Last update: 03/03/2021
Facial dermatitis is a facial skin disease that is inflammatory in nature. It manifests itself in the form of redness of the skin, noticeable rashes, accompanied by peeling and itching.
The disease affects the face, which causes not only physical discomfort and pain, but also psychological problems. Therefore, dermatitis on the face needs to be treated.
Facial dermatitis: symptoms and signs
If you have the following symptoms, you can confidently say that you have dermatitis on your face:
- Redness, dryness and flaking of the skin;
- Acne-like rashes;
- Pimples with dermatitis on the face are often located in groups;
- The rashes look like mounds filled with clear contents or purulent fluid;
- The area where rashes with skin dermatitis on the face are most often located is the chin and areas around the mouth;
- With dermatitis, swelling of the face is often observed.
Atopy is not only a disease of the body
Atopic dermatitis is a disease that can have a negative impact on the patient's psyche. Children and adolescents diagnosed with AD are more likely to have problems being accepted in their community. It is difficult to explain to your peers where the red spots and scars come from after an exacerbation of the disease.
Fortunately, only about 30% of patients continue to have symptoms into adulthood. In the remaining 70%, the symptoms disappear completely or appear in a milder form, which the patient can control with the help of a good dermatologist.
Facial dermatitis: causes
Statistics say that today every 8th person in the world suffers from facial dermatitis in one form or another, and adults and children suffer equally. And half a century ago, this disease occurred exclusively in children, and quite rarely. What changed?
It is not known exactly what exactly provokes the development of the disease: each case is individual. The main risk factors include heredity and poor lifestyle.
If you have a weakened immune system due to illness, you smoke, experience stress, do not take enough care of your facial skin, use low-quality cosmetics, neglect a healthy diet and vitamins, then sooner or later all this can affect your health and lead to dermatitis on the face.
Causes
A genetic mutation by itself cannot provoke the development of AD, since the disease occurs due to a number of provoking factors. These include:
- Atopenes (environmental allergens that provoke the production of allergic antibodies). They can be food (for example, milk, wheat, soy), pollen (wormwood, alder, ragweed), dust (bed mites, animal hair).
- Allergenic foods (spicy foods, alcohol, sweets, smoked foods, etc.).
- Medicines (vitamins, antibiotics, sulfonamides).
- Emotional stress.
- Frequent hypothermia.
In addition, we can identify factors that play a key role in exacerbation of the disease. This:
- Air pollution.
- Harmful working conditions (for example, if during work contamination occurs with solid oil particles or the skin is exposed to aggressive detergents).
- Viral infections (HIV, infectious hepatitis, etc.).
- Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (pancreatitis, infectious gastritis).
- Pathologies of the endocrine system (thyrotoxicosis, dysmenorrhea, etc.).
Important! It is impossible to become infected with atopic dermatitis from another person. The disease is not transmitted by contact or airborne droplets.
Types of dermatitis on the face
Depending on the main manifestations and course of the disease, there are several types of dermatitis that appear on the face.
Allergic dermatitis of the face
It develops when substances to which a person is hypersensitive—potential allergens—enter the body. Allergies do not occur immediately; the body needs time to produce antibodies. If the immune system fails, a reaction begins. Therefore, allergic dermatitis of the face manifests itself after a few days, sometimes even weeks.
In a mild form, the disease occurs with rashes, redness and swelling of the skin. If the allergen is not eliminated from the body (for example, you continue to eat the product that caused the allergy), then the manifestations of dermatitis may intensify.
Atopic dermatitis on the face
It is considered an advanced case of allergic dermatitis, provoked by other factors contributing to the development of the disease: for example, a hereditary predisposition to allergies.
Atopic dermatitis is manifested by itchy rashes, dryness, redness on the face; the skin in areas affected by dermatitis gradually becomes rougher.
Contact dermatitis of the facial skin
It can have both non-allergic origin (friction, thermal burn) and allergic origin. This could be a reaction to cosmetics, irritation from jewelry, or an allergy to bed linen detergent.
Dermatitis is manifested by dryness, peeling, redness of the skin and rashes. But unlike allergic, contact occurs exclusively at the site of skin contact with the allergen.
A type of contact dermatitis is photodermatitis (sun allergy).
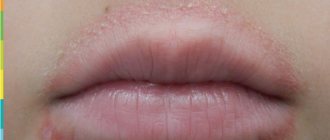
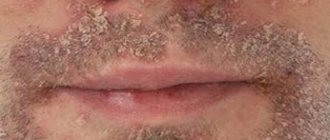
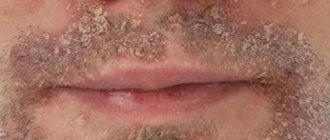
Perioral dermatitis on the face
It is also called rosacea-like due to its external resemblance to the disease rosacea: the skin on the face with dermatitis is covered with spots of different colors - from pale pink to bright red (they also change shade depending on environmental conditions, for example, in different weather). The main location is the area around the mouth.
The disease occurs mainly in women aged 15-45 years. Causes: metabolic disorders, prolonged use of glucocorticosteroids (topically or systemically) and medications containing them, mites of the genus Demodex, infectious agents: yeast-like fungi of the genus Candida, obligate anaerobic bacteria, stress. And external factors aggravate the situation.
Although the causes of perioral dermatitis on the face have not been thoroughly studied, excessive use of decorative cosmetics, skin care products, and sunscreens are considered a catalyst for the occurrence and development of the disease.
Seborrheic dermatitis on the face
Disruption of the sebaceous glands leads to increased sebum secretion, which in turn causes oily skin and clogged pores, and the development of seborrheic dermatitis is facilitated by the activation of the lipophilic yeast fungus Malassezia furfur.
Seborrheic dermatitis usually begins from the head (dandruff in the hair), and then “descends” to the face in the fattest parts - the wings of the nose, behind the ears, on the eyelids.
There are 2 types:
- Oily seborrheic dermatitis - pustules appear on the skin, the face acquires a grayish color and seems to shine.
- Dry dermatitis - the skin is very flaky, flaking scales form on the face.
Seborrheic dermatitis on the face can begin at any age.
What is atopy
The term “atopy” refers to an abnormal reaction of the body to an allergen, which generally explains the nature of the disease.
With the development of atopy, there is an overproduction of IgE antibodies, which are responsible for the appearance of an allergic reaction. AD belongs to the same group of diseases as urticaria, hay fever and bronchial asthma. The pathology is immune-dependent, since the main factor in its development is a mutation in genes. Specifically, we are talking about the genes encoding filaggrin. This structural protein is located in the skin and is involved in the formation of the skin barrier, preventing water loss and the entry of allergens and microorganisms. For this reason, the pathology is inherited from one of the parents, most often from the mother.
Interestingly, atopic dermatitis was essentially known back in ancient times. In those days, this disease was called “idiosyncrasy.” That is, the name reflected the mechanism of development of the pathology - as an increased reaction to an allergen - but did not explain its etiology.
The term “atopy” was first used in 1922 to define the body’s increased sensitivity to external factors.
Facial dermatitis:
To get rid of dermatitis on the face you will need a comprehensive approach. To eliminate the symptoms of a disease, it is necessary to determine the cause of its occurrence.
First of all, diagnosis is important. A dermatologist will identify the type of dermatitis, prescribe tests to find the allergen and prescribe treatment.
- A lifestyle adjustment will be required: a minimum of stress, regular sleep, sports and walks in the fresh air will have a beneficial effect on the condition of the body in general and the health of the skin in particular.
In advanced cases of chronic facial dermatitis, patients sometimes require a change in climate, place of work and place of residence. Don't let the disease get worse so you don't have to take extreme measures!
- Therapy includes a hypoallergenic diet. First of all, it is important to exclude the identified allergen product. Adjust your diet in favor of vegetables and fruits (except citrus fruits), boiled meat, fish and cereals. It is better to give up spicy, salty, sweet, smoked, and canned foods.
- Proper skin care is important. A cosmetologist-dermatologist will help you choose hypoallergenic cleansers and cosmetics individually for you.
Treatment of dermatitis on the face: ointments
- When treating allergic dermatitis, individuals are prescribed anti-inflammatory (hormonal and non-hormonal) topical agents (ointment, cream), which reduce all symptoms, and antihistamines.
- Treatment of contact dermatitis on the face begins with excluding any contact with the allergen and prescribing anti-inflammatory and healing ointments. If there has been prolonged contact with the allergen, and the disease is very advanced, it is possible to prescribe a steroid cream or ointment containing hormones. Only they can cope with serious ulcers on the face.
- For atopic dermatitis of the facial skin, anti-inflammatory drugs (hormonal and non-hormonal) are often used to relieve redness and itching.
- Seborrheic dermatitis is caused by a fungus, so it is treated with antifungal agents.
- When treating perioral facial dermatitis, the main symptoms are eliminated with antihistamine ointments; Hormonal creams are prescribed in special cases, if the cause of the disease is accurately diagnosed.
Cream “La-Cri” is an effective remedy for facial skin dermatitis
Experts recommend soothing the manifestations of dermatitis on the face with the help of La-Cri cleansing gel, enriched with life-giving extracts of licorice, violet, string and walnut, with the addition of avocado and olive oil. It gently cleanses irritated skin and helps reduce inflammation.
In addition, treatment of dermatitis involves the use of La-Cri emulsion and cream for sensitive skin, which help restore and disinfect the skin. The cream has an anti-inflammatory and regenerating effect, and the emulsion stimulates metabolism and restores the water balance of the epidermis, moisturizing and softening the skin.
Skin dermatitis on the face: folk ways to combat the disease
“Grandma’s recipes” are effective mainly for relieving symptoms of the disease. We urge you to take your health seriously and undergo treatment under the supervision of a doctor. Use natural remedies exclusively as auxiliaries and only after the doctor’s permission.
Homemade ointments
Tar: Add 6 g of tar to a regular tube of shaving cream. Heat to 600C. Use the cream 2-3 times a day.
Potato: mix 100 g of grated potatoes with 7 ml of liquid honey (if you are not allergic to it). Apply the ointment to your face and leave it overnight.
Herbal decoctions
It is recommended to store decoctions in a cool place for no more than 3 days. Use in courses: wipe the skin 2-3 times a day, course – 1 month.
Walnut: chop 6-7 walnut leaves, add 1 glass of water, boil over low heat for 5-6 minutes. Leave for 2 hours.
Hops: 10 g of hops and 10 g of string, pour 150 ml of boiling water. Leave for 40 minutes.
Oils
Oils can be used undiluted or added as an ingredient to various recipes. Oil formulations should be applied pointwise to areas affected by dermatitis 2-3 times a day.
Cypress and myrrh: add 2 drops of these essential oils to 10 g of baby hypoallergenic cream.
Geranium, cedar, mint: pour 5 drops of oil into 16 ml of milk (do not use inside!)
Essential oils of black currant, geranium, cedar, ylang-ylang, lavender, jojoba, almond, sea buckthorn, and chamomile help well in treatment.
How to recognize atopic dermatitis?
Tests often used in diagnosis are skin tests and atopic patch tests, but a negative test does not always mean that the disease is not present, it may only mean that the allergen has not yet been detected.
The laboratory also performs total serum IgE determinations, which determine the patient's allergies. Since atopic dermatitis is an allergic disease, we cannot completely cure it, we only treat it symptomatically. In some cases, it is possible to desensitize the patient.
Clinical researches
The conducted clinical study proves the high efficiency, safety and tolerability of products for daily care of children's skin. As a result of therapy, a decrease in the activity of the inflammatory process, a decrease in dryness, itching and flaking was noted. The products will also be effective in the treatment of minor burns.
The safety of “La-Cri” is confirmed by research by scientists from the AILC of the Federal State Institution “R.R. Vreden Russian Research Institute of Traumatology and Orthopedics” and numerous government certificates.
Cream "La-Cri" for sensitive skin:
- eliminates itching and irritation;
- relieves skin redness;
- moisturizes and carefully cares for the skin;
Emulsion "La-Cri":
- moisturizes and nourishes the skin
- relieves itching and irritation
- soothes and restores skin
Cleansing gel “La-Cri”:
- gently cleanses the skin
- relieves redness and itching
- restores and nourishes the skin.
Sources:
- N.M. Sharova, Approaches to the treatment and prevention of diaper dermatitis, Medical Council journal, 2018
- G.V. Molokova, E.V. Bukina, Diaper dermatitis in children with sensitive skin, Journal of Dermatology and Allergology, 2019
- N.L. Rybkina, Modern approaches to newborn skin care: pediatrician tactics, journal Bulletin of Modern Clinical Medicine, 2014
- V.V. Chebotarev, N.V. Chebotareva, M.S. Askhakov, E.V. Bronnikova, Sensitive skin: causes, methods of therapy, journal Medical Bulletin of the North Caucasus, 2015
Photos of dermatitis
Photo album on the diseaseDiagnosis of atopic dermatitis (AD): skin tests
When diagnosing atopic dermatitis, in addition to analyzing symptoms and laboratory tests, a series of skin tests, such as skin tests, atopic patch tests, or nutritional skin exposure tests, are performed to identify the substances responsible for an excessive allergic reaction.
The diagnosis is confirmed by immunological laboratory tests - determining the concentration of IgE antibodies - and a number of skin tests that can identify allergens responsible for an excessive allergic reaction.
Williams criteria for diagnosing AD
According to the Williams criteria, to diagnose atopic dermatitis, it is necessary to establish whether itching has occurred within the last year and at least 3 of 4 symptoms:
- involvement of skin folds (elbow and knee), changes in the neck or around the eyes;
- coexistence of other atopic diseases, for example, bronchial asthma or hay fever (when diagnosing children under 4 years of age, atopic diseases in 1st degree relatives are taken into account);
- general dry skin throughout the year;
- visible inflammatory changes in the flexion areas of the limbs and on the cheeks/forehead and elongated parts of the limbs in children under 4 years of age or onset of the disease before the age of 2 years (not applicable if the child is under 4 years of age).
Candidal dermatitis in a child
Candidal dermatitis occurs in childhood, is especially common in infants, has a characteristic localization (see photo), and when it appears, immediate treatment is required. At an early age, candidal dermatitis affects the inguinal folds and the area between the buttocks, especially when using reusable diapers and when the child rarely changes them, constant humidity and heat in this area are the causes of fungal growth and inflammation (as shown in the photo), and treatment is carried out first It’s all about following the rules of hygiene.
In addition to the complication of diaper dermatitis, this fungus often affects the tongue, cheeks, and can spread to the esophagus. A cheesy white coating forms against the background of reddened mucous membrane, which is easily removed with a spatula. Erosions and ulcers may form. This inflammation can be very painful. This leads to a disruption in general well-being, the baby has difficulty swallowing, he worries, cries, loses appetite and sleeps poorly.
Also, children sometimes experience sinusitis caused by candidiasis. Lesions of the external auditory canal with the release of a cheesy discharge from the ear are also common.
In rare cases, congenital candidiasis occurs - this condition is accompanied by a rash throughout the body, enlarged liver, sepsis, and respiratory distress.
Symptoms in infants include:
- Severe and persistent diaper dermatitis,
- Skin rash that resembles eczema
- White or yellow spots on the tongue or the inside of the mouth and cheeks,
- Colic and abdominal pain for longer than one month,
- Recurrent ear infections
- Symptoms are worse in wet weather.
In older children, signs of chronic candidal infection include:
- Constant craving for sweets
- School skills disorders
- Frequent irritability and bad mood,
- Frequent ear diseases
- High indoor humidity or humid weather worsens the condition.
How is atopic dermatitis diagnosed? Criteria for diagnosing blood pressure
When diagnosing atopic dermatitis, in addition to immunological laboratory blood tests, the key is to analyze the patient's skin condition and its symptoms in accordance with the criteria of Williams and colleagues or the criteria of Hanifin and Raika.
Atopic dermatitis (AD) is a chronic disease with a complex cause. Its appearance is influenced by immunological, genetic, non-immunological and environmental factors. Therefore, this is not just an allergic reaction. For this reason, the basis for correct diagnosis of AD is the overall picture of the disease, especially the appearance of the skin.
Atopic dermatitis is a disease that causes diagnostic problems - similar symptoms can occur with other types of dermatitis, such as seborrheic or sweat dermatitis, contact eczema, mycosis or psoriasis. The most common diagnosis of atopic dermatitis is the so-called Williams and colleagues criteria or Hanifin and Reike criteria.
Seborrheic dermatitis
Psoriasis