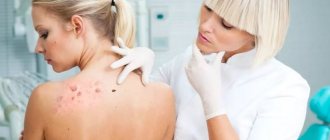
Papillomas are small skin growths caused by a virus that infects the human body. Despite the fact that in most cases such tumors are not dangerous, they cause a lot of discomfort and are often perceived as a cosmetic defect. Therefore, it is important for patients to ask whether it is possible to get rid of papillomas and whether there are methods for removing them at home.
It is important to have a good and strong immune system, this is the only way to protect yourself from many diseases! And of course, it is important to have a good and healthy diet, otherwise you will not be able to, so you can read about all the benefits and harms of Chinese cabbage here, just by clicking your mouse. How exactly does this vegetable affect the human body?
Why do papillomas occur?
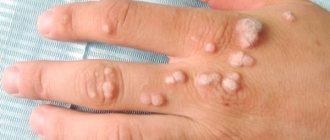
A papilloma, or wart, is a benign skin growth that is a process of increased cell proliferation and growth. These lichens can be of various shapes and sizes, appearing on almost any area of the skin and even on the mucous membranes. Despite such diversity, there is only one reason for the appearance of this pathology - the penetration of the human papillomavirus into the body.
To date, about one hundred strains of this virus are known. Some of them are completely harmless, but are dangerous and can lead to cancer. In most cases, the virus is transmitted from person to person during sexual intercourse. However, other methods of transmission are also possible, in particular at home (sharing of towels, bed linen, hygiene products, etc.) and contact (you can infect virus particles through close contact with a person, but only if there are wounds and lesions on the skin ). Sometimes the infection is transmitted to the baby from the mother during childbirth. Statistical studies show that almost 80-90% of the world's population are carriers of the virus.
On the other hand, not everyone has warts. External symptoms of the disease are associated with a decrease in immune activity. Inflammatory diseases, poor nutrition, vitamin deficiencies, constant stress, physical and emotional fatigue can trigger the appearance of skin structures.
Papillomas and warts: nature and causes of appearance
Papillomas and warts belong to the category of benign neoplasms, or tumors, that develop from epithelial tissue and can affect any part of the body, including mucous membranes and internal ducts. (Warts are often also called papillomas - due to the same source of occurrence, as well as due to external similarity. We will consider them separately, since the differences between these neoplasms will influence the choice of how to solve the problem.)
Papillomas and warts have a single source of appearance - the human papillomavirus (HPV). Damage occurs through direct contact (contact of skin or mucous membranes) or indirect (through contaminated objects, use of public baths, saunas, exercise equipment, etc.) subject to the presence of mechanical and other damage to the skin (wounds, scratches, chafing). Transmission of the virus is facilitated by excessive sweating. The immune characteristics of the body play a role: with a decrease in immunity, the formations may become larger and they are more resistant to elimination.
Human papillomavirus infection is widespread: according to some estimates, the problem affects 300 million people in the world (in Russia, about a third of the population suffers from it). Well, as mentioned earlier, more than 80 percent of the planet’s population are carriers of the virus. There are over 600 types of HPV strains.
Benign formations that arise due to HPV are divided according to the type of organisms affected (there is a human virus, but there are only animals), according to the appearance of the formation and its shape, according to the location (skin or mucous membranes), according to the rate of growth.
The virus manifests itself on the skin under the influence of the following factors: a decrease in immunity (including due to HIV infection, oncology, leukemia, taking immunosuppressive drugs such as glucocorticosteroids, cytostatics, radiation therapy), hormonal fluctuations, stress, hypovitaminosis, bad habits, skin damage (cuts, scratches, abrasions, etc.), ignoring the rules of personal hygiene, active sex life without the use of barrier contraception.
Is it safe to remove papillomas at home?
It is worth saying that there are many ways to get rid of warts. Medicine offers faster, safer and painless treatment. However, it is also possible to remove papillomas yourself. But here you need to pay attention to several main points:
- Treatment of papillomas can be started only after consultation with a doctor. The fact is that some viruses are dangerous because they contribute to the development of cancer. A careless attempt to remove a wart when infected with an oncogenic virus can lead to malignant transformation of cells. Therefore, a complete diagnosis is necessary first.
- Under no circumstances should nipples be torn off or cut, as there is a high risk of tissue infection, suppuration and inflammation.
- Papillomas should not be removed from the mucous membrane of the oral cavity, larynx, nasal passages and eyelid skin. Only a doctor has the right to perform such procedures.
- It is worth understanding that removing papillomas at home often takes a lot of time, so you should not count on an immediate effect.
Why do you need to remove papillomas and warts?
For the most part, benign neoplasms such as papillomas and warts do not cause direct harm to health. Some papillomas can remain on the skin for decades without changing their appearance or increasing in size. However, they create certain difficulties and risks. Thus, a wart on the foot often tends to grow and over time begins to poison life with everyday pain when walking. Warts on the fingers (these often appear in children) or hanging papillomas in the folds of the skin in women can lead to injury to soft tissues. For example, if papillomas are located in the chest or back area, then in the process of constant friction (for example, against a harness or bra clasp), the neoplasms can accidentally be torn off, bleed and become inflamed. Often others begin to appear near one papilloma.
There is an even more serious reason for timely removal of tumors. Among the numerous strains of papillomavirus, non-oncogenic, weakly oncogenic and types of HPV with a high level of oncogenicity are known. The latter are at risk of degeneration: neoplasms that appear due to their fault can, over time, turn from benign to malignant. By removing such tumors in a timely manner, skin cancer can be prevented.
The problem also lies in the fact that an ordinary person can mistake another, more dangerous neoplasm for a papilloma or wart, and either take up self-medication or simply not pay attention to it. Therefore, with all questions and doubts, it is important to go to a specialist (dermatologist), he will conduct a diagnosis, determine the origin of the tumors, the degree of danger and then suggest treatment methods that are optimal in this case.
It is highly not recommended to remove papillomas and warts on your own, without first examining a specialist: this may not only not bring the desired effect, but also aggravate the problem (especially you should not rip off or cut off the growths).
Alidzhan Ganemovich Khabbus, dermatovenerologist, cosmetologist, laser therapist, teacher at the Department of Dermatovenereology of North-Western State Medical University named after. I.I. Mechnikova, ICG certified specialist in fractional and laser devices Ilooda (Korea):
“Of course, viral warts require timely treatment, otherwise the process can spread significantly throughout the skin and also lead to infection of surrounding people. As for papillomas, the formations must be removed to prevent their growth, trauma, possible infection and for aesthetic reasons.”
What medications can be used to cauterize warts?
One of the most accessible and simplest ways to remove papillomas is to destroy them with chemically aggressive substances. There are many drugs designed to cauterize skin lesions:
- Such medicinal gels as “Antipapillom” and “Dermavit” contain a base, namely potassium or sodium hydroxide. It is worth understanding that this liquid is very caustic, so it must be used very carefully. Before the procedure, healthy areas of tissue around the nipple should be covered with rich baby cream to avoid burns. Small papillomas usually disappear after the first use, although sometimes the procedure is repeated several times.
- Acids are often used to cauterize warts. For example, an effective removal method is the Collomak solution, which contains polidocanol, lactic acid and salicylic acid. To treat papilloma, one drop of solution is enough.
- Special adhesive tapes for removing papillomas are becoming increasingly popular. This is a small piece of fabric soaked in a special solution. It is fixed on the skin with a patch and should remain there for 4-6 days. Usually during this time the papilloma is destroyed, and its remains are removed along with the patch.
In any case, we should not forget that such products must be used very carefully, since there is always a risk of burns and damage to healthy tissue, after which scars may remain on the skin.
Cryodestruction at home
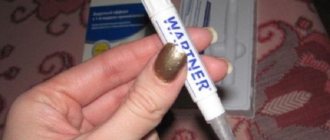
Cryosurgery is a fairly popular method of removing warts. Its essence is to influence the formation of skin using liquid nitrogen or other substances. When exposed to ultra-light temperatures, the cells of the nipple are destroyed, after which it turns black and falls off. This procedure is usually performed in a hospital, but modern pharmaceutical companies offer several products that can be used to remove warts at home.
For example, aerosols “Cryopharma” and “Cryo Wartner” are considered effective. The main active ingredient is dimethyl ether. It is recommended to carefully apply the solution to the wart using an applicator. This procedure immediately freezes the cells. It is worth saying that the drug must be used very carefully, trying not to touch healthy areas on the skin.
Equipping a room for laser tumor removal
General requirements for equipping an office for working with laser equipment, as well as other provisions governing work with laser equipment, are contained in the following regulatory documents:
- SanPiN 2.1.3.2630-10. Sanitary and epidemiological requirements for organizations engaged in medical activities.
- GOST R-50723-94. Laser safety. General safety requirements for the development and operation of laser products.
- Sanitary standards and rules for the design and operation of lasers No. 5804-91.
- OST 42-21-16-86. System of occupational safety standards. Departments, physiotherapy rooms. General safety requirements.
- Standard instructions on labor protection when working with laser devices (the instructions are developed by the head of the laser medicine department based on the Standard instructions on labor protection No. 06-14/20, taking into account the characteristics of a given medical institution).
- MU 287-113-00. Guidelines for disinfection, pre-sterilization cleaning and sterilization of medical devices.
Radio wave removal
This method of removing tumors involves cutting off the growth at its very base using an electrode attachment that emits high-frequency radio waves. This attachment is called a “radio knife”. During the procedure, the blood vessels are coagulated, which prevents the risk of infection of the wound. Depending on the location and size of the tumor, the doctor selects a nozzle of the required size and shape. To remove papilloma on a thin stalk, a loop attachment is used (the doctor pulls off the upper part of the papilloma with tweezers, and uses a loop attachment to cut it off at the base). The procedure is performed using local anesthesia.
The radio wave method can be used on all areas of the skin, but it is not used on mucous membranes. Its advantages are safety (no burns, complications), no bleeding and the possibility of conducting histological examination of excised tissue. The advantages also include a short rehabilitation period (lasts several days). As for the time of the procedure, it lasts about the same as electrocoagulation or laser removal (depending on the amount of work).
This procedure is most suitable for those papillomas and warts that have a narrow pedunculated base, as well as for thread-like papillomas. This method is ineffective for removing flat formations (laser removal or electrocoagulation will come to the rescue here).
Regardless of what equipment you decide to use to remove tumors, you will have to take care of good ventilation to remove combustion products, which should protect the doctor and patient from inhaling harmful substances during the work process. In addition, many serious clinics purchase a special smoke exhaust device for the office designed to perform such procedures.
What should you consider when choosing equipment?
- Availability of permits for the device.
- The price of the device and attachments, consumables.
- Technical characteristics (and at the same time the capabilities of the device).
- Reputation of the supplier company in the market.
- Experience of successful use of this device in other salons or clinics.
- Possibility of training doctors to use the device (when purchasing equipment and after). Will the training be paid or free (check in advance the cost and number of trainees if the training is paid).
- Conditions of warranty and post-warranty service of the device.
- If the company provides such an opportunity, test the device before purchasing.
It should be remembered that dermatovenereologists and surgeons who have received the necessary education and appropriate documentary evidence have the right to work on these types of equipment. To provide services for the removal of tumors using any type of equipment, an enterprise requires a medical license for dermatovenerology.
The editors would like to express gratitude for their assistance in preparing the material:
Alidzhan Ganemovich Khabbus, dermatovenerologist, cosmetologist, laser therapist, teacher of the Department of Dermatovenereology of Northwestern State Medical University named after. I.I. Mechnikov, ICG certified specialist in fractional and laser devices Ilooda (Korea);
Anna Vladimirovna Lopatina, dermatovenerologist, dermatocosmetologist, specialist in the field of laser technologies and rehabilitation, consultant doctor at the Educational Center (Russia, Moscow).
Celandine for the treatment of warts
When it comes to home treatment, almost every traditional healer recommends celandine juice. This plant has very valuable properties and helps to cauterize warts. There are several ways to use this drug:
- Freshly squeezed juice from the stems of celandine can be used if this plant is located somewhere close to home. The procedure is very simple - just cover the papillomas with juice for ten days or until they completely disappear.
- At the pharmacy you can buy celandine extract, which is a concentrate of its juice. This medication can remove warts faster, but should be handled with care as it can burn healthy tissue.
- You can prepare celandine oil at home. To do this, pour 100 g of plant stems with 100 ml of olive oil. Place the drug in a dark, not too warm place and leave for ten days. The resulting oil solution should be used to treat papillomas daily until they are destroyed.
Warts and papillomas: distinctive features and types
A wart is a rather dense growth formed by keratinized epidermal cells. The wart is nourished by an extensive network of capillaries. The durable surface protects the soft interior from damage. The upper part of the wart is usually uneven, but the growth itself has fairly clear boundaries. In this case, the wart may be irregular or round in shape. The size of the wart is 2–10 mm, its color can be flesh-colored, dirty gray or brown. A rod (a black dot surrounded by capillaries) may be located in the center of the wart. The most common locations for warts are the following: feet, palms, knees, elbows (that is, places of increased trauma). Most often, HPV type 2 causes warts.
Alidzhan Ganemovich Khabbus, dermatovenerologist, cosmetologist, laser therapist, teacher at the Department of Dermatovenereology of North-Western State Medical University named after. I.I. Mechnikova, ICG certified specialist in fractional and laser devices Ilooda (Korea):
“A wart is morphologically a dirty yellow or dirty gray papule with an uneven, rough surface, often round in shape. The main histological process is papillomatosis, which is the proliferation of dermal papillae. As is known, they contain the vessels of the superficial network of the middle layer of the skin, therefore, with papillomatosis, the doctor and the patient pay attention to the presence of “black dots”, which in essence represent thrombosed vessels. In addition to papillomatosis, hyperkeratosis and acanthosis (pigmentary papillary skin dystrophy, a type of dermatosis) may be observed, which give the warts a dirty tint.”
The most common types of warts are:
- simple, or vulgar, - round, usually flesh-colored (may darken over time), capable of rising above the surface of the skin up to 5 mm. Such warts often grow. This type makes up 70 percent of the total number of skin neoplasms and occurs most often in young people. It is caused by HPV strains such as 1–4, 27, 29, 57;
- plantar - located on the feet and palms and look like spikes grown into the surface of the skin. They often cause discomfort or pain and interfere with walking. Appear due to the activity of HPV types 1, 3, 27, 29 and 57;
- flat (juvenile) - they have a flat surface, are flesh-colored or brown, and can rise above the skin by 1-2 mm. Appear on the back of the hands or on the face. These warts are usually caused by HPV types 3, 10, 28, 41.
Alidzhan Ganemovich Khabbus, dermatovenerologist, cosmetologist, laser therapist, teacher at the Department of Dermatovenereology of North-Western State Medical University named after. I.I. Mechnikova, ICG certified specialist in fractional and laser devices Ilooda (Korea):
“Vulgar warts most often affect the area of the hands. With multiple warts, as a rule, there are “dropouts”. The most difficult in terms of destruction are periungual and subungual vulgar warts. Flat warts, as a rule, form in young people (usually on the skin of the face and back of the hands); proliferative processes such as acanthosis and hyperkeratosis are not so strongly expressed in them. It is necessary to differentiate flat warts from adenomas of the sebaceous glands, keratomas and other neoplasms.”
Papilloma has a round shape and has a soft structure. Often the papilloma has a wide papillary base and a thin stalk with which it is attached to the surface of the skin. The color of papilloma varies from flesh to brown. Usually papillomas do not cause pain, but sometimes they cause discomfort in the form of itching (if they grow during the period of virus activity). The size of the formation is usually in the range of 0.2–10 mm. HPV strains such as 6, 11, 16, 18, 30, 31, 33 and other types are related to the appearance of papillomas.
Here are the most common types of papillomas.
Simple (vulgar or ordinary) papillomas often appear on the back of the hand or in the groin area (but can occur on any part of the body), they rise slightly above the skin, reach 0.2–1 cm in diameter and usually do not differ in color from the surrounding ones skin areas. They occur due to HPV types 26–29, 41, 63, 77.
Flat papillomas most often appear on the arms, neck, external genitalia, around the anus, and on the cervix. They resemble flat, light yellow plaques in appearance, which rise slightly above the surface of the skin. They can lie deep in the skin. Flat papillomas of HPV types 16, 18, 31, 33 have a high risk of oncogenicity.
Thread-like papillomas, or acrochords, grow on a thin stalk; first appears as a tiny bulge, acquiring a long shape as it grows. These growths often hang from the skin and are soft and may feel watery to the touch. These tumors are caused by HPV types 2 and 7. Most often they appear in people after 40 years of age, located on the thin skin of the eyelids, neck, armpits, mammary glands, and also in the groin area.
Pointed papillomas, or condylomas (genital papillomas), are tiny papillary growths that, when growing in large quantities, form comb-like formations with a sharp edge. These types of papillomas are caused by sexually transmitted types of HPV (types 6 and 11). They are localized on the inner thighs, in the anogenital zone, on the surface of the vulva, inside the vagina and urethra, in the perianal region, on the cervix. They are characterized by rapid growth. Round papular pustules are one of the types of condyloma.
Alidzhan Ganemovich Khabbus, dermatovenerologist, cosmetologist, laser therapist, teacher at the Department of Dermatovenereology of North-Western State Medical University named after. I.I. Mechnikova, ICG certified specialist in fractional and laser devices Ilooda (Korea):
“Acuminate condylomata are caused only by viruses types 6 and 11, which have a low risk of oncogenicity. Clinically, they appear as soft pink areas of mucous membranes, papules with a slightly uneven surface, and may be elevated, pointed, or have a lobular structure.”
Basal cell papillomas most often appear after the age of 50, develop from the basal layer of cells, the diameter ranges from 1 mm to 4 cm. They are formed on the open surface of the skin, near the hair follicle, grow very slowly in size and, as a rule, do not pose a risk of degeneration into a malignant formation (except in very rare cases).
Sometimes papillomas and warts are confused with moles (nevi), but moles have a completely different nature (they do not appear due to HPV).
General properties of papillomas and warts:
- appear due to HPV;
- affect the surface layer of the epidermis;
- have common risk factors (weakened immunity, stress, infectious diseases);
- have blood vessels (damage to the growth can be accompanied by severe bleeding, and also cause itching, irritation, and swelling of surrounding tissues);
- benign nature (which can change under the influence of various factors, and some formations can degenerate into malignant).
Alidzhan Ganemovich Khabbus, dermatovenerologist, cosmetologist, laser therapist, teacher at the Department of Dermatovenereology of North-Western State Medical University named after. I.I. Mechnikova, ICG certified specialist in fractional and laser devices Ilooda (Korea):
“In my opinion, benign formations such as papillomas are not always formed in connection with HPV. The most common localizations of papillomas are the neck, axillary (axillary) hollows, folds under the mammary glands and inguinal-femoral folds, that is, those places where friction occurs on the surfaces of the skin and clothing, which are characterized by sweating. With such mechanical irritation, it is possible to form peculiar protrusions - papillomas, which, when traumatized, can become infected and degenerate into pyogenic granuloma.”
Differences between papillomas and warts:
- papillomas are usually localized in areas of profuse sweating (in the folds of the skin), while warts “grow” in open areas;
- usually papillomas are soft and have a thin stalk, and warts fit tightly to the surface of the skin (have a wide base);
- if the papilloma is able to change its size only in the direction of increasing, then the wart can decrease, and sometimes even disappear completely on its own;
- if the appearance of papilloma is caused by an oncogenic strain of the virus, then it can eventually degenerate from benign to malignant, and warts rarely create such a risk;
- papillomas, having appeared on the skin, do not “go away” on their own without therapy, but warts sometimes disappear on their own.
How to get rid of papillomas on the body using garlic and onions?
Onions and garlic are products that every housewife has in her kitchen. But not everyone knows that they can be useful in the fight against warts. The recipes for making these home remedies are quite simple:
- You can make a special ointment from garlic. To do this, you need to finely chop a few cloves of garlic, mix a teaspoon with two teaspoons of any cream. A small amount of the resulting mixture is applied to a bandage, applied to the wart and glued with a plaster. The compress should be left for 2 - 4 hours, then removed and rinsed with cool water. It is recommended to repeat the course of treatment daily for a week.
- In addition, you can simply gently rub the wart with a clove of garlic.
- In folk medicine, onion peels are often used. First, it is placed in a glass container, then filled with table vinegar, the jar is closed, and hidden in a dark place for two weeks. Then remove the husk from the container, dry it a little, and then apply a protective plaster or bandage in 2-3 layers to the wart. It is better to carry out the procedure before going to bed, and in the morning remove it, wash the skin and lubricate it with Vaseline.
Homemade mixtures for removing skin growths
Traditional herbalists often recommend removing papillomas with commonly available home remedies:
- A fairly effective drug is propolis. Small applications are made from it, applying the solution to a small piece of the bandage. It is applied to the wart and secured with a bandage. Gas systems must be replaced with new ones every 4-5 hours. The same procedure takes two days. Reviews say that after two days, small papillomas dry out and fall off, and larger tumors are reduced in size.
- You can make an effective ointment using castor oil and baking soda. To do this, the ingredients must be mixed until a paste is formed. The growths need to be treated twice a day. Therapy can take a long time - sometimes it takes 2-3 weeks of daily treatment until the papilloma completely disappears.
- Cauterization of nipples can be done with iodine. First, the skin around the nipples should be treated with a rich cream to avoid burns. Next, soak a cotton pad in the iodine solution and gently swab over each wart. The procedure should be repeated 2 to 4 times a day.
- Another affordable and cheap remedy is aloe vera juice. Dampen a cotton pad with it, and then apply it to the wart, securing it with a band-aid. The compress needs to be changed from time to time. It is believed that papillomas disappear after 6-7 days.
- Tea tree oil is another good remedy. It is very easy to use - just apply a drop of oil to the pacifier every day. By the way, this oil has antiviral, bactericidal and disinfectant properties.
- Kalanchoe is a houseplant that has many beneficial properties. The leaf of the plant should be cut and placed with the inside against the nipple, securing a bandage on it. Leave the compress overnight and rinse your skin thoroughly in the morning. It is believed that the first effects of treatment appear after 3-4 procedures.
- Some people have experience removing warts with soap. To do this, it is better to use laundry soap, which is famous for its beneficial properties and is widely used to treat various skin diseases. Papillomas should be covered with a thick layer of dry soap, preferably overnight, without rinsing. Depending on the skin reaction, the “therapy” lasts from 2 to 4 weeks. As soon as the skin around the nipple turns red, treatment should be stopped. The tumor dries out and is destroyed as a result of the inflammatory process.
- Egg white is an affordable remedy for removing papillomas. The tumor should be wiped with protein 2-3 times a day, allowing it to dry completely. Naturally, such treatment takes much longer. Nevertheless, there is an effect from such self-healing.
Hardware methods for removing papillomas and warts
There are different ways to combat warts and papillomas. We will conditionally divide them into those that are carried out without the use of devices, and hardware methods.
Among the non-hardware methods, the following are used: the surgical method, cryocoagulation and treatment with the external use of pharmaceuticals.
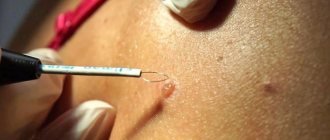
The surgical method involves excision of the growth with a scalpel. This is the most “ancient” method, which is rarely used today (in cases where other methods are not indicated). Excision of tumors with a scalpel has lost popularity due to high trauma, a long rehabilitation period, the risk of scars at the site of tumor removal, and the risk of viral particles getting into surrounding tissues. But it is used in a situation where it is necessary to take a tissue sample for histological examination.
Cryocoagulation, or cryodestruction, is the destruction of neoplasm tissue using low temperatures (100–180 degrees). This method is used to get rid of papillomas, condylomas, keratomas, and birthmarks. Most often, liquid nitrogen is used for work, but other substances (helium, argon) are also used. The doctor applies the required amount of the substance to the surface of the neoplasm, as a result of which the cells of the growth are destroyed, first a small blister forms in place of the affected tissue, and then a crust, which goes away as it heals. A significant disadvantage of this method (which is generally convenient and effective for small and shallow formations) is the inability to accurately control the depth of exposure, that is, during the procedure there is a risk of damage to healthy surrounding tissues. Experts note that sometimes after removal using the cryomethod, a ring-shaped wart forms on the skin around the former neoplasm.
The use of external pharmaceutical products is suitable for combating some warts. This method does not guarantee getting rid of the growth, but due to its simplicity, it is often the first method used for self-treatment of warts. Such self-medication can lead to chemical burns (for example, due to the spreading of liquid pharmaceutical products on the skin).
Hardware methods include electrocoagulation, laser and radio wave therapy. All these methods are popular and have their advantages and disadvantages. Next, we will look at the principle and specifics of the operation of each of them.
Electrocoagulation
Electrocoagulation is the process of thermal destruction of protein under the influence of electric current. Papillomas are removed using a special device - an electrocoagulator, equipped with a special attachment in the form of a loop, forceps, ball or disk. The temperature of the nozzle is adjustable. Modern devices also make it possible to regulate the physical parameters of the electric field and work with high and low frequency current. The device settings allow you to control the depth of exposure and current strength, ensuring the safety of the procedure.
The principle of operation of the electrocoagulator: under the influence of electric current supplied to the nozzle, the electrodes are heated to the desired temperature. When the nozzle comes into contact with the neoplasm, its tissues are exposed to current, coagulation (protein coagulation) occurs in them, as a result, the affected tissues are destroyed and the papilloma dies. At the same time, the thermal effect cauterizes the blood vessels, preventing bleeding and preventing the risk of infections. At the site of the resulting wound, a hard crust forms, which first dries out and then falls off. The skin healing period will require 7–14 days (during which it is necessary to self-treat this area according to the doctor’s recommendations).
Papillomas can be removed in just one session. The time required to remove one neoplasm takes from several seconds to 20 minutes (this depends on the diameter of the base: if it is wide, then the removal of the papilloma will occur in layers and will take much longer than the removal of a papilloma on a thin stalk, which can be burned out quickly, safely and without appearance blood).
Using electrocoagulation, you can remove papillomas and warts on any part of the body, including mucous membranes. This method does not require preliminary preparation. It is used to remove not only papillomas (including condylomas and senile keratomas) and warts, but also other tumors, such as nevi. In addition, this method is considered one of the most affordable due to the low cost of equipment.
The disadvantages of the method include its pain. The procedure is performed under local or injection anesthesia. Another important point is the risk of scars and depigmented areas appearing at the site of the removed papilloma (especially for deep-lying or large-volume tumors). For this reason, it is not recommended to use this method to remove papillomas and warts on the face (here it is better to use laser removal).
Laser removal (laser destruction)
The most popular laser method in the fight against papillomas and warts is the ablative method (ablation is the process of targeted, controlled removal of a certain part of biological tissue using a laser beam to the entire depth of its penetration). Ablation is carried out exclusively using VILI (high-intensity laser radiation). To do this, a dermatocosmetologist can use an ablative laser: CO2 or erbium .
Let us recall that any laser is a source of electromagnetic radiation in the optical range and consists of three main elements: a working fluid (active medium), an energy activation system (pumping mechanism) and a system of mirrors (optical cavity). The energy indicators of a laser are radiation power (W), radiation energy (J), wavelength (µm), energy density (J/sq. cm).
The operation of a laser is based on the principle of selectivity: it implies that laser radiation acts selectively, that is, it is mainly absorbed by chromophores - certain biological target structures that lie in the “absorption peak” of this radiation. For ablative lasers, the chromophore is water: the length and power of their beams heat water in tissues up to 300 degrees Celsius. The water in the skin cells absorbs the energy of the beam and instantly evaporates, and along with it, all the layers through which the beam passes are evaporated.
Laser removal (or destruction) is indicated for the following forms of neoplasms: warts on the hands caused by HPV type 2, plantar warts caused by HPV types 1 and 4, papillomas on the elbows and forearms caused by HPV type 7, any types of papillomas on the face, genital and flat condylomas (genital papillomas).
Removal of a papilloma or wart with a laser beam is carried out layer by layer until the tumor completely disappears. Healthy skin is not subject to destruction. During the procedure, local anesthesia is used if necessary. The procedure itself lasts from several minutes to half an hour, depending on the size and number of elements removed, the use of anesthesia, etc.
Laser destruction is especially suitable for removing papillomas on the face: this method ensures safe removal even in the eyelid area at the ciliary edge, and the risk of forming noticeable scars after removal is low (for example, compared to electrocoagulation). Also, after laser therapy, tissue healing occurs faster.
Sometimes, after the procedure for removing deep-lying flat papillomas, small depressions may remain on the skin, which are then corrected using other cosmetic procedures (resurfacing, peeling, etc.). Using an ablative laser, you can get rid of tumors of various sizes.
CO2 lasers
The active medium of a CO2 laser is a mixture of gases, in which carbon dioxide molecules play a leading role. The wavelength of this laser is 10,600 nm (far infrared). During procedures, the CO2 laser coagulates a significant layer of surrounding tissue (while the erbium laser has a weak coagulation effect). This in this case means a hemostatic (hemostatic) effect that is important for tumor removal procedures.
The CO2 laser is considered a leader in the removal of tumors: it is used to remove papillomas, condylomas, warts, moles, dermatofibromas and other benign formations on the skin and mucous membranes. For these procedures, a knife attachment with a fixed focal length (working spot diameter) is used. The method is also good because, in addition to removing the tumor, it prevents relapses by coagulating pathogenic cells during the procedure.
Alidzhan Ganemovich Khabbus, dermatovenerologist, cosmetologist, laser therapist, teacher at the Department of Dermatovenereology of North-Western State Medical University named after. I.I. Mechnikova, ICG certified specialist in fractional and laser devices Ilooda (Korea):
“Of course, the CO2 laser is widely used in modern practice for many procedures, including laser destruction: with its help, papillomas and deep plantar warts can be removed without a trace. As a rule, high-power devices with a wide range of basic parameters are used for these purposes. The presence of super-pulse modes will prevent excessive overheating of surrounding tissues and ensure good restoration of the skin or mucous membranes after laser destruction. Important features of CO2 lasers are their asepticity and hemostatic properties.
It should be remembered that the treatment of viral warts, in addition to removing the tumor, involves the use of antiviral and immunomodulatory drugs, as well as external agents that affect HPV, in order to prevent relapses.”
Erbium laser
The active medium is yttrium aluminum garnet crystals doped with erbium. The operating wavelength of the laser is 2940 nm. Since this wavelength occurs at the maximum peak of energy absorption by water, it evaporates so quickly that it does not have time to transfer thermal energy to the surrounding tissues (hence the weak coagulation effect). This laser is less popular for tumor removal procedures than the CO2 laser (since it provides a quick and most pronounced effect), but the erbium laser is considered more gentle, and skin restoration after the procedure with its use occurs faster.
Less commonly, some types of non-ablative lasers are used to remove tumors.
Neodymium laser (Nd:Yag)
This is a solid-state laser, the active medium of which is yttrium aluminum garnet crystals doped with neodymium ions. Has a working wavelength of 1064 nm. Experts working with this type of laser claim that the procedure for removing tumors using Nd:Yag allows you to carefully remove warts of varying complexity and size on different parts of the face and body, including in hard-to-reach places.
Anna Vladimirovna Lopatina, dermatovenerologist, dermatocosmetologist, specialist in the field of laser technologies and rehabilitation, consultant at the Educational Center (Russia, Moscow):
“Today the use of laser without rehabilitation is gaining popularity. The advantage of using a neodymium laser to remove warts is the safety of the technology: the beam acts very accurately and penetrates to the required depth. Exposure to a neodymium laser makes it possible to remove a wart without injuring the healthy skin around the formation and without damaging the epidermis, minimizing the risk of unaesthetic scars. During the procedure, coagulation of the vessels feeding the wart and cells affected by the virus occurs. This method allows you to avoid bleeding and infection (that is, without pain, without wounds and without rehabilitation). This allows the patient not to drop out of society, that is, to continue working, doing fitness, etc.”
In addition to the neodymium laser, it is known about the use of dye laser , which also works by destroying the capillaries that feed the tumor, and is suitable for removing flat warts on the face.
Is it possible to get rid of the papilloma virus forever?
All the methods described above help get rid of skin tumors. However, the root cause of the disease - the papilloma virus - cannot be completely cured. All drugs prescribed to patients help weaken the activity of viral particles and strengthen the immune system. But, unfortunately, there are no resources yet to completely cleanse the body of infection.
On the other hand, the modern pharmacological market offers special vaccines that provide stable immunity to the body. The procedure is usually performed on young girls who have not yet begun to be sexually active. Vaccines contain weakened strains and make the body immune to the most dangerous strains of the virus, including those that cause reproductive diseases and infertility. But this drug cannot protect against all types of infection. Moreover, it should be administered only if it is known for sure that the patient is not yet infected.
Strengthening the immune system as a means of prevention
All the methods described above allow you to remove papillomas. However, the cause of their appearance is infection, so there is always the possibility of new skin formations. Since there is no cure for human papillomavirus, the only way to prevent it is to strengthen your immune system. Only the immune system is able to control the activity and intensity of reproduction of viral particles.
A healthy lifestyle is the basis for the proper functioning of the immune system:
- First, you need to pay attention to nutrition. After all, with food, not only nutrients enter the body, but also vitamins and valuable minerals, which directly affect the immune system. The diet should be varied, including plenty of raw vegetables and fruits, as well as grains and dairy products.
- In some cases, to eliminate hypo- and vitamin deficiencies, it is necessary to take special preparations containing a complex of minerals and vitamins. Many doctors recommend this preventive treatment twice a year.
- There are other measures that can activate the immune system. For example, echinacea tincture is often taken to prevent immunodeficiency conditions. This is an inexpensive and inexpensive remedy, but the course of treatment really increases the body's resistance to various infections.
- An important element in strengthening the immune system is extinguishing - getting the body used to the cold. Obviously, this process takes a long time, and the temperature must be reduced very slowly to avoid complications.
- Hypodynamics is the enemy of the human body. Physical activity will have a positive effect on the functioning of all organ systems, including the immune system. Morning jogging, going to the gym, swimming, active walking or just long walks in the fresh air - choose the physical activity that is most suitable for you.
- Stress, emotional and nervous overload cause a sharp change in hormone levels, which primarily affects the immune system.
Although home methods for removing papillomas are more accessible and affordable, self-medication can be dangerous. And so, do not forget that before starting any procedures you need to consult a doctor.