumors form.
This virus is transmitted by contact.
For infection, an important condition is the presence of damaged epidermis.
Therefore, warts and papillomas on the face appear more often in men.
After all, they regularly shave their beard hair.
The blade causes microdamage to the skin.
Through these defects, a virus enters it, causing warts to grow on the face.
They look unattractive.
In addition, they can be damaged during shaving.
Other types of warts on the face are less common.
There are hereditary diseases that cause their multiple occurrence.
Also, a number of pathologies lead to the formation of a rash that looks like warts.
Folk remedies
When growths become a problem, people start thinking about removing them. If the wart has acquired an unusual color and causes discomfort, you should try to get rid of it the traditional way.
Alternative medicine offers many proven methods that can cope with this task. A wart that turns red can be removed using the following means:
- Onion juice. It is recommended to wipe each tumor with a natural product 2 times a day. It is advisable to carry out this procedure until the wart completely disappears. You can also make medicinal compresses based on onion juice. They are applied to the sore spot for 30 minutes.
- Flaxseed and castor oil. This mixture is also suitable for compresses. Additionally, you can add natural honey to the oils.
- Oats. Based on the product, a paste is prepared in water. It should be taken for a whole month.
- Wormwood tincture. The product is prepared according to a standard recipe. Take it for at least 1.5 months to achieve optimal results.
- Tea mushroom. With this product, medicinal bandages are made, which are applied directly to the location of the red wart. The procedures are carried out over 21 days.
- Copper sulfate. To treat a red wart, its solution is required. Treat with this remedy for 10 days.
If during treatment with a folk remedy discomfort appears or the wart begins to become inflamed, you must immediately stop therapy and immediately seek help from a specialist.
Vulgar warts
They form on the face and hands in both children and adults.
They are also called common or simple warts.
Morphological elements have the appearance of papules.
They can have different sizes.
Sometimes these are small warts on the face, the diameter of which does not exceed 1-2 mm.
There are also larger sizes – up to 1 cm.
In immunodeficiency states, they can grow to impressive sizes.
Upon inspection, it is noticeable that the surface layer of the element is covered with cracks.
Hyperkeratosis is observed on it.
That is, a layer of dead cells.
As a result, simple warts have a hard surface.
As a rule, they do not differ in color from the surrounding skin.
Although in some cases these may be red warts on the face.
At their location, the skin pattern is lost.
However, when the formation disappears, the relief of the epidermis is restored.
If a doctor examines a formation on the face under a magnifying glass, the warts are covered with black or brown dots.
They are capillaries (small blood vessels) that are blocked by blood clots.
This symptom is pathognomonic.
That is, it occurs only in warts.
Detection of this symptom makes it possible to differentiate them from other skin formations.
For example, from keratomas or skin tumors.
As a rule, small warts on the face are round in shape.
If they reach large sizes, they can acquire a polycyclic form.
More often, warts are single.
Less often they are located in groups of several pieces.
At the same time, no systematicity is observed.
The arrangement of the morphological elements of the skin is chaotic and asymmetrical.
If a wart on the face is removed poorly, new formations may appear in the same area.
They are located around the therapeutic area.
Human papillomavirus: symptoms and treatment
There are about 200 different types of HPV, of which more than 40 can infect the genitals, mouth and throat. Most people infected with HPV (Human Papilloma Virus) do not know they are infected. Some types cause common warts when they affect the skin. Other types cause sexually transmitted diseases. In fact, HPV is the most common sexually transmitted disease.
Human papillomavirus (HPV) can cause serious health problems, including genital diseases and some types of cancer.
Most people who have sexual contact and become infected with HPV do not develop any symptoms. Most HPV infections go dormant within two years. But in some cases, the infection causes long-term problems. These problems include cervical cancer in women, penile cancer in men, some types of rectal cancer in both sexes, and oropharyngeal cancer (cancer of the nasopharynx, tongue, and tonsil).
Previously, nasopharyngeal cancer was associated with smoking or alcohol abuse. Today, oral and nasal cancers associated with smoking and alcohol are much less common, while HPV cancers are on the rise. By 2022, HPV-related cancers of the mouth and throat are predicted to be more common than cervical cancers. Unfortunately, cancer of the oral cavity and oropharynx is most often invisible to the patient, provided it is at an early stage of development with minimal symptoms. This is why the main goal of the dentist or surgeon is to rule out or confirm this diagnosis. As with other cancers you know about, such as cervical, skin, prostate, colon and breast tumors, correct diagnosis is the only factor in effective treatment in the early stages of development.
At the first stage, a full examination by an ENT doctor is carried out, including an analysis of the medical history (symptoms, duration of symptoms, taking into account the patient’s profession, marital status, etc.). This is followed by an initial examination with examination of the nose, mouth, throat, palpation of the tonsils, and tongue. The diagnosis also includes examination of the cervix in women and a basic endoscopic examination of the nasopharynx with a flexible endoscope.
If there is some suspicion, we also perform other tests (blood tests, cultures, ultrasound, CT, MRI, etc.). If an HPV infection is suspected, a tissue sample can be taken and sent for histological and immunohistochemical examination.
What is HPV?
The same types of HPV that are localized in the genital area can infect the mouth and throat. Some types of HPV in the mouth, which have a high risk of malignancy, can cause cancer in the head and neck area. Other types of HPV lesions (known to have a low chance of becoming malignant) cause warts to appear in the mouth, throat, and tongue. In most cases, infection with all types of HPV can cause various health problems.
HPV is transmitted by direct contact with the skin or mucous membrane. However, simple transmission of the virus from person to person does not usually cause acute symptoms. The conditions for the virus to penetrate the epithelium imply the presence of abrasions and microtraumas. People often become infected through oral sex.
Is there a risk
Risk factors for HPV are:
- Increased sexual activity is a risk factor, especially if you have many sexual partners. If you have had 20 or more sexual partners, your chance of contracting HPV may be greater than 20%.
- Smoking is a risk factor. Inhaling tobacco reduces the protection of the mucous membrane, making the mouth more susceptible to infections. Oral leukoplakia (symptoms of leukoplakia are a firm, hard, white, slightly raised plaque or patch on the cheek, gum or tongue, and sometimes on the lower lip).
- Alcohol consumption is a risk factor. You are even more at risk if you smoke and drink.
- Men are more susceptible to oral HPV infection than women.
- Age is a risk factor for oropharyngeal cancer. These cases are more common in adults.
Symptoms
HPV in the mouth is often asymptomatic, so people do not know they are infected. At the same time, patients, out of ignorance, are less likely to take the necessary measures to limit the spread of the disease.
In some cases, it is possible to develop warts on the tongue, mouth or throat, but this is not common.
Some types of HPV can develop into oral and tongue cancer. With oropharyngeal cancer, cancer cells can be found on the tongue, tonsils, and throat walls. These cancer cells can “grow” from HPV in the mouth to become malignant.
How can I reduce my risk of getting oral HPV?
There are currently no experts who have researched how to prevent HPV infection. However, it is likely that condoms, when used frequently and correctly, can significantly reduce the likelihood of contracting HPV during sexual intercourse because they act as barriers and prevent the transmission of HPV from person to person.
More research is needed to understand how HPV (Human Papillomavirus) is transmitted, how infection can be prevented, and who is most susceptible to health problems from oral HPV infection.
Is there HPV testing for me to find out if I have oral HPV?
There is not yet a test to diagnose HPV in the mouth or throat. But if there is a suspicion of involvement of the mouth or throat, histological and immunohistochemical examinations can be carried out to identify HPV and its subtypes.
Can the HPV vaccine prevent oral and oropharyngeal cancer?
There are currently HPV vaccines on the market that prevent cervical cancer and other less common cancers. It is likely that HPV vaccines may also prevent oropharyngeal cancer because vaccination prevents initial infection with various types of HPV that can cause oropharyngeal cancer. However, no studies have been conducted to determine whether HPV vaccines will prevent oral cancer, tongue cancer, and nasopharyngeal cancer.
How is HPV in the mouth treated?
It takes a long time after you are infected with most types of HPV before they begin to cause damage to your mouth. If you have HPV-related warts in your mouth, a surgeon can remove them in the clinic under local or general anesthesia. Treating oral warts with topical therapy can be difficult as recurrences are unfortunately very common.
A doctor can use any of the following methods to treat warts: classical surgical removal, removal of warts using laser or radio frequency, cryotherapy, interferon alpha-2b (Intron A, Roferon-A) in injection form. Usually, if you have warts in the throat, tongue or mouth, they can be removed with a local anesthetic without pain.
If you notice any of these symptoms and you know or think that you may be infected with HPV, you should be examined by an ENT doctor to confirm the diagnosis.
Lots of warts
Sometimes a person develops a large number of warts on his face.
The reasons for this may be a disease called epidermodysplasia verruciformis.
Rashes appear that look like flat warts.
Most often they are quite large.
Arranged in groups.
The total number of warts is large.
They often merge with each other.
In appearance, such rashes can sometimes be confused with senile warts or solar keratosis.
Unlike many other types of warts, these pose a real threat to life.
Because they can develop into squamous cell carcinoma.
It is not always diagnosed in the early stages.
Considering that a large number of warts appear, it is very difficult to notice that any of them has changed shape or outline.
First, cancer develops locally.
Over time it can become invasive.
The color of such formations can be black or brown.
Hypopigmentation is less common.
In this case, the warts on the face turn white.
They have either a round or oval shape.
Sometimes warts reach large sizes and merge, forming a “geographic map”.
It is on the face that these formations most often transform into a malignant tumor.
Although they can also be located on the body and limbs.
Like simple warts, epithelial dysplasia is localized in areas of scratching and scratching.
How to distinguish from other formations
Depending on the shape, the growths can be convex or flat, varying in the degree of deepening into the subcutaneous layers and tissue inclusions. The differences are influenced by the causes, nature and form. There are these types of warts:
- flat, resembling a mole in appearance, only red;
- cavernous - of different sizes, protruding above the skin. Depending on the shape, they are divided into: nodular, pineal and branched;
- mixed, formed from capillary cells, muscle and nervous tissue;
- combined warts are located above the surface with a depression in the tissue.
In childhood, it is impossible to classify the formation; it is initially represented on the body as a dot. As a person grows, it acquires shape and color.