Papillomas arise from the human papillomavirus, and this is an STI.
Therefore, manifestations of HPV should be treated by a dermatovenerologist.
It is imperative to consult a specialist regarding the appearance of papillomas.
Self-medication and the use of drugs and methods of treatment of traditional medicine are dangerous for the health and even the life of the patient.
A person should know what type of HPV virus is the one that causes the rash.
If this is a highly oncogenic type, then treatment should be immediate, before the papillomas degenerate into malignant neoplasms.
There is currently no specific antiviral treatment.
Unfortunately, HPV is a lifelong disease.
You will need to fight it every day, even if there are no clinical manifestations, by increasing your immune response.
For this purpose, to guard your health, there is always a specialist - a dermatovenerologist who can help with any problems accompanying HPV.
To make treatment more effective, antiviral therapy must be combined with immunomodulators.
Immunocorrection is carried out based on immunogram data.
Often treated with lycopid and immunomax.
Doctor treating and removing papillomas
Along with general therapeutic treatment, surgical removal is necessary.
They are performed by a specially trained dermatovenerologist with a surgical profile.
Along with the traumatic surgical excision of papillomas, which is rarely used today, a number of modern, low-traumatic removal methods are also used.
Cryodestruction, electrocoagulation, excision of papillomas using a laser, radio wave method.
If the papillomas are small, then cauterization with special chemicals is sometimes effective.
After a thorough examination and an accurate diagnosis, the attending physician will prescribe the most effective method of removal in this particular case.
In the anogenital area, the attending physician has to deal with genital warts and simple papillomas.
They have a papillary shape, soft consistency and vary in size.
They are characterized by painlessness and poor aesthetics.
These are unnecessary elements on the skin of a person infected with HPV, and they must be removed.
HPV treatment
Since a complete cure for human papillomavirus infection is currently impossible to achieve (along with this, spontaneous, spontaneous recovery is often observed), the manifestations of HPV are treated, and not the presence of the virus in the body. Moreover, the effectiveness of various treatment methods is 50-70%, and in a quarter of cases the disease manifests itself again several months after the end of treatment. The question of the appropriateness of treatment for each patient is decided by the doctor individually. In this case, it is necessary to avoid factors that reduce immunity (hypothermia, severe emotional stress, chronic fatigue, vitamin deficiency). There are studies that suggest the preventative effect of retinoids (beta-carotene and vitamin A), vitamin C and micronutrients such as folate against diseases caused by HPV.
Among the methods of treating manifestations of HPV infection (genital warts and papillomas), the most commonly used are:
- Destructive methods
are local treatment aimed at removing condylomas.
There are physical ( cryodestruction, laser therapy, diathermocoagulation, electrosurgical excision
) and chemical (
trichloroacetic acid, feresol, solcoderm
) destructive methods, as well as
surgical removal of condylomas
.
Cytotoxic drugs
-
podophyllin, podophyllotoxin (
condylin ), 5-fluorouracil
. Women of childbearing age are advised to use reliable contraception or avoid sexual activity during treatment. - Interferons (
Laferon, Laferobion, Alfarekin, Reaferon, Viferon )
are most often used to treat HPV infection . They are a family of proteins that are produced by cells of the immune system in response to stimulation by viruses. A separate drug is Alokin-alpha, which stimulates the production of its own interferon and activates cellular immunity. - Specific antiviral drugs ( cidofovir, panavir, alpirazine
). The well-known antiviral drug acyclovir (Zovirax) has no effect on HPV. Of the local (vaginal) drugs, Epigen intimate spray and Betadine have an antiviral effect.
Which doctor should I contact for papillomas on the body, neck, groin and armpit?
If neoplasms are detected, you should immediately contact your family doctor.
The general practitioner will carefully examine you and refer you to a dermatovenerologist.
If you need advice from other specialized specialists, then you should definitely do it.
HPV may have caused pathology in other organs and systems in the body, and the sick person should know about this.
It is necessary to consult a specialist if:
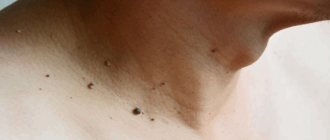
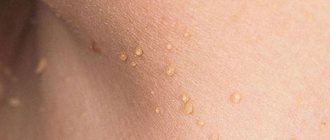
- papillomas on the body;
- warts all over the body;
- Condylomas appeared (external genitalia and perianal area).
Most types of HPV are low-oncogenic, but formations cannot be injured so as not to provoke the degeneration of a benign neoplasm into a malignant one.
When a benign papilloma is traumatized, it becomes infected with a secondary infection and suppurates, which can lead to sepsis.
A sick person cannot determine for himself which strain of HPV he is infected with – high-oncogenic or low-oncogenic.
You need to contact a specialist and get diagnosed.
To exclude or confirm the presence of highly oncogenic, primarily HPV types sixteen and eighteen.
Causes of polyps and papillomas of the anus
The anus is an area in which the growth of tumors is quite often observed. Polyps may form inside the rectum. Condylomas (a type of papillomas that resemble cauliflower in appearance) may appear in the perianal area (around the anus). In some cases, condylomas can also occur inside the anal canal.
Sometimes you may not even suspect the existence of such formations in yourself. A common situation is when their presence is established during an examination (or during an endoscopic examination) when treating for other diseases.
Polyp
- This is the growth of the mucous membrane in the form of a mushroom body. With its thin stalk, the polyp maintains contact with the wall of the rectum, and the body itself hangs freely inside the canal.
Papillomas (genital warts)
are caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV). HPV is a widespread disease; according to various sources, from 70 to 90% of people carry this infection. However, in most cases, the virus “sleeps” and becomes active when immunity decreases. This is when active growth of papillomas occurs.
In the perianal area, HPV manifests itself in the form of genital warts, which usually also affect the human genitals. Often condylomas become injured and bleed. The virus can be transmitted through blood from damaged condylomas.
Which doctor treats papillomas on the tongue, eyelid and eye?
In the oral cavity, a neoplasm is considered a papilloma if it:
- approximately one centimeter in size
- with rough surface
- has a thin leg or a wide bottom
- light or pinkish color
- painless when pressed
A dentist diagnoses papilloma on the tongue and in the oral cavity.
If the need arises, the papillomas are subsequently removed by a surgeon or oncologist.
The eyelids and periocular area are the prerogative of the ophthalmologist.
After the diagnosis is made, he is also sent to a surgeon or oncologist, depending on whether the tumor is benign or malignant.
Symptoms of polyps and papillomas of the anus
Polyps, genital anal condylomas and other benign neoplasms that arise in the rectum and perineum can transform into malignant ones. The likelihood of degeneration increases if the formation is constantly injured, as is often the case with this localization.
It should be taken into account that in the initial stage of development such formations may not manifest themselves in any way, and they can only be identified endoscopically (during recothoromanoscopy or colonoscopy). It is all the more important to pay attention to symptoms that may indicate the presence of formations.
Painful sensations
Subjectively, a large polyp may feel like a foreign body in the anus. There may be pain with different localization in the lower abdomen.
Diarrhea
The presence of a polyp in the intestinal lumen disrupts its functioning. The intestines are constantly trying to free themselves from contents - this is how diarrhea is stimulated.
Constipation
A large polyp obstructs the passage of stool and causes constipation.
Bleeding from the anus
If you detect even minor bleeding from the anus, you should definitely consult a proctologist.
Which doctor treats papillomas in men's intimate places?
For papillomas in men, you should contact a dermatovenerologist, urologist or andrologist.
Papillomas of the perianal area and on the anus are treated by a proctologist.
He performs not only a visual examination, but also anoscopy in order to have maximum information about HPV and the directions of its spread throughout the body of an infected man.
Most often, malignancies are observed on the penis and larynx.
In people infected with HPV, papillomas do not necessarily grow.
This requires a decrease in immune defense.
It occurs if:
- history of severe inflammatory diseases
- there was psycho-emotional stress
- were treated with hormonal drugs
- there was insolation
- consumed alcoholic beverages and tobacco products
For rashes to occur, you also need increased sweating or high humidity.
Such conditions are observed inside the elbow, in the groin and under the arms.
Super cleanser for papillomas - reviews from doctors
What is Supercleaner?
This is a remedy for removing warts and papillomas.
We talk about Supercleaner as a means for cauterizing warts, papillomas, keratomas and genital warts.
It is available in liquid form.
This liquid consists of celandine juice, sodium hydroxide and sodium bicarbonate.
The action of this liquid is based on chemical cauterization of tumors on skin surfaces.
Reviews from people who have tried this product on themselves are mostly positive.
It has one serious drawback, like any means for chemical cauterization of tumors.
Very careful work is required to prevent chemical burns of healthy tissue adjacent to the tumors.
But doctors speak differently about him.
Some people understand that sometimes this remedy can be very effective.
But most doctors prefer surgical methods of removing tumors.
Human papillomavirus (HPV)
Table of contents
- How is the virus transmitted and how does it manifest?
- Why is HPV infection dangerous?
- Symptoms of HPV in women
- Treatment of different types of HPV in women
- Is it possible to prevent infection?
- Advantages of contacting MEDSI
Human papillomavirus (HPV) today is the most common infection
that affects residents of numerous countries.
The disease affects the mucous membranes and skin. Moreover, the virus can exist in human blood for a long time without detecting itself. Symptoms of HPV in women (as well as in men) appear when immunity decreases.
How is the virus transmitted and how does it manifest?
The disease is transmitted in the following ways:
- Sexual. Genital, oral-genital and anal
- Contact-domestic (by touching, using certain objects, etc.)
- During childbirth (child from mother)
A person infected with the virus suffers primarily from aesthetic problems. Unsightly growths form on his skin and can grow. Moreover, after removal the risk of relapse is very high.
Why is HPV infection dangerous?
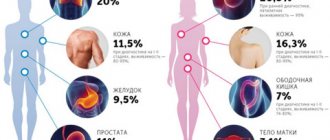
Today, cervical cancer (CC) still ranks second in the world among female cancer pathologies, with more than 270 thousand women dying from this serious disease every year.
However, the disease can be prevented. It has been convincingly proven that one of the conditions for the development of cervical cancer is the presence of the human papilloma virus. Today, about 150 types of this virus are known and about 34 of them are associated with lesions of the anogenital area. Types 16, 18, 31, 33 and 39 are highly oncogenic. They can trigger the development of cancer of the cervix, vagina, penis and anus.
Symptoms of HPV in women
The disease in women usually manifests itself by the appearance of the following neoplasms on the skin and mucous membranes:
External signs of pathology are often absent for a long time, so the patient does not suspect that she is at risk
- Genital warts.
Such formations are among the most dangerous and appear mainly in the genital area. Condylomas are characterized by a flesh-colored or pale pink color and the shape of the papilla. Over time, such formations can degenerate into malignant tumors. - Flat warts.
Such neoplasms are benign and relatively safe. They do not cause cancer, but are contagious and are transmitted from person to person even by simple contact. Typically, flat warts grow on the face, legs and hands, are round in shape and small in size (up to 5 mm) - Bowenoid papulosis.
These formations appear on the genitals and in the perineal area, are quite dense, have a yellow or pink tint and the shape of plaques that rise slightly above the skin and mucous membranes
Also, human papillomavirus in women can manifest itself in the form of dysplasia. The epithelial cells of the cervix are affected by pathology. When HPV is present, they begin to change rapidly, causing a precancerous condition. With early diagnosis, the patient can be cured! In advanced cases, cancer occurs.
Important! External signs of pathology are often absent for a long time, so the patient does not even suspect that she is at risk!
Treatment of different types of HPV in women
Important! Widely advertised immunostimulants are ineffective in treating the virus. They have not passed the necessary tests and are not included in the protocols.
There are currently no effective treatments for the virus. You can only eliminate those pathological conditions that are provoked by HPV: remove papillomas and other formations on the skin and mucous membranes, treat dysplasia and cancer.
Today, neoplasms are successfully removed using radioknife, laser, cryocoagulation, etc. The procedure is carried out quite quickly and does not cause significant discomfort to the patient. After removal there are no large scars left. Surgical excision may also be performed.
The method of removing formations is selected individually. In this case, the doctor focuses on the patient’s characteristics, the size and location of the papilloma or other growth, as well as concomitant pathologies and existing indications and contraindications.
In MEDSI clinics, tumor removal is carried out using techniques such as:
- Electrocoagulation.
The formation is destroyed due to the effect of high-frequency current on it. A small wound usually heals quickly without leaving a scar. - Laser exposure.
This procedure allows you to quickly “burn out” the formation without leaving any traces. The intervention takes a couple of minutes and is suitable for removing warts and papillomas on open areas of the body (including the face) - Cryodestruction.
This technique involves exposing the formation to cooled nitrogen. Warts and papillomas are destroyed by very low temperatures and are independently rejected by the body - Radiosurgery.
To carry out the procedure, a modern instrument is used - a radio knife. It is capable of heating tissue in a non-contact mode and ensuring the evaporation of pathological cells. Radiosurgery, like laser surgery, is used to remove growths on open areas of the body - Chemical destruction.
During such interventions, acids and other drugs are used. They locally affect formations, violating their integrity - Surgical excision.
This technique is relevant for large or deeply sprouted formations. Due to the fact that the surgeon works manually, he can quickly remove the formation and send pieces of tissue for examination (to determine whether they are benign or malignant)
Important! If a woman has no complaints and no papillomas or dangerous changes are detected as a result of exposure to the papilloma virus on the body, treatment is not carried out! In this case, the patient should undergo regular examinations (PAP test and colposcopy).
Is it possible to prevent infection?
Yes! The high incidence rate has provoked the interest of scientists in the development of not only therapeutic, but also preventive measures. A real breakthrough was the creation and introduction of vaccines into world practice.
HPV vaccination in women and men: what is it and what vaccines are there?
Vaccination is a preventive measure! It protects against infection and helps prevent the risks of health and life-threatening consequences of the virus.
Today, 2 drugs are registered in Russia - Gardasil and Cervarix! Both vaccines are effective and safe. They have undergone extensive clinical trials and have proven almost 100% effective in preventing diseases associated with HPV (including cervical cancer pathologies).
A real breakthrough was the creation and introduction of vaccines into world practice.
However, it is better to use Gardasil. This is due to the fact that such a vaccine acts against 4 types of virus. It protects against cervical cancer, vulvar, vaginal, anal cancer, anogenital condylomas, cervical, anal, vulvar and vaginal intraepithelial neoplasia and adenocarcinoma in situ.
"Gardasil" can be used:
- Girls and women from 9 to 45 years old
- Boys and men from 9 to 26 years old
Vaccination involves the administration of 3 doses of the drug and is carried out according to the schedule: 0‑2‑6 months.
It can be prescribed even to previously unvaccinated people who have been diagnosed with the virus. This is due to the fact that the patient may not be infected with all types of HPV!
Important! Vaccination does not replace the need for screening tests and regular examinations by a gynecologist.
Today, Gardasil is included in the compulsory vaccination schedule in many European countries and the USA. Some countries have already proven effective reductions in morbidity rates.
Important data on reducing the incidence of cervical cancer among those vaccinated were obtained in Australia, where, from 2007 to 2016, 78% of 15-year-old girls and 72% of boys of the same age were vaccinated in this way. As a result, the prevalence of HPV among women 18–24 years of age decreased from 22.7% to 1.1% from 2005 to 2015, and the incidence of precancerous cervical lesions in the population of girls under 18 years of age decreased by 38%.
Advantages of contacting MEDSI
- Experienced specialists.
Our doctors are always ready to provide comprehensive medical support to all categories of patients. They will not only advise you, but will also carry out diagnosis, treatment (including the consequences of HPV in women) and prevention of various pathologies, if necessary. - Opportunities for effective diagnosis of HPV.
In our laboratory, you can take tests to detect the presence of oncogenic HPV serotypes (categories) in the body. This examination is especially relevant when immunizing patients over 25 years of age. - Possibilities for removing tumors.
We use classic and modern technologies. This allows you to choose the appropriate option for each patient. - Timely vaccination.
The drug for vaccination is always available. By contacting us, you will not be forced to delay vaccination. It is possible on the day of application - Using a modern, highly effective drug.
The safety and effectiveness of Gardasil have been confirmed by international clinical trials, which were conducted with the participation of a large number of study subjects.
Our doctors are always ready to provide comprehensive medical support to all categories of patients.
If you are planning to visit our clinic for the purpose of vaccination against HPV, examination for this virus, or treatment of precancerous conditions and cancer, call (495) 7-800-500. Our specialist will answer all questions and make an appointment for you at a convenient time.
Papillomas in a child: which doctor should I contact?
Even children can have papillomas, not only adults.
Molluscum contagiosum is common in childhood.
Weak immunity in children also increases the chances of getting HPV.
Children are characterized by the development of this type of papillomas:
- vulgar
- filiform
- flat
- plantar
- on the larynx
- wart dysplasia
- epithelial hyperplasia
If neoplasms occur, you need to show the child to a pediatrician.
And he will decide which specialist should be contacted next.
Depending on the location of the papilloma, this may be a surgeon, dermatologist, proctologist, gynecologist, dentist, ophthalmologist or otolaryngologist.
Visit your doctor immediately if:
- the papilloma has become dark red or black in color
- papilloma is actively growing
- the shape of the papilloma has become unusual
- papilloma became painful when pressed
This indicates the degeneration of benign papilloma into cancer. Consultation and treatment with an oncologist is necessary.
Which doctor treats papillomas in intimate places?
Several specialists may be involved in the treatment of papilloma in an intimate area. Their circle is usually limited to an oncologist, gynecologist, dermatologist, virologist and immunologist. Such specialists are sometimes replaced by one therapist who has a broader profile. This doctor is often called a family doctor.
Consultation with an oncologist for papillomas in intimate places
Before you decide which doctor will remove papilloma in an intimate place, you need to visit an oncologist. Physicians from other industries usually give referrals to such a specialist if there is a suspicion of malignant processes. His tasks are to examine the formation for ulcerations, take a sample for a biopsy, and prescribe the necessary tests that can detect pathological processes in the body.
You can contact such a doctor either in a regular clinic or in a specialized medical institution called an oncology clinic. If possible, it is better to choose a gynecologist-oncologist who combines the responsibilities of two specialists.
Before you consult any doctor to remove papilloma in intimate places, you need to make an appointment with an oncologist. This is due to the fact that not very experienced specialists in other fields sometimes confuse such a growth with a nevus, which it is he who should eliminate, that is, not a dermatologist or cosmetologist!
- Read more about the causes of warts on the genitals
Examination by a gynecologist for papilloma in intimate places
A consultation with this doctor is mandatory for women who have discovered papilloma in an intimate area. He will provide guidance on safety issues during sexual intercourse, explain how to behave in order to avoid infecting a partner, and write out a referral for a smear test and other necessary tests to make a correct diagnosis.
If you don’t know which doctor removes papillomas in intimate places, you need to remember that the gynecologist’s task is to prevent the spread of the formation and exclude cervical cancer, the development of which can be triggered. He has the right to prescribe external agents such as Verrucacid, Lapis Pencil, CryoPharma, etc. for cauterization of tumors.
- See also what papillomas look like in intimate places in women
Consultation with a dermatologist for papilloma in an intimate area
A dermatologist is competent to prescribe antiviral and cauterizing folk remedies, but, unlike a gynecologist, he makes a decision on this based on the results of the patient’s complaints and the recommendations of other specialists. It should be noted that this doctor does not externally assess the condition of papilloma in an intimate place.
When trying to figure out which doctor removes papillomas in intimate places, it is worth paying attention to the fact that a dermatologist can be involved in the process, suggesting the use of liquid nitrogen, electric current, laser or radio knife. He selects the most appropriate technique, depending on the situation, and controls the process itself and the restoration of the mucous membranes after the end of the session.
Important! If possible, it is better to consult a dermatologist-oncologist, who can independently determine the malignancy of the tumor. This is very important because physical therapy removal methods are ineffective if the growth consists of cancer cells. In this case, there is a possibility of its increase in size and the appearance of metastases.
Visiting a virologist for papillomas in intimate places
Before choosing any doctor to remove papilloma in intimate places, you need to remember that, in particular, the role of a virologist is one of the most important. The fact is that eliminating the growth without suppressing the activity of the virus does not give positive results. As a result of this, it becomes possible for re-formation of papilloma in an intimate place in the same areas or in others.
The virologist’s task is first of all to determine the type of HPV, for which he performs the Digene test. This helps to select the most effective drugs for treatment, to which the pathogen will be less resistant. For this purpose, a smear is taken from the mucous membranes affected by the formations.
If you have not yet decided which doctor treats papillomas in intimate places, then it is worth considering that this specialist also prescribes antiviral drugs, which are needed to strengthen the body’s resistance to HPV. Otherwise, therapy may take many months and not bring the desired results. Such a doctor prescribes medications such as Likopid, Kagocel, Tsitovir-3.
Consultation with an immunologist for papilloma in an intimate area
Doctors in this area pursue the goal of improving immunity and increasing the body’s resistance to the papilloma virus. They have the right to issue a referral for blood, urine, and stool tests. Such specialists do not treat the consequences of HPV in the form of growths, but eliminate the causes of their appearance.
Before choosing any doctor to remove papilloma in intimate places, you need to pay attention to the fact that, for example, an immunologist must select the most effective immunostimulants to strengthen the body’s protective properties. These can be both herbal dietary supplements and medical products. They often prescribe Immunal, Imudon, Lymphomyosot, etc. to patients. At the same time, immunologists also monitor the treatment process, making sure there are no side effects.
Oncological assessment of papillomas by a doctor
We know that neoplasms on the cervix very often lead to cancer.
Intracellular changes occur - at first there is mild dysplasia and it all ends in invasive cancer.
This is a protracted process, it lasts from three to fifteen years.
It all depends on various factors and the specifics of the immune defense.
To make a correct and timely diagnosis, the attending physician does:
- taking a smear from the cervix for cytology and performing a PAP test - the gold standard for oncological diagnosis of pathologies in the cervix
- PCR diagnostics determines the type of HPV that caused the appearance of tumors
- colposcopy
- biopsy
- cleansing the cervical canal
The period of a Pap test is two to three years after entering into an intimate relationship.
Even if the papillomavirus has already taken hold in the female body, there will be no cancer yet.
If the PAP test is negative, it must be repeated after a couple of years.
This diagnosis is carried out until the age of thirty.
The young female body copes with highly oncogenic HPV types sixteen and eighteen on its own.
To detect cervical cancer at the initial stage of development, you need to take smears for analysis annually.
Only with such rigorous screening can cancer pathology be determined at the initial stage, when cancer responds well to therapy.
What tests does the doctor refer for for papillomas?
If papillomas are detected, it is necessary to undergo tests to clarify the diagnosis.
It is important not only to establish the fact of the presence of HPV, but also what type of virus it is - highly oncogenic or not.
Diagnostic tests are also carried out when planning pregnancy, as well as to clarify the causes of infertility, miscarriage and other pathological conditions during pregnancy. It is especially important to get tested for HPV for all sexual partners.
HPV is easily transmitted through unprotected sex.
If papillomas are detected, the doctor will refer you for cytological studies.
For this purpose, smears are taken from the cervical canal in the female population, and from the urethra in the male population.
The method is simple and cheap, but it has low reliability.
Often, laboratory assistants doing analysis see something that is not what actually exists.
This leads to false results.
In addition to cytological studies, histological studies are carried out.
Women's cervix is examined using colposcopy.
But the best and most reliable result is obtained by using the PCR diagnostic method.
Moreover, for this it is important to follow the rules of the analysis, because without this you can get a false positive or false negative result.
Who diagnoses HPV?
A dermatologist treats skin diseases, and you should first make an appointment with him if you find epithelial growths in the form of a wart or polyp on your skin or mucous membrane. A dermatologist will conduct an examination, and if papilloma is suspected, he will prescribe an examination to confirm the diagnosis and determine the type of virus.
To diagnose HPV, cytological examination of polyp tissue is usually sufficient. This is a PCR (polymerase chain reaction) analysis based on identifying the DNA structure of the pathogen. The PCR method is considered the most accurate and objective; it makes it possible to determine not only the type of virus, but also its quantity in the body.
If necessary, the following can also be carried out:
- enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, which identifies marker proteins indicating the presence of infection;
- Digene test (this method is used to determine the type of papillomavirus in a smear taken from the cervical mucosa);
- cytological analysis of tissue for the presence of malignant cells.
Histology of papilloma
We talk about the histological method of studying papillomas as an addition to cytological research.
With this research method, a biopsy specimen is examined - a small fragment of tissue.
The biopsy specimen, fixed on a glass slide, is examined under a microscope, after which the cells are evaluated.
Histological examination determines whether the neoplasm belongs to one or another type of HPV.
A conclusion is made whether the neoplasm is benign or a malignant tumor.
The results of the study are ready on the third day after it was conducted.
Then, as a rule, a PCR test is done.
What if a histological examination revealed atypical cells?
It is necessary to carry out therapeutic measures in the form of surgery, radiation therapy or chemotherapy as early as possible, depending on the stage of the oncological pathology.
Thus, timely histological examination helps to identify cancer in the first stages of its development, when real help can still be provided.