+38 +38
- HomeStatsArticlesOn gynecology
Nowadays, patients are often diagnosed with human papillomavirus (HPV), and after this the eternal question begins to arise, what to do?
To begin with, I would like to talk a little about it: the definition of the human papillomavirus.
To summarize, HPV infection can be in the following forms:
- Latency is defined as the persistence of papillomavirus in the basal layer of the epithelium. In this case, the virus is in episomal form (the viral DNA molecule is not embedded in the cell DNA molecule) and does not lead to pathological changes in cells. The latent course of the infection is characterized by the absence of clinical manifestations, colposcopic, cytological and histological norms. The presence of HPV infection is determined by DNA methods (PCR).
- Dysplasia (neoplasia) develops when the DNA of the virus is integrated (introduced) into the cell genome. With neoplasia, changes occur in the structure of epithelial cells. Most often, lesions are localized in the transition zone of the cervix. At the junction of stratified squamous and columnar epithelium, basal cells, sensitive to viral infection, are in close proximity to the surface layers, which facilitates contact with the virus during infection. HPV infection is confirmed by histological examination and colposcopy.
- In the case of invasive tumor carcinoma, the virus in the cell exists in an integrated form. In this case, altered, “atypical” cells are identified, indicating the malignancy of the process. The most common location is the transition zone of the cervix. Identified by colposcopic and histological examination.
A productive infection involves clinical manifestations of infection (papillomas, warts, condylomas). In this case, the virus, which exists in episomal form, is copied in infected cells. At the same time, there is an increased proliferation of cells in the basal layer of the epithelium, which leads to the progression of infection and the appearance of vegetations (growths). Clinically, productive infection is defined as warts or papillomas. The virus is detected by PCR. Histological examination reveals the phenomena of hyperkeratosis (increased keratinization, i.e. cell aging).
How does HPV infection manifest?
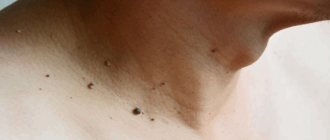
The main symptom of infection caused by the human papillomavirus is the formation of so-called genital warts.
Externally, genital warts are similar to ordinary warts. They can be small in size (from a few millimeters to a centimeter), pinkish or flesh-colored, and have a smooth or slightly bumpy surface.
Most often, genital warts form in the area of the external genitalia.
In women, genital warts can occur near the clitoris, on the labia minora and majora, in the vagina and on the cervix. In case of irritation of condylomas located close to the entrance to the vagina, itching and minor bleeding may occur during sexual intercourse.
In men, genital warts form on the penis and scrotum.
Condylomas can also form in the anus, in the urethra, or in any other place on the skin (skin of the neck, armpits). Several condylomas located nearby can merge into one large “wart”.
Generally, genital warts are painless. In some cases, mild itching and discomfort are felt in the area of condylomas.
Papillomas in men: causes of occurrence
The cause of the appearance of papillomas on the body in men and women is a virus that can enter the body in various ways:
- Due to unprotected sexual contact: the most common type of infection, including because a person can be a carrier of the virus for a long time, without even knowing it, since the virus has the ability to manifest itself only under the influence of external factors. Transmission is also possible through direct contact of mucous membranes. In this case, the risk of infection increases if the skin or mucous membranes are damaged (there are cracks, scratches, cuts, etc.). Due to the prevalence of this cause of infection, it is understandable that quite often papillomas (condylomas) in men and women appear in the intimate area, at points of contact, from which the risk of infection in men is usually higher, due to their greater sexual activity, but the mucous membranes of women are less protected .
- Through household contact: it has now been proven that the HPV virus can enter the human body through ordinary contact (even a handshake), especially in public places (baths, swimming pools, gyms, etc.).
It is also necessary to remember that infection with the specified virus does not mean its manifestation.
Most often, the disease becomes more active and makes itself felt if:
- the patient's immunity is weakened;
- there were great physical or mental stress, stress, exhaustion;
- There are various types of sexually transmitted diseases.
HPV in men: consequences
The virus can cause condylomas, or genital warts, which, as the name suggests, are located in the groin, as well as on the head of the penis and foreskin. This kind of condylomas has very dangerous consequences for men and requires treatment.
Condylomas on the penis can lead to a narrowing of the foreskin, which can make it difficult to expose the head of the penis and lead to problems in your personal life.
It must also be remembered that in some cases such formations are not an indicator of HPV, but of other sexually transmitted diseases that have not yet manifested themselves (for example, syphilis).
Another danger of HPV is that a carrier of the virus can transmit it to their partner, also putting them at risk of developing cancer. Transmission of the virus is also possible to the fetus from an infected mother, so couples wishing to have children should pay special attention to HPV and other diseases of this kind.
Diagnosis of HPV?
To confirm the diagnosis of human papillomavirus infection, the PCR (polymerase chain reaction) method is used, which allows you to determine the DNA of the virus and determine exactly what type of virus a person is infected with.
In modern diagnostic laboratories, the type of virus, its quantity (viral load) and integration of the virus into the genome are determined. At the beginning of the article, information is provided that shows that the most dangerous HPV are high-oncogenic risk (HOR). In addition to the type of virus, the definition and its quantity are important. Treatment tactics depend on this. Unfortunately, the integration of the virus into the cell genome is not determined in our laboratories. This analysis is important in the early diagnosis of cervical epithelial dysplasia and non-invasive carcinoma.
It is very important that everyone understands that even if a PCR test reveals oncogenic forms of HPV in you, this does not mean that you already have cervical cancer or that you will inevitably get it in the near future, since not in all cases does HPV lead to to the development of cancer. It can take years from the moment of infection to the appearance of precancer.
In order to determine whether HPV has caused changes in the cells of the cervix and whether there is a risk of developing cancer, it is necessary to undergo a thorough gynecological examination, which necessarily includes:
- Colposcopy (examination of the cervix with a device that resembles a microscope and allows viewing under a magnification of 8 to 20 times).
- Cytological smear (PAP test), which is used to determine dysplastic changes in the cells of the cervix.
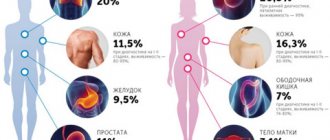
- Bacterioscopic examination of vaginal discharge. Often, HPV infection is combined with other sexually transmitted infections (in approximately 20% of cases), so additional examination may be necessary to determine chlamydia, mycoplasmosis, ureaplasmosis and trichomoniasis.
- Targeted biopsy is the removal of a piece of cervical tissue in cases of dysplasia or suspected malignant tumor of the cervix.
Protecting women from the oncogenic type of human papillomavirus
Types of HPV - danger rating
- Non-oncogenic group. Non-oncogenic strains are HPV 1-5, 7, 10, 12, 14-15, 17, 19, 20-24, 26-29, 57. These types of papillomavirus cause gray warts with uneven edges, plantar calluses, “butcher’s warts” ", multiple growths of various shapes.
- Group with low oncogenic risk. Includes strains 6, 11, 42-44, 53-55. The first two are more common than others and are associated with genital warts of the cervix. It cannot be said that this type of HPV is the most dangerous, but the growths it causes are recommended to be removed as soon as possible.
- Group with average oncogenic risk. Includes strains 31, 33, 35, 52, 58. The most common type is 31, the culprit of bowenoid papulosis - smooth nodules on the mucous membrane of the external genitalia. We can say that this is the most dangerous type of HPV of the group. It can turn into a benign and then into a malignant formation, but in the initial stages it is amenable to immunostimulating therapy.
- Group with high oncogenic risk. The most dangerous types of HPV for humans are 16.18, 36, 39, 45, 51, 56, 59, 68. The risk of oncogenicity is more often manifested in the presence of strains 16.18 and 51. The first two cause cervical cancer. Type 51 manifests itself in the form of bowenoid papulosis and flat condylomas, reminiscent of an allergic rash. All three forms cause precancer and require immediate treatment.
HPV is dangerous for women of any age
The virus is transmitted in different ways, most often through a handshake, towels, kisses and, of course, sexual intercourse.
Gynecologists at the MC “Private Medical Practice” remind you of the importance of protected sex and invite women to a consultation.
Infection with oncogenic types of HPV is dangerous at any age! The risk of precancerous conditions and cervical cancer in women with the HPV virus increases many times over.
Stress, strict diets, poor ecology and weak immunity make a woman’s body vulnerable, so the virus causes cancer within a fairly short time from the moment of infection.
Gynecologist, doctor of the highest category Svetlana Valerievna Turanina, recommends regular examination for the presence of HPV in a woman’s body.
Prevention of the development of cervical HPV involves careful adherence to intimate hygiene, and during sex it is necessary to use a condom.
A consultation with a gynecologist at the MC “Private Medical Practice” costs 1,200 rubles.
Analysis for the presence of various types of HPV in the body - from 1000 rubles.
Treatment prescribed in the early stages has been proven effective.
Make an appointment with a gynecologist by phone or on our website www.4vp74.ru .
The site also offers a call back service and online registration.
“Private medical practice” means a long and healthy life. There are contraindications.
A doctor's consultation is required. #papillomavirus #HPV #gynecologist #uterine cancer #HPV analysis #pre-uterine cancer
HPV treatment
Since a complete cure for human papillomavirus infection is currently impossible to achieve (along with this, spontaneous, spontaneous recovery is often observed), the manifestations of HPV are treated, and not the presence of the virus in the body. Moreover, the effectiveness of various treatment methods is 50-70%, and in a quarter of cases the disease manifests itself again several months after the end of treatment. The question of the appropriateness of treatment for each patient is decided by the doctor individually. In this case, it is necessary to avoid factors that reduce immunity (hypothermia, severe emotional stress, chronic fatigue, vitamin deficiency). There are studies that suggest the preventative effect of retinoids (beta-carotene and vitamin A), vitamin C and micronutrients such as folate against diseases caused by HPV.
Among the methods of treating manifestations of HPV infection (genital warts and papillomas), the most commonly used are:
- Destructive methods
are local treatment aimed at removing condylomas.
There are physical ( cryodestruction, laser therapy, diathermocoagulation, electrosurgical excision
) and chemical (
trichloroacetic acid, feresol, solcoderm
) destructive methods, as well as
surgical removal of condylomas
.
Cytotoxic drugs
-
podophyllin, podophyllotoxin (
condylin ), 5-fluorouracil
. Women of childbearing age are advised to use reliable contraception or avoid sexual activity during treatment. - Interferons (
Laferon, Laferobion, Alfarekin, Reaferon, Viferon )
are most often used to treat HPV infection . They are a family of proteins that are produced by cells of the immune system in response to stimulation by viruses. A separate drug is Alokin-alpha, which stimulates the production of its own interferon and activates cellular immunity. - Specific antiviral drugs ( cidofovir, panavir, alpirazine
). The well-known antiviral drug acyclovir (Zovirax) has no effect on HPV. Of the local (vaginal) drugs, Epigen intimate spray and Betadine have an antiviral effect.
Human papillomavirus - which HPV treatment is effective?
What is human papillomavirus?
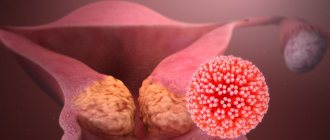
The HPV group of viruses is part of the papillomavirus family, which includes 5 genera, about 43 varieties and almost 170 types, and it is HPV that causes the formation of warts. There is a direct connection between it and cervical cancer: this virus is detected in 92% of cancer cases.
What tests are done for human papillomavirus?
The main areas of research are determining the viral load, that is, a quantitative indicator and determining the type of virus using the PCR method.
Are papillomas dangerous?
In essence, papilloma is a benign tumor, but it is also fraught with danger. Firstly, damage to its integrity is possible, leading to the formation of scars and, rarely, blood poisoning. It is not recommended to remove papillomas mechanically on your own; this can lead to generalization of the process and the spread of papillomas throughout the body. The main danger of papillomas is that they are viral. Most types of HPV do not pose a threat to human health and life, but HPV types 16 and 18 can provoke the development of malignant tumors. Benign papillomas, as a rule, cause a lot of trouble to a person. They can grow to large sizes and can form in the genital area. Some types of HPV cause precancerous lesions.
Is human papillomavirus contagious?
HPV can be transmitted in various ways. With contact and household transmission, the virus is transmitted through the skin through handshakes and the use of personal hygiene products, after trying on someone else's clothes and underwear, and when visiting public swimming pools and saunas. Sexual transmission of the virus is considered especially dangerous, since there is a high risk of infection with oncogenic HPV. The likelihood of sexual transmission of the virus is much higher if the partner has genital warts. HPV can be passed from mother to child during childbirth, although it rarely occurs during pregnancy. In this case, most often children develop laryngeal papillomatosis, which can cause serious respiratory problems. It is possible for a child to become infected from the mother during breastfeeding.
How is human papillomavirus treated?
Drug treatment of the virus is carried out using drugs that act on the cause of the disease and also restore the function of the immune system. There are various schemes for intravenous drug administration; doctors, as a rule, prescribe treatment individually; there are no standard schemes. What drugs are usually prescribed? Cycloferon, Interferon alfa, Panavir, Ingaron. Tablet forms of antiviral drugs: Isoprinosine, Lykopid, Lavomax, Alpizarin. Candles: Genferon, Betadine, Viferon. Ointments: Oxolinic ointment, San Fen Zhong ointment, Stefalin, Salicylic ointment. Vitamins: Aevit, Alphabet.
Vaccination against HPV (Gardasil)
It is still impossible to completely get rid of HPV at the current level of the pharmaceutical industry, but it is possible to prevent infection and for this purpose vaccination is carried out with a drug such as Gardasil. In some countries, these vaccinations are already mandatory; in Russia, vaccination can be done voluntarily. When choosing this method of preventing HPV, it is necessary to undergo a preliminary examination to determine the presence of the virus in the body. Vaccines contain synthetically modified proteins similar to the structure of the virus. The introduction of these proteins into the body activates the immune system and leads to the production of antibodies that protect against the development of HPV after the pathogen enters the body. Vaccine developers advise giving the drug to girls and boys aged 10 to 12 years. This is due to the fact that at this age, in the vast majority of cases, there is no sexual intercourse, and the immune system works at full strength, which contributes to a good response to the drug.
Can human papillomavirus cause cancer?
The most dangerous type of HPV that causes malignant tumors is the following: HPV-16; HPV-18; HPV-31, 33, 45, 56, 58; HPV-51, 59, 68; HPV-35, 39, 52.
What types of cancer does HPV cause?
Most often, cervical cancer is caused by human papillomavirus types 16 and 18, which also cause genital cancer. HPV 16 is the cause of laryngeal cancer in 50% of cases.
Is HPV sexually transmitted?
HPV is transmitted sexually, and sexual contact itself becomes the main cause of infection with the papilloma virus. Let's talk about this in more detail.
Papillomas located on the penis are a sign of human papillomavirus infection, therefore sexually transmitted infection is quite logical. The incubation period for HPV lasts from 1 to 12 months. In this case, the papillomas themselves may not grow at all, and only with a decrease in the function of the immune system can their formation begin. Therefore, detection of HPV in the body in the early stages of disease development is possible only with the help of special tests. Currently, HPV is one of the most common diseases and the risk of infecting a partner during unprotected sexual intercourse is almost 100%.
Are papillomas a cancer?
All types of HPV, according to the degree of risk of malignant degeneration, can be divided into the following: low risk, medium risk and high oncogenic (carcinogenic) risk. Genital warts in the genital area, as a rule, are not caused by a highly oncogenic virus. Squamous cell papillomas are malignant neoplasms. Patients diagnosed with squamous cell papillomas are at increased risk and require immediate treatment.
If a patient is diagnosed with HPV of the oncogenic group, in order to prevent the appearance of oncological processes in the body, it is necessary to pay attention to the immune system, regularly undergo tests and be observed by a doctor.
Is it possible to give birth if you have the human papillomavirus?
If HPV is detected in a woman’s body, but there are no external manifestations in the form of papillomas, then you can give birth calmly and not worry. If there are genital warts in the genital area, then there is a very high risk of the child becoming infected with HPV while passing through the birth canal. The child’s first independent breath can occur right in the birth canal; the virus entering the baby’s throat leads to the growth of papillomas on his vocal folds. Therefore, in the presence of genital papillomas and an active form of HPV, a cesarean section is indicated.
Can human papillomavirus go away without treatment?
According to statistics, in 85% of cases, HPV after infection is eliminated by the body on its own, thanks to the good functioning of the immune system. This process can last from several months to several years. Sometimes the presence of the virus in the human body may not be detected even during a medical examination. The presence of HPV can be fully confirmed by the presence of formations on the skin - papillomas.
What to do if you are diagnosed with human papillomavirus?
Dermatologists recommend:
HSV and HPV: similarities and differences
First of all, it is important to understand that the herpes simplex virus (HSV) and the human papillomavirus (HPV), which provoke herpes and human papillomavirus infections, respectively, are fundamentally different from each other.
"Galavit" for herpes virus infection helps:
- Pronounced elimination of viruses from the body
- Increasing the effectiveness of antiviral therapy
- Reducing the period of rashes and accelerating regeneration processes
- Increased duration of remission
In adults and adolescents over 12 years of age in complex therapy:
Suppositories
- 5 days, 1 suppository, then one every other day. Course - 2 packs of suppositories.
Sublingual tablets
— 10 days, 1 tablet 4 times a day. Then continue taking it every other day for 10 days, 4 tablets per day.
THERE ARE CONTRAINDICATIONS. YOU SHOULD CONSULT WITH A SPECIALIST.
HSV
Genital herpes is associated with infection with HSV type 1 or 2. According to statistics, the disease affects about 12% of the population [1]. Once it has penetrated the body, the virus “settles” in it forever - today there is no treatment method for the herpes virus that would allow one to finally get rid of the pathogen. Symptoms of genital herpes, which occur periodically during relapses, significantly reduce the quality of life. Interestingly, the frequency of new episodes of the disease depends on the type of virus: with HSV-1 infection, approximately 1 relapse is recorded per year, while with HSV-2 infection, their number can reach 6 or more [2].
Despite the fact that there is no specific treatment for HSV, a number of drugs can alleviate the condition during exacerbations. According to domestic and Western recommendations, oral antiviral agents for herpes based on acyclovir and valacyclovir are used for this purpose. However, in Russia local therapy is also recommended, which is not included in Western standards. Abroad, such methods are not included in the recommendations due to their lower activity compared to tablets [3].
HPV
The situation with papillomavirus infection (HPV) is somewhat different. It is considered the most common sexually transmitted disease in the world [4]. Most adults become infected with HPV at some point in their lives, but in 90% of cases the virus clears naturally within two years of infection. Otherwise, the infected person becomes a lifelong carrier.
Unfortunately, there is no cure for the human papillomavirus, just as there is no cure for the herpes simplex virus. However, the first, unlike the second, can be deadly: HPV types 16 and 18 are associated with malignant neoplasms - in particular, cervical cancer and some other tumors. The only effective drug treatment for human papillomavirus infection today is the eradication of condylomas, which are manifestations of clinical and subclinical forms of infection. For this purpose, a number of local antiviral drugs that have proven activity in studies are used in the treatment of human papillomavirus. At the same time, in domestic practice, doctors also prescribe drugs that have a dubious evidence base. Let's look at their advantages and disadvantages in more detail.