When purulent formations form, a large pimple appears on the skin. It does not bring serious consequences for health or life, but discomfort appears that develops into severe pain. The cosmetic defect causes stiffness of movement and suppresses the patient’s psycho-emotional state. Timely treatment is required so that the pathology does not spread and enter the systemic bloodstream.
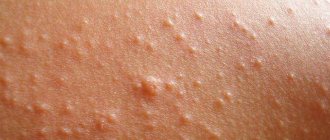
What does a boil look like in the intimate area at different stages of maturation?
Trouble in a woman’s intimate area is indicated by soreness and swelling of the skin. As the inflammatory process progresses, body temperature increases. A furuncle on the pubis matures in less than ten days, and often bursts prematurely due to mechanical damage when it comes into contact with tight underwear.
The anterior abdominal wall has well-developed subcutaneous fatty tissue, and therefore, to a greater or lesser extent, depending on the woman’s weight, protrudes slightly forward. If two or more hair follicles are affected in this area, there may be several boils and a carbuncle is formed.
Stages of boil maturation:
- At the infiltration stage, the pathogen infects the hair follicle, actively multiplies and inflammation spreads to the sebaceous gland and connective tissue. The surface of the skin rises in the form of a bump and turns red.
- The inflammatory process in the lesion continues and an internal core filled with pus is formed from the necrotic contents. On the surface, its edge is visible in the form of a dirty white ball.
- After the breakthrough, the healing stage begins. During the regeneration process, the wound heals and a scar forms on the skin.
Squeezing out boils in the intimate area on your own, especially if the boil is located on the labia majora, is dangerous for a woman due to the risk of infection of surrounding tissues and the development of complications.
Mechanism of boil formation
A boil in an intimate area is formed as a result of penetration of Staphylococcus aureus into the hair follicle. In its normal state, it lives on the surface of the skin of every person. However, when the skin is irritated and damaged, it penetrates into the dermis and epidermis.
Instructions for the use of Taktivin injections and analogues
Important: this is why it is so important to treat wounds and microcracks on the skin with antiseptics in a timely manner.
The mechanisms of formation of a boil on the skin look like this:
- Staphylococcus that penetrates the skin provokes an inflammatory process. This affects the hair follicle itself, the tissue and fatty tissue around it. At this point, the patient may feel painful swelling and slight redness in the affected area. There may be a slight burning sensation. This condition lasts from one to three days.
- Next, a purulent-necrotic process begins in the skin. That is, a purulent core forms in the affected area. During its maturation, the patient may experience even more severe pain, clearly defined swelling and compaction in the affected area. In this case, the boil takes on a cone-shaped shape, and in its center a pustule appears - the head of a purulent rod. At this stage, a person can feel all the symptoms of the intoxication process - headache, fever up to 38°, body aches, apathy and lack of appetite.
- Approximately on the sixth or seventh day from the beginning of the development of the boil, the lid of the abscess breaks through and the purulent core comes out. From this moment the healing of the wound begins. Initially it may have a blue-red color, and then gradually fades.
Important: trying to squeeze out a boil is strictly prohibited. This can lead to rupture of the purulent core inside the tissue and further blood poisoning. As a result, the boil can metastasize - appear in different parts of the body at regular intervals (furunculosis develops).
Why do boils occur?
Boils in the groin area in women are not uncommon due to the fact that the skin in this area has many sebaceous and sweat glands. If hygiene is insufficient or the skin is damaged due to unsuccessful depilation, the pathogen has the opportunity to penetrate the layers of the dermis. Boils can also be caused by inflammation of the Bartholin gland.
Other risk factors:
- infectious diseases in the chronic stage;
- hyperhidrosis;
- violation of metabolic processes;
- endocrine pathologies.
Any sluggish chronic disease undermines a woman’s immunity, and at the same time the protective properties of the skin decrease. As a result, the “guardians of the body” are unable to cope with the task of containing the population and repelling attacks from pathogenic strains of staphylococci. Boils appear in the groin area.
Causes
Abscesses in intimate places can form in any person. This disease is not divided into only male or female disease. Absolutely anyone can sit in a cold place and catch a cold. Even a temporary decrease in immunity can cause the formation of a boil. Pimples can occur if you do not adhere to all hygiene requirements. In men, boils often become inflamed due to uncomfortable clothing that constantly rubs the skin.
During pregnancy
During pregnancy, all the strength and reserves of immunity go to the child. The body gives valuable microelements, “building substances” for the development of a healthy fetus. At the same time, immunity naturally decreases. Pregnant women may encounter problems such as boils. You can't ignore a pimple. This can lead to serious consequences that may affect the child. For example, a carbuncle (a collection of several boils) may occur.
If the pimple is not treated immediately, the woman may develop furunculosis. This is the repeated appearance of a boil. Features of the disease:
- This form of the disease leads to intoxication and negatively affects the fetus at any stage of pregnancy.
- A boil that is subject to constant friction leads to an abscess, which allows the infection to go beyond the infiltrate and penetrate into the blood, overcoming the placental barrier.
Possible diseases that boils on the perineum may indicate
The cause of boils in the groin may be due to a number of infectious diseases. With inflammation of the Bartholin gland caused by staphylococci, the gland increases in size, turns red and becomes extremely painful. The inflammatory process is accompanied by a significant increase in body temperature (can reach 40 degrees).
The infection can enter the gland duct through the blood or lymph, as well as with urethritis or colpitis from the vagina or urethra. In addition to staphylococci, extensive inflammation can be provoked by E. coli, streptococci, Candida fungus and other pathogens.
If there is an infection in the body, boils affect the intimate area when one or another provoking factor occurs. For example, the trigger for starting the process can be banal hypothermia.
Stages, symptoms of the disease
The table lists each stage of abscess formation and negative symptoms leading to discomfort.
| Stage | Symptoms |
| Infiltrate | The skin turns red, thickens, and swells. A large number of immune complexes are released that develop an inflammatory response. Up to 3 cm of infiltrate can accumulate inside. The skin thickens and enlarges, causing severe pain. The hair follicle and the hair itself are preserved in the center of the formation. An area of inflammation remains inside the follicle, causing burning and tingling |
| Purulent-necrotic area | Forms by 4 days after the onset of the pathological process. The purulent formation is actively maturing and a core is forming. The head increases in size, so it rises above the surface of the skin. The pain syndrome becomes brighter and intensifies with pressure, walking, and other movements. There is strong pulsation, a rise in body temperature, and an increase in regional lymph nodes. Due to intoxication, arthralgia and myalgia appear. Lymphocytes, pus, and abundant bacteria accumulate inside the formation. The skin bursts, the infiltrate comes out. |
| Regeneration | When the purulent contents come out along with the rod, all discomfort and symptoms stop. Pain, itching, redness are eliminated. If the opening occurs spontaneously, the liquid gradually comes out. A large wound is formed that will heal within 3 days. Then she turns pale. Thanks to active tissue regeneration, the skin actively heals. But a large connective tissue scar may form at the site of the wound. |
If the doctor eliminates the boil, the removal of the rod is required. Otherwise, the bacteria in it will multiply again, causing another purulent infiltrate.
Complications
A boil in an intimate place creates a risk of developing serious complications. If the pathogen manages to reach the woman’s inguinal lymph nodes, lymphadenitis begins. When a lymphatic vessel is affected, it is called lymphangitis.
When pathogens spread to surrounding tissues, perilymphangitis may occur, accompanied by damage to muscles and joints. Treatment of these pathologies is long-term and always complex. Its most important part is to stop the spread of infection, stop the inflammatory process and prevent the disease from becoming chronic.
If a woman thought that the opening of the abscess had solved the problem and did not consult a doctor, there is a high risk of sepsis, the spread of infection to the lymphatic system through nearby nodes and the occurrence of complications in the form of cyst formation. In this case, more serious surgical intervention will be required.
This is especially important in the case of bartholinitis. In most cases, the abscess breaks out on its own after a week or a couple of days longer. At the same time, the woman notes clear signs of recovery: body temperature drops to normal, swelling of the problem area subsides, and pain decreases.
Treatment
A purulent abscess in the groin is a very unpleasant and extremely painful phenomenon, so it is necessary to get rid of it in the early stages of development, before secondary symptoms appear. To slow down (or completely stop) the formation process, it is enough to use compresses. As a rule, there are two varieties:
- cotton wool soaked in salicylic alcohol;
- Vishnevsky ointment or ichthyol ointment.
These methods are the most effective and can significantly alleviate the condition. However, they do not guarantee that a boil on the pubis will be cured, so it is necessary to consult a doctor who, depending on the stage of development and other accompanying symptoms, will prescribe surgical or therapeutic intervention.
Surgical treatment is the direct intervention of a surgeon to remove accumulated subcutaneous pus. The operation takes place under local anesthesia, followed by opening of the abscess and complete cleansing of pus. Afterwards, the patient undergoes postoperative physical therapy and can leave the medical facility. There is practically no pain in the postoperative period, the chances of a successful operation are 100%. The only drawback is a small scar that may remain as a result of surgery to remove the abscess.
Sakania Luiza Ruslanovna
Dermatovenerologist, cosmetologist, trichologist
Ask a Question
Therapeutic treatment consists of treating the resulting abscess with various antibacterial agents. The entire therapeutic session of the procedure is aimed at reducing the abscess, reducing inflammation and preventing possible negative consequences. The procedure must be carried out under the direct supervision of a specialist who, in an emergency, will refer you for surgery. In exceptional cases, topical antibiotics - erythromycin, dicloxacillin or tetracycline - can be prescribed to treat an abscess.
It is worth noting that self-removal of a subcutaneous abscess can lead to various consequences. From the return of former discomfort to severe damage to the epidermis. It is also not possible to completely clear the accumulated pus or transfer foci of inflammation to adjacent unaffected tissue. In the most severe cases, blood poisoning can occur, as bacteria can quite easily leak into the circulatory system.
Boil during pregnancy
A boil in the groin especially causes a lot of trouble for women during pregnancy. Symptoms of the disease are even more pronounced:
- severe weakness;
- headache;
- increased body temperature;
- extremely severe pain at the location of the abscess.
If a boil appears in the intimate area, a pregnant woman should immediately seek help from a doctor. In an uncomplicated form, it will be enough to control the process of its maturation; in a severe form, the abscess will be removed surgically.
Ignoring the problem threatens the health of both the woman herself and her unborn child. Furunculosis suffered by a pregnant woman can result in mastitis after childbirth. During pregnancy, the boil threatens to infect the amniotic membranes, which is fraught with disturbances in the development of the fetus even at the stage of formation of internal organs and systems, and spontaneous interruption of gestation.
How to treat a boil in an intimate place
A boil in the groin should not be treated as an ordinary abscess that will ripen, burst and leave no trace. Due to its proximity to the genitals and pelvic lymph nodes, furunculosis can cause serious consequences for a woman's health.
Pharmacy medicines
Treatment of a boil in the groin in women is standard and depends on the general condition of the body, the presence of other chronic diseases, the stage of maturation of the boil and the severity of the furunculosis.
In most cases (for uncomplicated boils), local therapy is used. Heparin, Ichthyol ointments and Vishnevsky's liniment help to cure the boil and accelerate its maturation.
If the abscess suddenly opens, medical alcohol or hydrogen peroxide is used to remove the leaked necrotic contents and treat the edges of the wound. Antibiotics are used only in extreme cases when there is a risk of complications.
How to get rid of it surgically or with hardware
Under no circumstances should you remove a boil in the intimate area yourself. If the boil is located on the skin of the thighs, buttocks, or in the pubic area, surgical intervention is performed according to standard procedures. Manipulations are performed under local anesthesia.
After anesthesia, the surgeon makes an incision in the problem area to remove purulent-necrotic contents. Using a special tool, the dense core of the boil is removed.
The wound is additionally cleaned of residual pus and disinfected. Over the next three days, the problem area will require special attention from the woman. Sterile dressings should be changed and strong pressure should be avoided.
After surgery (removal of the root of the boil and disinfection of the inflammation zone), antibacterial ointments are used to accelerate wound healing: Levomekol, Syntomycin, Gentamicin and other drugs.
If the boil was located on the labia or there was an abscess of the Bartholin gland, the specialist will evaluate its truth: the swelling of the gland has softened, and a purulent capsule-rod has formed in its cavity and is clearly visible.
How to treat at home
Boils should be treated at home only as directed by a doctor. In uncomplicated forms, the use of ichthyol ointment may be recommended. It is applied to a sterile bandage folded several times and not too tightly fixed at the location of the boil.
You can make a compress and leave it for several hours. The bandage should be changed at least three times a day. Manipulations should be performed only after treating your hands with an antibacterial agent. When a convex purulent center is clearly visible on the surface of the boil, you need to contact a surgeon to remove it.
Therapy methods
The selection of treatment depends on the stage at which the boil is developing. Home therapy is usually sufficient. If complications occur, hospitalization will be required. For example, if the abscess has reached the subcutaneous fat or systemic blood flow, a large abscess has formed.
Most often, local therapy is prescribed; in the absence of its effect, surgical techniques are prescribed:
- Treatment with antiseptics
. Salicylic alcohol, hydrogen peroxide, and other antiseptic drugs are prescribed. They treat tissues using cotton wool to prevent the spread of infection. The hair in the affected area is cut off. - Anti-inflammatory therapy
. To eliminate excessive activity of the immune system, the application of alcohol compresses is required. Additionally, Chlorhexidine and Miramistin are used for disinfection. Compresses can be used with Levomekol, Ichthyol. They relieve inflammation, pain, and destroy infection. A keratoplasty effect develops. To make a compress, first apply ointment to the affected area. Apply cotton wool or several layers of bandage on top. Leave for several hours, then remove. Physiotherapeutic procedures have a qualitative anti-inflammatory effect. For example, the use of ultraviolet or laser. - Second stage therapy
. It is necessary to create all the conditions so that the boil matures faster and prepares for spontaneous opening. Pre-treat the affected area with ointments that cause ripening. For example, Vishnevsky, Ichthyolova. An antibiotic ointment is then prescribed to reduce the number of pathogenic microorganisms. The abscess is opened through surgery and all contents are removed. - Injections of antibiotic and novocaine
. This helps to simultaneously eliminate pain and reduce infection. The doctor prescribes injections until the core of the boil is completely eliminated. Compresses based on silver nitrate have a similar effect. - Systemic antibiotics
. Used as injections or oral tablets. Penicillins, macrolides, cephalosparins are prescribed. Additionally, NSAIDs are used to relieve pain, inflammation, and relieve elevated body temperature. Use drugs based on paracetamol or ibuprofen. - Surgical extraction
. Pre-treatment with salicylic acid is carried out. It helps the skin burst so that the contents of the abscess begin to come out. The rod is removed using a clamp. A rubber band is left inside for 3 days to allow further drainage of pus. After time has passed, it is removed. Surgical methods can be resorted to only if there is no effect from conservative techniques. - Sanitation
. The technique is applicable after opening and complete elimination of the abscess. They are treated with antiseptics and antibiotics. For example, hydrogen peroxide is used, thanks to which the remains of lymph and pus are eliminated. After the healing stage has begun, it is allowed to use Vishnevsky ointment in the form of a compress for another 3 days. Ichtheol ointment is not recommended at this stage, since the bacterial infection will be difficult to eliminate.
If the treatment is not of sufficient quality, there will be a risk of relapse. Therefore, it is necessary to pay close attention to all stages of processing.
When treatment is carried out, all hygiene rules must be carefully observed. Additionally, it is prohibited to visit baths, saunas, and gyms. As soon as the wound healing stage has begun, Contractubex is allowed to be used. It prevents the formation of a large connective tissue scar.
Video ideology and stages of furunculosis
How not to treat an abscess
Due to the high risk of complications of a boil in the intimate area, it is prohibited to perform any cauterizing manipulations, much less use iodine, brilliant green and other coloring solutions for these purposes. When removing an abscess, due to such actions, difficulties may arise in determining its true size, and therefore the stage of maturation.
If there is severe pain in the problem area, headache and elevated body temperature, a woman should seek help from a doctor. You should temporarily refrain from water procedures (bath, shower). Contact with water can cause loosening of the purulent core, and the infection will spread to nearby tissues.
Danger of infection
Patients are often interested in whether pustules that occur in the perineum are transmitted. Such abscesses in themselves do not pose a danger to others, but when they open, exudate with a high concentration of pathogens comes out.
Inflammation caused by staphylococcus develops in stages, starting after purulent masses enter healthy areas of the skin with hair. This is how phlegmon can form, when many infected foci appear over a large area, between which there is a small distance. For this reason, experts do not recommend opening and removing the abscess on your own.
There is a high risk of purulent exudate entering the bloodstream due to the abscess not having time to completely clear, its improper squeezing, and failure to comply with basic hygiene rules. As a result of this process, an abscess or blood poisoning develops . A specialist will tell you what to do in such a situation.
Preventing the recurrence of boils
If a single boil appears, we are clearly talking about the need to increase immunity. Since the formation of boils is caused by certain strains of staphylococci, the doctor will prescribe medications to suppress the pathogen on an individual basis. It is prohibited to take antibiotics on your own. Multiple boils will require complex treatment.
Instead of self-medication, it is important to follow simple rules of prevention:
- monitor general hygiene and genitals in particular;
- if sexually transmitted infections are detected, it is imperative to treat them further - complete the course prescribed by the doctor even if the visible symptoms of the disease cease;
- prevent the presence of chronic foci of infection in the body;
- avoid hypothermia - women, like men, are not recommended to sit on cold surfaces and perform genital hygiene procedures with too cold water;
- control your water balance, drink clean water in small sips between meals;
- balance your diet and include foods rich in vitamins A, C, E, and group B.
Boils in a woman’s intimate area, regardless of the severity of the disease, should always be a reason to consult a doctor.
Prevention methods
You can always use certain measures to reduce the risk of bacterial infection accumulating on the skin and penetrating into the deeper layers. To do this, use the following rules:
- for excessive sweating, use talc and powders that remove moisture from the epidermis;
- daily use of hygiene procedures;
- consumption of high-quality foods and multivitamins that supply the body with the maximum amount of nutrients;
- strengthening the immune system, hardening procedures;
- elimination of situations leading to hypothermia;
- proper treatment of skin wounds to prevent infection.
If redness and thickening of the skin begins on the patient’s body, it is necessary to carefully monitor this area. If symptoms of furunculosis appear, it is recommended to promptly consult a therapist who will prescribe treatment methods. It is important to start antiseptic and antibacterial therapy in a timely manner so that the infectious area decreases. If treatment methods are carried out in a timely manner, the lesion can be completely eliminated within 7-10 days. This will help eliminate the risk of complications and the need for surgical intervention.