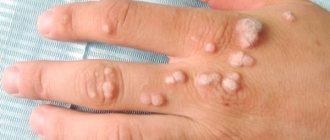
The appearance of genital warts in the perianal area is usually observed in homosexuals, but can also appear in men of traditional orientation. In women, condylomas can affect the posterior commissure of the lips, as well as the labia minora and/or labia majora. Less commonly, genital warts are localized on the walls of the vagina and the walls of the cervix. During oral and anal sexual contact, condylomas can occur in the oropharynx and anus. Condylomas can also affect the external opening of the urethra.
Genital warts usually do not pose a threat to human life or health. However, the appearance of condylomas in the intimate area can develop certain complexes (fear, uncertainty about intimacy), as well as cause significant aesthetic and psychological discomfort. Genital warts are prone to growth and degeneration into malignant neoplasms, so they must be treated. Since drug treatment of papillomas does not guarantee one hundred percent elimination of condylomas in a delicate area, the most effective method will be surgical treatment, which is carried out using one of the destructive methods.
The procedure for removing papilloma in an intimate area (the price will depend on the number, scale, location and prevalence of genital warts) should be carried out in a clinic by a qualified specialist. This will be the key to successful and safe treatment of genital papillomas.
Methods for excision of papilloma in the intimate area
In modern clinical medicine, there are several effective ways to treat genital warts in the intimate area:
- Cryodestruction (removal of genital papillomas with liquid nitrogen);
- Cauterization of genital warts with radio waves;
- Electrocoagulation (burning out papilloma with electric current);
- Surgical excision of condylomas;
- Removal of genital papillomas with laser.
Each method has its own characteristics, limitations, advantages and disadvantages, which should be taken into account when choosing the most suitable method for treating warts in a delicate area. Regardless of what method of papilloma removal is used, the patient is advised to use antiviral, restorative and immunostimulating drugs. This will prevent infection and inflammation of the postoperative wound, as well as increase the body's defenses and strengthen the immune system.
Treatment during pregnancy
Papillomas in the intimate area can grow greatly during pregnancy and subsequently interfere with childbirth. To avoid this, doctors prescribe laser excision of growths and treatment with antiviral substances. During pregnancy, Viferon and Betadine are allowed to be used.
Papillomavirus detected during pregnancy must be treated without fail, as it threatens to infect the fetus (most often during the child’s passage through the birth canal) and cause the baby’s nasopharynx and larynx to be affected by condylomas.
Papillomas on the genitals are an unpleasant and very dangerous phenomenon, since if left untreated for a long time, there is a high probability of developing cancer. Therefore, it is important not to hesitate to consult a doctor if suspicious growths are found in the groin.
Surgical removal of warts on intimate places
The method of traditional excision of genital warts is used for the following indications:
- Lack of positive effect after other methods of treating genital warts;
- Malignancy of papilloma;
- The presence of large and deeply ingrown neoplasms;
- Impossibility of carrying out other destructive techniques due to objective reasons.
Surgical removal of papillomas involves complete excision of the condyloma under local anesthesia using a scalpel. After the procedure, sutures are placed on the wound, which, if necessary, are removed 10-12 days after the intervention. In order to eliminate all pathologically changed cells during the procedure, quite extensive damage to healthy surrounding tissue occurs, which can lead to bleeding of the postoperative wound. The disadvantages of surgical treatment of genital papilloma include:
- Long and painful rehabilitation period;
- High risk of bacterial infection and inflammation of the postoperative wound;
- Formation of scars and scars.
To relieve pain and reduce the likelihood of postoperative complications, the patient may be prescribed antibacterial and painkillers.
Routes of infection
HPV is very easily transmitted from person to person. Entry into the body occurs in several ways.
| Method of infection | Description |
| Sexual | When genital warts occur in intimate places in women, this is the main method of infection. The virus can enter the body through oral-genital and anal contact. |
| Contact and household | The virus can survive for a short time in exfoliating skin cells, so the presence of damage to the skin and mucous membranes, even of a microscopic nature, allows viral particles to penetrate the human body. Infection occurs when visiting public toilets, swimming pools, baths, and gyms. |
| Autoinfection | The woman herself can spread the virus to new areas of the skin when shaving and epilating. This route of infection is also called autoinoculation. |
| From mother to child | The viral infection can be transmitted from mother to child during childbirth. This causes the appearance of papillomas in a newborn on the mucous membranes of the mouth, pharynx, genitals, and in the anus. |
The likelihood of infection increases in the presence of predisposing factors.
Removal of papillomas in intimate areas using electrocoagulation
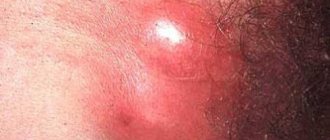
Electrocoagulation of genital warts involves applying electric current to pathologically altered tissues of the neoplasm. Through various electrodes, microcurrent is directed to the papilloma, which leads to the destruction and further death of pathological cells. Cauterization of condylomas by electrocoagulation is a rather painful procedure, so it is performed using anesthesia. Treatment of genital warts with an electric charge is most effective when combating fresh tumors. Electrocoagulation of deeply ingrown condylomas can lead to re-formation of the growth, which is due to incomplete excision of the wart.
Removal of genital papillomas by cryodestruction
Cryodestruction (cryotherapy) of condylomas is one of the most common and effective methods of combating genital warts. Cryotherapy is a procedure for hardware or manual cauterization of condyloma with liquid nitrogen, which leads to the destruction and destruction of pathologically altered tissues. Before cryodestruction, the doctor determines the required intensity and depth of exposure by assessing the size, location and number of condylomas. An insufficient level of exposure can provoke incomplete destruction of the wart, which will lead to recurrence of the tumor. For excision of small and single condylomas, one session is sufficient. Cauterization of multiple and large genital warts may require multiple procedures.
A few hours after the procedure, a bubble forms at the site of exposure to liquid nitrogen, which can cause significant discomfort. Damage to it is fraught with infection and inflammation of the postoperative wound, so the blister should be protected from various types of mechanical influences and not pierced. If the blister strongly tightens the skin, limits the patient’s movements and interferes with wearing underwear, a specialist can puncture it in a clinic and apply a sterile bandage.
Cauterization of papillomas in intimate places with a laser
Laser excision of genital warts is one of the effective methods of combating condylomas, which is characterized by a short rehabilitation period and a high cosmetic effect. Under the influence of narrowly directed laser beams, the liquid inside the cells evaporates, followed by the destruction of the pathological neoplasm. The frequency and depth of radiation is selected in such a way as not to affect healthy areas of the epidermis. Due to this, the risk of postoperative complications is minimal. During the procedure, the doctor can control the intensity and level of laser exposure, which makes it possible to combat formations of various sizes and locations.
After 2-3 days, a crust forms at the site of laser exposure, under which the skin restoration process occurs. Injuring it can lead to the formation of scars and the spread of infection. After a while, the crust falls off on its own and a small scar appears in its place. With the help of various healing medications, plastic surgery and physiotherapeutic techniques, maximum aesthetic results can be achieved, making it almost invisible.
The benefits of laser excision of genital warts include:
- Coagulating properties of the laser, which eliminates the possibility of bleeding during and after the procedure;
- The disinfecting effect of laser beams, which reduces the risk of bacterial contamination and the spread of infection;
- Short rehabilitation period;
- Efficiency and efficiency of the procedure;
- Minimal number of postoperative complications.
The laser treatment procedure for condylomas, like any surgical intervention, has a number of contraindications. These include:
- Tanned skin;
- Suspicion of the malignancy of the wart;
- Increased sensitivity to light exposure;
- Herpetic infection in the acute stage;
- Exacerbation of chronic diseases;
- Acute course of inflammatory and infectious diseases.
Forms of existence of HPV in the body
Once in the female body, the virus penetrates the epithelial cells of the skin and mucous membranes, where it can exist in two forms.
| Form of existence of HPV | Characteristic |
| Episomal | The inactive stage of virus development, which is considered benign. Viral particles are located outside the cell's chromosomes. Observed in asymptomatic carriers of the virus. It is observed in patients with good general body resistance. |
| Introsomal | The active stage of HPV development is regarded as a malignant form of parasitism of viral particles in the body. The virus integrates into the genome of epithelial cells and begins to control the cellular genetic material for the reproduction of HPV-encoded proteins, which leads to the appearance of clinical symptoms. |
Burning out papillomas on intimate places with radio waves
Radio wave excision of genital warts is considered the most effective and safe method of combating condylomas. Radio wave treatment of genital warts is carried out using a special radio wave surgery device - Surgitron. Under the influence of narrowly directed radio waves emitted by the device, intracellular evaporation of fluid occurs and the destruction of condyloma. Before performing the procedure, the specialist assesses the number, size and location of genital warts, and then selects the appropriate instrument. This will allow you to control the depth and intensity of radio wave exposure. Excision of genital warts using radio waves is carried out using anesthetic drugs.
The benefits of treating warts with radio waves include:
- Short rehabilitation period;
- Minimal damage to surrounding healthy tissue;
- Possibility of excision of large and multiple condylomas;
- No postoperative side effects;
- Efficiency of the procedure.
The disadvantages of this method include a fairly wide list of contraindications.
Choosing the most effective method for removing papilloma
Before choosing the most appropriate method of treating genital warts, the patient undergoes a preliminary comprehensive diagnosis, which includes an examination by a dermatologist, as well as a number of instrumental and laboratory tests. A consultation with an oncologist will also be required to confirm or deny the malignancy of the tumor. If papillomas are removed using painkillers, the patient should consult with an anesthesiologist who will select the optimal painkiller, its dose and method of administration (injection, gel or spray).
The choice of papilloma removal method will depend on the following factors identified during the diagnostic process:
- Age and health status of the patient (presence of chronic diseases, mental disorders);
- Presence of allergic reactions;
- The nature of the neoplasm;
- Number, size and prevalence of condylomas.
Should I go to the doctor if my papillomas itch?
If one or more papillomas begin to itch for no reason, it is important to immediately contact a specialist to find out the cause of the discomfort and, if necessary, undergo treatment.
The appearance of itching is often associated with a decrease in the body’s immune defense, which provokes the activation of HPV and the formation of new rashes on the skin.
In the case when, after pressing the papilloma, it stops itching, then you can calm down.
If the growth is not always manifested by the presence of discomfort, does not change color, or increases in size, then these symptoms indicate that nothing terrible is happening.
However, if symptoms of itching occur frequently, then it is better to see a doctor.
If itching appears and the papilloma turns red, then this is a dangerous sign, so a visit to the doctor is inevitable.
Moreover, this must be done as soon as possible in order to avoid dangerous consequences.
If relapses occur after removal of papillomas, you should visit a doctor to undergo an examination and find out the reasons.
In this case, you will most likely have to see an oncologist.
Recovery period after papilloma removal
Regardless of which method of surgery for genital warts is used, the procedure is followed by a course of rehabilitation, during which the patient should adhere to the following recommendations:
- Refrain from intimacy;
- Women are not recommended to use vaginal suppositories and tampons;
- Do not douche;
- Do not wet the postoperative wound during the first 2-3 days;
- Do not scratch or subject the resulting crust to mechanical impact;
- Maintain regular genital hygiene and treat the surgical wound with prescribed medications.
Compliance with these recommendations will reduce the recovery period and prevent the occurrence of adverse complications (infection, bleeding, inflammation of the postoperative wound).
You can carry out effective and prompt removal of papillomas using any of the existing destructive methods in our clinic, where experienced and professional specialists work. The availability of advanced equipment and an individual approach to the patient will be the key to successful and safe treatment of any skin tumors. The price of the papilloma removal procedure will depend on the qualifications of the doctor who performs the operation, as well as the location, size and number of condylomas.
Attention!
This article is posted for informational purposes only and under no circumstances constitutes scientific material or medical advice and should not serve as a substitute for an in-person consultation with a professional physician.
For diagnostics, diagnosis and treatment, contact qualified doctors! Number of reads: 9645 Date of publication: 09/17/2018
Dermatologists - search service and appointment with dermatologists in Moscow
Symptoms
Genital papillomas in women can be single or multiple (see photo), small or large in size. Usually, during initial growth, they look like small flesh-colored or pink nodules, and later turn into growths in the form of papillae, similar in appearance to the comb of a rooster or cauliflower inflorescences. They are soft in consistency and have a so-called stem. Sometimes they grow up to several centimeters in diameter. The most common sites of localization in women:
- vaginal part of the cervix;
- walls and vaults of the vagina;
- labia;
- urethra;
- perineal skin;
- area around the anus;
- groin area.
Genital warts often exist asymptomatically. In this regard, women do not complain, especially with small lesions. Bleeding and weeping appear when the growths are traumatized, itching, pain, and sometimes an unpleasant odor - when ulceration and the addition of a secondary bacterial infection. Discomfort during urination occurs when papillomas are localized in the urethra, and during defecation - in the anus.